Maps
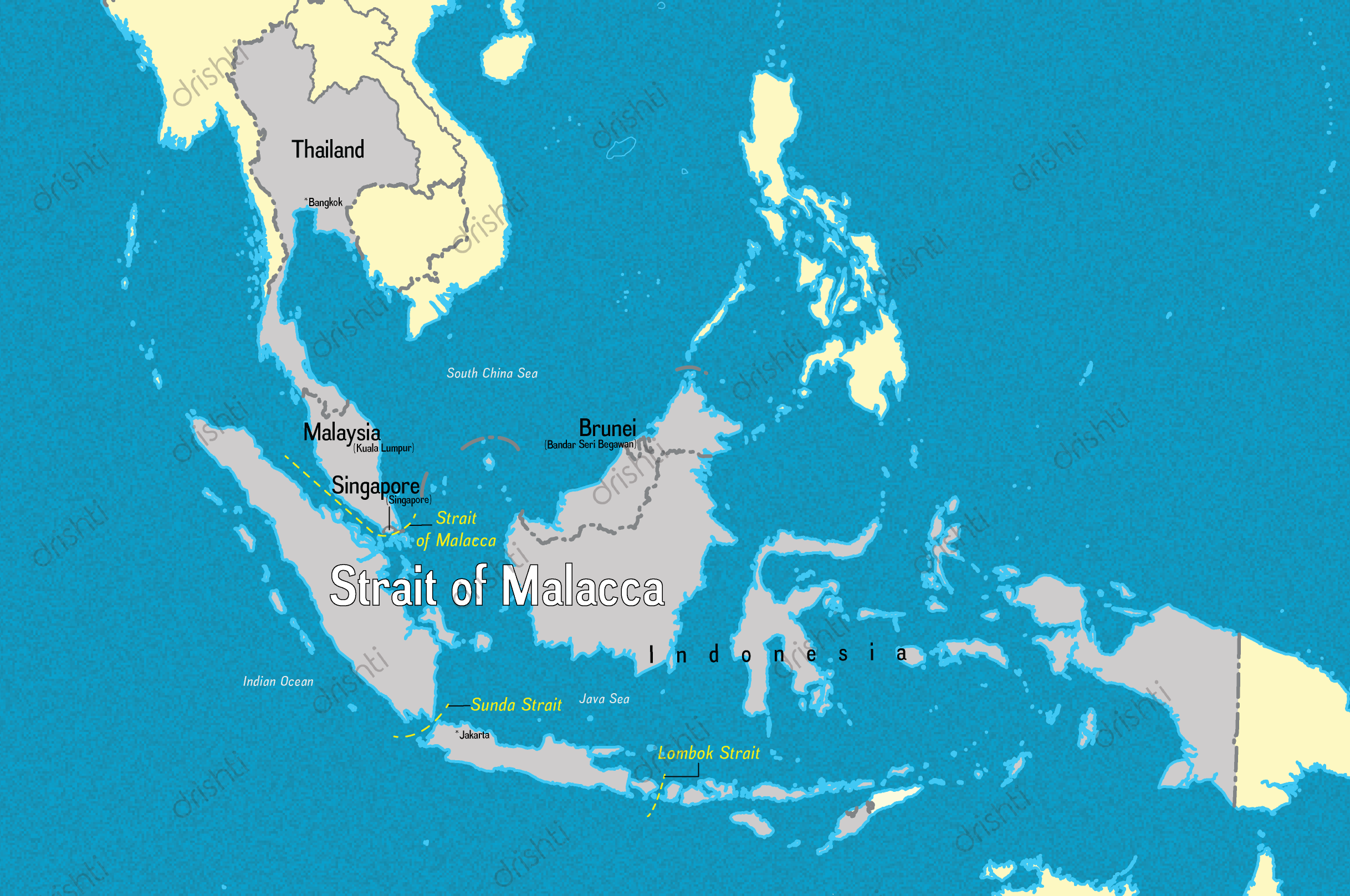
Strait of Malacca
Key Points
- Physical Geography:
- Connects the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pacific Ocean).
- Runs between the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the west and peninsular (West) Malaysia and extreme southern Thailand to the east.
- Strategic Importance:
- Shortest sea route between the Middle East and East Asia, helping to reduce the time and cost of transportation among Asia, the Middle East and Europe.
- Through this corridor, approximately 60% of the world's maritime trade transits, and is the main source of oil supply for two of the main Asian consumers: the People's Republic of China and Japan.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) was created in 2001 to safeguard India's strategic interests in Southeast Asia and the Strait of Malacca by increasing rapid deployment of military assets in the islands.


Infographics
Social Justice
Global Hunger Index 2022
For Prelims: Global Hunger Index, Child wasting, stunting, mortality and undernourishment, India’s initiatives to eradicate hunger, NFHS - 5.
For Mains: India’s performance in Global Hunger Index, Status of Hunger and Malnutrition in India, Relation of Hunger and Poverty, India’s initiatives to eradicate hunger and their progress.
Why in News?
Barring the war-torn Afghanistan, India has performed worse than all the countries in the South Asian region in the Global Hunger Index 2022. It has ranked 107 out of 121 countries.
- India ranked 101 out of 116 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2021.
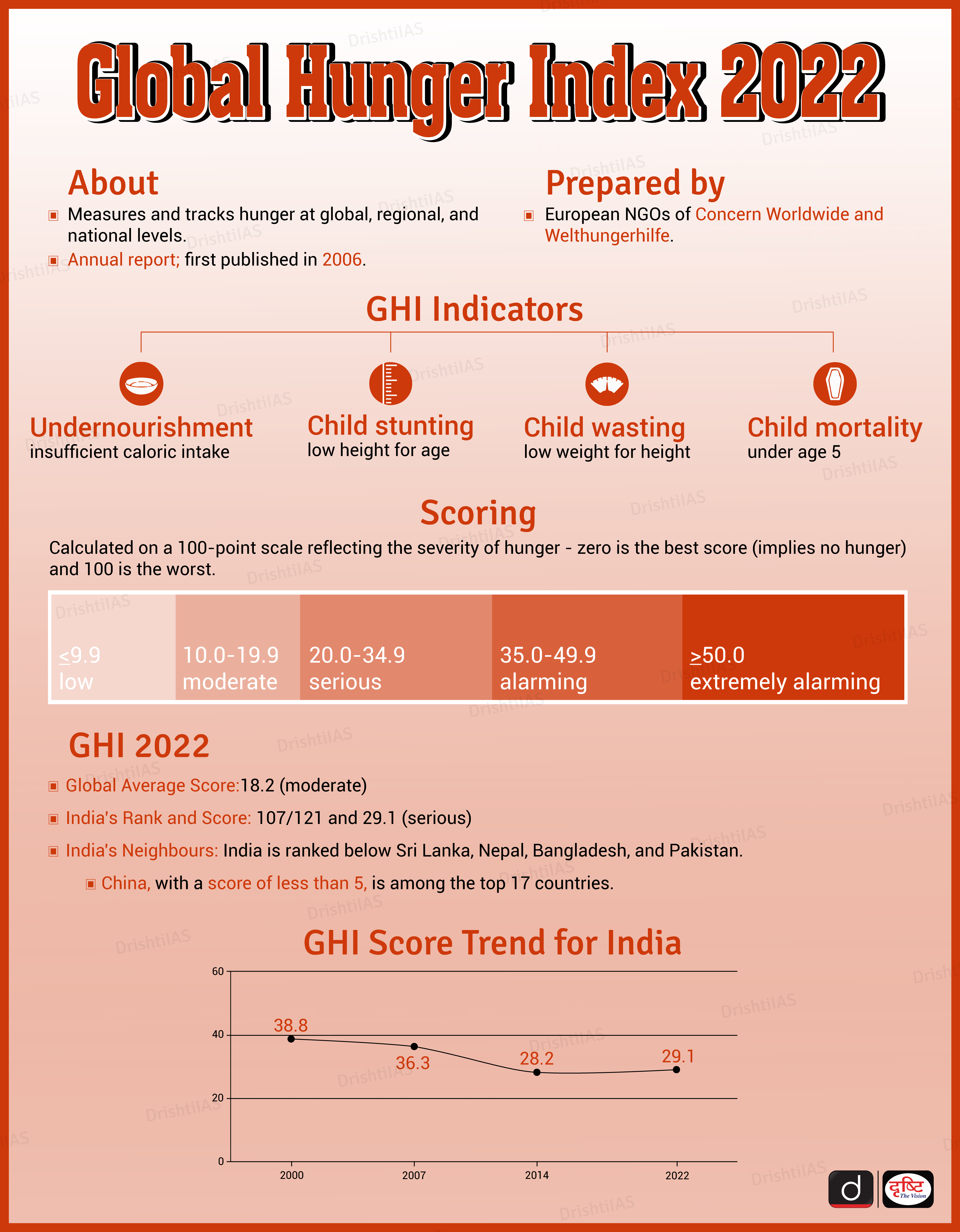
What is the Global Hunger Index?
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a tool for comprehensively measuring and tracking hunger at global, regional, and national levels.
- GHI scores are based on the values of four component indicators:
- Undernourishment
- Child stunting
- Child wasting
- Child mortality
- The GHI score is calculated on a 100-point scale reflecting the severity of hunger - zero is the best score (implies no hunger) and 100 is the worst.
- The GHI is prepared by European NGOs of Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe.
- The GHI is an annual report and each set of GHI scores uses data from a 5-year period. The 2022 GHI scores are calculated using data from 2017 through 2021.
What is the Performance of Countries on GHI 2022?
- Global Progress: Globally, the progress against hunger has largely stagnated in recent years, with a global score of 18.2 in 2022 as compared to 19.1 in 2014, there is only a slight improvement. However, the 2022 GHI score is still considered “moderate”.
- The plausible causes for the stagnation in this progress are overlapping crises such as conflicts among countries, climate change, the economic fallout of the Covid-19 pandemic as well as the Russia-Ukraine war, which has increased global food, fuel, and fertiliser prices and is expected to “worsen hunger in 2023 and beyond”.
- As per the index, there are 44 countries that currently have “serious” or “alarming” hunger levels and “without a major shift, neither the world as a whole nor approximately 46 countries are projected to achieve even low hunger as measured by the GHI by 2030.
- Top and Worst Performers:
- Belarus, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Chile, China and Croatia are the top five countries in GHI 2022.
- Chad, Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, Central African Republic and Yemen are the countries ranked at the bottom of the index.
- India and Neighboring Countries: Among the South Asian countries, India (107) is ranked below Sri Lanka (64), Nepal (81), Bangladesh (84), and Pakistan (99).
- India has a score of 29.1 which places it under ‘serious’ category.
- Afghanistan (109) is the only country in South Asia that performs worse than India on the index.
- China, with a score of less than 5, has topped the chart, topped the chart, together with 16 other countries.
- India’s Performance in the Four Indicators:
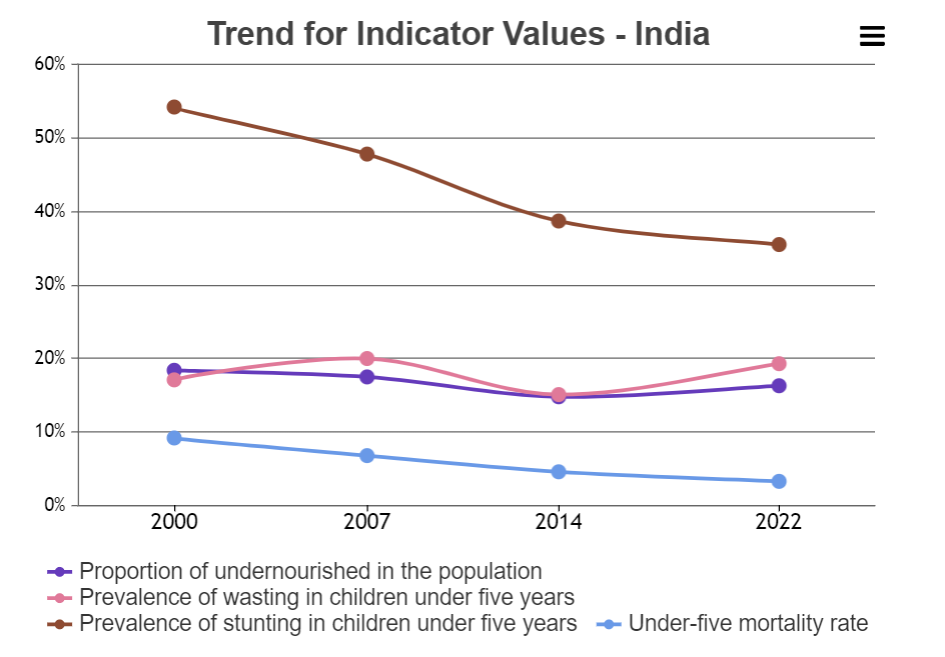
- Child Wasting: India’s child wasting rate (low weight for height), at 19.3%, is worse than the levels recorded in 2014 (15.1%) and even 2000 (17.15%).
- It is the highest for any country in the world and drives up the region’s average owing to India’s large population.
- Undernourishment: Prevalence of undernourishment has also risen in the country from 14.6% in 2018-2020 to 16.3% in 2019-2021.
- It implies that 224.3 million people in India (out of 828 million globally) are considered undernourished.
- The indicator measures the proportion of the population facing chronic deficiency of dietary energy intake.
- Child Stunting and Mortality: India has shown improvement in child stunting and child mortality.
- Child stunting (low height for age) has declined from 38.7% to 35.5% between 2014 and 2022.
- Child mortality (mortality rate under the age of five) has dropped from 4.6% to 3.3% in the same comparative period.
- Child Wasting: India’s child wasting rate (low weight for height), at 19.3%, is worse than the levels recorded in 2014 (15.1%) and even 2000 (17.15%).
What Other Similar Indices/Reports are There?
- State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World:
- Presented by the Food and Agriculture Organization, the International Fund for Agricultural Development, the UNICEF, the World Food Programme and the World Health Organization.
- Global Nutrition Report, 2021:
- It was conceived following the first Nutrition for Growth Initiative Summit (N4G) in 2013.
- National Family Health Survey (NFHS):
- It comprises detailed information on key domains of population, health and family welfare - fertility, family planning, infant and child mortality, maternal and child health, nutrition and anaemia, morbidity and healthcare, women’s empowerment etc.
What are India’s Initiatives to Eradicate Hunger/Malnutrition?
- Eat Right India Movement: An outreach activity organised by the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) for citizens to nudge them towards eating right.
- POSHAN Abhiyan: Launched by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 2018, it targets to reduce stunting, undernutrition, anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls).
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana: A centrally sponsored scheme executed by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, is a maternity benefit programme being implemented in all districts of the country with effect from 1st January, 2017.
- Food Fortification: Food Fortification or Food Enrichment is the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content.
- National Food Security Act, 2013: It legally entitled up to 75% of the rural population and 50% of the urban population to receive subsidised food grains under the Targeted Public Distribution System.
- Mission Indradhanush: It targets children under 2 years of age and pregnant women for immunisation against 12 Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (VPD).
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme: It offers a package of six services (Supplementary Nutrition, Pre-school non-formal education, Nutrition & health education, Immunisation, Health check-up and Referral services) to children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Which of the following is/are the indicator/ indicators used by IFPRI to compute the Global Hunger Index Report? (2016)
- Undernourishment
- Child stunting
- Child mortality
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (c)
Q2. Very recently, in which of the following countries have lakhs of people either suffered from severe famine/acute malnutrition or died due to starvation caused by war/ethnic conflicts? (2018)
(a) Angola and Zambia
(b) Morocco and Tunisia
(c) Venezuela and Colombia
(d) Yemen and South Sudan
Ans: (d)
Q3. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. There is a growing divergence in the relationship between poverty and hunger in India. The shrinking of social expenditure by the government is forcing the poor to spend more on non-food essential items squeezing their food-budget. Elucidate. (2019)
Q. Hunger and Poverty are the biggest challenges for good governance in India still today. Evaluate how far successive governments have progressed in dealing with these humongous problems. Suggest measures for improvement. (2017)


Governance
International Day of Rural Women
For Prelims: International Day of Rural Women, Civil society Organisations, MGNREGA, UPSC, IAS, UPSC CSE Previous Year Question
For Mains: Issues of Women in Rural Economy, Measures that can be taken to Uplift Rural Women Workers
Why in News?
Every year, International Day of Rural Women is celebrated on 15th October.
Why do we Celebrate the International Day of Rural Women?
- Background:
- The idea of honouring rural women with a special day was put forward by international NGOs at the Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing in 1995.
- The first International Day of Rural Women was observed on 15th October 2008. This new international day was established by the General Assembly in its resolution 62/136 in 2007.
- About:
- The day aims to create awareness about the fact that the engagement of rural women diversifies family livelihood, yet their efforts largely go unappreciated.
- It recognizes “the critical role and contribution of rural women, including indigenous women, in enhancing agricultural and rural development, improving food security and eradicating rural poverty.”
- Theme for 2022:
- "Rural Women, key for a world free from hunger and poverty."
What are the Challenges Faced by Rural Women Workers in India?
- Incomplete Presentation of Data:
- The rural economy suffers when women stop looking for work because they believe there is no work available, often incorrectly described as "dropping out" or "Leaving the market".
- Absence of Pay Parity:
- In the field of manual labour work, women are being paid less than men in terms of piece rate due to physical constraints in lifting heavy weights.
- Lack of Education:
- Majority of women construction workers are not registered as “Construction Workers” and therefore ineligible for any benefit accruing to them from the Construction Workers’ Welfare Board.
- The paid formal jobs go to men and women with higher educational qualifications, leaving women with education till secondary level for non-agricultural, construction, house care and other roles.
- Limitation of MGNREGA:
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), a labour demand-driven programme, is limited to providing only 100 days of paid labour on public works projects per year.
- For the rest of the period, women workers have to continuously look for alternative sources of income to meet expenses.
- Financial Constraints:
- What the women earn from multiple tasks, for which there are no fixed rates is in no way equal to the amount of labour they do.
- Due to non-availability of sufficient funds and lack of knowledge, they’re most vulnerable to land in debt traps.
What Initiatives Taken for the Upliftment for Rural Women Workers?
- e-Shram Portal:
- e-Shram Portal was launched to register 38 crore unorganised workers such as construction labourers, migrant workforce, street vendors, and domestic workers, among others.
- The Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP):
- Launched in 2011, it is aimed at imparting skill development and capacity building programmes for rural women.
- This scheme was introduced as a sub component of DAY-NRLM (Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana — National Rural Livelihoods Mission) and implemented through State Rural Livelihoods Mission (SRLM) across India.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY):
- Launched in 2015, it aims to train over 40 crore people in India in different skills by 2022. It aims at vocational training and certification of Indian youth for a better livelihood and respect in the society.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
- PMJDY has boosted confidence and prospects of rural women participation in economic activities. The Jan Dhan campaign has ensured access to financial services, viz, banking/ savings and deposit accounts, remittance, credit, insurance, pension in an affordable manner to rural women.
- Other Initiatives
Way Forward
- Survey Conduction:
- Timely village surveys should be conducted which could reveal the real image of ground reality, as with the deep penetration of capitalist processes in rural India, there is a crisis of livelihood options for rural workers.
- Widespread surveys of poor rural women and how they spend their time are an urgent necessity.
- Adult Education and Training:
- Women lack access to quality adult education and training, which is one of the greatest barriers to their sustainable development.
- Women should receive life skills, and social skills training as part of capacity building and adult training.
- MGNREGA Standards:
- The performance standards set under MGNREGA should be established gender-wise and the work sites made more worker friendly.
- The ‘compulsory’ woman worker must be recognised and protected by laws and policies that address her issues.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. ‘Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action’, often seen in the news, is (2015)
(a) a strategy to tackle the regional terrorism, an outcome of a meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization
(b) a plan of action for sustainable economic growth in the Asia-Pacific Region, an outcome of the deliberations of the Asia-Pacific Economic Forum
(c) an agenda for women’s empowerment, an outcome of a World Conference convened by the United Nations
(d) a strategy to combat wildlife trafficking, a declaration of the East Asia Summit
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action is a global commitment to achieve equality, development and peace for women worldwide. It was adopted in September, 1995 at the Fourth World Conference on Women held in Beijing. It builds upon consensus and progress made at earlier UN Conferences, particularly the Conference on Women in Nairobi in 1985.
- The Platform for Action is an agenda for women’s empowerment. It aims at accelerating the implementation of the Nairobi Forward-looking Strategies for the Advancement of Women and at removing all the obstacles to women’s active participation in all spheres of public and private life through a full and equal share in economic, social, cultural and political decision-making.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. “Micro-Finance as an anti-poverty vaccine, is aimed at asset creation and income security of the rural poor in India”. Evaluate the role of the Self Help Groups in achieving the twin objectives along with empowering women in rural India. (2020)


International Relations
India-New Zealand Relations
For Prelims: QUAD, Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI), Indo-Pacific Region
For Mains: Strategic relations of India-Australia
Why in News?
Recently, External Affairs Minister (EAM) of India has visited New Zealand and Australia.
- The meeting consisted of various geo-political issues like how India-New Zealand contributions together will shape the larger region, the Indo-Pacific region. They also discussed the present security situation in the Indo-Pacific and also the consequences arising out of the Ukraine conflict.
What are the Different Aspects of India-New Zealand Relations?
- Historical Relations: India and New Zealand have a longstanding, friendly and growing relationship. Our ties go back to the 1800s, with Indians settling in Christchurch as early as the 1850s. Larger numbers of immigrants from Punjab and Gujarat came to New Zealand in the 1890s. Indian troops fought alongside the Anzacs in Gallipoli in 1915.
- Political Relations: India and New Zealand have cordial and friendly relations rooted in the linkages of the Commonwealth, parliamentary democracy, and the English language. Both countries became independent in the same year and diplomatic representation of India was established in 1950 with the opening of a Trade Commission, which was later upgraded to High Commission.
- Both countries are fellow travellers in their commitment to disarmament, global peace, North-South Dialogue, human rights, ecological preservation and combating international terrorism.
- Cooperation on the Covid-19 pandemic: Both countries cooperated extensively both bilaterally in fighting against the pandemic by ensuring the continuity of supply chains of essential commodities, medicines, and vaccines. Both countries also facilitated the repatriation of each other’s nationals stranded in the wake of Covid-19.
- Trade Relations: 11th largest two-way trading partner with total two-way trade valued at US$1.80 bn during 2020. Education and tourism are NZ’s growth sectors with India. Indian students numbering approximately 15000 (before the pandemic) are the 2nd largest source of international students for NZ.
- The number of Indian visitors to NZ in 2018 was the 9th largest at 67,953.
- India primarily imports logs and forestry products, wood pulp, wool, and edible fruit & nuts from NZ.
- Indian exports to NZ mostly are pharmaceuticals/medications, precious metals and gems, textiles and motor vehicles and non-knitted apparel and accessories.
- India shares Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with New Zealand.
- Business Alliances: India NZ Business Council (INZBC) and India NZ Trade Alliance (INZTA) are the two prominent organizations working to promote India-NZ trade and investment relations.
- Cultural Relations: All Indian festivals including Diwali, Holi, Rakshabandhan, Baisakhi, Guruparv, Onam, Pongal, etc. are celebrated with much enthusiasm all over NZ. A set of four new stamps depicting the story of Diwali has been issued by New Zealand Post in 2021. NZ has approximately 2,50,000 persons of Indian origin & NRIs, a vast majority of which has made NZ their permanent home.
What are the Different Aspects of India-Australia Relations?
- Historical Relations: India and Australia established diplomatic relations in the pre-Independence period, with the establishment of India Trade Office in Sydney in 1941. The end of the Cold War and simultaneously India’s decision to launch major economic reforms in 1991 provided the first positive move towards development of closer ties between the two nations. With the passage of time, the relationship gained momentum towards a strategic relationship, alongside the existing economic engagement.
- India-Australia Strategic Relationship: With the changing global scenario, Australia has come to look at India as an important partner in promoting regional security and stability. This led to upgradation of bilateral relationship to a ‘Strategic Partnership’, including a Joint Declaration on Security Cooperation in 2009. Bilateral mechanisms include high level visits, Annual Meetings of Prime Ministers, Foreign Ministers’ Framework Dialogue, Joint Trade & Commerce Ministerial Commission, India-Australia '2+2' Foreign Secretaries and Defence Secretaries Dialogue, QUAD, Defence Policy Talks, Australia-India Education Council,etc.
- Trade Relations: Growing India-Australia economic and commercial relations contribute to the stability and strength of a rapidly diversifying and deepening bilateral relationship between the two countries.
- Australia is the 17th largest trading partner of India and India is Australia’s 9th largest trading partner.
- India-Australia bilateral trade for both merchandise and services is valued at USD 27.5 billion in 2021.
- India’s merchandise exports to Australia grew 135% between 2019 and 2021. India’s exports consist primarily of a broad-based basket largely of finished products and were USD 6.9 billion in 2021.
- India’s merchandise imports from Australia were USD 15.1 billion in 2021, consisting largely of raw materials, minerals and intermediate goods.
- India signed a historic trade agreement with Australia in 2022, the India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (Ind- Aus ECTA).
- India and Australia are partners in the trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) arrangement along with Japan which seeks to enhance the resilience of supply chains in the Indo-Pacific Region.
Way Forward
India’s strong economy, large population, and international influence make it a key partner in the Indo-Pacific region. Our relationship with the countries of the Indo-Pacific is a priority due to the increasing influence and assertiveness of China in the region. It also represents an enormous potential for India to emerge as a key leader in the region.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) is transforming itself into a trade bloc from a military alliance, in present times Discuss. (2020)


Governance
Multi-State Cooperatives
For Prelims: Multistate Cooperatives, Constitution (97th Amendment) Act, 2011, Constitutional Provisions Related to Cooperatives.
For Mains: Loopholes in the Multi State Cooperative Societies (MSCS) Act, 2002.
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved the Multi-State Cooperative Societies (MSCS) Amendment Bill, 2022, which seeks to amend the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002
- A new Ministry of Cooperation was formed in July 2021 with an objective to provide renewed impetus to the growth of Cooperative Sector.
What are the Changes Proposed in the Bill?
- The amendments seek to improve ease of doing business, bringing greater transparency and enhance governance.
- It has included provisions relating to representation of women and Scheduled Caste/Scheduled Tribe members on the board of multi-state cooperative societies.
- The amendments have been brought to reform the electoral process, strengthen monitoring mechanisms and enhance accountability.
- It will also widen the composition of board and ensure financial discipline, besides enabling the multi-state cooperative societies to raise funds.
- To improve the governance of multi-state cooperative societies, the Bill has specific provisions for setting up of Cooperative Election Authority, Cooperative Information Officer and Cooperative Ombudsman.
- There will also be a provision for issuing non-voting shares in multi-state co-operative societies to help them raise funds.
- Further, the newly proposed Rehabilitation, Reconstruction & Development Fund will help in revitalising sick co-operative societies.
- The Bill will incorporate the provisions of the 97th Constitutional Amendment.
- Moreover, the provision for stipulating prudential norms will bring in financial discipline. The amendments relating to auditing mechanism will ensure more accountability.
What are the Key Points of MSCS Act, 2002?
- About:
- Multi State Cooperative Societies: Although Cooperatives is a state subject, there are many societies such as those for sugar and milk, banks, milk unions etc whose members and areas of operation are spread across more than one state.
- For example, most sugar mills along the districts on the Karnataka-Maharashtra border procure cane from both states.
- Maharashtra has the highest number of such cooperative societies at 567, followed by Uttar Pradesh (147) and New Delhi (133).
- The MSCS Act was passed to govern such cooperatives.
- Legal Jurisdiction: Their board of directors has representation from all states they operate in.
- Administrative and financial control of these societies is with the central registrar, with the law making it clear that no state government official can wield any control on them.
- The exclusive control of the central registrar was meant to allow smooth functioning of these societies, without interference of state authorities.
- Multi State Cooperative Societies: Although Cooperatives is a state subject, there are many societies such as those for sugar and milk, banks, milk unions etc whose members and areas of operation are spread across more than one state.
- Associated Concerns:
- Lack of Checks and Balances: While the system for state-registered societies includes checks and balances at multiple layers to ensure transparency in the process, these layers do not exist in the case of multi state societies.
- The central registrar can only allow inspection of the societies under special conditions.
- Further, inspections can happen only after prior intimation to societies.
- Weak Institutional Infrastructure of Central Registrar: The on-ground infrastructure for central registrar is thin — there are no officers or offices at state level, with most work being carried out either online or through correspondence.
- Due to this, the grievance redressal mechanism has become very poor.
- This has led to several instances when credit societies have launched ponzi schemes taking advantage of these loopholes.
- Lack of Checks and Balances: While the system for state-registered societies includes checks and balances at multiple layers to ensure transparency in the process, these layers do not exist in the case of multi state societies.
What are Cooperatives in India?
- Definition:
- The International Cooperative Alliance (ICA) defines a Cooperative as “an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social, and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly-owned and democratically-controlled enterprise.”
- Examples of Successful Cooperatives in India:
- Constitutional Provisions:
- The Constitution (97th Amendment) Act, 2011 added a new Part IXB regarding the cooperatives working in India.
- The word “cooperatives” was added after “unions and associations” in Article 19(1)(c) under Part III of the Constitution.
- This enables all the citizens to form cooperatives by giving it the status of fundamental right of citizens.
- A new Article 43B was added in the Directive Principles of State Policy (Part IV) regarding the “promotion of cooperative societies”.
- The word “cooperatives” was added after “unions and associations” in Article 19(1)(c) under Part III of the Constitution.
- The Constitution (97th Amendment) Act, 2011 added a new Part IXB regarding the cooperatives working in India.
- Supreme Court Judgement:
- In July, 2021, the Supreme Court struck down certain provisions of the 97th Amendment Act, 2011.
- As per the SC, Part IX B (Articles 243ZH to 243ZT) has “significantly and substantially impacted” State legislatures’ “exclusive legislative power” over its co-operative sector.
- Also, the provisions in the 97th Amendment were passed by Parliament without getting them ratified by State legislatures as required by the Constitution.
- The SC held that states have exclusive power to legislate on topics reserved exclusively to them (cooperatives are a part of State list).
- The 97th Constitutional Amendment required ratification by at least one-half of the state legislatures as per Article 368(2).
- Since the ratification was not done in the case of the 97th amendment, it was liable to strike it down.
- It upheld the validity of the provisions of Part IX B which are related to Multi State Cooperative Societies (MSCS).
- It said that in case of MSCS with objects not confined to one state, the legislative power would be that of the Union of India.
- In July, 2021, the Supreme Court struck down certain provisions of the 97th Amendment Act, 2011.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “In the villages itself no form of credit organization will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural finance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural finance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (200 words) (2014)


Biodiversity & Environment
Galápagos Islands
For Prelims: World Heritage Site, Charles Darwin, Cold Ocean currents, Ocean Currents
For Mains: Factors that Influences Ocean Current
Why in News?
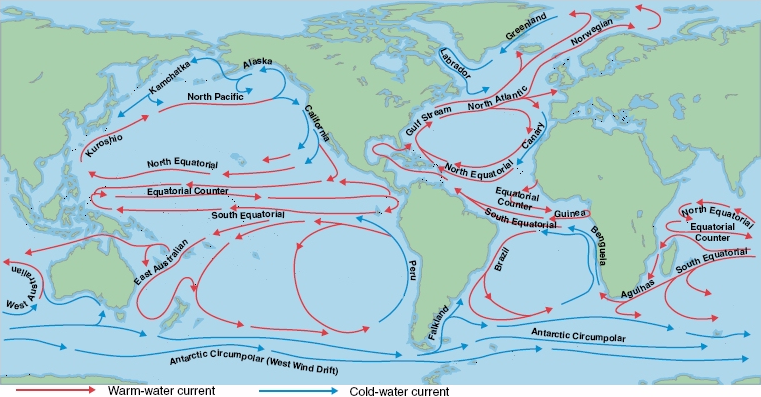
According to a recent study, Cold ocean currents have sheltered the Galápagos Islands from global warming.
- The islands are protected from an otherwise warming the Pacific Ocean by a cold, eastward equatorial ocean current.
- The equatorial undercurrent in the Pacific Ocean is bound to the equator by the force of the planet’s rotation. Under the ocean’s surface, a swift circulation of cold, nutrient-rich water flows from west to east.
What is Galapagos Archipelago?
- Location:
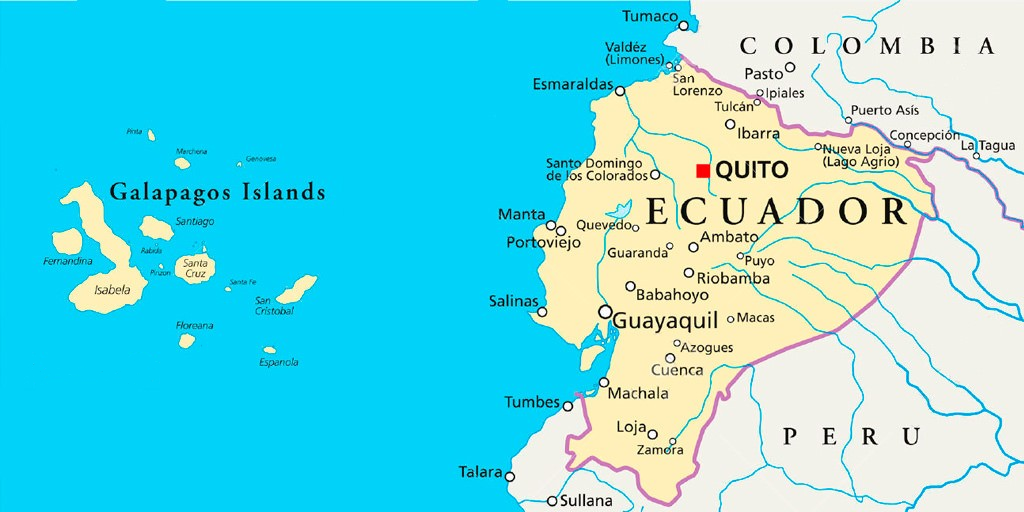
- The Galapagos Islands, spread over almost 60,000 sq km, are a part of Ecuador.
- These are located in the Pacific Ocean around 1,000 km away from the South American continent.
- Protection Status:
- Ecuador made a part of the Galapagos a wildlife sanctuary in 1935, and the sanctuary became the Galapagos National Park in 1959.
- In 1978, the islands became UNESCO’s first World Heritage Site.
- Wildlife:
- It contains aquatic species such as manta rays and sharks which have been endangered by commercial fishing.
- It also hosts a wide array of aquatic wildlife, including marine iguanas, and waved albatrosses.
- Galápagos is home to the critically endangered — Galápagos penguin, Galápagos fur seal and Galápagos sea lion.
- Also, the giant tortoises found here – 'Galápagos' in old Spanish – give the islands its name.
- Significance:
- The British naturalist Charles Darwin made key observations in 1835 that shaped his theory of evolution.
- Darwin described the islands as a “world in itself”.
- Corals do not bleach and die in these waters off the west coast of Ecuador.
What are Ocean Currents?
- About:
- Ocean currents are the continuous, predictable, directional movement of seawater. It is a massive movement of ocean water that is caused and influenced by various forces. They are like river flows in oceans.
- Types:
- Cold currents: It brings cold water into warm water areas. These currents are usually found on the west coast of the continents in the low and middle latitudes (true in both hemispheres) and on the east coast in the higher latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Examples: Canary Current, California Current, Benguela Curren etc.
- Warm currents: It brings warm water into cold water areas and is usually observed on the east coast of continents in the low and middle latitudes (true in both hemispheres).
- Examples: North Atlantic, Gulf Stream, the Kuroshio Current etc.
- Cold currents: It brings cold water into warm water areas. These currents are usually found on the west coast of the continents in the low and middle latitudes (true in both hemispheres) and on the east coast in the higher latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere.
Which are the Factors that Influences Ocean Current?
- Ocean Currents are Influenced by Two types of Forces:
- Primary Forces:
- Heating by solar energy: Heating by solar energy causes the water to expand. That is why, near the equator the ocean water is about 8 cm higher in level than in the middle latitudes. This causes a very slight gradient and water tends to flow down the slope.
- Wind: Wind blowing on the surface of the ocean pushes the water to move. Friction between the wind and the water surface affects the movement of the water body in its course.
- Gravity: Gravity tends to pull the water down the pile and create gradient variation.
- Coriolis Force: The Coriolis force intervenes and causes the water to move to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere.
- These large accumulations of water and the flow around them are called Gyres.
- These produce large circular currents in all the ocean basins.
- Secondary Forces:
- Differences in Water Density: Water with high salinity is denser than water with low salinity and in the same way cold water is denser than warm water.
- Denser water tends to sink, while relatively lighter water tends to rise.
- Temperature of Water: Cold-water Ocean currents occur when the cold water at the poles sinks and slowly moves towards the equator.
- Warm-water currents travel out from the equator along the surface, flowing towards the poles to replace the sinking cold water.
- Differences in Water Density: Water with high salinity is denser than water with low salinity and in the same way cold water is denser than warm water.
- Primary Forces:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following factors: (2012)
- Rotation of the Earth
- Air pressure and wind
- Density of ocean water
- Revolution of Earth
Which of the above factors influence the ocean currents?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What are the forces that influence ocean currents? Describe their role in fishing industry of the world. (2022)


Indian Economy
4th Heli-India Summit 2022
For Prelims: 4th Heli-India Summit 2022, Civil Aviation Sector of India, UDAAN Scheme, Heli-Sewa Portal, Heli Disha, Helicopter Emergency Medical Services.
For Mains: Growth & Development, Infrastructure, Indian Aviation Market.
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of Civil Aviation has inaugurated the 4th Heli-India Summit 2022 in the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Theme: Helicopters for Last Mile Connectivity.
What are the Highlights of the Summit?
- Announcing the achievements in the Civil Aviation sector, it was noted that the country had only 74 airports from 1947 to 2014, but it now has 141, with 67 added in the last seven years.
- It is proposed to build a civil enclave in Jammu and the Srinagar’s present terminal will be expanded three times.
- Announced to develop Fractional Ownership Model and HEMS (Helicopter Emergency Medical Services) pilot called Project.
- Fractional Ownership Model: It helps to grow the non-scheduled operations.
- It will lower the barrier on the cost of acquisition of helicopters and airplanes through pooled capital by multiple owners.
- HEMS: It is called Project Sanjeevani; a helicopter will be deployed to provide emergency medical services at AIIMS Rishikesh.
- The helicopter will be based at the hospital at 20-minute notice and will have a service covering an area of 150 km radius.
- Fractional Ownership Model: It helps to grow the non-scheduled operations.
What is the Scenario of the Civil Aviation Sector of India?
- About:
- Helicopters have multifarious roles, providing urban connectivity and the other roles of helicopter service have been the emergency medical services and disaster management during floods, rescue operations etc.
- The civil aviation industry in India has emerged as one of the fastest growing industries in the country during the last three years and can be broadly classified into scheduled air transport service which includes domestic and international airlines, non-scheduled air transport service which consists of charter operators and air taxi operators, air cargo service, which includes air transportation of cargo and mail.
- Significance:
- India is currently the 7th largest civil aviation market in the world and is expected to become the third-largest civil aviation market within the next 10 years.
- India is expected to overtake China and the United States as the world's third-largest air passenger market in the next ten years, by 2030, according to the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- In FY22, airports in India pegged the domestic passenger traffic to be 166.8 million, a 58.5% YoY increase, and international passenger traffic to be 22.1 million, a 118% YoY increase, as compared to FY 2020-21.
- Opportunity:
- FDI: 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) allowed under Automatic route for Ground Handling Services and Maintenance Repair and Overhaul Services (MRO) and for both green and brownfield projects.
- Scope of Growth: The Indian civil Aviation MRO market, at present, stands at around USD 900 million and is anticipated to grow to USD 4.33 billion by 2025 increasing at a CAGR of about 14-15%.
- The nation's airplane fleet is projected to quadruple in size to approximately 2500 airplanes by 2038.
- Connecting New Airports: The government aims to develop 100 airports by 2024 (under the UDAN Scheme) and create world-class civil aviation infrastructure to be at par with global standards.
What are the Related Initiatives?
- Heli-Sewa Portal:
- HeliSewa portal is fully online and being used by all operators for obtaining landing permissions to helipads, and it also is creating a database of helipads in the country.
- Heli-Disha:
- HeliDisha, the guidance material on helicopter operations for State administration, has been distributed to 780 districts.
- It contained all regulations and issues related to helicopter size, weight, operations, etc, and it would be distributed so that awareness about them is created in the district administrations across the country.
- Helicopter Accelerator Cell:
- The Helicopter Accelerator Cell is fully active in resolving helicopter issues and the advisory group of industry representatives is helping identify problems areas.
- Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik:
- Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik (UDAN) was launched as a regional connectivity scheme under the Ministry of Civil Aviation in 2016.
- It is an innovative scheme to develop the regional Aviation market.
- Krishi UDAN 2.0 scheme:
- It lays out the vision of improving value realization through better integration and optimization of agri-harvesting and air transportation and contributing to agri-value chain sustainability and resilience under different and dynamic conditions.
Way Forward
- Civil Aviation has now become the need of the hour not only for India but for humankind across the world as it always brings with it two important multipliers, the economic multiplier and the employment multiplier.
- The industry stakeholders should engage and collaborate with policy makers to implement efficient and rational decisions that would boost India’s civil aviation industry.
- With the right policies and relentless focus on quality, cost and passenger interest, India would be well placed to achieve its vision of becoming the third-largest aviation market by 2020.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Examine the development of Airports in India through joint ventures under Public–Private Partnership (PPP) model. What are the challenges faced by the authorities in this regard? (2017)
Q. International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above their territory. What do you understand by ‘airspace’? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggest ways to contain the threat. (2014)


Important Facts For Prelims
Purple Revolution
Why in News?
Recently, the Union State Minister for Science and Technology stated that the Purple Revolution offers attractive StartUp avenues.
- The Ministry of Science and Technology initiated the Purple Revolution or Lavender Revolution in 2016 through the Aroma Mission of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
What is Purple Revolution?
- About:
- It aims to promote the indigenous aromatic crop-based agro-economy by shifting from foreign aromatics to homegrown kinds.
- First-time producers were offered free lavender seedlings as part of the goal, and those who had previously produced lavender were paid Rs. 5-6 per plant.
- The CSIR-Aroma Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM)’s Initiative have begun lavender cultivation in the Ramban district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Lavender farming is done in nearly all of Jammu and Kashmir’s 20 districts.
- Particularly, the districts of Kathua, Udhampur, Doda, Kishtwar, Rajouri, Srinagar, Bandipora, Budgam, Ganderbal, Anantnag, Kulgam, Baramulla etc. have made huge progress in this direction.
- Products:
- The main product is Lavender oil which sells for at least Rs. 10,000 per litre
- Lavender water, which separates from lavender oil, is used to make incense sticks.
- Hydrosol, which is formed after distillation from the flowers, is used to make soaps and room fresheners.
- Significance:
- It is significant since it aligns with the government’s objective of doubling agricultural earnings by 2022.
- It would provide a livelihood for aspiring farmers and agri-entrepreneurs, as well as strengthen the Start-Up India programme and encourage an entrepreneurial spirit in the region.
- Over 500 young people benefited from the purple revolution, which eventually led to the doubling of their income.
- Agricultural development is one of the most powerful tools to end economic constraints, boost shared prosperity and feed a projected 9.7 billion people by 2050.
What is Aroma Misson?
- The CSIR Aroma Mission aims to bring about transformational change in the aroma sector by implementing targeted interventions in agricultural, processing, and product development in order to boost the aroma industry's growth and rural employment.
- It will encourage the development of aromatic crops for the production of essential oils, which are in high demand in the aroma sector.
- It is anticipated that Indian farmers and the aroma business will be able to become worldwide leaders in the production and export of various essential oils in the menthol mint pattern.
- Aroma Mission is drawing entrepreneurs and farmers from all across the country. CSIR assisted in the cultivation of 6000 hectares of land in 46 Aspirational districts across the country during Phase I.
- In addition, almost 44,000 employees were trained. The CSIR has started Phase II of the Aroma Mission, which will include over 45,000 skilled human resources and help over 75,000 farming families.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Norman Ernest Borlaug who is regarded as the father of the Green Revolution in India is from which country? (2008)
(a) United States of America
(b) Mexico
(c) Australia
(d) New Zealand
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Dr. Norman Ernest Borlaug was an American agronomist who was awarded the ‘Nobel Peace Prize’ for his lifetime work in the field of agriculture and for contribution to the society. He was also regarded as the father of the Green Revolution.
- The Green Revolution started in 1965 with the introduction of High Yielding Variety (HYV) seeds in Indian agriculture. This has resulted in high agricultural productivity, output and efficiency. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer
Mains
Q. Assess the role of National Horticulture Mission (NHM) in boosting the production, productivity and income of horticulture farms. How far has it succeeded in increasing the income of farmers? (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
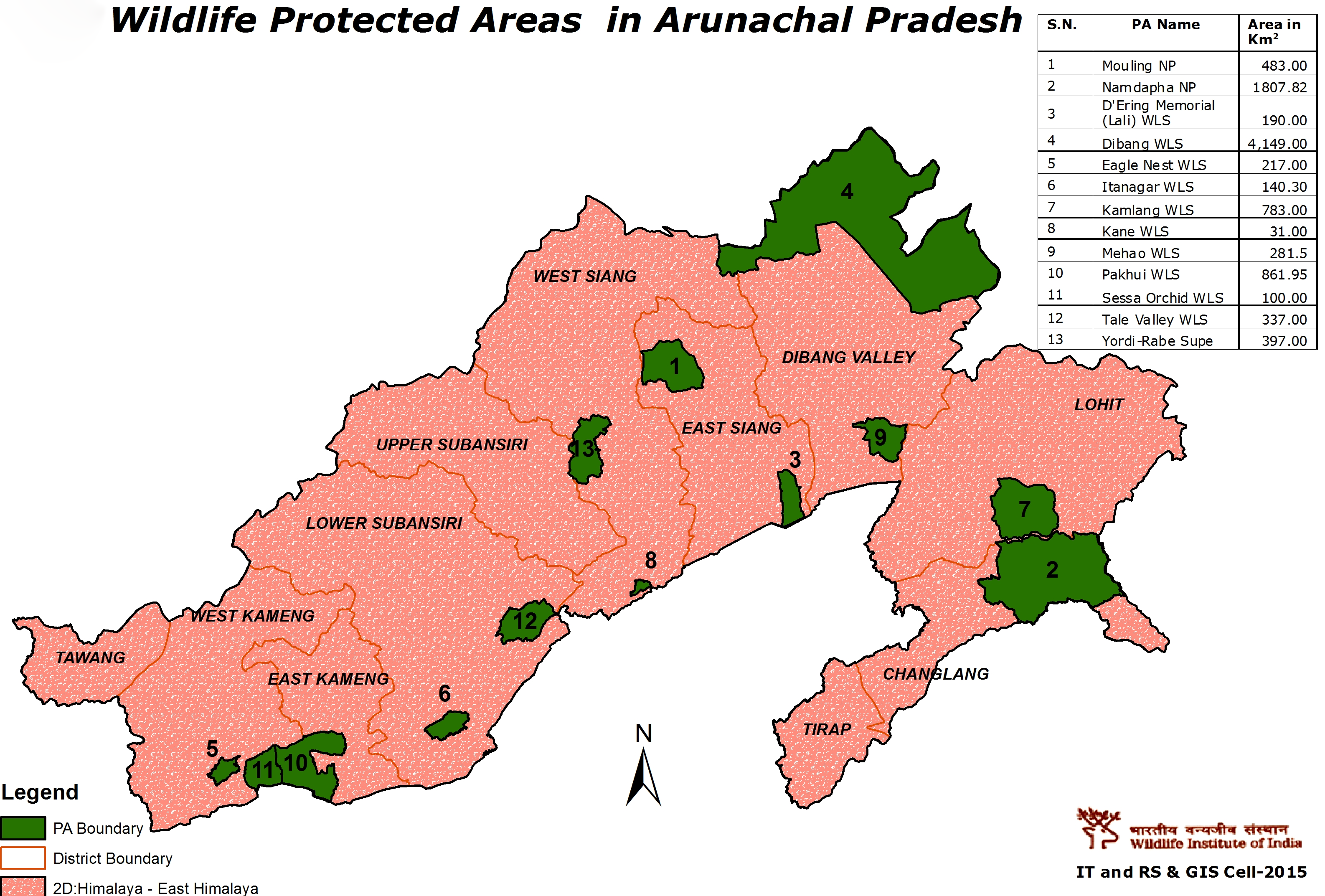
Namdapha National Park
Why in News?
The Changlang district administration has declared cultivation of large cardamom in the Namdapha National Park (NP) illegal.
What are the Key Points About Namdapha National Park?
- About:
- Namdapha is in fact the name of a river originating in the park and it meets Noa-Dehing river.
- The Noa-Dehing river, is a tributary of the Brahmaputra and flows in a North-South direction in the middle of the National Park.
- Namdapha is in fact the name of a river originating in the park and it meets Noa-Dehing river.
- Climate:
- Enjoys the sub-tropical climate. The mountainous part has a mountain type of climate while the low-lying plains and valleys experience tropical climate.
- Location:
- It is located in the State of Arunachal Pradesh and it covers 1,985 sq km.
- It lies in close proximity to Indo-Myanmar-China trijunction.
- The park is located between the Dapha bum range of the Mishmi Hills and the Patkai range.
- It the fourth largest national park in India.
- The first three are Hemis National Park in Ladakh, Desert National Park in Rajasthan, and Gangotri National Park in Uttarakhand.
- Legal Status:
- It was established as a national park in 1983, and it was declared as a Tiger Reserve in the same year of 1983 in the same year.
- It is also on the Tentative Lists of UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India.
- Biodiversity:
- This protected area has more than 1000 floral species and more than 1400 faunal species.
- It is also a part of biodiversity hotspot.
- It is only park in the World to have the four Feline species of big cat namely the Tiger (Panthera Tigris), Leopard (Panthera Pardus), Snow Leopard (Panthera Uncia) and Clouded Leopard (Neofelis Nebulosa).
- It is also famous for Critically Endangered species like the Namdapha flying squirrel, species that was last spotted in 1981.
- Hoolock Gibbons, the only ‘ape’ species found in India is found in this National Park.
- Vegetation: The vegetation is characteristic of tropical evergreen forests (Tropical Rain Forests)
What are the Other Protected Areas in Arunachal Pradesh?
- Pakke Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Mouling National Park
- Kamlang Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Itanagar Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Eagle Nest Wildlife Sanctuary.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Which one of the following National Parks has a climate that varies from tropical to subtropical, temperate and arctic? (2015)
(a) Khangchendzonga National Park
(b) Nandadevi National Park
(c) Neora Valley National Park
(d) Namdapha National Park
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following pairs: (2013)
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve: Garo Hills
- Logtak (Loktak) Lake: Barail Range
- Namdapha National Park: Dafla Hills
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Nokrek Biosphere Reserve is located near Tura Peak in West Garo Hills district of Meghalaya, India. Nokrek has a remnant population of the Red Panda and is also an important habitat of the Asian Elephants. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Loktak Lake is the largest freshwater (sweet) lake in North-East India, also called the only floating lake in the world due to the floating phumdis (heterogeneous mass of vegetation, soil, and organic matter at various stages of decomposition) on it, is located near Moirang in Manipur State, India. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- Barail is the highest hill range in Assam and it separates the State of Manipur from the State of Nagaland.
- Namdapha National Park is the largest protected area in the Eastern Himalaya biodiversity hotspot and is located in Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India. It is also the third largest national park in India in terms of area. It is located between the Dapha Bum range of the Mishmi Hills and the Patkai range. Hence, pair 3 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Detection of Barium in the Exoplanet Atmospheres
Why in News?
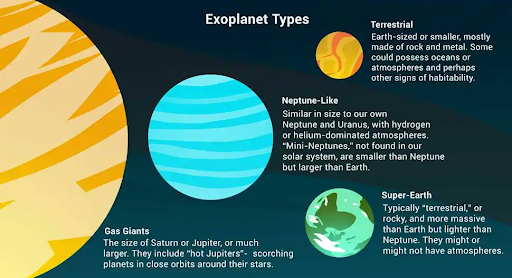
Recently, in a new study, scientists have detected barium in the upper atmosphere of two giant exoplanets for the first time.
- Ultra-hot Jupiters are a class of hot gaseous planets that matches the size of Jupiter, but they have short orbital periods, unlike Jupiter.
What are Exoplanets?
- An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmation of detection of exoplanets occurred in 1992.
- More than 4,400 exoplanets have been discovered till now.
- They are very hard to see directly with telescopes. They are hidden by the bright glare of the stars they orbit. So, astronomers use other ways to detect and study exoplanets such as looking at the effects these planets have on the stars they orbit.
What are the Findings of the Study?
- The exoplanets are two ultra-hot Jupiters — WASP-76b and WASP-121b — which orbit their host stars WASP 76 and WASP 121.
- The former is about 640 light-years away from the Earth and the latter around 900 light-years away.
- Both WASP-76b and WASP-121b complete one orbit in two days.
- Surface temperatures in these bodies reach as high as 1,000 degrees Celsius. These bodies have unique features owing to their high temperatures. For instance, WASP-76b experiences iron rain.
- The presence of hydrogen, lithium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, vanadium, chromium, manganese and iron in the atmosphere of the WASP-76 b has also been confirmed in addition to barium.
- In WASP 121b, they confirmed the presence of lithium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron and nickel.
- Additionally, the team found elements such as cobalt and strontium. They also found indications of titanium in the exoplanet.
What are the Characteristics of Barium?
- About:
- Barium, which is slightly harder than lead, has a silvery white luster when freshly cut.
- It readily oxidizes when exposed to air and must be protected from oxygen during storage.
- In nature it is always found combined with other elements.
- It is very light and its density is half of that of iron.
- Uses:
- Barium is often used for spark-plug electrodes and in vacuum tubes as a drying and oxygen-removing agent. As well as fluorescent lamps: impure barium sulfide phosphorescence after exposure to light.
- Its compounds are used by oil and gas industries to make drilling mud. Drilling mud simplifies drilling through rocks by lubricating the drill.
- Barium compounds are also used to make paint, bricks, tiles, glass, and rubber.
- Barium nitrate and chlorate give fireworks a green colour.