Annual Arctic Report Card: NOAA
For Prelims: Annual Arctic Report Card, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Arctic, Permafrost, Global Warming, Greenland’s ice sheet, Wildfires.
For Mains: Annual Arctic Report Card: NOAA, Environmental pollution and degradation.
Why in News?
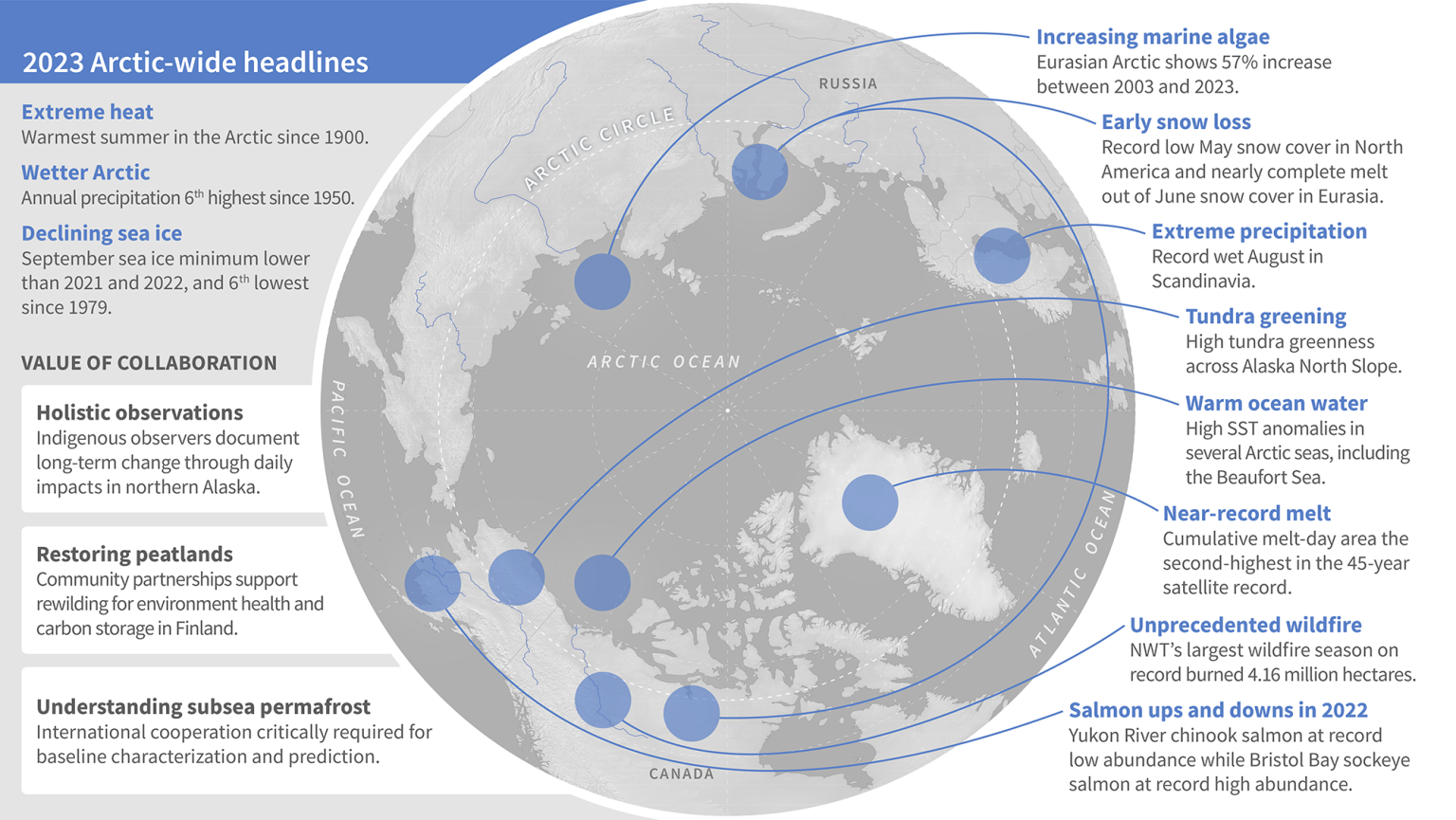
Recently, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has released its 18th Annual Arctic Report Card, highlighting the profound impact of extreme weather and Climate Events on the Arctic.
- NOAA is a United States government agency that is responsible for providing accurate and timely information about weather forecasts, climate, oceans, coasts, and even the exploration of outer space.
What is the Arctic Report Card?
- It has been Issued annually since 2006, the Arctic Report Card is a timely and peer-reviewed source for clear, reliable and concise environmental information on the current state of different components of the Arctic environmental system relative to historical records.
What are the Key Highlights of the Arctic Report Card?
- Record High Temperatures:
- The 2023 summer was the warmest on record in the Arctic, which, due to climate change, has warmed nearly four times faster than the globe since 1979.
- This year was noted as the sixth warmest in the Arctic since reliable records began in 1900.
- Impact of Rising Temperatures:
- The soaring temperatures led to unprecedented wildfires, forcing community evacuations, a decline in sea ice extent, severe floods, food insecurity, and rising sea levels.
- These impacts directly affect ecosystems, human health, and cultural practices.
- The soaring temperatures led to unprecedented wildfires, forcing community evacuations, a decline in sea ice extent, severe floods, food insecurity, and rising sea levels.
- Thawing of Subsea Permafrost:
- Warmer ocean temperatures are accelerating the thawing of subsea Permafrost, releasing methane and carbon dioxide.
- This process contributes to Global Warming and exacerbates ocean acidification. There's concern about the unknown extent and impact of these released greenhouse gasses.
- Food Insecurity Due to Salmon Decline:
- Western Alaska experienced significantly reduced populations of Chinook and chum salmon (81% and 92% below the 30-year mean, respectively), impacting Indigenous communities reliant on these fish for sustenance.
- This decline has cultural, food security, and economic implications.
- Wildfires in Arctic Regions:
- Canada witnessed its worst wildfire season on record, affecting 40% of its land mass considered Arctic and Northern.
- High temperatures and dry conditions facilitated the burning of over 10 million acres in the Northwest Territories, leading to evacuations and diminished air quality.
- Glacier Thinning and Flooding:
- Rising temperatures have led to dramatic thinning of the Mendenhall Glacier, located in Alaska, over the past 20 years
- As a result, over the years, the meltaway water has annually caused floods in the region.
- One such disaster took place in August 2023, when “a glacial lake on a tributary of the Mendenhall Glacier burst through its ice dam and caused unprecedented flooding and severe property damage” in Alaska’s Juneau.
- Greenland Ice Sheet Melting:
- Greenland’s ice sheet experienced melting for only the fifth time in the 34-year record. Not only this, the ice sheet continued to lose mass despite above-average winter snow accumulation — between August 2022 and September 2023, it lost roughly 350 trillion pounds of mass. Notably, Greenland’s ice sheet melting is the second-largest contributor to sea-level rise.
What is the Arctic?
- The Arctic is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth.
- Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover.
- It consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Alaska (United States), Canada, Finland, Greenland (Denmark), Iceland, Norway, Russia, and Sweden.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’? (2019)
- Global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits.
- Large deposits of ‘methane hydrate’ are found in Arctic Tundra and under the sea floor.
- Methane in atmosphere oxidizes to carbon dioxide after a decade or two.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Methane hydrate is a crystalline solid that consists of a methane molecule surrounded by a cage of interlocking water molecules. It is an “ice” that only occurs naturally in subsurface deposits where temperature and pressure conditions are favourable for its formation.
- Regions with suitable temperature and pressure conditions for the formation and stability of methane hydrate– sediment and sedimentary rock units below the Arctic permafrost; sedimentary deposits along continental margins; deep-water sediments of inland lakes and seas; and, under Antarctic ice. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Methane hydrates, the sensitive sediments, can rapidly dissociate with an increase in temperature or a decrease in pressure. The dissociation produces free methane and water, which can be triggered by global warming. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Methane is removed from the atmosphere in about 9 to 12-year period by oxidation reaction where it is converted into Carbon Dioxide. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. How do the melting of the Arctic ice and glaciers of the Antarctic differently affect the weather patterns and human activities on the Earth? Explain. (2021)
Q. What are the economic significances of discovery of oil in Arctic Sea and its possible environmental consequences? (2015)
e-Cigarettes
For Prelims: e-Cigarettes, World Health Organization (WHO), Tobacco, Nicotine Addiction, Carcinogenic Substances.
For Mains: e-Cigarettes, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has urged governments to treat e-cigarettes similarly to tobacco and ban all flavors, threatening cigarette companies' bets on smoking alternatives.
- Some researchers, campaigners and governments see e-cigarettes, or vapes, as a key tool in reducing the death and disease caused by smoking. But the WHO said "urgent measures" are needed to control them.
What are e-Cigarettes?
- e-Cigarettes are battery powered devices that work by heating a liquid into an aerosol that the user inhales and exhales.
- The e-cigarette liquid typically contains nicotine, propylene glycol, glycerin, flavorings, and other chemicals.
- There are many different types of e-cigarettes in use, also known as electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) and sometimes electronic non-nicotine delivery systems (ENNDS).
What are the Concerns Raised by WHO Regarding e-Ciggeretas?
- Ineffectiveness for Smoking Cessation:
- E-cigarettes as consumer products are not shown to be effective for quitting tobacco use at the population level. Instead, alarming evidence has emerged on adverse population health effects.
- E-cigarettes have been allowed on the open market and aggressively marketed to young people.
- Thirty-four countries ban the sale of e-cigarettes, 88 countries have no minimum age at which e-cigarettes can be bought and 74 countries have no regulations in place for these harmful products.
- Impact on Youth:
- The recruitment and potential trapping of children and young people at an early age into using e-cigarettes, potentially leading to nicotine addiction.
- The aggressive marketing of e-cigarettes, along with insufficient regulations in many countries, contributes to this issue.
- Rising Usage among Youth:
- Children 13–15-years old are using e-cigarettes at rates higher than adults in all WHO regions.
- In Canada, the rate of e-cigarette use among 16–19-year-olds has doubled between 2017–2022, and in England (the United Kingdom) the number of young users has tripled in the past three years.
- Health Risks:
- Although the long-term health effects of e-cigarettes are not fully understood, these devices generate toxic substances, some of which are known to cause cancer and increase the risk of heart and lung disorders.
- E-cigarette use can also affect brain development, cause learning disorders in young people, and adversely affect fetal development in pregnant women.
- Nicotine Addiction and Addictive Nature:
- E-cigarettes containing nicotine are noted to be highly addictive, posing health risks to both users and bystanders. The addictive nature of nicotine in e-cigarettes raises concerns about countering nicotine addiction, especially among young users.
Note
In India, the possession of e-cigarettes and similar devices is a violation of the Prohibition of Electronic Cigarette Act (PECA) 2019.
What are the Arguments in Favour of e-Ciggrettes?
- Harm Reduction:
- Proponents argue that e-cigarettes offer a harm reduction strategy compared to traditional tobacco products.
- They contain nicotine but lack many of the harmful carcinogens present in conventional cigarettes. As a result, they are often seen as a safer alternative for adult smokers who are unable or unwilling to quit using nicotine altogether.
- Economic Revenue:
- There's an economic argument suggesting that legalizing and regulating e-cigarettes could generate substantial tax revenue for governments. By taxing e-cigarettes, authorities could benefit from revenues while also controlling and monitoring their use.
- Consumer Choice:
- Supporters argue for the importance of consumer choice and access to alternatives. They believe that adult smokers should have the option to choose less harmful nicotine delivery systems if they find traditional smoking cessation methods ineffective.
What is Nicotine?
- Nicotine is a plant alkaloid that contains nitrogen, which is found in several types of plants, including the tobacco plant and can also be produced synthetically.
- Nicotine is both a sedative and a stimulant.
- Nicotine is used as a direct substance in e-cigarettes and the content ranges up to 36 mg/mL. Although regular cigarettes too have nicotine, but it ranges between 1.2 to 1.4 mg/mL.
- Karnataka has notified nicotine as Class A poison.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Tobacco Consumption?
- National Tobacco Control Programme
- Cigarettes and other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Amendment Rules, 2023.
- National Tobacco Quitline Services (NTQLS)
- The Union Finance Minister of India announced a 16% increase in National Calamity Contingent Duty (NCCD) on cigarettes in the Budget 2023-24.
- The Union Health Ministry of India has announced new regulations requiring Over-The-Top (OTT) platforms to display tobacco-related health warnings during streamed content.
Way Forward
- There is a need for urgent measures to prevent the uptake of e-cigarettes, counter nicotine addiction, and promote a comprehensive approach to tobacco control, considering national circumstances.
- Advocates suggest regulating and taxing e-cigarettes similarly to other "sin goods" like cigarettes and alcohol. This approach aims to disincentivize excessive use while allowing access to a potentially less harmful alternative for smokers.
Waste Management Initiatives
For Prelims: Extended Producer Responsibility, Plastic Packaging, E-waste, Battery Waste, Bio-medical Waste, Swachh Bharat Mission, Bio-remediation, Waste Management Rules
For Mains: Waste Management Initiatives and Rules, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
In a recent written reply in the Rajya Sabha, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change highlighted the significant steps taken to tackle waste management in the country.
What are the Highlighted Initiatives Related to Waste Management?
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Mechanism:
- EPR is a policy approach in waste management that makes producers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including their collection, recycling, and disposal.
- It aims to reduce the environmental impact of products by shifting the financial and physical burden of waste management from governments and taxpayers to producers.
- In 2022, EPR initiatives utilizing market mechanisms were implemented for plastic packaging, E-waste, battery waste, and used oil. This strategic move is anticipated to stimulate growth in the waste management sector.
- EPR is a policy approach in waste management that makes producers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including their collection, recycling, and disposal.
- Waste Processing Capacity:
- Out of the approximately 1.5 lakh metric tons per day(MT/D) waste generated in urban areas, around 76% is processed.
- Since 2014, there has been a notable increase in the capacity for processing various types of waste, including solid waste, hazardous waste, bio-medical waste, E-waste, plastic waste, and construction and demolition waste.
- Solid waste processing capacity has seen an increase of around 1.05 lakh MT/D in the last eight years, particularly under the Swachh Bharat Mission (Urban).
- Swachh Bharat Mission for Solid Waste Management:
- Central assistance is provided under Swachh Bharat Mission for solid waste management including plastic waste management in urban and rural areas, as per scheme guidelines.
- The Central Government launched Swachh Bharat Mission Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0) in 2021 with the overall vision of creating "Garbage Free Cities", which would involve achieving the target that all Urban Local Bodies will become at least 3-star certified (as per Star Rating Protocol for Garbage Free Cities) covering door to door collection, source segregation, and scientific processing of municipal solid waste.
- The mission focuses on source segregation, reducing single-use plastic, managing waste from construction-and-demolition activities, and bio-remediation of legacy waste dump sites.
- Under Swachh Bharat Mission – Grameen Phase II, the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation has issued operational guidelines to the States and Union Territories which include solid waste management activities at the village level.
- Central assistance is provided under Swachh Bharat Mission for solid waste management including plastic waste management in urban and rural areas, as per scheme guidelines.
- Waste Management Rules and Guidelines:
- The Ministry, under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, has implemented various waste management rules and guidelines to ensure environmentally sound practices. These include:
- Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Bio-medical Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Construction and Demolition Waste Management Rules, 2016.
- Hazardous and other wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2016.
- E-waste Management Rules, 2022.
- Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022.
- Guidelines have also been issued on environmentally sound waste management.
- Guidelines have been developed for the levy of environmental damages /environmental compensation charges based upon the polluter pays principle, for hazardous waste, E-waste, and plastic waste.
- The Ministry, under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, has implemented various waste management rules and guidelines to ensure environmentally sound practices. These include:
Note
- The 'polluter pays' principle is the commonly accepted practice that those who produce pollution should bear the costs of managing it to prevent damage to human health or the environment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. As per the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 in India, which one of the following statements is correct? (2019)
(a) Waste generator has to segregate waste into five categories.
(b) The Rules are applicable to notified urban local bodies, notified towns and all industrial townships only.
(c) The Rules provide for exact and elaborate criteria for the identification of sites for landfills and waste processing facilities.
(d) It is mandatory on the part of the waste generator that the waste generated in one district cannot be moved to another district.
Ans: (c)
Advocates Amendment Bill, 2023
For Prelims: Advocates Amendment Bill, 2023, Touts, Advocates Act, 1961, Bar Councils, All-India Bar,
For Mains: Significance of Advocates Amendment Bill, 2023 in improvement of legal Practices in Court.
Why in News?
Recently, the Advocates Amendment Bill, 2023, was passed in the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. Its purpose was to weed out ‘touts’ from the legal system.
- The Bill repeals the Legal Practitioners Act, 1879 and amended the Advocates Act, 1961, to reduce “the number of superfluous enactments in the statute book” and repeal all “obsolete laws”.
What are the Key Highlights of the Advocates Amendment Bill, 2023?
- Touts:
- The Bill provides that every High Court, district judge, sessions judge, district magistrate, and revenue officer may frame and publish lists of touts.
- Tout refers to a person who:
- Either proposes to procure or procures the employment of a legal practitioner in a legal business in return of any payment.
- Frequents places such as the precincts of civil or criminal courts, revenue-offices, or railway stations to procure such employment.
- The Court or judge may exclude from the premises of the Court any person whose name is included in the list of touts.
- Preparation of lists:
- The authorities empowered to frame and publish the list of touts may order subordinate courts to hold an inquiry into the conduct of persons alleged or suspected to be touts.
- Once such a person is proven to be a tout, his name may be included by the authority in the list of touts.
- No person will be included in such lists without getting an opportunity of showing cause against his inclusion.
- Penalty:
- Any person who acts as a tout while his name is included in the list of touts will be punished with imprisonment up to three months, a fine up to Rs 500, or both.
What is the Advocate Act, 1961?
- The Advocates Act, 1961, was enacted to amend and consolidate the law relating to legal practitioners and to provide for the constitution of Bar Councils and an All-India Bar.
- This Act repealed a majority of the Legal Practitioners Act, 1879 but left behind provisions relating to its extent, definitions, and powers to frame and publish lists of touts.
Legal Insights: Advocates Amendment Bill, 2023
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelim:
Q. With reference to India, consider the following statements:
- Government law officers and legal firms are recognised as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
- Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Impact of Covid Vaccination on Mental Health
For Prelims: Impact of Covid Vaccination on Mental Health, Mental Health, Covid-19, National Mental Health Programme (NMHP), Ayushman Bharat – Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWC), National Tele Mental Health Programme.
For Mains: Impact of Covid Vaccination on Mental Health, Status of Mental Healthcare in India, Government Initiatives Related to Mental Health, Population and associated issues.
Why in News?
Some studies have suggested a lower incidence of Mental Health issues among vaccinated individuals compared to the unvaccinated post-Covid-19 infection.
- The additional risk of depression at 6 months following Covid-19 was 449 per 100,000 among vaccinated individuals, while it was 1009 per 100,000 among the unvaccinated.
How Severe was the Issue of Mental Health after Covid-19?
- Anxiety and Depression:
- Individuals who survived Covid-19 hospitalization faced persistent mental health challenges, including anxiety and depression, lasting at least a year post-recovery.
- Long Covid, affecting about 5% of individuals regardless of its severity, overlaps with these mental health conditions, adding to the burden.
- Increased Burden on Healthcare Systems:
- The burden of mental health issues post-Covid-19 added strain to healthcare systems, requiring additional resources for diagnosis, treatment, and support for individuals facing these challenges.
- Children and Vulnerable Groups Affected:
- School closures, disrupted routines, and limited social interaction affected children's mental health, leading to increased anxiety and other psychological challenges.
- Marginalized populations faced compounded challenges due to socioeconomic disparities, leading to increased mental health vulnerabilities.
- Isolation and Grief Amplifying Mental Health Issues:
- Social isolation, limited access to communication devices, domestic stress, and grief from the loss of friends and relatives to Covid-19 amplified mental health challenges, especially among vulnerable groups like the elderly.
What is the link Between Mental Health and Vaccination?
- Reduction in Mental Health Challenges:
- The reduction in mental health issues among vaccinated individuals was observed irrespective of whether they had a prior history of mental illness.
- This suggests that vaccination's impact on mental health outcomes was independent of pre-existing conditions.
- Reduced Anxiety:
- Vaccination created a sense of safety and decreased anxiety among individuals.
- Feeling protected against severe illness or death from Covid-19 contributed to lower levels of anxiety and stress associated with the pandemic.
What is the Status of Mental Health Illness in India?
- About:
- Mental health refers to a person's emotional, psychological, and social well-being, encompassing their overall mental and emotional state.
- It involves a person's ability to cope with stress, manage their emotions, maintain healthy relationships, work productively, and make rational decisions.
- Mental health is an integral part of overall health and well-being, just as important as physical health.
- Status in India:
- In India, according to National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro-Sciences data, more than 80% of people do not access care services for a multitude of reasons, ranging from lack of knowledge, stigma and high cost of care.
- The economic loss due to mental health conditions, between 2012-2030, is estimated at USD 1.03 trillion (WHO).
- In India, according to National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro-Sciences data, more than 80% of people do not access care services for a multitude of reasons, ranging from lack of knowledge, stigma and high cost of care.
- Government Initiatives Related to Mental Health:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Mains
Q. Why suicide among young women is increasing in Indian society? (2023)
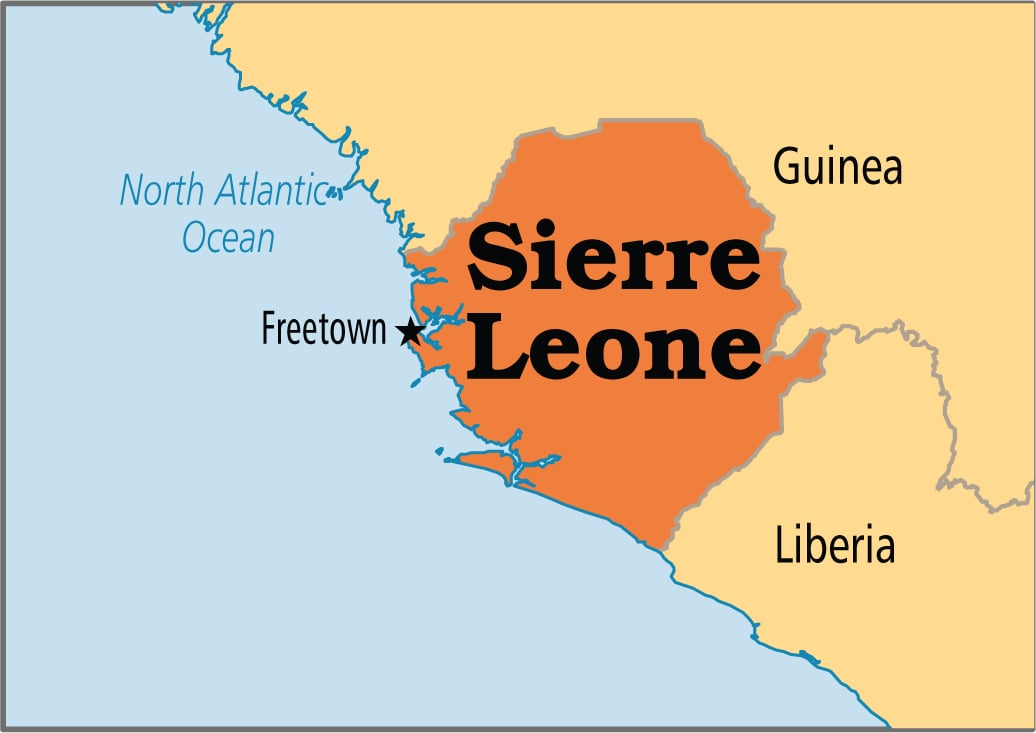
Coup Attempt in Sierra Leone
Why in News?
In the wake of an unsuccessful coup attempt in Sierra Leone, the West African nation finds itself at the crossroads of political turmoil and economic crisis.
- Sierra Leone is a member country of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) and hence if any security concern arises in the future, ECOWAS and the member countries will step in to maintain constitutional order.
What are the Factors Contributing to Unrest in Sierra Leone?
- Political Instability: The President's re-election in June 2023 triggered political unrest. The opposing party contested the results, alleging manipulation. Opposition contestation led to a parliamentary boycott until October 2023.
- Economic Instability: High cost of living and severe poverty contribute to the crisis.
- The President's economic policies worsened the situation, leading to protests and demands for the resignation of the President.
- Police Aggression: The government's use of force, including live ammunition, in handling protests and prison riots has fueled resentment.
What are the Key Facts About Sierra Leone?
- Sierra Leone is located between Liberia and Guinea, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean. The country is situated on the southwest coast of West Africa.
- Capital: Freetown.
- Languages: English, Krio.
- Mount Bintumani (also known as Loma Mansa) is the highest peak in Sierra Leone.
- A tropical climate is found in Sierra Leone.
- Sierra Leone’s terrain is characterized by mountains in the eastern region, an upland plateau, a wooded hill country, and a coastal belt of mangrove swamps.
- Sierra Leone is one of the members of the International Solar Alliance.
- India was among the first countries to contribute to the UN Mission in Sierra Leone (UNAMSIL) with the deployment of 4000 strong Indian Military contingent.
Other Recent Upheavals in Africa
- Coup in Niger (2023).
- Crisis in Sudan (2023 and 2021).
- Burkina Faso Coup (2022).
- Military Coup in Mali (2021, 2020).
What is Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)?
- Established in 1975 through the Lagos Treaty, the ECOWAS (CEDEAO in French) is a regional intergovernmental organization promoting economic integration and cooperation among West African nations.
- Headquarters: Abuja, Nigeria.
- ECOWAS consists of 15 member states: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Cote d’ Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Senegal, and Togo.
- It aims to achieve economic integration, free movement of people and goods, and regional cooperation across sectors. Additionally, it seeks to establish a borderless region governed by democratic principles and address security challenges through collaborative conflict resolution.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Prelims
Q. In the recent years Chad, Guinea, Mali and Sudan caught international attention for which one of the following reasons is common to all of them? (2023)
(a) Discovery of rich deposits of rare earth elements
(b) Establishment of Chinese military bases
(c) Southward expansion of Sahara Desert
(d) Successful coups
Ans: (d)
Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
Why in News?
Recently, the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development for 2023 has been jointly awarded to Daniel Barenboim and Ali Abu Awwad for their efforts in bringing together the youth and peoples of Israel and the Arab World for a non-violent resolution of the Israel-Palestine conflict.
- Barenboim is an Argentine-born distinguished classical pianist, and Awwad is an eminent Palestinian peace activist who has been working for a peaceful resolution of the ongoing conflict in the Middle East.
What is the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development?
- About:
- The Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development award has been conferred every year since 1986 by Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust in honor of Indira Gandhi, the former Prime Minister of India.
- The award recognizes individuals or organizations for their exceptional contributions to international peace, disarmament, and development.
- The prize is awarded annually and is considered one of the highest honors in the field of peace and development.
- It consists of a monetary award of 25 lakh rupees along with a citation.
- Categories:
- The award is bestowed in three categories: peace, disarmament, and development.
- Criteria for Recognition:
- The recipients are chosen based on their exceptional and sustained efforts to address critical global challenges related to peace, disarmament, and development.
- Their work should demonstrate a positive impact on the international community and contribute to the betterment of human welfare.
India's Participation in TIWB Programme
India's participation in the Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) programme for strengthening Saint Lucia's (an island country in the Caribbean) tax administration marks a significant step in international cooperation in tax matters.
- India has been chosen as the Partner Administration and will provide Tax Experts for this 12-18 months programme.
- TIWB is a joint initiative of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD),
- The focus is on strengthening Saint Lucia's tax administration by transferring technical knowledge and skills, specifically emphasizing the effective use of OECD's Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI) under the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) framework.
- The CRS, established in response to a G20 request and approved by the OECD Council in 2014, mandates jurisdictions to exchange financial information obtained from their institutions annually.
- This framework outlines the types of accounts, taxpayers, and due diligence procedures for financial institutions. It aims to combat tax evasion globally.
Read more: Common Reporting Standard: OECD
Joint Anti-terrorism Exercise of SCO
Recently, the authorities of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization( SCO) member states, with the support of the Executive Committee of the Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure of the SCO, conducted a joint anti-terrorism drill to curb terrorist, separatist, and extremist online activities.
- Hosted by India, this exercise focused on curtailing the Internet's exploitation for terrorist, separatist, and extremist purposes.
- SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international organization that aims to promote a new democratic, fair and rational international political and economic international order. It was created in 2001.
- The SCO Charter was signed in 2002, and entered into force in 2003.
- Membership: Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan and Iran.
Read more: Shanghai Cooperation Organization
Microsoft's Phi-2: Small Model, Big Impact
Microsoft's recent release of Phi-2, a small language model marks a significant leap in the world of language models.
- Positioned as an upgraded version of Phi-1.5, this model boasts capabilities in generative AI that challenge larger counterparts like Llama-2, Mistral, and Gemini-2.
- The key lies in Phi-2's training on diverse, "textbook-quality" datasets, empowering it with common sense, language understanding, logical reasoning, and even prowess in solving complex mathematical and physics problems.
Read more: Generative Artificial Intelligence
Improvement in India's Trade Deficit
Recently, India's trade deficit showed significant improvement, with exports and imports both declining, leading to a narrower trade gap.
- Merchandise exports in November 2023 decreased by 2.8% Year over Year (YoY) to USD 33.9 billion, while imports contracted by 4.3% to USD 54.98 billion, resulting in a trade deficit of USD 20.58 billion.
- The trade deficit showed a significant decline from the high of USD 29.9 billion recorded in October 2023.
- Trade Deficit is an amount by which the cost of a country's imports exceeds its exports. It is a part of the Current Account Deficit.
- Decline in petroleum and engineering product shipments, which constitute nearly half of India's exports, contributed to the overall export contraction.
- Emerging sectors like electronics (23.56% growth) and positive contributions from gems and jewelry, iron ore, pharma, and minerals provided some support in November.
Read more: Current Account Deficit, India's Export Outlook