Science & Technology
ISRO’s new NavIC Satellite NVS-01
- 30 May 2023
- 7 min read
For Prelims: NVS-01, GSLV, NavIC, IRNSS, GPS, IMO, ISRO.
For Mains: ISRO’s new NavIC satellite NVS-01, Significance of NavIC
Why in News?
The NVS-01 satellite was successfully launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) using the GSLV-F12, and after a 19-minute flight, it was accurately placed into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit.
- GSLV-F12 is the 15th flight of India’s GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) and the 9th flight with indigenous cyro stage. This is the 6th operational flight of GSLV with indigenous cryogenic stage.
What is NVS-01?
- About:
- This satellite is the first of the second-generation satellites of ISRO’s NVS (Navigational Satellite) series of payloads.
- It weighs 2,232 kg, making it the heaviest in the constellation.
- The NVS-01 carried navigation payloads L1, L5 and S bands.
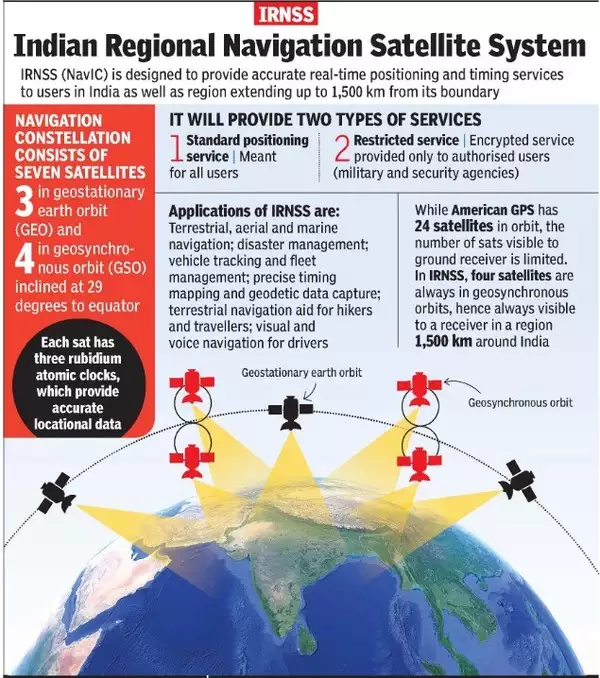
- Its purpose is to provide continuity for the NavIC (Navigation in Indian Constellation) services, which is an Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (similar to GPS) that offers accurate and real-time navigation within India and up to a 1,500 km region around the country.
- In the First generation, there are seven satellites in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) constellation, operationally named NavIC, weighing much less — around 1,425 kg — at liftoff.
- Atomic Clock:
- The satellite will have a Rubidium atomic clock onboard, a significant technology developed by India.
- Some of the existing satellites in the navigation constellation lost their ability to provide accurate location data due to failed atomic clocks. Satellite-based positioning systems rely on precise time measurements from atomic clocks to determine object locations. When the clocks fail, the satellites cannot provide accurate location information anymore.
- The satellite will have a Rubidium atomic clock onboard, a significant technology developed by India.
- L1 signals for better use in wearable devices:
- It will send signals in a third frequency, L1, besides the L5 and S frequency signals that the existing satellites provide, increasing interoperability with other satellite-based navigation systems.
- The L1 frequency is among the most commonly used in the Global Positioning System (GPS), and will increase the use of the regional navigation system in wearable devices and personal trackers that use low-power, single-frequency chips.
- Longer Mission Life:
- It will have a longer mission life of more than 12 years. The existing satellites have a mission life of 10 years.
What is NavIC?
- About:
- NavIC or the IRNSS is designed with a constellation of 7 satellites and a network of ground stations operating 24×7.
- There are a total of eight satellites however only seven remain active.
- Three satellites in geostationary orbit and four satellites in geosynchronous orbit.
- The constellations' first satellite (IRNSS-1A) was launched on 1st July 2013 and the eighth satellite IRNSS-1I was launched in April 2018.
- With the seventh launch of the constellation's satellite (IRNSS-1G), IRNSS was renamed NavIC by India’s Prime Minister in 2016.
- It was recognised by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) as a part of the World-Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) for operation in the Indian Ocean Region in 2020.
- NavIC or the IRNSS is designed with a constellation of 7 satellites and a network of ground stations operating 24×7.
- Potential Uses:
- Terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation;
- Disaster management;
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management (especially for mining and transportation sector);
- Integration with mobile phones;
- Precise timing (as for ATMs and power grids);
- Mapping and geodetic data capture.
What is the Advantage of Having a Regional Navigation System?
- Regional Navigation System:
- NavIC is India's own regional navigation system developed by ISRO. It covers the Indian landmass and extends up to 1,500 km around it. The primary purpose of NavIC is to cater to the positioning and navigation needs of users in this specific region.
- Ground Stations:
- ISRO is working on setting up ground stations in countries like Japan, France, and Russia. These additional ground stations will enhance the accuracy and coverage of NavIC signals through better triangulation.
- Signal Reception:
- NavIC signals reach India at a 90-degree angle, making it easier for the signals to penetrate congested areas, dense forests, and mountainous terrain. In contrast, GPS signals arrive at an angle, which can sometimes pose challenges for reception in certain locations.
- Availability:
- NavIC signals are primarily designed to serve the Indian region. Therefore, users within the coverage area can expect reliable access to NavIC signals, even in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
Which are the other Navigation Systems operational in the world?
- Four Global Systems:
- GPS from the U.S.
- GLONASS from Russia.
- Galileo from European Union
- BeiDou from China.
- Two Regional Systems:
- NavIC from India
- QZSS from Japan.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
a. Australia
b. Canada
c. Israel
d. Japan
Ans: d
Navigation Systems Operational in the World:
- GPS from the U.S.
- GLONASS from Russia.
- Galileo from European Union
- BeiDou from China.
- NavIC from India
- QZSS from Japan. Hence, option D is correct.
Q.2 With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements: (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. Km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) None
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Why is Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS) needed? How does it help in navigation? (2018)