International Relations
India-Mongolia Relations
- 13 Feb 2023
- 9 min read
Prelims: India-Mongolia Relations, Covid-19 Pandemic, Buddhism, Act East Policy.
Mains: India-Mongolia Relations.
Why in News?
Recently, the 11th meeting of the India-Mongolia Joint Working Group was held in India.
- While acknowledging the growing ties between both the countries, they expressed satisfaction at the ongoing defense cooperation despite the limitations imposed by Covid-19 pandemic.
How have been the India-Mongolia Relations?
- Historical Relations:
- India and Mongolia have interacted through Buddhism throughout history.
- Mongolia regards India as its “third” neighbor along with US, Japan, and Germany and a “spiritual neighbour”.
- Diplomatic Relations:
- India established diplomatic relations with Mongolia in 1955 and it was the first country outside the Soviet bloc to open diplomatic relations with Mongolia.
- The Indian Resident Mission in Ulaanbaatar was opened in 1971.
- This relationship was upgraded to “strategic partnership” in 2015 when the Indian Prime Minister visited Mongolia and declared it as an essential component of ‘Act East Policy’.
- International Cooperation:
- Mongolia has publicly reiterated its support for India’s membership to the permanent seat of the expanded United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
- India has played an important role in getting Mongolia membership to key international forums, including the United Nations (UN), despite strong opposition from China and Taiwan.
- India also championed the inclusion of Mongolia in the Non-Aligned Movement.
- In a reciprocal gesture, Mongolia co-sponsored a 1972 UN resolution with India and Bhutan for the recognition of the newly liberated Bangladesh.
- Economic Cooperation:
- In 2022, an India-built oil refinery at the cost of more than USD 1 billion and with a capacity of 1.5 million metric tonnes was opened near Sainshand in southern Dornogovi province of Mongolia.
- This refinery will take care of 75 % of Mongolia’s oil refining needs.
- India - Mongolia bilateral trade was USD 35.3 million in 2020, down from USD 38.3 million in 2019.
- In 2022, an India-built oil refinery at the cost of more than USD 1 billion and with a capacity of 1.5 million metric tonnes was opened near Sainshand in southern Dornogovi province of Mongolia.
- Cultural Cooperation:
- The India-Mongolian Agreement on Cultural Cooperation, signed in 1961, has governed the Cultural Exchange Programme (CEP) between the two countries.
- The Agreement envisages co-operation in the fields of education by way of scholarships, exchange of experts, participation in conferences, etc.
- Defence Cooperation:
- Joint defence exercises code-named Nomadic Elephant.
- India is also an active participant in an annual week-long joint training exercise called the Khaan Quest, hosted by Mongolia.
- Cooperation over Environmental Issues:
- Part of the Bishkek Declaration (snow leopard).
What are the Key Facts Related to Mongolia?
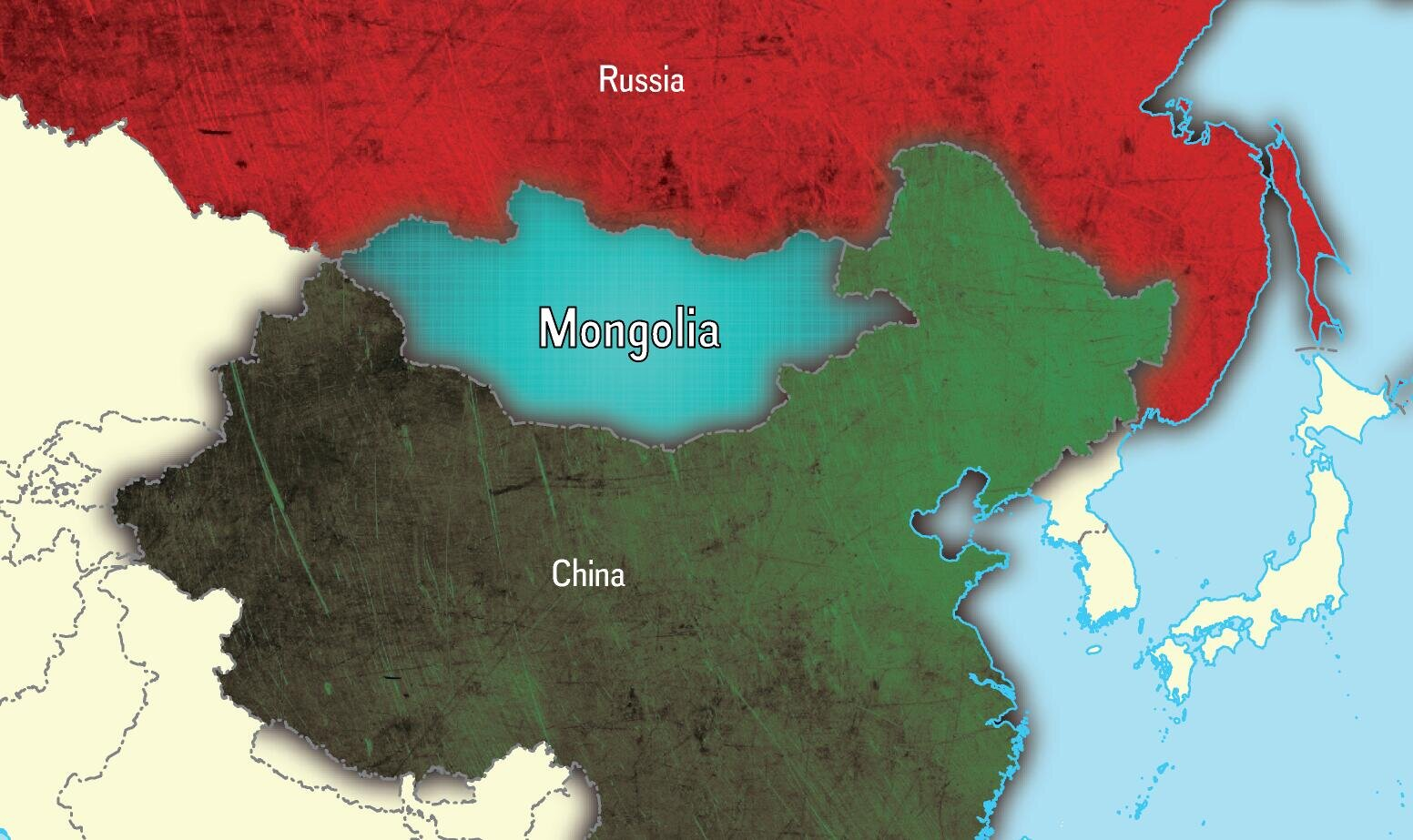
- Mongolia is a landlocked country located in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west.
- It is the world's second-largest landlocked country and the most sparsely populated country in the world.
- The majority of the population still practices traditional nomadic herding, and Mongolia is home to a variety of ethnic groups, including Mongols, Kazakhs, and Tuvans.
- The country is known as the "Land of the Eternal Blue Sky" and as the "Land of the Horse".
- Mongolia's landscape is dominated by the Gobi Desert in the south and the towering Altai Mountains in the west.
- Despite its rapid modernization in recent years, Ulaanbaatar still retains a strong traditional Mongolian identity, with many historical temples, monasteries, and other cultural landmarks to explore.
- The country was once the center of the Mongol Empire, which was the largest contiguous empire in history, spanning from Europe to Asia.
Way Forward
- The way forward for India-Mongolia relations is to build on the existing foundation of historical and cultural ties, while also seeking to expand political, economic, and cultural cooperation.
- Mongolia’s strategic position at the cross junction of Central Asia, Northeast Asia, far East, China and Russia attract major powers towards it. India should consider Mongolia as a green zone of economic development that absorbs hi-tech features and production skills in a modernization process.
- With both countries facing common challenges in the region, there is tremendous potential for further strengthening the relationship in the coming years.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “Climate is extreme, rainfall is scanty and the people used to be nomadic herders.” (2013)
The above statement best describes which of the following regions?
(a) African Savannah
(b) Central Asian Steppe
(c) North American Prairie
(d) Siberian Tundra
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- African Savannah: It is a tropical grassland and covers half the surface of Africa. Weather is typically warm with temperatures ranging from 20º to 30ºC. Rainfall in the savannas is moderate, up to 75 cm per year. The people living in this biome are mainly farmers who grow cereals and other plants that can resist long dry spells, such as millet, sorghum, barley and wheat, as well as peanuts, cotton, rice and sugarcane, while breeding prevails in drier Savannah areas.
- Temperate Grassland: Temperature varies much more in temperate grasslands than in the Savannas. Temperate grasslands have hot summers where temperatures can exceed 38ºC and cold winters that can drop below –40ºC.
- Central Asian Steppe: Grasslands (steppes) have temperate environments, with warm to hot summers and cool to very cold winters. Temperatures are often extreme in these mid continental areas. These are often located between deserts and temperate forests, and annual precipitation falls between the amounts characteristic of these zones. The grassland steppes of Eurasia spread from eastern China across Mongolia and Russia to Europe. People of this region used to be nomadic herders.
- North American Prairie: Prairies are the temperate grasslands of North America. The word ‘Prairie’ originated from the Latin word ‘Priata’ which means meadow. They are located in the heart of a continent. The climate is of the continental type with extreme temperatures. The summers are warm with temperatures of around 20ºC and winters are very cold with temperatures of around –20ºC. The people of this region are very industrious. They are successfully harnessing the technology to utilize its natural resources.
- Siberian Tundra: These are found in regions north of the Arctic Circle and south of the Antarctic Circle. The lowlands – coastal strip of Greenland, the barren grounds of northern Canada and Alaska and the Arctic seaboard of Eurasia, have tundra climate. The climate is characterized by a very low mean annual temperature. In mid-winter, temperatures are as low as 40-50°C below freezing point. Summers are relatively warmer. Normally not more than four months have temperatures above freezing-point. Precipitation is mainly in the form of snow and sleet. Convectional rainfall is generally absent. People live a semi-nomadic life. Human activities of the tundra are largely confined to the coast.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.