Important Facts For Prelims
Cloudburst, Landslide, and Flash Flood
Why in News?
Torrential rain in Ramban tehsil of Jammu and Kashmir has caused casualties, significant infrastructure damage, and forced emergency relocations. Officials have cited cloudbursts, landslides and flash floods as the main triggers of the widespread destruction.
What is a Cloudburst?
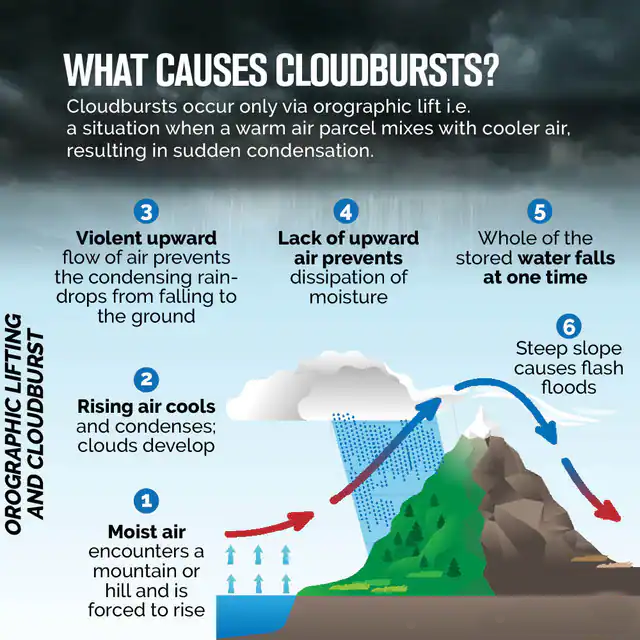
- Definition: A cloudburst is a sudden, intense rainstorm that results in more than 10 cm of rain in less than an hour over a small area (approximately 10 km²).
- It can also be accompanied by hail and thunder. Cloudbursts are common in mountainous areas, especially in the Himalayas.
- Due to their localised nature, cloudbursts are hard to predict or detect but can unleash sudden, devastating rainfall, leading to flash floods and landslides.
- Causes:
- Orographic Lifting: It occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain range. As the air ascends, it cools and condenses, resulting in heavy rainfall.
- Strong upward air currents can cause raindrops to grow larger before they fall. When these currents weaken, the accumulated raindrops fall suddenly, leading to intense rainfall.
- Monsoon Dynamics: In the Indian subcontinent, a cloudburst typically occurs when a monsoon cloud moves northwards from the Bay of Bengal or Arabian Sea, crosses the plains, and reaches the Himalayas, releasing rainfall of up to 75 millimeters per hour.
- Orographic Lifting: It occurs when moist air is forced to rise over a mountain range. As the air ascends, it cools and condenses, resulting in heavy rainfall.
- Examples: Cloudbursts in Himachal Pradesh (2024) and Uttarakhand (2021) caused fatal floods, landslides, and extensive damage to infrastructure.
What is a Landslide?
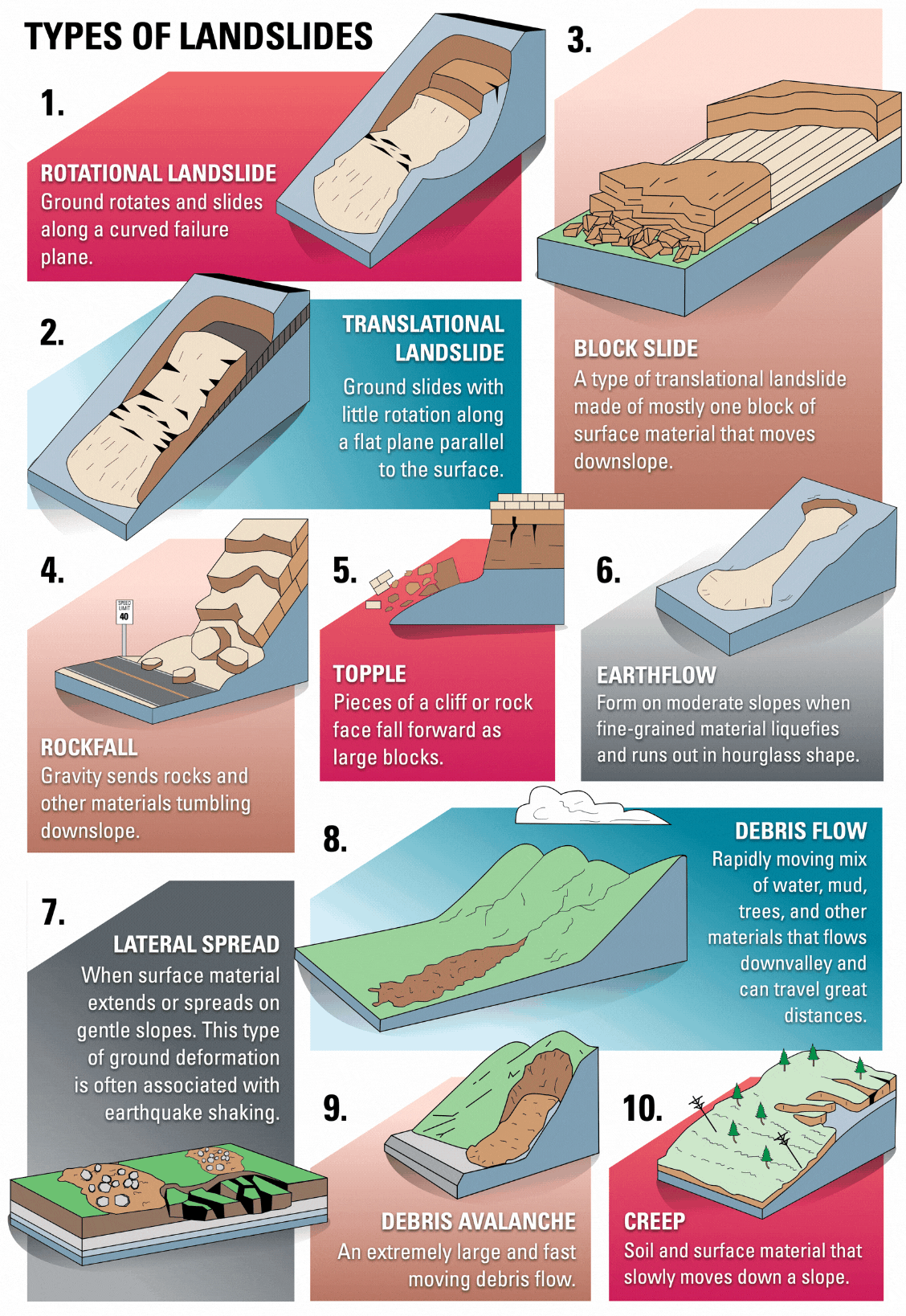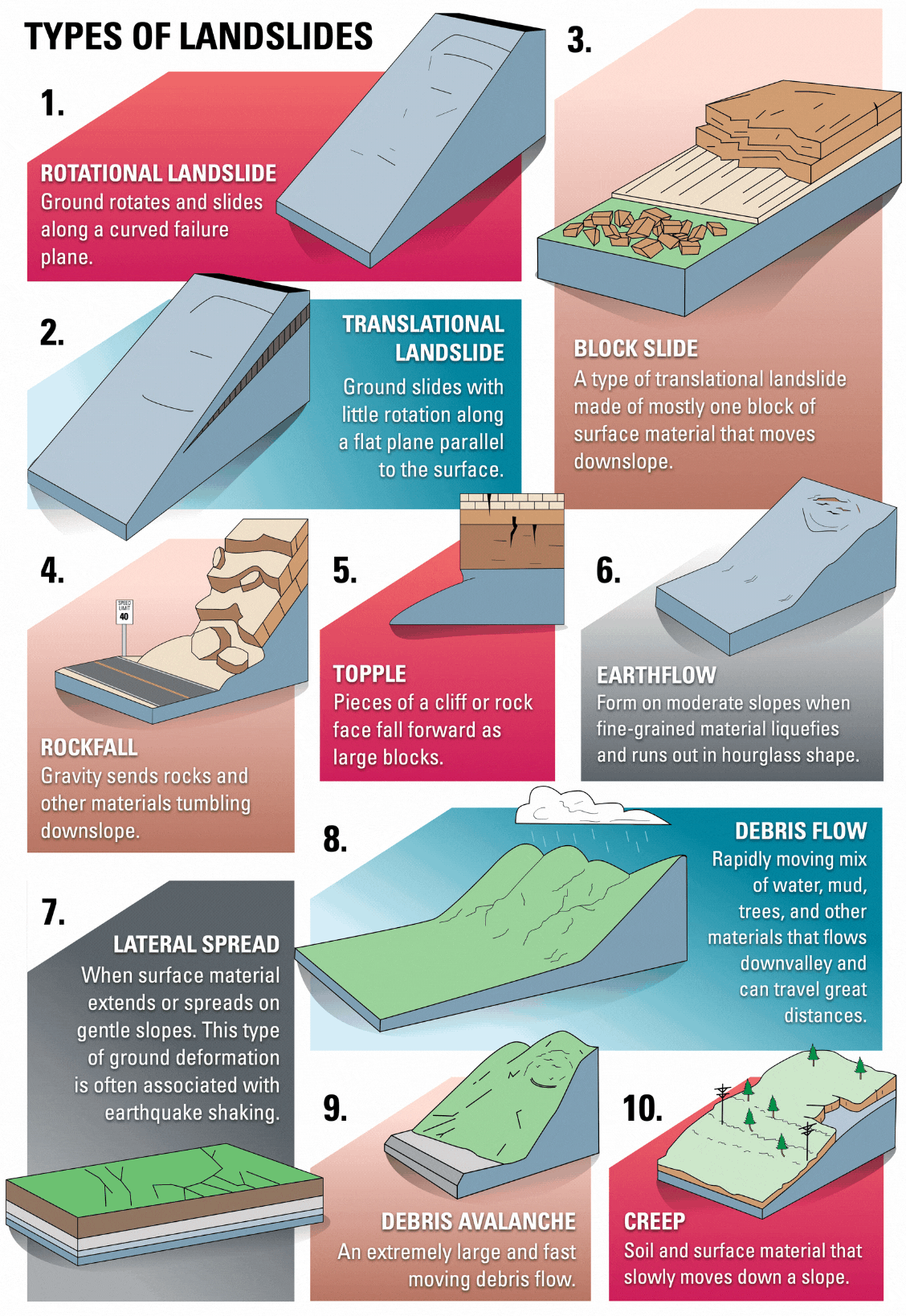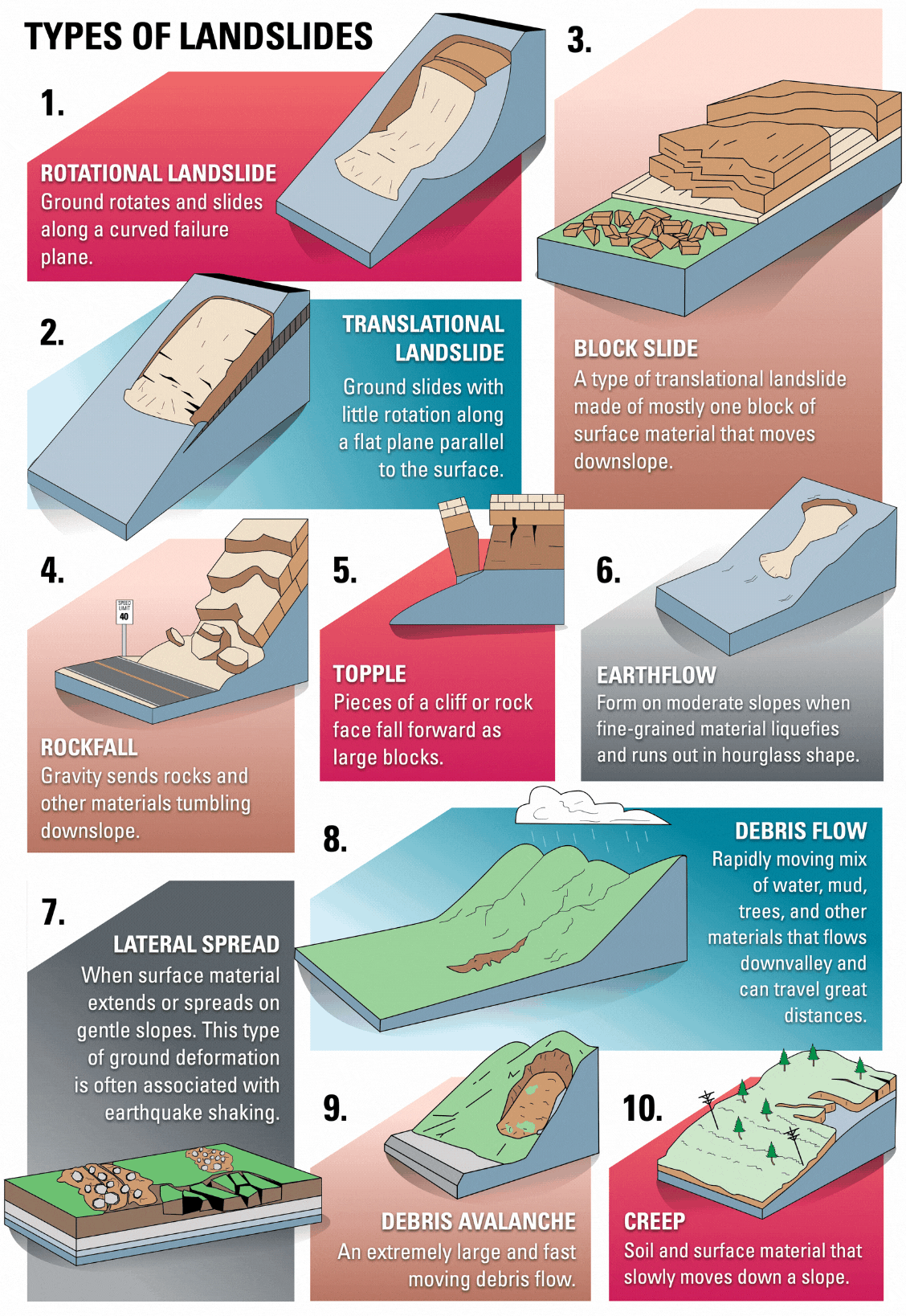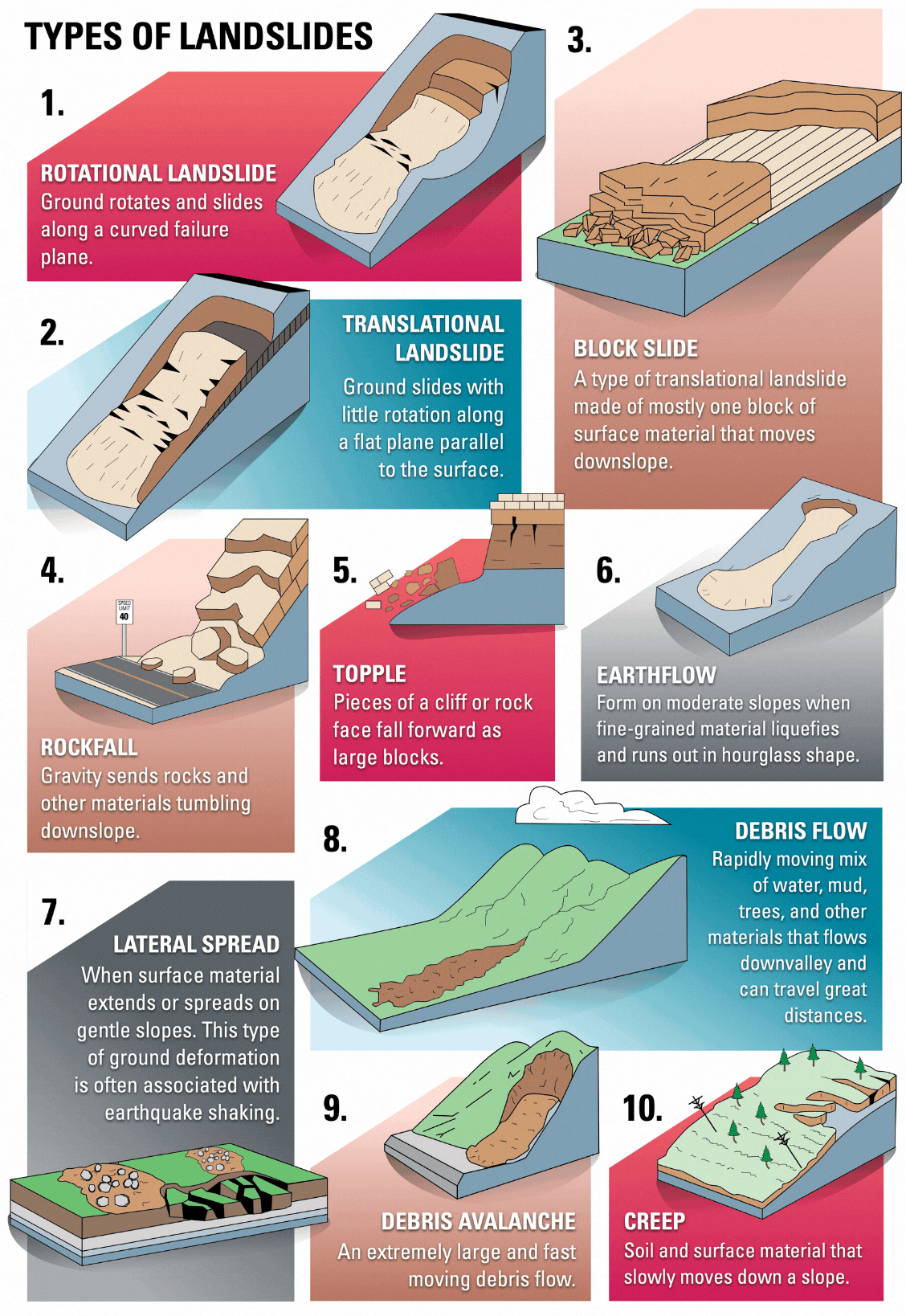
- Definition: A landslide is the downward movement of rock, soil, or debris on a slope due to gravity.
- It is a form of mass wasting, where earth materials move down a slope under the influence of gravity.
- Types:
- Causes: Natural factors like heavy rainfall, earthquakes, and water seepage weaken slopes, while human activities such as deforestation and construction increase risks. Geological factors, such as soil composition and terrain, also affect slope stability and can lead to landslides.
- Landslide Prone Areas: In India, 0.42 million sq. km (12.6% of land area) is prone to landslides, with the North East Himalaya, North West Himalaya, Western Ghats, Konkan hills, and Eastern Ghats being the most affected.
- Examples: In 2024, Wayanad (Kerala) faced significant landslides, while the 2013 Kedarnath (Uttarakhand) landslide caused over 5,700 deaths.
- The 2021 Chamoli landslide, triggered by heavy rain and a glacier burst, led to widespread flooding and fatalities.
What is a Flash Flood?
- Definition: Flash floods are sudden increases in water levels during or immediately after intense rainfall. They are highly localized and short-lived events, typically occurring within 6 hours of rainfall.
- Causes: Flash floods are primarily caused by intense rainfall that overwhelms the soil’s absorption capacity and drainage systems.
- Apart from heavy rain, flash floods can also result from rapid snowmelt due to sudden temperature rise, dam or levee breaches, ice or debris jams, and sudden glacial lake outbursts.
- Additionally, urbanisation with impervious surfaces like roads and buildings increase runoff, reducing water absorption and intensifying flood risks.
- Examples: Himachal 2023, Uttarakhand 2013, and Mumbai 2005 each caused by intense rain, leading to heavy loss of life and property.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (2011)
- La Nina is characterised by an usually cold ocean temperature in the equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Nino is characterised by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino has an adverse effect on the south-west monsoon of India but La Nina has no effect on the monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Differentiate the causes of landslides in the Himalayan region and Western Ghats. (2021)
Q. The Himalayas are highly prone to landslides.” Discuss the causes and suggest suitable measures of mitigation. (2016)
Rapid Fire
17th National Civil Services Day
The Prime Minister addressed civil servants on the occasion of the 17th National Civil Services Day (21st April 2025) and honored the Prime Minister’s Awards for Excellence in Public Administration (PMAEPA).
- On National Civil Services Day, the historic representation of women in civil services was highlighted, with 74 women officers comprising 41% of the 2023 Indian Administrative Service (IAS) batch.
- National Civil Services Day: It is observed on 21st April each year to honor the dedication of civil servants. First celebrated in 2006, it commemorates Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel’s address to the probationers of Administrative Services Officers at Metcalf House in Delhi, where he referred to the civil servants as the “steel frame of India” on 21st April 1947.
- PMAEPA: Instituted to recognize outstanding and innovative work by officers of the Central and State Governments. All government officers and organizations are eligible.
- The selection process includes evaluation by a Screening Committee, Expert Committee, and final approval by the Cabinet Secretary and Prime Minister.
- The award includes a trophy, a scroll, and Rs 20 lakh to support public welfare initiatives.
- Initiatives Related to Civil Services: Mission Karmayogi, Lateral Entry Scheme (LES), e-Samiksha, and Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS).
| Read more: Civil Services Day |
Important Facts For Prelims
World Heritage Day 2025
Why in News?
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has declared free entry to its protected monuments on International Day for Monuments and Sites (World Heritage Day) on 18th April 2025.
What is World Heritage Day?
- It is a day observed globally to promote awareness about the importance of cultural heritage and the need to preserve it. It was declared by the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) in 1982 and later approved by UNESCO in 1983.
- The theme for 2025 is “Heritage under Threat from Disasters and Conflicts: Preparedness and Learning from 60 Years of ICOMOS Actions”.
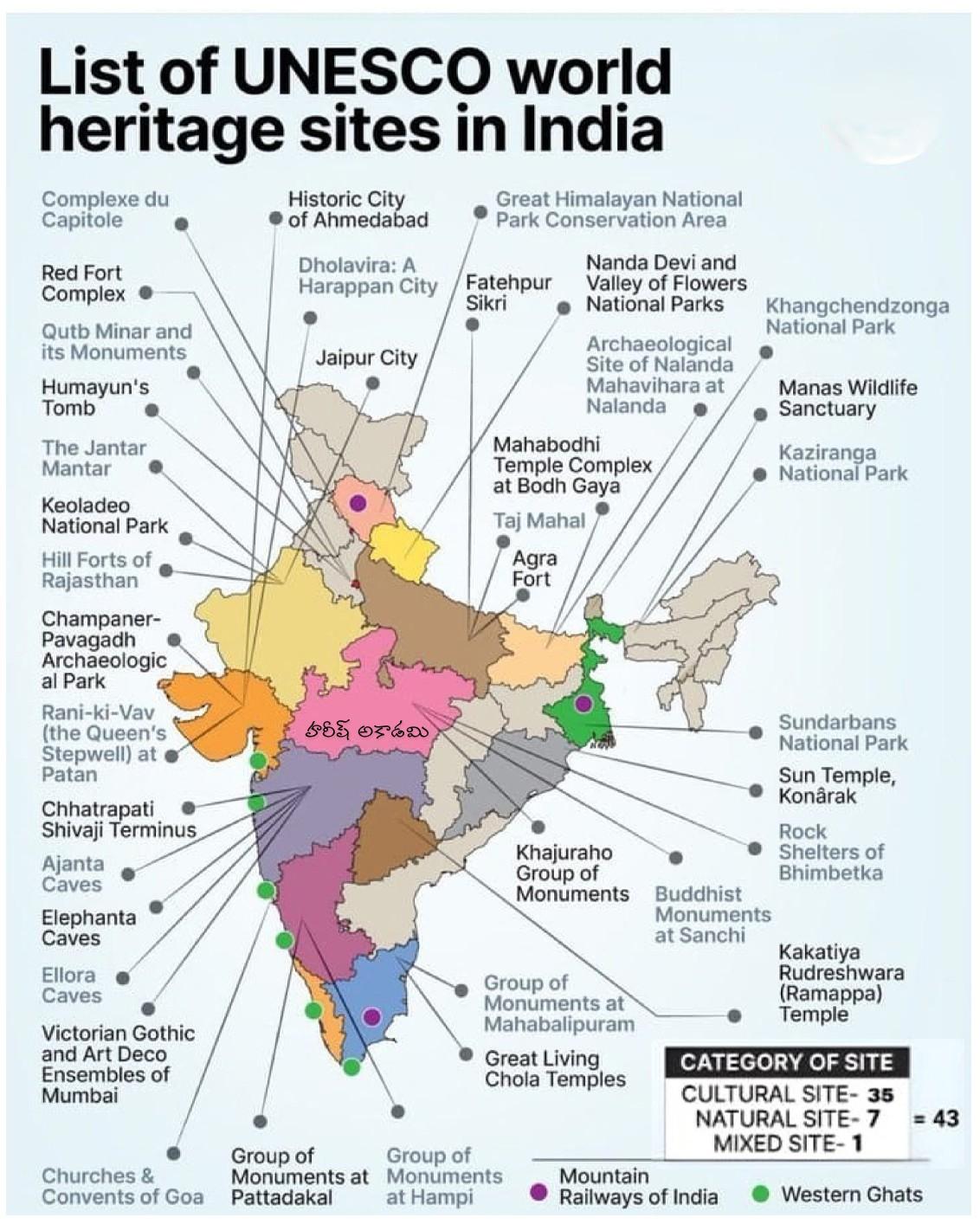
What are World Heritage Sites?
- About: World Heritage Sites (WHS) are locations recognized for their outstanding universal value to humanity and are inscribed on the World Heritage List for protection and preservation for future generations.
- These sites may be cultural, natural, or mixed in nature. WHS are safeguarded under the World Heritage Convention, 1972, an international agreement adopted by UNESCO member countries.
- The Convention outlines the responsibilities of State Parties in identifying, protecting, and preserving such sites.
- The list of WHS are maintained by the international 'World Heritage Programme', administered by the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
- India ratified the Convention in 1977.
- WHS Around the World: As of October 2024, there are around 1,223 sites in 196 countries comprising 952 cultural, 231 natural, and 40 mixed sites.
- WHS in India: As of April 2025, India has 43 World Heritage Sites (34 Cultural, 7 Natural, and 2 Mixed) and 62 sites on the Tentative List.
What are the Key Government Initiatives to Promote India’s Cultural Heritage?
- Restoration of Antiquities: India has intensified efforts to bring back cultural artifacts from foreign countries, retrieving 655 antiquities since 1976.
- In 2024, literary classics like the Ramcharitmanas, Panchatantra, and Sahrdayāloka-Locana were added to UNESCO’s 2024 Memory of the World Committee for Asia and the Pacific Regional Register.
- Heritage Scheme and Corridor Projects: Through the Adopt a Heritage Programme launched in 2017, public and private bodies can support heritage site upkeep via CSR funding.
- Digital Documentation: Over 12.3 lakh antiquities and 11,400 heritage sites have been digitized under the National Mission on Monuments and Antiquities (NMMA). The ‘Indian Heritage in Digital Space’ initiative uses technology to create immersive heritage experiences.
- The ASI’s ‘Must See’ portal showcases nearly 100 major monuments with detailed information and panoramic views.
- Global Cultural Leadership: India hosted the 46th Session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Delhi (July 2024).
Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)
- About: ASI is the key government body responsible for archaeological research and protection of India’s cultural heritage.
- Establishment: It was established in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, who is known as the “Father of Indian Archaeology” and served as its first Director-General.
- Functions: Its main functions include survey, exploration, excavation, conservation, and maintenance of ancient monuments.
- It also documents and protects antiquarian remains and archaeological heritage.
- Governing Framework: It works under the Ministry of Culture and operates under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act, 1958.
- It manages over 3,698 monuments and sites of national importance.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
(a) Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of Waghora river.
(b) Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of Chambal river.
(c) Pandu-lena Cave Shrines lie in the gorge of Narmada river.
(d) Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of Godavari river.
Ans: (a)