Governance
Credit Assistance Program for Jan Aushadhi Kendras
For Prelims: Jan Aushadhi Kendras, SIDBI, Goods and Services Tax, Digital Public Infrastructure, PMBJP Scheme
For Mains: India’s Pharma Sector and issues, Generic Medicines and its need, Steps taken to promote generic medicine in India, Government Policies & Interventions, Health.
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister for Chemicals & Fertilizers and Health & Family Welfare, inaugurated a credit assistance program for Jan Aushadhi Kendras (JAK), aiming to enhance accessibility to affordable medicines across India.
- As a part of the program a memorandum of understanding (MoU) was signed between the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Bureau of India (PMBI) to provide financial assistance and support infrastructure development for JAKs.
What is the Credit Assistance Program for Jan Aushadhi Kendras?
- The Government of India under this program will provide credit/loan assistance to operators/entrepreneurs running Jan Aushadhi Kendras across the country.
- The credit assistance program utilizes both Goods and Services Tax (GST) and India's Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to offer unsecured working capital loans to small businesses.
- Through this program, operators can access unsecured working capital loans and infrastructure funding to establish and maintain their Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- The program seeks to empower small entrepreneurs, enhance the accessibility of affordable medicines, and strengthen the healthcare ecosystem in India.
What are Jan Aushadhi Kendras?
- About:
- Jan Aushadhi Kendras (JAKs) is a government initiative launched to provide affordable and quality medicines to the public.
- They operate under the Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) scheme of the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- Jan Aushadhi Kendras (JAKs) is a government initiative launched to provide affordable and quality medicines to the public.
- PMBJP Scheme:
- The Jan Aushadhi Scheme, revamped as Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Yojana (PMJAY) in September 2015, aimed to make quality medicines available at affordable prices, particularly for the poor and disadvantaged.
- In November 2016, the scheme underwent further enhancement and was renamed as PMBJP to strengthen its impact.
- PMBJP, focuses on providing generic drugs through exclusive outlets known as Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- These stores offer generic medicines at significantly lower prices compared to branded drugs, ensuring reduced out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare.
- Generic drugs provided by PMBJP stores are equivalent in quality and efficacy to expensive branded drugs, promoting the rational use of medications.
- Benefits of Jan Aushadhi Kendras:
- Increased affordability of medicines: JAKs have significantly reduced healthcare costs for many people and reduced out-of-pocket expenditure.
- Indian citizens have collectively saved over Rs. 28,000 crores over the last decade by purchasing medicines from Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- Improved access to medicines: JAKs have made essential medicines more readily available in underserved areas.
- Around 10 to 12 lakh people visit JAKs daily.
- Promotion of rational medicine use: JAKs provide information and counselling on the appropriate use of medicines, which can help to reduce misuse and overuse.
- Increased affordability of medicines: JAKs have significantly reduced healthcare costs for many people and reduced out-of-pocket expenditure.
- Expansion of Jan Aushadhi Kendras:
- PMBJP has expanded significantly in recent years, from only 80 Jan Aushadhi Kendras in 2014, to around 11,000 units operating across the country today.
- The government aims to further increase the number of Jan Aushadhi Kendras to 25,000 in the next two years.
SIDBI
- The Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) is the primary financial institution for promoting, financing, and developing the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprise (MSME) sector in India.
- SIDBI was established in 1990 and is the apex regulatory body for licensing and regulating MSME finance companies. It is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance, SIDBI is headquartered in Lucknow and has offices all over the country.
- SIDBI also supports national climate change action plans and promotes responsible business practices, such as energy efficiency, cleaner production, and sustainable financing.
PMBI
- The PMBI is a government agency that coordinates the supply, procurement, and marketing of generic drugs through the PMBJKs.
- The PMBI is part of the Department of Pharmaceuticals and is responsible for implementing the PMBJP.
What are India's other Initiatives for Affordable Healthcare?
- Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana.
- National Health Mission (NHM).
- Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana .
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK).
- Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK).
- Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN).
- Affordable Medicines and Reliable Implants for Treatment (AMRIT) Deendayal Outlets.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q.1 How is the Government of India protecting traditional knowledge of medicine from patenting by pharmaceutical companies? (2019)
Q.2 Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector could help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives would you suggest? (2015)


Internal Security
Role of the Internet in Drug Trafficking
For Prelims: Role of the Internet in Drug Trafficking, International Narcotics Control Board, Drug Trafficking.
For Mains: Role of the Internet in Drug Trafficking, Initiatives taken to tackle Drug Menace.
Why in News?
Recently, the International Narcotics Control Board in its 2023 Annual Report, highlighted that online Drug Trafficking has increased the availability of drugs on the illicit market.
Drug Trafficking:
- Drug trafficking refers to the illegal trade involving the cultivation, manufacture, distribution, and sale of illicit drugs.
- It encompasses a wide range of activities associated with the illegal drug trade, including the production of drugs such as cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, and synthetic drugs, as well as the transportation and distribution of these substances.
- Drug trafficking operates within a complex network of criminal organisations that span across borders, regions, and even continents.
What are the Key Highlights of the Annual Report by the International Narcotics Control Board?
- Regional Drug Supply Trends:
- In Afghanistan, illicit opium poppy cultivation and heroin production declined dramatically.
- The opioid crisis continues to have serious consequences in North America with the number of deaths that involve synthetic opioids other than methadone continuing to increase, reaching more than 70,000 in 2021.
- Drug trafficking organisations continue to expand their operations in the Amazon Basin into illegal mining, illegal logging and wildlife trafficking.
- Record levels of illicit coca bush cultivation were recorded in Colombia and Peru, rising by 13% and 18% respectively.
- Seizures of cocaine reached a record level in 2021 in West and Central Africa, a significant transit region for cocaine.
- South Asia appears to be increasingly being targeted for the trafficking of methamphetamine illicitly manufactured in Afghanistan to Europe and Oceania.
- Pacific island States have transformed from solely transit sites along drug trafficking routes to destination markets for synthetic drugs.
- This is posing significant challenges to communities and their public health systems.
- Challenges in Online Drug Trafficking:
- There is an evolving landscape of online drug trafficking, presenting new challenges to drug control.
- The increased availability of illicit drugs on the Internet, exploitation by criminal groups of online platforms, and the risk of overdose deaths due to the online presence of synthetic opioids like fentanyl are significant challenges.
- Exploitation of Online Platforms:
- Criminals are exploiting legitimate e-commerce platforms, social media, and other online platforms for drug trafficking.
- Encryption methods, anonymous browsing on the darknet, and cryptocurrencies are used to avoid detection, making it difficult to prosecute online trafficking offences.
- France’s law enforcement authorities collected more than 120 million text messages from 60,000 mobile phones.
- Concerns about Patient Safety:
- Patient safety is at risk from illicit Internet pharmacies that sell drugs without a prescription directly to consumers.
- It is impossible for consumers to know whether the drugs are counterfeit, unapproved or even illegal.
- The global trade in illicit pharmaceuticals is estimated to be worth 4.4 billion USD.
- Recommendations:
- Despite challenges, there are opportunities to use online platforms for drug use prevention, awareness campaigns, and improving access to drug treatment services.
- Governments can use social media platforms to conduct drug use prevention campaigns to prevent substance misuse among young people in particular.
- Telemedicine and Internet pharmacies could improve access to healthcare and help reach patients with drug use disorders and deliver drug treatment services to more people.
- Online platforms could also be used for sharing information about the adverse consequences of drug use and communicating warnings of adulterated drugs which could save lives.
- Placing certain amphetamine-type stimulant precursors and fentanyl precursors under international control to prevent illicit drug manufacturers from substituting controlled chemicals with closely related substitutes.
- Given the global nature of online platforms, collaborative efforts between governments, international organizations, regulatory authorities, and the private sector are essential to identify new threats and develop effective responses.
- INCB encourages voluntary cooperation to tackle the misuse of legitimate e-commerce platforms for drug trafficking.
- Despite challenges, there are opportunities to use online platforms for drug use prevention, awareness campaigns, and improving access to drug treatment services.
International Narcotics Control Board
- The International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) is the independent and quasi-judicial monitoring body for the implementation of the United Nations international drug control conventions.
- It was established in 1968 in accordance with the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961.
- Its secretariat is located in Vienna, Austria.
- India’s Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB), cooperates with the INCB.
Narcotics Control Bureau
- It was constituted by the Government of India in 1986 under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985.
- It is the apex coordinating agency under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The National Policy on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances is based on Article 47 of the Indian Constitution which directs the State to endeavour to bring about prohibition of the consumption, except for medicinal purposes, of intoxicating drugs injurious to health.
What are the Initiatives Taken by India to Curb the Drug Menace?
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985: It prohibits a person from producing, possessing, selling, purchasing, transporting, storing, and/or consuming any narcotic drug or psychotropic substance.
- The National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse was also created under a provision of the NDPS Act, 1985, to meet the expenditure incurred in the implementation of the Act.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has prepared a plan for Drug Demand Reduction for 2018-25.
- This plan focuses on preventive education, awareness generation, identification, counselling, treatment, and rehabilitation of drug-dependent persons, as well as training and capacity building of service providers through collaborative efforts of government and Non-governmental Organizations (NGOs).
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Campaign (NMBA): NMBA was launched in 2020 to tackle the issue of Substance Abuse and a vision to make India drug-free. It is a three-pronged attack combining:
- The supply curb by the Narcotics Control Bureau
- Outreach and Awareness and Demand Reduction efforts by Social Justice and Empowerment
- Treatment through the Health Department.
- International Treaties and Conventions to Combat Drug Menace: India is a signatory of the following international treaties and conventions:
- United Nations (UN) Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961)
- UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (1988)
- UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances (1971)
- UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) 2000
Conclusion
- Addressing the issue of drug trafficking requires comprehensive strategies that encompass law enforcement efforts, international cooperation, border control measures, and robust demand reduction initiatives.
- By tackling both the supply and demand sides of the illicit drug trade, governments and communities can work together to mitigate its harmful effects and safeguard public health and safety.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements:
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. In one of the districts of a frontier state, narcotics menace has been rampant. This has resulted in money laundering, mushrooming of poppy farming, arms smuggling and near stalling of education. The system is on the verge of collapse. The situation has been further worsened by unconfirmed reports that local politicians as well assume senior police officers are providing surreptitious patronage to the drug mafia. At that point of time a woman police officer, known for her skills in handling such situations is appointed as Superintendent of Police to bring the situation to normalcy.
If you are the same police officer, identify the various dimensions of the crisis. Based on your understanding, suggest measures to deal with the crisis. (2019)


Important Facts For Prelims
NITI for States Platform
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Electronics & Information Technology inaugurated the 'NITI for States' platform, a digital initiative aimed at empowering states and union territories (UTs) in their pursuit of national development goals.
- The ‘Viksit Bharat Strategy Room’ at NITI Aayog was also inaugurated.
What is NITI for States Platform?
- About: Developed by NITI Aayog, “the NITI for States” platform serves as a repository of valuable resources, aiming to integrate data across states, centralising findings to inform future decisions by state governments based on data-driven insights.
- The platform incorporates real-time data updation and monitoring, spanning 10 sectors and two cross-cutting themes.
- Sectors include agriculture, education, energy, health, livelihoods and skilling, manufacturing, micro, small and medium enterprise, tourism, urban, water resources, and WASH (water, sanitation, and hygiene).
- Cross-cutting themes encompass gender and climate change.
- The platform incorporates real-time data updation and monitoring, spanning 10 sectors and two cross-cutting themes.
- Features:
- Extensive Knowledge Base: Curated best practices, policy documents, datasets, data profiles, and NITI Aayog publications.
- Multilingual Accessibility: Inclusive access in major Indian languages and foreign languages.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Tailored digital training modules for officials at block, district, and state levels.
- Expert Help Desk: Specialised guidance through partnerships with leading institutions.
- Data Integration: Leverages data from the National Data & Analytics Platform (NDAP) for comprehensive insights.
What is the Viksit Bharat Strategy Room?
- The Viksit Bharat Strategy Room is an interactive space where users will be able to visualise data, trends, best practices and policies in an immersive environment and make a holistic assessment of any problem statement.
- It also allows users to interact through voice-enabled AI, and connect to multiple stakeholders through video conferencing.
- It is designed to become a plug-and-play model to enable replication at state, district and block levels.
What are the NITI Aayog’s Initiatives Driving Development Across States?
- Development Support Services for States (DSSS): NITI Aayog assists with project planning, financing, and implementation to ensure successful infrastructure creation.
- It also aims to establish Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) as governance tools supporting larger development agenda.
- Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP): It aims to quickly and effectively transform 112 most under-developed districts across the country.
- NITI Aayog works with them to improve core metrics in education, health, nutrition, and basic infrastructure.
- Composite Water Management Index (CWMI): It provides an annual snapshot of the water sector status and water management performance of the states and union territories (UTs) in India.
- SDG India Index: This index tracks India's progress towards achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- It provides valuable data for states to identify areas needing greater focus and promotes collaborative action.
- SATH (Sustainable Action for Transforming Human Capital): It was launched in 2017 to identify and build three ‘role model’ States for the school education sector.
- Jharkhand, Odisha and Madhya Pradesh were chosen for the same.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): It aims to create and promote an ecosystem of innovation and entrepreneurship across the country at school, university, research institutions, MSME and industry levels.
- Recently, Atal Innovation Mission and Meta collaborated to launch Frontier Technology Labs (FTLs) in schools across India.
- AIM has already established 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) in schools nationwide, focusing on fostering curiosity and creativity among students.
- FTLs are an advanced version of ATLs, equipped with state-of-the-art infrastructure to empower students in frontier technologies like AI, AR/VR, Blockchain, Cybersecurity, Robotics, 3D Printing, and IoT.
- Recently, Atal Innovation Mission and Meta collaborated to launch Frontier Technology Labs (FTLs) in schools across India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
(a) Department of Science and Technology
(b) Ministry of Labour and Employment
(c) NITI Aayog
(d) Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Ans: (c)
Q. The Government of India has established NITI Aayog to replace the (2015)
(a) Human Rights Commission
(b) Finance Commission
(c) Law Commission
(d) Planning Commission
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
PM-SURAJ and NAMASTE Scheme
Why in News?
The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment launched the 'Pradhan Mantri Samajik Utthan and Rozgar Adharit Jankalyan' (PM-SURAJ) national portal online aimed at offering credit support to the marginalized segments of society, with the Prime Minister as the Chief Guest.
- The PM distributed Ayushman Health Cards and Personal Protective Equipment to Safai Mitras(sewer and septic tank workers), under the National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) scheme, which was previously a rehabilitation scheme for manual scavengers.
What is PM-SURAJ?
- The 'PM-SURAJ' national portal aims to uplift the most marginalized sections of society and provide credit assistance to one lakh entrepreneurs from disadvantaged communities.
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment and its departments.
- The portal serves as a one-stop point where people from disadvantaged sections of society can apply for and monitor the progress of all loan and credit schemes already available to them.
- The credit support will be facilitated through banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies Finance Institutions (NBFC-MFIs), and other organizations, ensuring accessibility across the country.
- An NBFC MFI is a non-deposit taking NBFC with a minimum Net Owned Funds (NOF) of Rs. 5 crore (Rs. 2 crore for those registered in the North Eastern Region of the country) and having at least 85% of its net assets as “qualifying assets (intended use or sale)”.
What is the NAMASTE Scheme?
- About:
- The NAMASTE Scheme is a central Sector Scheme formulated in 2022, by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- It aims to ensure safety, dignity, and sustainable livelihoods for urban sanitation workers.
- The Self-Employment Scheme for Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS) has been renamed as the NAMASTE.
- The SRMS scheme was launched in 2007 to help rehabilitate manual scavengers and their dependents.
- The NAMASTE scheme is to be implemented over 4800 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) of the country, during the next three years i.e. up to 2025-26.
- The National Safai Karamchari Financial Development Corporation (NSKFDC) is the implementing agency for NAMASTE.
- The NAMASTE Scheme is a central Sector Scheme formulated in 2022, by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment (MoSJE) and the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- Objectives:
- Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (MS) and Persons Engaged in Hazardous Cleaning of Sewer and Septic tanks (SSWs).
- Promotion of safe and mechanised cleaning of sewers and septic tanks through trained and certified sanitation workers.
- Intended Outcomes:
- Zero fatalities in sanitation work in India.
- All sanitation work is performed by formalized skilled workers.
- No sanitation workers come in direct contact with human faecal matter.
- Sanitation workers are collectivised into Self Help Groups (SHGs) and are empowered to run sanitation enterprises.
- Sewers and SSWs and their dependents also have access to livelihoods by providing capital subsidies for purchase of sanitation-related equipment.
- Increased awareness amongst sanitation services seekers (individuals and institutions) to seek services from registered skilled & certified sanitation workers
- Extending Health Insurance Scheme benefits under Ayushman Bharat, Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) to SSW & manual scavengers and their family members.
What are India's Other Credit Schemes to Empower Marginalized Sections?
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- Stand-Up India Scheme
- Ambedkar Social Innovation and Incubation Mission
- Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana
- Special Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme
- Rashtriya Garima Abhiyaan:
- National campaign for dignity and eradication of the practice of manual scavenging and rehabilitate the manual scavengers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. ‘Rashtriya Garima Abhiyaan’ is a national campaign to (2016)
(a) rehabilitate the homeless and destitute persons and provide them with suitable sources of livelihood
(b) release the sex workers from their practice and provide them with alternative sources of livelihood
(c) eradicate the practice of manual scavenging and rehabilitate the manual scavengers
(d) release the bonded labourers from their bondage and rehabilitate them
Ans: C


Important Facts For Prelims
BBNJ Treaty
Why in News?
The Blue Leaders High-Level Event on Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction took place in Belgium, encouraging nations to ratify the Marine Biodiversity of Areas Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) treaty aimed at protecting the high seas from pollution, climate change, and overfishing.
What is the BBNJ Treaty?
- About:
- The BBNJ treaty commonly referred to as the Treaty of the High Seas was agreed upon in March 2023 for the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
- It represents a crucial step towards conserving and sustainably managing marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
- The BBNJ treaty commonly referred to as the Treaty of the High Seas was agreed upon in March 2023 for the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
- Ratification Progress:
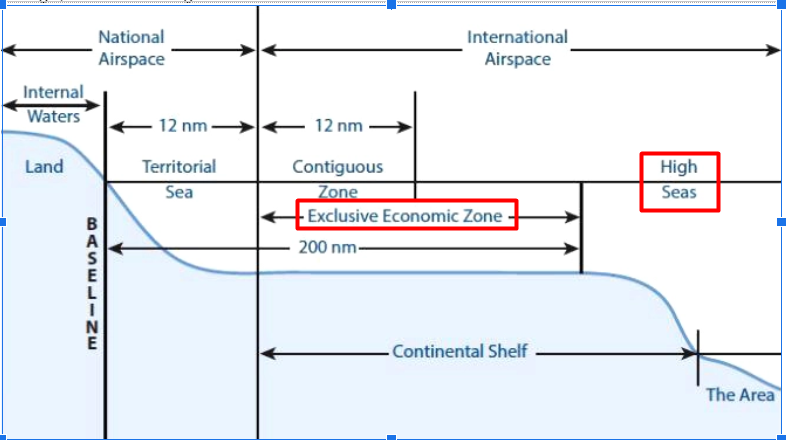
- The treaty aims to address the challenges faced by the high seas, which constitute areas beyond 200 nautical miles from the exclusive economic zones of coastal countries.
- So far, 88 countries have signed the treaty, with Chile and Palau being the only two to have ratified it.
- However, at least 60 ratifications are necessary for it to come into force.
- The treaty aims to address the challenges faced by the high seas, which constitute areas beyond 200 nautical miles from the exclusive economic zones of coastal countries.
- Objectives:
- The treaty seeks to increase the percentage of protected areas on the high seas, which currently stands at a mere 1.44%, despite covering more than two-thirds of the global ocean.
- Additionally, it aims to ensure fair and equitable sharing of profits from marine genetic resources (MGR) and establish rules for conducting Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA), which deal with identifying and evaluating the potential impacts an activity could have on the ocean.
- This aligns with the 30x30 target, it is a global commitment to protect at least 30% of the planet for nature by 2030. It was agreed upon at the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) at the Conference of Parties (COP15) to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity in 2022 and is included in the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
- Challenges:
- Despite widespread support for the treaty, concerns persist regarding potential delays in ratification, echoing past challenges faced by similar international agreements like the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Seas.
- Additionally, operationalising the treaty poses logistical hurdles, including defining procedural frameworks and securing adequate funding.
- Moving Forward:
- Efforts towards the treaty's entry into force and subsequent implementation require concerted global collaboration.
- The upcoming United Nations Ocean Conference in 2025 is identified as a crucial platform for advancing these objectives.
- Efforts towards the treaty's entry into force and subsequent implementation require concerted global collaboration.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 With reference to the United Nations Convention on the Law of Sea, consider the following statements: (2022)
- A coastal state has the right to establish the breadth of its territorial sea up to a limit not exceeding 12 nautical miles, measured from baseline determined in accordance with the convention.
- Ships of all states, whether coastal or land-locked, enjoy the right of innocent passage through the territorial sea.
- The Exclusive Economic Zone shall not extend beyond 200 nautical miles from the baseline from which the breadth of the territorial sea is measured.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
Centre Amends IT Rules for Interception Record Destruction
The government has amended the Information Technology (IT) rules to allow for the Home Secretary or other bureaucrats in the Centre to issue directions to destroy digital records of interception or decrypt information.
- So far, the power lies with security agencies, such as law enforcement bodies.
- The amendment, outlined in a gazette notification by the IT Ministry, involves a modification to Section 23 of the Information Technology (Procedure and Safeguards for Interception, Monitoring, and Decryption of Information) Rules, 2009.
- Specifically, the term "security agency" has been replaced with "competent authority and the security agency," granting the Centre broader powers to issue directives for the destruction of digital evidence.
- Rule 23 of the law mandates that all records, including electronic ones related to interception, monitoring, or decryption of information, must be destroyed by security agencies every six months, unless deemed necessary for functional purposes.
Read more: New IT Rules


Rapid Fire
CDSCO Caution on Unapproved New Drugs
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) has issued a cautionary statement regarding the manufacture and sale of unapproved drugs, particularly emphasising the category of "New Drugs."
- Notably, drugs like Meropenem, an antibacterial agent, and Disodium EDTA, used to treat calcium overload, were highlighted as examples of such unapproved medications.
- CDSCO emphasised that no new drug should be manufactured for sale without approval from the licensing authority.
- CDSCO is the Central Drug Authority for discharging functions assigned to the Central Government under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- Major functions of CDSCO include regulatory control over the import of drugs, approval of new drugs and clinical trials, and approval of certain licences as Central License Approving Authority.
Read more: Regulatory Issues in Indian Pharmaceutical Sector


Rapid Fire
Boosting Fintech Education and Innovation
The Government of India and the Asian Development Bank (ADB) have signed a USD 23 million loan agreement to enhance access to quality fintech education, research, and innovation at the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT-City).
- The project will establish an International Fintech Institute (IFI) to strengthen fintech education, boost startup success rates, and drive fintech research and innovation.
- Emphasis will be placed on market-driven fintech skills programs, private sector investment, and collaboration between industry, institutes, and partners for holistic growth.
- IFI will offer industry-aligned fintech training programs meeting international standards and supporting innovation and entrepreneurship.
- The ADB program will support research in climate fintech, regulatory technology, social inclusion, and gender equality in finance to develop new solutions and a state fintech readiness index.
- GIFT-City is a business district and the first operational greenfield smart city in India. It's located on the banks of the Sabarmati River in Gujarat
- It is inclined to provide a conducive business ecosystem at par or above with leading global financial hubs.
- It consists of a multi-service Special Economic Zone (SEZ), which houses India’s first International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) and an exclusive Domestic Tariff Area (DTA).
Read more: GIFT City and Bullion Exchange, ADB Regional Conference and PM Gati Shakti


Rapid Fire
India's First Green Hydrogen Plant in the Stainless Steel Sector
Recently, the Union Minister for Steel, virtually inaugurated India's 1st Green Hydrogen Plant in the Stainless Steel Sector located at Jindal Stainless Limited, Hisar. It is the world's first off-grid green hydrogen plant dedicated to the stainless steel industry.
- Conventional steel production relies heavily on coal, a major source of greenhouse gasses. This dependence is problematic for India's environmental goals. Green hydrogen offers a cleaner alternative.
- The plant targets a considerable reduction in carbon emissions, aiming to cut around 2,700 Metric Tonnes per annum and 54,000 tons of CO2 emissions over the next two decades.
- Stainless steel is a type of steel alloy that contains a minimum of 10.5% chromium by mass.
- It is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it highly suitable for various applications where durability and resistance to rust and staining are essential.
- India is the world's second-largest producer of crude steel, with an output of 125.32 million tonnes (MT) of crude steel and 121.29 MT of finished steel production in FY23.
- India is also a net exporter of steel witnessing an export of 6.72 MT of finished steel against the import of 6.02 MT in 2022-23.
Read more: Steel Sector, Green Hydrogen


Rapid Fire
India and Dominican Republic to Strengthen Economic Ties with JETCO Protocol
The protocol for the establishment of the Joint Economic and Trade Committee (JETCO) between India and the Dominican Republic was signed at Santo Domingo (Capital of the Dominican Republic).
- The protocol envisages strengthening and develop cooperation on trade, services, industrial technologies and various other sectors by means of technical assistance, training programmes and capacity building.
- Diplomatic relations between India and Dominican Republic were established in May 1999. However, at present, there is no bilateral institutional mechanism between India and the Dominican Republic on trade and commerce.
- India primarily imports gold from the Dominican Republic and exports pharmaceuticals, marine products, motor vehicles, two and three-wheelers etc.
Read more: India-Dominican Republic Relations


Rapid Fire
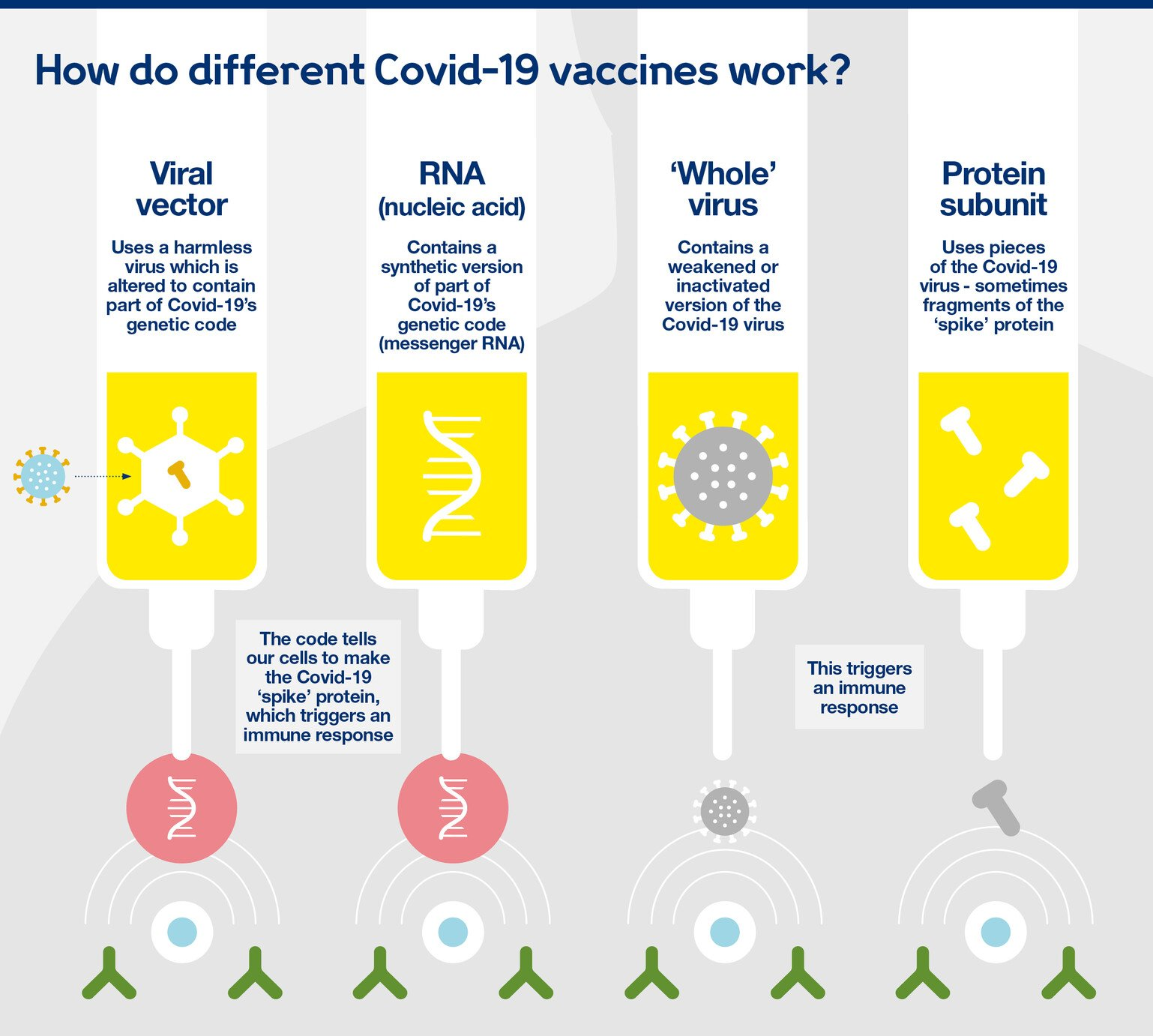
Covishield and Covaxin Immunogenicity
A recent study led by scientists from the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) and conducted across 11 institutes has provided compelling insights into the immunogenicity of 2 primary Covid-19 vaccines in India: Covishield and Covaxin.
- Immunogenicity refers to the ability of a substance, such as a vaccine or antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body.
- This response typically involves the production of antibodies and activation of immune cells, leading to protection against infection or disease.
- The recent study examined the immune responses induced by Covishield and Covaxin vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.
- Covishield, utilising a virus vector to deliver the coronavirus spike protein, consistently elicited a more robust immune response (higher antibody levels in both seronegative (individuals without prior exposure) and seropositive (individuals with prior exposure)) compared to Covaxin, an inactivated virus vaccine.
- Additionally, Covishield elicited a greater number of T cells, indicating a stronger immune response.
Read more: Covishield and Covaxin




 Agreement (UN HIGH SEAS Treaty).png)