World Desertification Day 2023
For Prelims: World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought, United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), Drought, Gender Action Plan
For Mains: Drought and Desertification: Causes & Impact on Women, Gender Equality
Why in News?
World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought is observed every year on the 17th of June.
- The theme for this year is “Her Land. Her Rights” which focuses on women’s land rights, essential for achieving the interconnected global goals of gender equality and land degradation neutrality by 2030 and contributing to the advancement of several other Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What are the Highlights of World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought?
- Background:
- Desertification, along with climate change and the loss of biodiversity, were identified as the greatest challenges to sustainable development during the 1992 Rio Earth Summit.
- Two years later, in 1994, the UN General Assembly established the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), the sole legally binding international agreement linking environment and development to sustainable land management and declared 17 June "World Day to Combat Desertification and Drought".
- Later on, in 2007, the UN General Assembly declared 2010-2020 the United Nations Decade for Deserts and the fight against Desertification to mobilise global action to fight land degradation, led again by the UNCCD Secretariat.
- Issues Addressed:
- Women's control over land is crucial. However, they often lack rights and face barriers worldwide. This limits their well-being and prosperity, especially when land degradation and water scarcity occur.
- Investing in women's land access is an investment in their future and the future of humanity.
- Desertification, land degradation and drought disproportionately impact women and girls, as they often do not have access to and control of land resources. They are most affected by reduced agricultural yields and increased water scarcity.
- In most countries, women have unequal and limited access and control to land. In many regions, they remain subject to discriminatory laws and practices that impede their right to inherit, as well as their access to services and resources.
- Women's control over land is crucial. However, they often lack rights and face barriers worldwide. This limits their well-being and prosperity, especially when land degradation and water scarcity occur.
- Gender Equality: An Unfinished Business:
- According to UNCCD’s landmark study “The Differentiated Impacts of Desertification, Land Degradation and Drought on Women and Men,” gender equality remains unfinished business in every part of the world.
- Today, nearly half of the global agricultural workforce is female – yet less than one in five landholders worldwide are women.
- Women’s rights to inherit their husband’s property continue to be denied in over 100 countries under customary, religious, or traditional laws and practices.
- Globally, women already spend a collective 200 million hours every day collecting water. In some countries, a single trip to fetch water can take over an hour.
- According to UNCCD’s landmark study “The Differentiated Impacts of Desertification, Land Degradation and Drought on Women and Men,” gender equality remains unfinished business in every part of the world.
- Initiative Taken & Recommendations:
- A Global Campaign:
- Together with partners, high-profile personalities and influencers, UNCCD has launched a global campaign to recognize excellence, leadership, and efforts in sustainable land management by women and girls.
- Recommendations:
- Governments can promote laws, policies and practices that end discrimination and secure women’s rights to land and resources.
- Businesses can prioritise women and girls in their investments and facilitate access to finance and technology.
- Individuals can support women-led initiatives that are restoring land.
- A Global Campaign:
What is UNCCD’s Gender Action Plan, 2017?
- The gender action plan, 2017 was adopted during the Conference of the Parties (COP23), in Bonn, Germany to incorporate gender equality and women’s empowerment in climate change discourse and actions.
- The aim is to ensure that women can influence climate change decisions and that women and men are represented equally in all aspects of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), as a way to increase its effectiveness.
What are Desertification and Drought?
- Desertification:
- About:
- Degradation of land in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid areas. It is caused primarily by human activities and climatic variations.
- Causes:
- Climate change
- Deforestation
- Overgrazing
- Unsustainable Agricultural Practices
- Urbanisation
- About:
- Drought:
- About:
- Drought is generally considered as a deficiency in rainfall /precipitation over an extended period, usually a season or more, resulting in a water shortage causing adverse impacts on vegetation, animals, and/or people.
- Causes:
- Variability in rainfall
- Deviation in the route of monsoon winds
- Early withdrawal of the monsoon
- Forest fires
- Land degradation in addition to Climate change
- About:
What are the Related Initiatives to Reduce Desertification?
- Indian Initiatives:
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme, since 2009-10:
- It was launched by the Department of Land Resources, Ministry of Rural Development that aims to restore ecological balance by harnessing, conserving and developing degraded natural resources with the creation of Rural Employment.
- Desert Development Programme:
- Launched in 1995 by the Ministry of Rural Development to minimise the adverse effect of drought and to rejuvenate the natural resource base of the identified desert areas.
- National Mission on Green India:
- It was approved in 2014 and implemented under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change with the objective of protecting, restoring and enhancing India’s diminishing forest cover with a deadline of 10 years.
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme, since 2009-10:
- Global Initiatives:
- Bonn Challenge:
- The Bonn Challenge is a global effort to bring 150 million hectares of the world’s deforested and degraded land into restoration by 2020, and 350 million hectares by 2030.
- At the UNFCCC Conference of the Parties (COP) 2015 in Paris, India also joined the voluntary Bonn Challenge pledge to bring into restoration 21 million hectares of degraded and deforested land by the year 2030.
- The target has now been revised to restore 26 million hectares of degraded and deforested land by 2030.
- Bonn Challenge:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2014)
| Programme/Project | Ministry | |
| 1. | Drought-Prone Area | Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare |
| 2. | Desert Development Programme | Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change |
| 3. | National Watershed Project Development for Rainfed Areas | Ministry of Rural Development |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. The process of desertification does not have climate boundaries. Justify with examples. (2020)
Q. In what way micro-watershed development projects help in water conservation in drought-prone and semi-arid regions of India? (2016)
Q. “Empowering women is the key to control population growth”. Discuss. (2019)
Remittance Inflow
For Prelims: World Bank, Remittances, Foreign exchange, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Gulf Cooperation Council, National Payments Corporation of India, E-commerce
For Mains: Remittance Trends Across the Globe, Factors Affecting Remittance Flows to India.
Why in News?
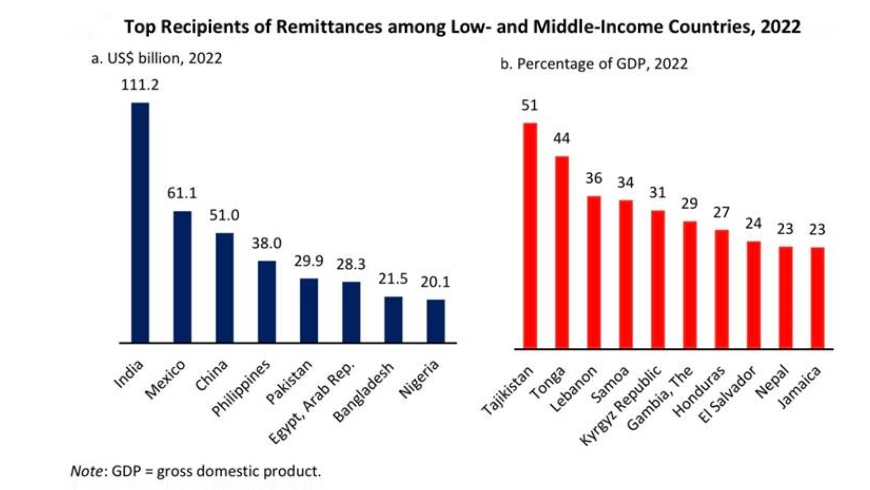
According to the World Bank’s latest Migration and Development Brief, India, which saw a record-high of USD 111 billion in remittances in 2022, is expected to experience minimal growth of just 0.2% in remittance inflows in 2023.
- The main reasons for this are the slower growth in OECD economies, especially in the high-tech sector, and the lower demand for migrants in the GCC countries.
- Overall, remittance growth is projected to be slower globally, with Latin America and the Caribbean showing the highest growth while South Asia lags behind.
What are Remittances?
- Remittances are money transfers that migrants send to their families and friends in their home countries.
- They are an important source of income and foreign exchange for many developing countries, especially those in South Asia.
- Remittances can help reduce poverty, improve living standards, support education and health care, and stimulate economic activity.
What are the Remittance Trends Across the Globe?
- The top five recipient countries for remittances in 2022 were India, Mexico, China, the Philippines, and Pakistan.
- Remittance flows to low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) are projected to moderate to 1.4% in 2023, with total inflows estimated at USD 656 billion.
- East Asia and the Pacific region may witness a decline in remittance growth due to tight monetary stances, limited fiscal buffers, and global uncertainty surrounding geopolitical events.
- Remittances to Europe and Central Asia are anticipated to grow by 1%, influenced by a high base effect, weakened flows to Ukraine and Russia, and a depreciating Russian ruble.
- Remittances in the Middle East and North Africa may recover with declining oil prices, particularly for countries like Egypt.
- Remittance growth rates for East Asia and Pacific, as well as Sub-Saharan Africa, are projected to be around 1% in 2023.
- Remittance inflows played a vital role in funding current account and fiscal shortfalls in countries like Tajikistan, Tonga, Lebanon, Samoa, and the Kyrgyz Republic.
What are the Factors Affecting Remittance Flows to India?
- Top Sources of Remittances for India
- Approximately 36% of India's remittances originate from high-skilled Indian migrants in three high-income destinations: the US, United Kingdom, and Singapore.
- The post-pandemic recovery led to a tight labor market in these regions, resulting in wage hikes that boosted remittances.
- Other high-income destinations for Indian migrants, such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, experienced favorable economic conditions, including high energy prices and curbed food price inflation, which increased remittance inflows.
- Factors Affecting Remittance Flows to India:
- Slower Growth in OECD economies: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is a grouping of 38 high-income democratic countries. These countries are major destinations for high-skilled and high-tech Indian migrants, who account for almost 36% of India’s remittances.
- The World Bank expects that the growth of these economies will moderate from 3.1% in 2022 to 2.1% in 2023 and 2.4% in 2024.
- This could affect the demand for IT workers and lead to a diversion of formal remittances toward informal money transfer channels.
- The World Bank expects that the growth of these economies will moderate from 3.1% in 2022 to 2.1% in 2023 and 2.4% in 2024.
- Lower Demand for Migrants in GCC countries: GCC is a political and economic alliance of six Middle Eastern countries—Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, and Oman.
- These countries are the single largest destination for less-skilled South Asian migrants, who account for about 28% of India’s remittances.
- The World Bank expects that the growth of these countries will slow from 5.3% in 2022 to 3% in 2023 and 2.9% in 2024.
- This is mainly due to the declining oil prices, which have dented their fiscal revenues and public spending.
- Slower Growth in OECD economies: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is a grouping of 38 high-income democratic countries. These countries are major destinations for high-skilled and high-tech Indian migrants, who account for almost 36% of India’s remittances.
What are the Ways to Enhance Remittance Inflow in India?
- Unified Payment Interface: UPI can enable real-time fund transfers, allowing remittances to be sent and received instantly. This eliminates the need for lengthy processing times associated with traditional remittance methods, providing recipients with quicker access to funds.
- In January 2023, The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) allowed NRIs living in 10 countries to use UPI using their international mobile numbers.
- The ten countries include Singapore, Australia, Canada, Hong Kong, Oman, Qatar, USA, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Driven Risk Assessment: India can utilize AI algorithms to analyze transaction patterns, detect potential fraud, and assess risk factors associated with remittance transfers.
- This approach can enhance security and help prevent illegal activities, ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Integration with E-commerce Platforms: India can collaborate with e-commerce platforms to integrate remittance services directly into their platforms.
- This enables recipients to utilize remittance funds for online purchases or bill payments, enhancing financial inclusion and expanding the scope of remittance utilization.
Addition of More Castes to Central OBC List
For Prelims: National Commission for Backward Classes, Constitutional provisions related to OBC.
For Mains: National Commission for Backward Classes, Issues related to Reservation.
Why in News?
National Commission for Backward Classes(NCBC) is processing the request for the approval of about 80 more castes in six States, (Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Haryana) for the inclusion in the OBC list.
What is Other Backward Class (OBC)?
- About:
- The term OBC includes all classes of citizens who are socially and educationally backwards.
- Supreme Court concluded that in order to identify OBC’s, the principle of exclusion of creamy layer should be applied.
- A creamy layer can be defined as those classes of people within the OBC category who are no longer backward and are socially and economically at par with other forward classes of the country.
- Process of Inclusion:
- NCBC is a constitutional body that examines requests for inclusion of castes in Central OBC list.
- NCBC constitutes a Bench to examine proposals and forwards its decision to the Union government.
- Cabinet approves the additions and brings legislation, President notifies the change Cabinet approves the additions and brings legislation, President notifies the change.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Under Article 15(4) of the Constitution, the State has the power to make special provisions for the advancement of any socially and educationally backward class i.e., the OBC.
- The term “special provision for advancement” includes several aspects like reservation of seats in educational institutions, financial assistance, scholarships, free housing etc.
- Under Article 16(4), the state is empowered to enact laws for the reservation of appointments or posts in favour of OBCs.
- Under Article 15(4) of the Constitution, the State has the power to make special provisions for the advancement of any socially and educationally backward class i.e., the OBC.
- Union Government’s Achievements:
- Added 16 communities to Central OBC list in Himachal Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir since 2014
- Brought 105th Amendment to Constitution to re-affirm States’ right to maintain their own OBC lists, saving 671 State OBC communities from losing benefits
What is the National Commission for Backward Classes?
- About:
- 102nd Constitution Amendment Act, 2018 provides constitutional status to the NCBC.
- It has the authority to examine complaints and welfare measures regarding socially and educationally backward classes.
- Previously NCBC was a statutory body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- Background:
- Two Backward Class Commissions were appointed in 1950s and 1970s under Kaka Kalelkar and B.P. Mandal respectively.
- Kaka Kalelkar commission is also known as the First Backward Classes Commission.
- In Indra Sawhney case of 1992, Supreme Court had directed the government to create a permanent body to entertain, examine and recommend the inclusion and exclusion of various Backward Classes for the purpose of benefits and protection.
- In pursuant to these directions' parliament passed the National Commission for Backward Classes Act in 1993 and constituted the NCBC.
- 123rd Constitution Amendment bill of 2017 was introduced in Parliament to safeguard the interests of backward classes more effectively.
- Parliament has also passed a separate bill to repeal the National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993, thus 1993 act became irrelevant after passing the bill.
- The bill got the President assent in August 2018 and provided the constitutional status to NCBC.
- Two Backward Class Commissions were appointed in 1950s and 1970s under Kaka Kalelkar and B.P. Mandal respectively.
- Structure
- The Commission consists of five members including a Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson and three other Members appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal.
- The conditions of service and tenure of office of the Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson and other Members is determined by President.
Miyawaki Plantation Method
Why in News?
Prime Minister of India in his recent episode of 'Mann ki Baat', discussed the concept of Miyawaki plantation. He shed light on the Japanese technique of establishing dense urban forests in limited spaces.
- He also mentioned the inspiring story of Raafi Ramnath, a teacher from Kerala, who utilized the Miyawaki method to convert a barren piece of land into a miniature forest named Vidyavanam.
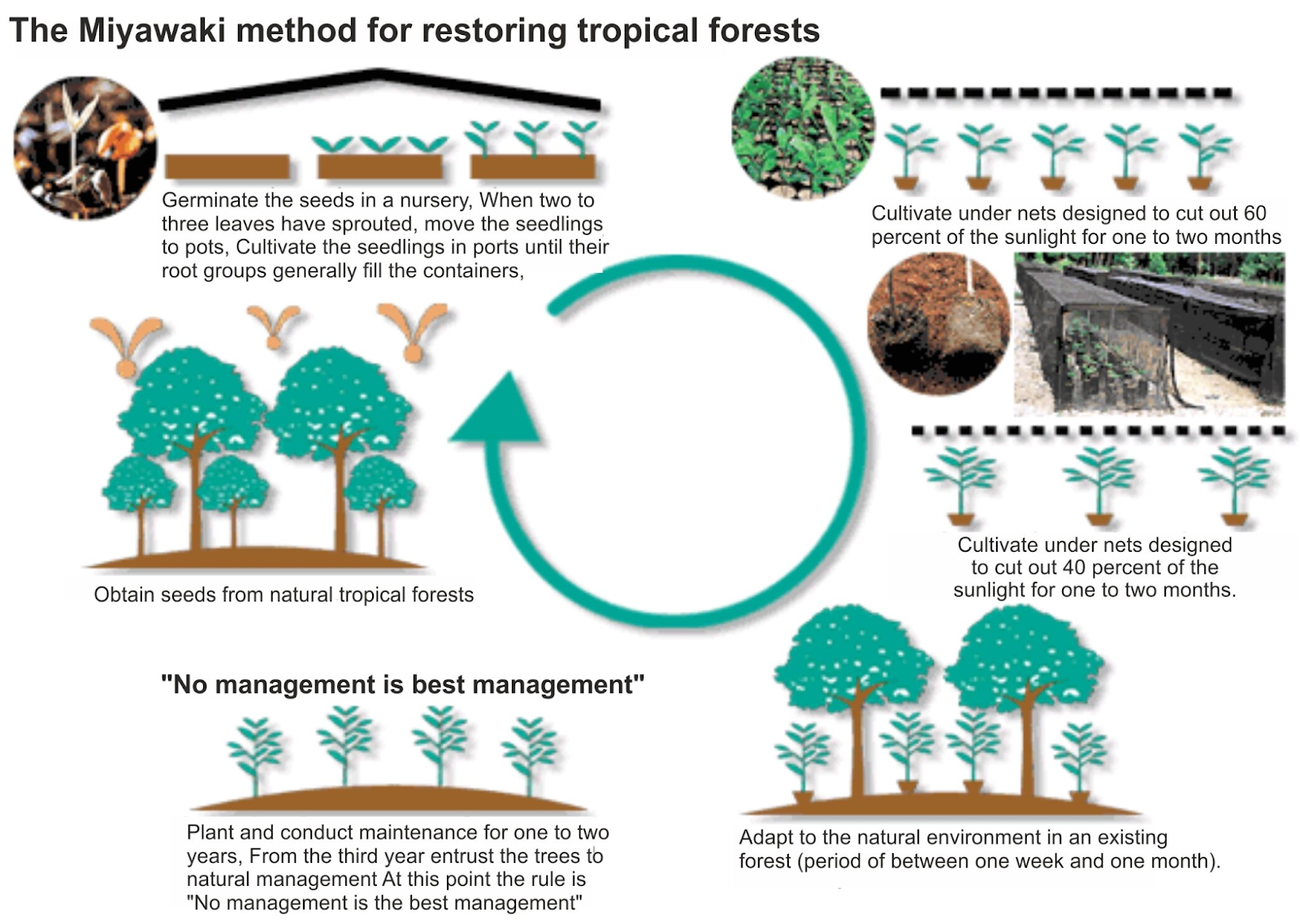
What is the Miyawaki Plantation Method?
- About:
- It was named after Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, this method involves planting two to four different types of indigenous trees within every square metre.
- The methodology was developed in the 1970s, with the basic objective to densify green cover within a small parcel of land.
- In this method, the trees become self-sustaining and they grow to their full length within three years.
- The plants used in the Miyawaki method are mostly self-sustaining and don’t require regular maintenance like manuring and watering.
- Significance:
- The dense green cover of indigenous trees plays a key role in absorbing the dust particles of the area where the garden has been set up. The plants also help in regulating surface temperature.
- Some of the common indigenous plants that are used for these forests include Anjan, Amala, Bel, Arjun and Gunj.
- These forests encourage new biodiversity and an ecosystem which in turn increases the fertility of the soil.
- The dense green cover of indigenous trees plays a key role in absorbing the dust particles of the area where the garden has been set up. The plants also help in regulating surface temperature.
Miyawaki Forest Method in Mumbai
- Over the years, the cost-effective Miyawaki Plantation Method has become the go-to solution to restore the green cover in a space-starved city like Mumbai.
- The Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) has been implementing the Miyawaki forest approach in various vacant land areas of Mumbai to combat climate change, reduce pollution levels, and enhance the city's green cover.
- 64 Miyawaki forests have been planted in Mumbai so far.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. The "Miyawaki method" is well known for the: (2022)
(a) Promotion of commercial farming in arid and semi-arid areas
(b) Development of gardens using genetically modified flora
(c) Creation of mini forests in urban areas
(d) Harvesting wind energy on coastal areas and on sea surfaces
Ans: (c)
Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope
Why in News?
The Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT), developed by Pune's Inter-University Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), has been delivered to the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- This unique space telescope will be integrated with ISRO's ADITYA-L1 mission, set to launch in mid-August 2023.
What is SUIT?
- About:
- SUIT aims to study the Sun’s ultraviolet (UV) emissions and capture high-resolution images of the Sun’s atmosphere, known as the corona, in various UV wavelengths.
- It will operate in the far and near ultraviolet regions, covering wavelengths of 200-400 nanometers.
- It will observe the hotter and more dynamic regions of the Sun’s atmosphere, such as the transition region and the corona.
- Significance:
- The Sun is one of the most difficult things to study outside Earth due to its high emissions and radiation.
- SUIT will enable scientists to unravel the secrets of the Sun and its impact on Earth and other planets.
- SUIT will also measure the UV radiation hazardous for skin cancer.
- SUIT will monitor the Sun’s activity and provide early warning of potential solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which can affect satellites, communication systems, power grids and human health on Earth.
- The Sun is one of the most difficult things to study outside Earth due to its high emissions and radiation.
What is Aditya-L1 Mission?
- About:
- The ADITYA-L1 mission will be dedicated to studying the Sun and will fly approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth to the Lagrange point 1 (L1), one of the five favorable spots for observing the Sun.
- The mission is expected to be launched using a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) rocket.
- It will provide regular images and updates on the Sun's surface phenomena and space weather.
- Features:
- ADITYA-L1 will carry seven different payloads capable of studying various phenomena on the Sun across the electromagnetic spectrum and solar wind. The 7 payloads include:
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC)
- Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT)
- Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS)
- Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX)
- High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS)
- Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA)
- Advanced Tri-axial High Resolution Digital Magnetometers
- ADITYA-L1 will carry seven different payloads capable of studying various phenomena on the Sun across the electromagnetic spectrum and solar wind. The 7 payloads include:
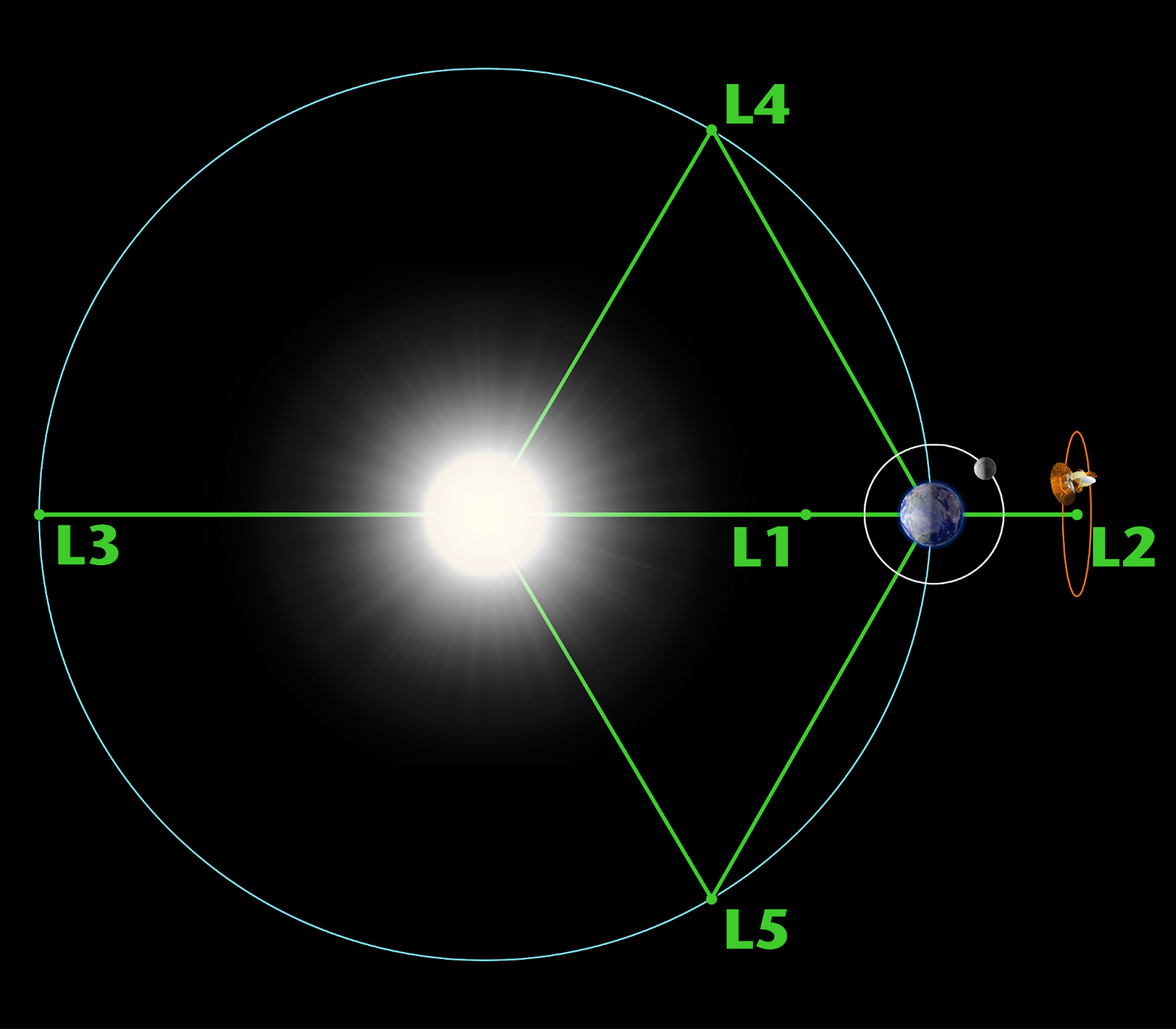
What is L1?
- "L1" refers to the Lagrange point 1. Lagrange points are specific points in space where the gravitational forces of two large bodies, such as the Sun and the Earth, balance the centrifugal force felt by a smaller body.
- They are named in honor of Italian-French mathematician Josephy-Louis Lagrange.
- These can be used by spacecraft to reduce fuel consumption needed to remain in position.
- L1 is one of the five Lagrange points in the Sun-Earth system. Of the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable.
- The unstable Lagrange points - labeled L1, L2 and L3 - lie along the line connecting the two large masses.
- The stable Lagrange points - labeled L4 and L5 - form the apex of two equilateral triangles that have the large masses at their vertices.
- L4 leads the orbit of earth and L5 follows.
- The L1 point of the Earth-Sun system affords an uninterrupted view of the sun and is currently home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite.
- The L2 point of the Earth-Sun system was the home to the WMAP spacecraft, current home of Planck, and future home of the James Webb Space Telescope.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
Impact of Ground Water Extraction on Earth’s Spin
Why in News?
A recent study published in Geophysical Research Letters has shed light on the significant impact of Groundwater Extraction on Earth's Rotational Axis and its contribution to global sea-level rise.
- Researchers analyzed changes in the drift of Earth’s rotational pole and water movement — first, by accounting for just ice sheets and Glaciers and then by adding different groundwater redistribution scenarios.
What are the Factors Affecting Earth's Rotation?
- Factors contributing to polar motion include Weather, Seasonal Changes, the molten Core, and powerful Hurricanes.
- Polar motion is the movement of the Earth's rotational axis relative to its crust, reflecting the influence of the material exchange and mass redistribution of each layer of the Earth on the Earth's rotation axis.
- Generally, polar motion is caused by changes in the hydrosphere, atmosphere, oceans, or solid Earth.
- Earth’s Geographic North and South Poles are where its axis intersects the surface; however, they are not fixed. The axis and hence the poles fluctuate due to variations in the Earth’s mass distribution.
- In the past, the poles’ drift was only caused by natural forces like ocean currents and the convection of heated rock deep beneath the Earth.
- But the new research pitched the redistribution of groundwater as the primary culprit for the drift.
- Water’s role in altering the Earth’s rotation was discovered in 2016, and until now, the contribution of groundwater to drifts has been unexplored.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Earth’s Tilt:
- Groundwater pumping has tilted Earth nearly 80 centimeters east between 1993 and 2010 alone.
- The water circulated across the planet determines how mass is distributed.
- Between 1993 and 2010, people pumped 2,150 gigatons of groundwater, or more than 6 millimeters of sea level increase.
- Impact on Polar Drift:
- Excessive groundwater pumping has caused the Earth's pole to drift at a rate of 4.36 centimeters per year between 1993 and 2010, making it the climate-related factor with the greatest impact on polar motion.
- Redistributing water from the mid-latitudes significantly influences polar drift; therefore, the location of redistribution determines polar drift.
- During the study period, most redistribution occurred in western North America and northwestern India — both located at mid-latitudes.
- Impact of Groundwater Pumping on Sea-Level Rise:
- Groundwater pumping contributed to a sea-level rise of 6.24 mm during the mentioned period.
- Pumping from mid latitude areas, such as northwest India and western North America, has the most substantial influence on Earth's axis drift.
- Impact of Polar Drift:
- The rotational pole normally changes by several metres within about a year, so changes due to groundwater pumping don’t run the risk of shifting seasons.
- But on geologic time scales, polar drift can have an impact on climate.
- Recommendations:
- Attempts to slow groundwater depletion rates, especially in those sensitive regions, can theoretically alter the change in drift, but only if such conservation approaches are sustained for decades.
What is the Significance of the Study?
- The findings emphasize the need to address groundwater depletion and its consequences on a global scale.
- This finding underscores the importance of considering groundwater depletion as a crucial factor in analyzing Earth's rotational dynamics and rising sea levels.
Alligator Gar Fish
Why in News?
The discovery of an Alligator Gar fish (Atractosteus spatula), an invasive species in Kashmir's Dal Lake has raised concerns.
- The Lake Conservation and Management Authority (LCMA) and the Department of Fisheries are collaborating to understand the extent of the invasion and its potential impact.
What are Alligator Gar Fish and the Risks Associated?
- About:
- The alligator gar is a close relative of the bowfin species. It is a ray-finned euryhaline fish (creature's ability to adapt to a wide range of water types that range in salinity) and is one of the biggest freshwater fish in North America and the largest species in the ‘gar’ family.
- It is found in some parts of India such as Bhopal and Kerala.
- They grow rapidly and have a life span of 20-30 years.
- The alligator gar is a close relative of the bowfin species. It is a ray-finned euryhaline fish (creature's ability to adapt to a wide range of water types that range in salinity) and is one of the biggest freshwater fish in North America and the largest species in the ‘gar’ family.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN: Least Concern.
- Concerns:
- Gar fish can grow up to eight feet. They can be dangerous for indigenous fish species. During winter, they can even sustain themselves in the cold waters of Dal because the temperature they mostly live in is 11-23 degrees Celsius
- The Biological Diversity Act 2002:
- The Biological Diversity Act 2002 prohibits the presence of invasive fish species that could harm natural fish populations.
Dal Lake
- It is a lake in Srinagar, the capital of the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K).
- It is one of the world's largest natural lakes and the second largest lake in J&K.
- It is integral to tourism and recreation in Kashmir and is named the “Jewel in the crown of Kashmir” or “Srinagar’s Jewel”.
- It is also an important source for commercial operations in fishing and water plant harvesting.
- It covers an area of 18 square kilometres and is part of a natural wetland including its floating gardens.
- The floating gardens, known as “Raad” in Kashmiri, blossom with lotus flowers during July and August.
Women 20 Summit 2023
Why in News?
Recently, as a part of India’s G20 Presidency, the Women 20 (W20) Summit with the theme 'Women-Led Development- Transform, Thrive and Transcend' held in Mahabalipuram, Tamil Nadu.
- The summit aimed to celebrate the power of women empowerment and address key issues related to economic empowerment, trade and investment, and care economy.
What are the Key Highlights of the W20 Summit?
- Discussions on breaking the invisible barriers and biases that prevent women from reaching higher positions and leadership roles in various fields were held.
- Government initiatives such as Self Help Groups(SHGs), PM Mudra Scheme and GeM portal which allow women access to market and finance are highlighted.
- Gender disparities in economic participation are highlighted as women often face inequalities in accessing economic opportunities, including financial resources, markets, and trade networks.
- Participants have discussed systemic barriers, such as lack of access to credit, limited property rights, and discriminatory practices, which hinder women's economic empowerment.
- Celebration of strength, resilience, and progress in women's empowerment was witnessed .
What is W20?
- About:
- W20 is an official engagement group under the G20.
- It was established in 2015 with the aim of focusing on gender equity and women's empowerment.
- First W20 Summit was held during Turkey’s G20 Presidency in 2015.
- The group seeks to mainstream gender considerations into G20 discussions and translate them into policies and commitments.
- It influences the G20 agenda and promotes gender-sensitive approaches to various global challenges.
- Priorities:
- Women's Entrepreneurship
- Grassroot Women Leadership
- Bridging the Gender Digital Divide
- Education & Skill Development
- Climate Change
- Composition:
- W20 comprises a transnational network of delegates.
- Delegates represent non-government women's organizations, civil society, female entrepreneurs, businesses, and think tanks.
- The network spans across G20 member states.
- W20 India Presidency:
- W20 India assumed the presidency from W20 Indonesia on December 12, 2022.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Ex Khaan Quest 2023
The multinational peacekeeping joint exercise called "Ex Khaan Quest 2023" has begun in Mongolia with the participation of military contingents and observers from over 20 countries.
The 14-day exercise is aimed at enhancing the interoperability of the participating nations, sharing experience and training uniformed personnel for the United Nations Peacekeeping Operations (UNPKO). The exercise will prepare participants for future UN Peacekeeping missions, develop peace operations capabilities and enhance military readiness.
Mongolia is in Asia between Russia to the north and China to the south. It has a parliamentary form of government. The capital of Mongolia is Ulaanbaatar. Languages that are spoken in Mongolia include Khalkha Mongol (official), Turkic, and Russian. The major mountain ranges are Altai, Khangai and Khentii. The major river is the Orkhon.
Read More: Ex Khaan Quest, India-Mongolia Relations
National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI)
The National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI) marks its 20th Foundation Day, reaffirming its strong commitment to the development of India's internet infrastructure.
NIXI is a not-for-profit organisation (section 8 of the Companies Act 2013) working since 2003 for spreading the internet infrastructure to the citizens of India through services like Internet Exchanges through which the internet data is exchanged amongst Internet Service Providers (ISP’s), Data Centers and Content Delivery Network (CDNs), .IN Registry, managing and operation of .IN country code domain and .BHARAT IDN (Internationalized Domain Name) domain for India, Indian Registry for Internet Names and Numbers (IRINN), managing and operating Internet Protocol (IPv4/IPv6).
Pv6 Expert Panel (IP Guru) is a group to extend support to all the Indian entities that are finding it technically challenging to migrate and adopt IPv6.
Read More: National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI)
DAKSHTA: Empowering Young Professionals in Government Administration
The recently launched curated collection, DAKSHTA (Development of Attitude, Knowledge, Skill for Holistic Transformation in Administration) For Young Professionals, on the iGOT Karmayogi Platform aims to equip young professionals and consultants in government with the necessary competencies to effectively discharge their duties and responsibilities.
Consisting of 18 courses, the collection covers a wide range of subjects crucial to their roles, including data-driven decision making, code of conduct, communication skills, public policy research, stress management, and more.
The iGOT Karmayogi Platform, an online portal established under the Mission Karmayogi, offers a comprehensive resource for capacity building, career management, and networking for government officials.
Read more: iGOT Karmayogi Platform, Mission Karmayogi.
NewSpace India to Enhance Maritime Communication with MSS Terminals
NewSpace India Ltd (NSIL), the commercial arm of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), has embarked on a project to improve communication with vessels at sea and enhance the monitoring of Indian waters.
The company plans to install mobile satellite service (MSS) terminals on approximately one lakh motorised and fishing boats across 13 coastal states. The MSS terminals will enable efficient monitoring, control, and surveillance of marine fishing vessels. The system will be powered by India’s own navigation satellite system, Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC).
This ambitious initiative aims to strengthen emergency communication capabilities and asset tracking in the maritime domain, fostering safer and more secure operations along India's coastline.
Read more: Indian Space Research Organisation