Infographics
Social Issues
State of World Population Report: UNFPA
For Prelims: UNFPA, Fertility Rate, Demographic Dividend, SDG, ECOSOC.
For Mains: State of World Population Report.
Why in News?
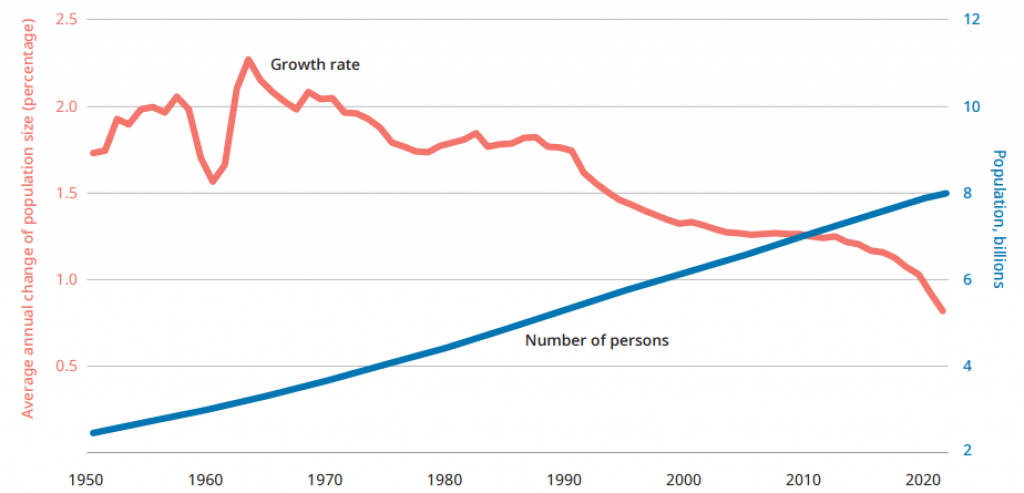
Recently, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) has released the State of World Population report 2023, which states that India will overtake China to become the world’s most populous country by the middle of 2023.
- The State of World Population is published annually which covers and analyses developments and trends in world population and demographics, as well as shedding a light on specific regions, countries and population groups and the unique challenges they face.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Population Estimation:
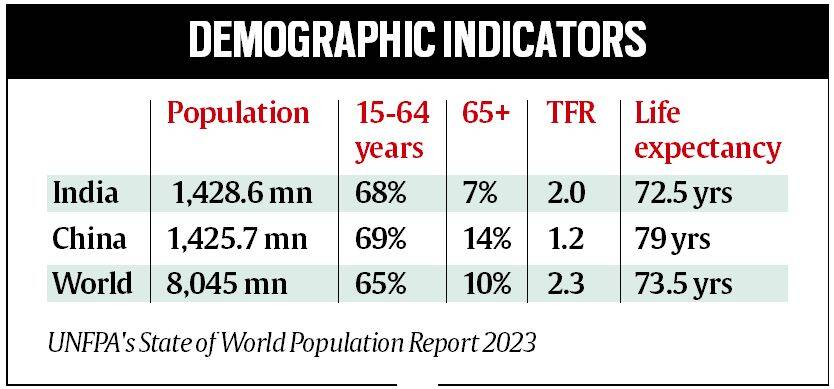
- India’s population is pegged to reach 142.86 crore against China’s 142.57 crore by July 2023.
- 25% of India's population is in the age group of 0-14 years, 18% in the 10-19 age group, 26% in the age bracket of 10-24 years, 68% in the 15-64 years age group, and 7% above 65 years.
- India will have 29 lakhs more people than its Asian neighbour.
- The United States is a third populated country, with a population of 340 million.
- India’s population is pegged to reach 142.86 crore against China’s 142.57 crore by July 2023.
- Slowing Population:
- Population growth in both India and China has been slowing, despite accounting for more than one-third of the estimated global population.
- Fertility Rate:
- India’s total Fertility Rate, was estimated at 2, lower than the world average of 2.3.
- Developed regions projected a fertility rate of 1.5, less developed regions 2.4 and less developed countries 3.9.
- Life Expectancy:
- The average life expectancy for an Indian male was projected as 71 and 74 for females.
- On average, the life expectancy for males globally was projected to be 71 and 76 for females.
- For developed regions, the average life expectancy for males was projected at 77 and 83 for females — the highest of all.
- For less developed regions, the ages are 70 for males and 74 for females, while for least developed countries, it is 63 for males and 68 for females.
- Gender Rights:
- Violence by an intimate partner in the last 12 months was reported by 18% of women, while 66% of women had decision-making on sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights in India.
- A little over 80% of women had some say in decision-making regarding their own healthcare.
- Population Growth Concentrations:
- More than half of the projected increase in global population up to 2050 will be concentrated in eight countries — the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and the United Republic of Tanzania.
What are the Recommendations?
- With almost half the population under 25 years of age, India has a time-bound opportunity to benefit from the Demographic Dividend. The focus should be on giving women more power to control when and how they have children.
- Ensuring gender equality, empowerment and advancing greater bodily autonomy for women and girls—is one of the key determinants of a sustainable future.
- Thriving and inclusive societies can be built, regardless of population size, if countries are prepared to radically rethink how we talk about, and plan for, population change.
- In high-fertility countries, empowerment through education and family planning, is known to yield enormous dividends in the form of economic growth and human capital development.
- All governments should uphold human rights, strengthen pension and healthcare systems, promote active and healthy aging, protect migrants’ rights, and seek to mitigate the damaging impact of climate change.
What are the Opportunities and Drawbacks for India?
- Opportunities:
- Demographic Dividend:
- India's population offers a significant advantage in terms of a large workforce, which can help drive economic growth.
- India’s 68 % population are in the 15 to 64 years age group, providing a significant contribution to the working or able-to-work population.
- It certainly looks like a demographic dividend when a lot of advanced countries in the world struggle due to their population growing old thus reducing the number of those who could work.
- Attracting Businesses and Innovation:
- With a large population, India represents a vast and growing consumer market, which can attract investments and spur domestic production.
- India can leverage its demographic dividend to attract big businesses from Western countries which had chosen China for manufacturing.
- A large and diverse population can be a source of innovation, as it brings together different perspectives, ideas, and approaches.
- Permanent Member at Security Council:
- With India’s growing population, India will likely claim more power and influence on the global stage.
- India can claim to be a Permanent Member at United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- Leader of Global South:
- The status of the most populous country will also help India claim leadership of the global south for which it has been striving after assuming the G20 leadership in 2022.
- Demographic Dividend:
- Drawbacks:
- Unemployment and Social Problems:
- High unemployment is a very big challenge for India's young population, which is compounded by the limited availability of productive and remunerative jobs.
- For instance, in the civil services sector, nearly 6.5 lakh candidates compete for only 700 positions, while in the railways, thousands of youths vie for a few hundred low-ranking jobs.
- Unemployment not only leads to economic stress but also exacerbates social problems, especially when a significant portion of the working-age population is unable to find suitable employment.
- High unemployment is a very big challenge for India's young population, which is compounded by the limited availability of productive and remunerative jobs.
- Poor Labour Force Participation:
- India's huge population is poor labour force participation, especially of women.
- India's female labor force participation rate in 2021 was 19%, lower than the world average at 25.1%, and has been declining for a long.
- Prime Minister of India aims at 50% female workforce by 2047.
- Poverty:
- India's population includes a significant number of people living in poverty, which can exacerbate issues such as inequality, crime, and social unrest.
- Unemployment and Social Problems:
What is the UNFPA?
- About:
- It is a subsidiary organ of the UN General Assembly and works as a sexual and reproductive health agency.
- The UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) establishes its mandate.
- Establishment:
- It was established as a trust fund in 1967 and began operations in 1969.
- In 1987, it was officially renamed the United Nations Population Fund but the original abbreviation, ‘UNFPA’ for the United Nations Fund for Population Activities was retained.
- Objective:
- UNFPA works directly to tackle Sustainable Development Goals on health (SDG3), education (SDG4) and gender equality (SDG5).
- Fund:
- UNFPA is not supported by the UN budget, instead, it is entirely supported by voluntary contributions of donor governments, intergovernmental organizations, the private sector, foundations and individuals.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. In the context of any country, which one of the following would be considered as part of its social capital? (2019)
(a) The proportion of literates in the population
(b) The stock of its buildings, other infrastructure and machines
(c) The size of population in the working age group
(d) The level of mutual trust and harmony in the society
Ans: (d)
Q2. India is regarded as a country with “Demographic Dividend”. This is due to (2011)
(a) Its high population in the age group below 15 years
(b) Its high population in the age group of 15-64 year
(c) Its high population in the age group above 65 years
(d) Its high total population
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q1. Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (2021)
Q2. ‘’Empowering women is the key to control the population growth.’’ Discuss. (2019)
Q3. Critically examine whether growing population is the cause of poverty or poverty is the main cause of population increase in India. (2015)


International Relations
India-UAE Food Security Partnership
For Prelims: Food security, POSHAN Abhiyaan, Public Distribution System, I2U2 Summit 2022, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), International Year of Millets.
For Mains: Key Areas of India-UAE Food Security Partnership, Major Challenges to Global Food Security.
Why in News?
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), whose food security has been built on imports from global markets, is now focusing on the twin objectives of food access and readiness to confront supply chain crises.
- India, the world’s second-largest food producer, is an essential partner in the UAE’s ambition to strengthen food security.
- The India-UAE food security partnership stands to benefit from multiple points of convergence.
How is India Strengthening its Global Food Security Partnership with UAE?
- India's Capabilities:
- Strong Hold on Agri-exports:
- India has a strong position as a global agri-export powerhouse due to its abundant arable land, favourable climate, and growing food production and processing sector.
- Humanitarian Assistance:
- India has also been involved in humanitarian food aid to developing countries, demonstrating its commitment to regional and global food security.
- Food Parks and Supply Chain Management:
- India has made significant investments in food parks and modern supply chain management to benefit from bilateral trade agreements, showcasing its intent to excel in the global food marketplace.
- Government Initiatives:
- India runs the world's largest food subsidy program, the Public Distribution System, providing affordable grains to nearly 800 million citizens, ensuring access to daily meals.
- India's POSHAN Abhiyaan' is the world's largest nutrition program for children and women, emphasising the importance of nutrition in food security.
- Strong Hold on Agri-exports:
- UAE's Contribution:
- Investment:
- The UAE has committed USD 2 billion in investment towards constructing food parks in India during the I2U2 Summit 2022.
- Food Security Corridor:
- The UAE has signed a food security corridor on the sidelines of the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), enhancing India's presence on the global food value chain.
- Agriota:
- The Dubai Multi Commodities Centre has launched Agriota, an agri-trading and commodity platform, connecting Indian farmers to the UAE's food ecosystem and enabling direct access to Emirati markets.
- Investment:
- Significance:
- Gateway to New Markets for India:
- The UAE's strategic location between Asia and Europe can serve as India's food export gateway to West Asia and Africa, offering benefits beyond maintaining and diversifying its food reserves.
- India stands to gain from the UAE's private sector projects, generating non-farm agri-jobs and providing better prices for farmers' products.
- Template for Global Food Security Partnership:
- India's G-20 presidency provides an opportune moment to showcase successful strategies and frameworks for food security in the Global South.
- India can leverage and strengthen trade pathways with the UAE to build a sustainable, inclusive, efficient, and resilient future of food as it sets the global developmental agenda.
- Gateway to New Markets for India:
What are the Major Challenges to Global Food Security?
- Menace of Climate Change: The United Nations called out climate change, extreme weather events as the key factors driving growing food insecurity.
- Increased temperatures, weather variability, invasive crops and pests, and more frequent extreme weather events have detrimental effects on farming – from diminishing agricultural yields, to weakening the nutritional quality of produce on farms, to reducing farmer incomes
- Volatile Market Pricing: The concept of globalisation has given more openness to agricultural commerce, but it is unable to assure more stable market pricing.
- The lack of remunerative prices for end goods, distressed sales, high cultivation costs combined with inappropriate market prices act as a barrier in the path of food security.
- Trade Disruptions: Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes can result in trade disruptions, including embargoes, sanctions, and tariffs, which can impact food trade and affect food prices and availability.
- This can particularly affect countries that rely heavily on food imports, leading to food shortages and increased food prices, making food less accessible for vulnerable populations.
Way Forward
- Enhancing Climate Resilience: Investing in climate change adaptation and mitigation measures, such as water management, soil conservation, and climate-smart technologies, can help reduce the impact of climate change on food production and food security.
- Incentivising Climate Resilient Crops: Investment is needed for the development and distribution of climate-resilient crops that can handle temperature variation and precipitation fluctuations.
- The governments should incentivise the production of water- and nutrient-efficient crops (such as millets and pulses) and announce a lucrative Minimum Support Price and input subsidies for farmers.
- The United Nations (UN) General Assembly at its 75th session declared 2023 the International Year of Millets is a significant step in this direction.
- Agricultural Diplomacy: India can extend its support to other developing countries in Africa and Asia through technology partnerships, joint research in promoting drought resistant crops, promoting climate smart agriculture, thereby establishing India as a major player of Global South.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of India’s preparation for Climate-Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (2021)
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2 With reference to the provisions made under the National Food Security Act, 2013, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The families coming under the category of ‘below poverty line (BPL)’ only are eligible to receive subsidised food grains.
- The eldest woman in a household, of age 18 years or above, shall be the head of the household for the purpose of issuance of a ration card.
- Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a ‘take-home ration’ of 1600 calories per day during pregnancy and for six months thereafter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.1 In what way could replacement of price subsidy with Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) change the scenario of subsidies in India? Discuss. (2015)


International Relations
Hope for Peace in Yemen
For Prelims: Houthis, Location of Yemen and the neighborhood, Operation Rahat.
For Mains: Yemen civil war, Significance of the Houthi conflict, India’s Interest
Why in News?
The warring sides in Yemen are swapping hundreds of prisoners - a move which has built hopes for a permanent ceasefire between the Saudi-backed government forces and the Iranian-backed Houthi rebels.
How did the War in Yemen Begin?
- The Yemeni Civil War began in 2011 after the ousting of authoritarian president Ali Abdullah Saleh. The new president, Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi, was unable to stabilize the country due to economic and security problems.
- The Houthis, a Zaidi Shia Muslim minority group, took advantage of this and seized control of the north and the capital, Sanaa in 2014.
- This alarmed Saudi Arabia, which feared that the Houthis would become allies to their rival, Iran. Saudi Arabia then led a coalition that included other Arab countries and sent troops to Yemen in 2015. However, they were unable to drive out Houthis from Sana’a as well as from the north of the country.
- In April 2022, the UN brokered a ceasefire between the Saudi-led coalition and the Houthi rebels, though the sides failed to renew it six months laters.
What is the Stockholm Agreement?
- The warring parties in control of parts of Yemen had signed the Stockholm Agreement in December 2018, committing to freeing conflict-related detainees.
- The agreement brokered by the United Nations had three main components:
- The Hudayah agreement:
- The Hudayah agreement included a ceasefire in the city of Hodeidah and other clauses like no military reinforcements in the city and strengthened United Nation presence
- The Prisoner Exchange Agreement:
- The agreement was supervised by the Office of the Special Envoy of the Secretary-General for Yemen, and the International Committee of the Red Cross will oversee and facilitate the process.
- They aim to ensure that fundamental humanitarian principles and procedures that facilitate the release, or transfer or repatriation of all persons who were deprived of their liberty during the events in Yemen.
- The agreement was supervised by the Office of the Special Envoy of the Secretary-General for Yemen, and the International Committee of the Red Cross will oversee and facilitate the process.
- Taiz Agreement:
- The Taiz agreement includes the formation of a joint committee with participation from civil society and the UN.
- The Hudayah agreement:
How has this War Affected Yemen?
- According to the UN, Yemen is now the largest humanitarian crisis in the world, with 80% of its population dependent on aid and protection.
- Over three million people have been displaced from their homes since 2015, and public service sectors like healthcare, water, sanitation, and education have either collapsed or are in a dire situation.
- Economically, Yemen is in the trenches, having lost USD 90 billion in economic output, and more than 6,00,000 people have lost their jobs. More than half of the country's population is living in extreme poverty.
What are the Concerns for India and the World in the Yemen Crisis?
- Global:
- Yemen's location at the strait linking the Red Sea with the Gulf of Aden is critical for global oil shipments, raising concerns about the impact of the conflict on global oil prices.
- The presence of groups like al-Qaeda and IS affiliates in Yemen poses a risk to global security.
- India:
- Yemen is a major source of crude oil for India, and any disruption to the oil supply chain could have a significant impact on India's energy security.
- The large population of Indian expats in Yemen, Saudi Arabia, Iran presents a significant challenge for India.
- India has a responsibility to ensure the safety and security of its citizens and manage the impact of any disruption to remittances, which are a significant source of income for many families in India.
What are India’s Initiatives?
- Operation Rahat:
- India launched a massive air and sea operation to evacuate over 4000 Indian nationals from Yemen in April 2015.
- Humanitarian Assistance:
- India has provided food and medical aid to Yemen in the past and thousands of Yemeni nationals have availed of medical treatment in India over the past few years.
- India also continues to facilitate education of a large number of Yemeni nationals in various Indian institutions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Very recently, in which of the following countries have lakhs of people either suffered from severe famine/acute malnutrition or died due to starvation caused by war/ethnic conflicts? (2018)
(a) Angola and Zambia
(b) Morocco and Tunisia
(c) Venezuela and Colombia
(d) Yemen and South Sudan
Ans: (d)


Governance
Nagaland's Opposition to Women's Reservation in ULB Polls
For Prelims: Urban Local Bodies, Reservation for Women.
For Mains: special provisions granted by Article 371A of the Constitution to Nagaland, The structure and functions of Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in India
Why in News?
The recent controversy in Nagaland over the reservation of seats for women in urban local body (ULB) polls has sparked a heated debate among various stakeholders in the state.
- The issue centers around the Nagaland Municipal Act of 2001, which mandated a 33% reservation for women in ULB polls, as per the 74th Amendment to the Constitution of India.
What is the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act?
- Urban local governments were constitutionalized through the 74th Amendment Act during the regime of P.V. Narsimha Rao's government in 1992. It came into force on 1st June 1993.
- It added Part IX -A and consists of provisions from Articles 243-P to 243-ZG.
- In addition, the act also added the 12th Schedule to the Constitution. It contains 18 functional items of Municipalities.
Why is there Opposition to ULB Polls in Nagaland?
- Reservation for Women Against the Customs:
- Most of the traditional tribal and urban organizations oppose the 33% reservation of seats for women, arguing that it would violate the special provisions granted by Article 371A of the Constitution to Nagaland.
- According to Article 371A, Parliament cannot make laws about the religious or social practices of the Nagas, their traditional laws, and how they solve legal problems, or who owns and uses the land unless the Nagaland Legislative Assembly agrees.
- The apex tribal body of Nagaland, Naga Hoho argues that women have traditionally not been part of decision-making bodies.
- Nagaland is the only state where ULB seats are not reserved for women.
- Most of the traditional tribal and urban organizations oppose the 33% reservation of seats for women, arguing that it would violate the special provisions granted by Article 371A of the Constitution to Nagaland.
- Demand of Protestors:
- The tribal bodies and civil society organizations threatened to boycott the polls until the Municipal Act of 2001 factoring in women's reservation is "reviewed and rewritten in complete consonance of the voice of the Naga people" so that it does not infringe upon Article 371A.
- Previous ULB Polls in Nagaland:
- The first and only civic body election in Nagaland was held in 2004 without any reservation of seats for women.
- In 2006, the State govt amended the Municipal Act 2001 to include 33% reservation for women, triggering widespread opposition that led to the indefinite postponement of the ULB polls in 2009.
- Efforts to hold the elections in March 2012 also met with strong protests, and in September 2012, the State Assembly passed a resolution to exempt Nagaland from Article 243T of the Constitution related to the reservation for women.
- This resolution was revoked in 2016, and elections to the civic bodies with 33% reservation were notified a month later, again leading to widespread mayhem.
- The government declared the process to conduct elections null and void in February 2017.
- In 2006, the State govt amended the Municipal Act 2001 to include 33% reservation for women, triggering widespread opposition that led to the indefinite postponement of the ULB polls in 2009.
- The first and only civic body election in Nagaland was held in 2004 without any reservation of seats for women.
What are Urban Local Bodies (ULB)?
- About:
- Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) are small local bodies that administer or govern a city or a town of a specified population.
- ULBs are vested with a long list of functions delegated to them by the state governments broadly related to public health, welfare, regulatory functions, public safety, public infrastructure works, and development activities.
- Structure:
- The Urban Local Government consists of eight types of Urban local bodies.
- Municipal Corporation:
- Municipal corporations are usually found in big cities such as Bangalore, Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, etc
- Municipality:
- The smaller cities tend to have the provision of municipalities.
- The Municipalities are often called upon by other names such as the municipal council, municipal committee, municipal board, etc.
- Notified Area Committee:
- Notified area committees are set up for the fast-developing towns and the towns lacking the basic amenities.
- All the members of the notified area committee are nominated by the state government.
- Town Area Committee:
- The town area committee is found in small towns.
- It has minimal authority such as street lighting, drainage roads, and conservancy.
- Cantonment Board:
- It is usually set up for a civilian population living in the cantonment area.
- It is created and run by the central government.
- Township:
- Township is another form of urban government to provide basic facilities to the staff and workers living in the colonies established near the plant.
- It has no elected members and is merely an extension of the bureaucratic structure.
- Port Trust
- Port trusts are established in the port areas such as Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, etc.
- It manages and takes care of the port.
- It also provides basic civic amenities to the people living in that area.
- Special Purpose Agency:
- These agencies undertake the designated activities or specific functions belonging to the municipal corporations or municipalities.
- Municipal Corporation:
- The Urban Local Government consists of eight types of Urban local bodies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Recent directives from the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas are perceived by the ‘Nagas’ as a threat to override the exceptional status enjoyed by the State. Discuss in light of Article 371A of the Indian Constitution. (2013)


Governance
Sangathan se Samriddhi: DAY-NRLM
For Prelims: Sangathan se Samriddhi, DAY-NRLM, SHG, GDP, Rural Household, Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
For Mains: Impact of DAY-NRLM on Rural India and Indian Economy.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Rural Development's Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) launched a national campaign called “Sangathan Se Samridhhi– Leaving no Rural Woman Behind”, aiming to mobilize a significant number of women into Self Help Groups (SHGs).
What is Sangathan Se Samridhhi Campaign?
- About:
- The campaign is a part of the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav Samaveshi Vikaas and aims to mobilize 10 crore women from eligible rural households into SHGs.
- It aims to mobilize disadvantaged rural communities who are unaware of the benefits of the DAY-NRLM program.
- The campaign will be organized in all states and form more than 1.1 lakh SHGs through interventions like:
- Organising general Body Meetings of Village Organizations
- Experience sharing by SHG champions to motivate left-out households to join SHGs
- Conducting Community Resource Person drives
- Opening SHG bank accounts, and creation of a common database of SHGs promoted by other stakeholders.
- Need for Such a Campaign:
- India’s rural population accounts for 65% of its total population, and it is crucial to accord women from these areas all possible opportunities to enable them to contribute significantly to making India a 5 trillion dollar economy.
- When women in such a big number become part of SHGs, it will automatically have a considerable effect on the country’s GDP (Gross Domestic Product).
How can SHGs help in Women Empowerment?
- Economic Empowerment:
- SHGs provide women entrepreneurs with micro-loans to sustain their businesses, while also creating an environment for them to develop greater agency and decision-making skills.
- A 2022 study by Institute for Financial Management and Research (IFMR) suggested that women aided by SHGs were 10% more likely to save on a regular basis, resulting in economic empowerment, while working towards a better future for the next generation.
- SHGs provide women entrepreneurs with micro-loans to sustain their businesses, while also creating an environment for them to develop greater agency and decision-making skills.
- Women Entrepreneurship:
- SHGs also deliver services ranging from entrepreneurial training, livelihood promotion and community development for women entrepreneurs.
- In Maharashtra alone, there are 527,000 SHGs, which have accounted for over 50% of all women-led small-scale industrial units in India.
- This is a clear indication that SHGs can lead to the overall development of women entrepreneurship.
- Skill Development:
- SHGs also provide training and capacity building to their members. Women can learn new skills, such as tailoring, handicrafts, or farming techniques.
- This not only helps them to improve their earning potential but also enhances their self-confidence and self-esteem.
- Social Empowerment:
- SHGs provide a platform for women to come together and share their experiences. This creates a sense of solidarity among women and helps to break down social barriers.
- It also enables women to participate in decision-making at the household and community level, giving them a voice and greater control over their lives.
What is Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission?
- About:
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Programme, launched by the Ministry of Rural Development in 2011.
- It aims to eliminate rural poverty through the promotion of multiple livelihoods and improved access to financial services for the rural poor households across the country.
- Functioning:
- It involves working with community institutions through community professionals in the spirit of self-help which is a unique proposition of DAY-NRLM.
- It impacts livelihoods by
- Mobilizing rural households into SHGs.
- Organizing one-woman member from each rural poor household into SHGs
- Providing training and capacity building to SHG members
- Providing access to financial resources from their own institutions and banks.
- Sub Programs:
- Mahila Kisan Shashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): It aims to promote agro-ecological practices that increase women farmers’ income and reduce their input costs and risks.
- Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP): It aims to support entrepreneurs in rural areas to set up local enterprises.
- Aajeevika Grameen Express Yojana (AGEY): It was launched in August 2017, to provide safe, affordable and community monitored rural transport services to connect remote rural villages.
- Deendayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDUGKY): It aims at building placement-linked skills of the rural youth and placing them in relatively higher wage employment sectors of the economy.
- Rural Self Employment Institutes (RSETIs): DAY-NRLM, in partnership with 31 Banks and State Governments, is supporting Rural Self Employment Institutes (RSETIs) for skilling rural youth to take up gainful self-employment.
- Outcome:
- By July 2022, 8.35 crore women were connected to NRLM and there were 5.9 lakh crore bank linkages, while the NPAs have reduced to 2.5 %.
- Till 2014, It involved 2.35 lakh houses, had 80,000 crore bank linkages with Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) at 9.58 %.
- As of May 2021, there are 6.9 million SHGs in India with 75 million members across 7,83,389 villages.
- The NRLM has enabled rural families to negotiate for greater access to essential services such as education and healthcare.
- It has improved food security, improved school enrolment, access to land for women to grow food, and created an impact on gender issues with women’s groups taking on issues like dowry, child marriage, and discrimination against girls.
- By July 2022, 8.35 crore women were connected to NRLM and there were 5.9 lakh crore bank linkages, while the NPAs have reduced to 2.5 %.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. How does the National Rural Livelihood Mission seek to improve livelihood options of rural poor? (2012)
- By setting up a large number of new manufacturing industries and agribusiness centres in rural areas
- By strengthening ‘self-help groups’ and providing skill development
- By supplying seeds, fertilizers, diesel pump-sets and micro-irrigation equipment free of cost to farmers
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. “The emergence of Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in contemporary times pointsto the slow but steady withdrawal of the State from developmental activities”. Examine the role of the SHGs in developmental activities and the measures taken by the Government of India to promote the SHGs (2017)
Q. The Self-Help Group (SHG) Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP), which is India’s own innovation, has proved to be one of the most effective poverty alleviation and women empowerment programmes. Elucidate. (2015)


Governance
Animal Birth Control Rules, 2023
For Prelims: Prevention of Cruelty to Animal Act, 1960, Animal Welfare Board of India, Rabies, National Centre for Disease Control , One Health .
For Mains: Status of Rabies India, Animal Birth Control Rules, 2023.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying has issued the Animal Birth Control Rules, 2023. These Rules supersede the Animal Birth Control (Dog) Rules, 2001, and are issued under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animal Act, 1960.
What are the Major Points Related to Animal Birth Control Rules, 2023?
- Background:
- India recorded a whopping 160 million cases of street/stray dog bites between 2019 and 2022, according to data submitted in Parliament till November 2022.
- This has also led to an increase in revenge crime and atrocities against dogs, feeders of dogs and caregivers as well as conflicts among urban residents.
- Provisions:
- The Rules have been formulated in accordance with the guidelines provided by the Hon'ble Supreme Court related to Animal Welfare Board of India and People for Elimination of Stray Troubles.
- The Supreme Court has specifically mentioned in various orders that relocation of dogs cannot be permitted.
- The Rules aim to provide guidelines for the sterilisation and immunisation of stray dogs through Animal Birth Control (ABC) programmes.
- The responsibility of carrying out ABC programmes lies with the respective local bodies, municipalities, municipal corporations, and panchayats.
- The Municipal Corporations are required to implement the ABC and Anti Rabies Program jointly.
- It provides guidelines on how to deal with human and stray dog conflicts without relocating the dogs in an area.
- It also emphasises addressing the cruelty involved in carrying out ABC programmes, ensuring animal welfare.
- The Rules have been formulated in accordance with the guidelines provided by the Hon'ble Supreme Court related to Animal Welfare Board of India and People for Elimination of Stray Troubles.
Rabies
- About:
- Cause:
- It is caused by a Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) virus that is present in the saliva of a rabid animal (dog, cat, monkey, etc).
- It is invariably transmitted following a bite of an infected animal that leads to deposition of the saliva and the virus in the wound.
- According to WHO, Dogs are the main source of human rabies deaths, contributing up to 99% of all rabies transmissions to humans.
- Status in India:
- India is endemic for rabies, and accounts for 36% of the world’s rabies deaths.
- According to WHO, about 30-60% of reported rabies cases and deaths in India occur in children under the age of 15 years as bites that occur in children often go unrecognised and unreported.
- Treatment:
- Rabies can be prevented by vaccinating pets, and seeking medical care after potential exposures before symptoms start.
- Initiatives Related to Rabies Control:
- Global:
- United Against Rabies Forum: The UAR Forum brings together global experts from various organisations, ministries and countries so that they can work towards specific objectives and activities to facilitate efforts towards achieving Zero dog-mediated human rabies deaths by 2030.
- Indian:
- National Action Plan for Dog Mediated Rabies Elimination by 2030 (NAPRE): The NAPRE was drafted by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) in association with the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry, and Dairying.
- Its approach for elimination of rabies is based on recommendations of several international agencies like WHO and the Global Alliance of Rabies Control (GARC).
- Global:
Conclusion
India is looking forward to creating a One Health network that will not only serve rabies but will also strengthen surveillance and health systems for multiple health risks at the human-animal-environment interface through better coordination and communication between the animal- and human health and other relevant sectors.


Important Facts For Prelims
Ningaloo Eclipse
Why in News?
The Ningaloo Eclipse was witnessed on April 20, 2023. It is a rare ‘hybrid solar eclipse’ , caused by the curvature of the earth's surface and a shift from annular to total eclipse.
- The last one was seen in 2013, and the next one will appear in 2031.
What are the Major Points Related to Hybrid Solar Eclipse?
- A total solar eclipse was visible in Australia, Timor-Leste and Indonesia (West Papua and Papua).
- At the same time, a partial solar eclipse was visible in southeast Asia, East Indies, Australia, Philippines and New Zealand. It was not visible in India.
- Its uniqueness is such that it has already been named as Ningaloo, a part of western Australia from which the eclipse was most visible.
- The Ningaloo region is also designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
What is a Solar Eclipse?
- About:
- A solar eclipse is a natural phenomenon that occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, casting a shadow on the Earth's surface, resulting in a temporary darkening of the Sun.
- The moon's shadow has two parts: a central region (umbra) and an outer region (penumbra).
- A solar eclipse is a natural phenomenon that occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, casting a shadow on the Earth's surface, resulting in a temporary darkening of the Sun.
- Types of Solar Eclipse:
- Total Solar Eclipse: A total eclipse happens when the Moon completely blocks out the Sun while passing between the Earth and the Sun.
- The Baily's Beads effect, also known as the diamond ring effect, is a phenomenon that occurs during a total solar eclipse or annular solar eclipse.
- Annular Eclipse: It happens when the Moon is at its farthest point from the Earth.
- The sun is covered in such a way that only a small ring-like sliver of light is seen from the sun's disc. This ring is known as the ring of fire.
- Partial Eclipse: It occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun but is not perfectly aligned.
- Hence, only a part of the Sun appears covered.
- Hybrid Eclipse: A hybrid solar eclipse occurs when the eclipse is total from some locations on Earth and annular from others, due to the viewer's position relative to the Moon's shadow.
- It means that for some observers, the Moon appears to fully cover the Sun, resulting in a total solar eclipse, while for others, the Moon only partially covers the Sun, resulting in an annular solar eclipse.
- Total Solar Eclipse: A total eclipse happens when the Moon completely blocks out the Sun while passing between the Earth and the Sun.


Important Facts For Prelims
Twitter's Hateful Conduct Policy and Deadnaming
Why in News?
Twitter recently changed its hateful conduct policy that once prohibited misgendering and deadnaming of transgender individuals on its platform.
- This has sparked controversy among many who believe that the social media platform's safety standards for marginalized groups are being compromised under the leadership of Elon Musk.
What are the Changes in the Twitter’s Policy?
- The policy once read, “We prohibit targeting others with repeated slurs, tropes, or other content that intends to dehumanize, degrade or reinforce negative or harmful stereotypes about a protected category. This includes targeted misgendering or deadnaming of transgender individuals”.
- Twitter has removed this protection for transgenders.
- In addition to changing its “hateful conduct policy,” Twitter has announced that it will only put warning labels on some tweets that might violate its rules against hateful conduct. Previously, tweets that violated these rules were removed from the platform entirely.
- This change could lead to an increase in harmful content on the platform, which could negatively impact the safety of marginalized groups.
- Critic's Views:
- Concerns about the safety of marginalized groups on Twitter have surfaced several times, with many critics arguing that the platform has become less safe under the leadership of Elon Musk.
- Critics believe that the platform can no longer protect users from "trolling, state-coordinated disinformation, and child sexual exploitation".
What is Deadnaming?
- Deadnaming is the act of calling a trans, non-binary, and/or gender-expansive person by their birth name or the name they used before they adopted their chosen name.
- This practice is harmful because it invalidates a person's identity and may reveal personal information that the person does not want to be disclosed.
- Deadnaming is harmful because refusing to use a person’s chosen name or pronouns is a form of transphobia or cis-sexism which may result in harassment, discrimination, and assault, and contributes to mental health conditions such as depression and suicidality.


Important Facts For Prelims
Off-Budget Liabilities
Why in News?
The Indian government ended its practice of off-budget borrowings in FY2022 to increase fiscal transparency. And it is planning to pre-pay the remaining such Off-Budget liabilities.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India and the 15th Finance Commission had red-flagged the off-Budget funding of welfare schemes through public sector entities and had urged the Centre to come clean on these.
What are Off-Budget Liabilities?
- Off-Budget liabilities refer to debts taken by state-run agencies to finance government programs and subsidies outside the traditional budget.
- These agencies raise funds through bonds that offer higher interest rates than government securities (G-secs).
- But since the liability of the loan is not formally on the Centre, the loan is not included in the national fiscal deficit. This helps keep the country’s fiscal deficit within acceptable limits.
- By end-FY21, the Centre had off-budget liabilities close to Rs 6.7 trillion.
- The outstanding off-budget liabilities of the Centre include about Rs 49,000 crore for the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Rural, Rs 20,164 crore for various irrigation projects, Rs 12,300 crore for Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen, etc.
What are the Government's Efforts to Eliminate Off-Budget Liabilities?
- Efforts:
- The Indian government took a significant step towards fiscal transparency by ending its practice of off-budget borrowings through state-run agencies in the FY22 budget.
- The government also took over Rs 5 trillion or 75% of its off-Budget liabilities from the National Small Saving Fund (NSSF) in FY21-FY22.
- However, the remaining off-Budget liabilities of Rs 1.7 trillion are proving challenging to eliminate due to bondholders' reluctance to forego high-yield bonds.
- Challenges:
- Bondholders are unwilling to give up their high-yield bonds and lose interest income for the remaining period of the bonds.
- The investors are worried that they won't find other secure and highly rated bonds with similar attractive coupon rates to invest in if they accept the prepayment offer.
- Furthermore, bondholders usually demand a premium or a higher interest rate than promised to them to recoup their loss of interest income in the residual period of the bonds, in case an issuer wants to prepay.
- Bondholders are unwilling to give up their high-yield bonds and lose interest income for the remaining period of the bonds.
- Implications of Off-Budget Liabilities:
- Pushing the government's debt-to-GDP to a 15-year high of about 61.6% in FY21.
- Hindering the government's efforts to achieve financial transparency and accountability.
- Diverting funds from priority sectors such as health, education, and infrastructure development to finance other government programs and subsidies.
- Contributing to the accumulation of non-performing assets in state-run agencies.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
India's 100 Food Streets Initiative
The Health Ministry of India, in partnership with the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, (MoHUA) has proposed the development of 100 food streets in 100 districts across the country. The initiative aims to promote safe and healthy practices in the food industry, reduce food-borne illnesses, and improve overall health outcomes. The project will be implemented as a pilot scheme to demonstrate best practices for food businesses. This initiative will not only support the "eat right campaign" and food safety but also enhance the credibility of local food businesses. The project's benefits include creating employment opportunities, improving tourism potential, and boosting the economy.
The initiative will be implemented through the National Health Mission (NHM) in convergence with the MoHUA and with technical support from the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI). States and Union Territories will receive financial assistance of ₹1 crore per food street/district, with assistance under the NHM provided in the ratio of 60:40 or 90:10, subject to standard branding according to FSSAI guidelines.
Read more: National Health Mission, Eat Right Campaign
Civil Services Day
The Vice-President of India addressed a gathering of civil servants at the 16th Civil Services Day (CVD) in New Delhi, the date 21st April is chosen to commemorate the day when the first Home Minister of Independent India, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel addressed the probationers of Administrative Services Officers in 1947 at Metcalf House, Delhi and he referred the Civil servants as the ‘Steel Frame of India’.
On this 16th CVD, the crucial role played by civil servants in ensuring the inclusive development of the nation was emphasized. Civil servants were called upon to facilitate uniformity in administration across the Union and the States so that federalism could flourish into cooperative federalism. Highlighted the Mission Karamyogi, a National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building, which is shaping the future-ready civil service aligned to the vision of New India. The importance of technology in complementing the leadership of civil servants for accelerated service delivery and citizen-centric governance is recognized. The Vice-President unveiled an e-book on the ‘National Good Governance Webinar Series’ and inaugurated an exhibition on ‘Good Governance Practices in India- Awarded Initiatives’.
Read more: Civil Services Day
MEF Leaders Discuss Climate Action and Initiatives
Recently, the virtual meeting of the Major Economies Forum on Energy and Climate Change was held, chaired by US President and attended by Heads of State and Ministers from 20 major economies worldwide. The International Energy Agency , stressed the urgency for climate action to limit global temperature rise and mentioned Indian Prime Minister’s call for LiFE, a lifestyle for the environment. All MEF leaders recognized climate change as one of the biggest challenges and voiced the need for joint efforts to upscale climate action.
Indian Minister of Environment, Forest & Climate Change, and Labour & Employment emphasized India's leadership in combating climate change, with per capita emissions one-third of the global average. India's initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from various sectors, support for climate finance, and the importance of LiFE in individual behavior change towards combating climate change are highlighted. The meeting also discussed efforts to strengthen the financial capacity of Multilateral Development Banks (MDB) to address global challenges, including poverty reduction and SDGs.
Read more: LiFE
Heat Index
The heat index, which takes into account both air temperature and humidity, is an important indicator of the perceived heat that people experience. In Delhi, the heat index in April 2022 reached dangerous levels, ranging from 44oC to 49oC. The recorded heat index figures in Delhi are in the "danger" category of the US National Weather Service classification, which points to the likelihood of heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and possible heat stroke in case of continued activity. The concentration of the slum population, lack of access to amenities, poor housing conditions, and non-availability of healthcare and health insurance, can aggravate the heat-related vulnerabilities in Delhi.
There is direct relationship between the air temperature and relative humidity and the heat index, meaning as the air temperature and relative humidity increase (decrease), the heat index increases (decreases).
Read more: Heat Index, Heatwaves