Social Justice
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
- 03 Sep 2022
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Skill Indian Mission, National Skills Development Corporation, Recognition of Prior Learning.
For Mains: Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana and its Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Education informed Lok Sabha that, during 2021-22, more than 3 Lakh women were trained under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) scheme.
What is PMKVY?
- Background:
- Skill India Mission was launched by the government in 2015 under which the flagship scheme Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is run.
- It aims to train over 40 crore people in India in different skills by 2022. It aims at vocational training and certification of Indian youth for a better livelihood and respect in the society.
- PMKVY is implemented by the National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC) under the guidance of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- PMKVY 1.0:
- Launch: India’s largest Skill Certification Scheme - Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) - was launched on 15th July, 2015 (World Youth Skills Day).
- Aim: To encourage and promote skill development in the country by providing free short duration skill training and incentivizing this by providing monetary rewards to youth for skill certification.
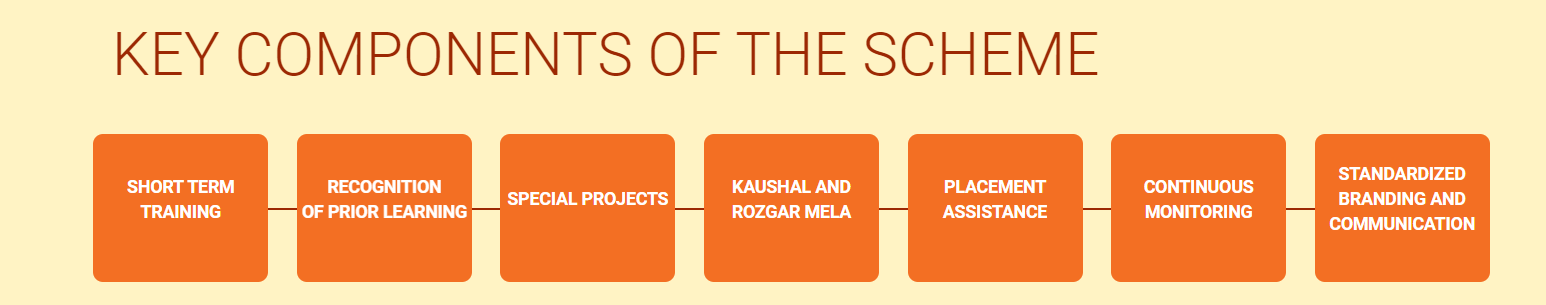
- Key Components: Short Term Training, Special Projects, Recognition of Prior Learning, Kaushal & Rozgar Mela, etc.
- Outcome: In 2015-16, 19.85 lakh candidates were trained.
- PMKVY 2.0:
- Coverage: PMKVY 2016-20 (PMKVY 2.0) was launched by scaling up both in terms of Sector and Geography and by greater alignment with other missions of the Government of India like Make in India, Digital India, Swachh Bharat, etc.
- Budget: Rs. 12,000 Crore.
- Implementation Through Two Components:
- Centrally Sponsored Centrally Managed (CSCM): This component was implemented by National Skill Development Corporation. 75% of the PMKVY 2016-20 funds and corresponding physical targets have been allocated under CSCM.
- Centrally Sponsored State Managed (CSSM): This component was implemented by State Governments through State Skill Development Missions (SSDMs). 25% of the PMKVY 2016-20 funds and corresponding physical targets have been allocated under CSSM.
- Outcome: More than 1.2 Crore youth have been trained/oriented through an improved standardized skilling ecosystem in the country under PMKVY 1.0 and PMKVY 2.0.
- PMKVY 3.0:
- Coverage: Launched in 717 districts, 28 States/eight UTs, PMKVY 3.0 is a step towards ‘Atmnanirbhar Bharat’.
- Implementation: It will be implemented in a more decentralized structure with greater responsibilities and support from States/UTs and Districts.
- District Skill Committees (DSCs), under the guidance of State Skill Development Missions (SSDM), shall play a key role in addressing the skill gap and assessing demand at the district level.
- Features:
- It envisages training of eight lakh candidates over a scheme period of 2020-2021 with an outlay of Rs. 948.90 crore.
- It will be more trainee- and learner-centric. The focus is on bridging the demand-supply gap by promoting skill development in areas of new-age and Industry 4.0 job roles.
- It will be a propagator of vocational education at an early level for youth to capitalize on industry-linked opportunities.
- The National Educational Policy 2020 also puts focus on vocational training for holistic growth and increased employability.
- By taking the bottom-up approach to training, it will identify job roles that have demand at the local level and skill the youth, linking them to these opportunities (Vocal for Local).
- It will encourage healthy competition between states by making available increased allocation to those states that perform better.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. ‘Recognition of Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to (2017)
(a) Certifying the skills acquired by construction workers through traditional channels.
(b) Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
(c) Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
(d) Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme.
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL), introduced as a component of PMKVY, largely refers to an assessment process used to evaluate a person’s existing skill set, knowledge and experience gained either by formal, non-formal or informal learning and not under the National Skill Development Program.
- It has threefold objectives:
- To align the competencies of the un-regulated workforce of the country to the standardized National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- To enhance the employability opportunities of an individual as well as provide alternative routes to higher education.
- To provide opportunities for reducing inequalities based on privileging certain forms of knowledge over others.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)