Biodiversity & Environment
Project Tiger
For Prelims: Project Tiger, Tiger Reserves, Pug-mark method, Tiger Census, Camera-trap method, The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH), National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Tiger Task Force, The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH), IAS, UPSC.
For Mains: Project tiger and its contribution in conservation of tiger population.
Why in News?
Over time, the tiger conservation initiative has evolved, establishing Tiger Reserves (55) and implementing crucial wildlife protection laws.
- However, conflicts in Tiger Reserves between the forest bureaucracy and forest dwellers have intensified due to violations of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, and the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change announced the merger of the two flagship programmes Project Tiger (PT) and Project Elephant as Project Tiger and Elephant (PTE).
What are the Shortcomings in Tiger Conservation?
- The Wildlife Protection (Amendment) Act, 2006 didn’t prohibit the diversion of a “tiger’s forest” for development projects and allowed wildlife to be killed as a last resort if they threatened human lives.
- The government planned to notify the FRA Rules in 2009 and operationalise the Act.
- But in November 2007, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) passed an order that gave the Chief Wildlife Wardens 13 days’ time to submit a proposal to delineate Critical Tiger Habitats (CTHs), each with an area of 800-1,000 sq. km.
- As a result, the government ended up notifying 26 Tiger Reserves in 12 States Section 38 (V) of WLPA, and without complying with its provisions.
- Tiger Reserves in Similipal, Odisha, the Critical Tiger Habitats (CTHs) lacked a Buffer Area.
- It was only in 2012 that they were included following a directive from the Supreme Court, which gave the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) a three-month ultimatum.
- The Tiger Task Force found the approach of using guns, guards, and fences wasn’t protecting tigers, and that the increasing conflict between the forest/wildlife bureaucracy and those who coexist with the tigers was a recipe for disaster.
What are Initiatives Taken for Tiger Conservation?
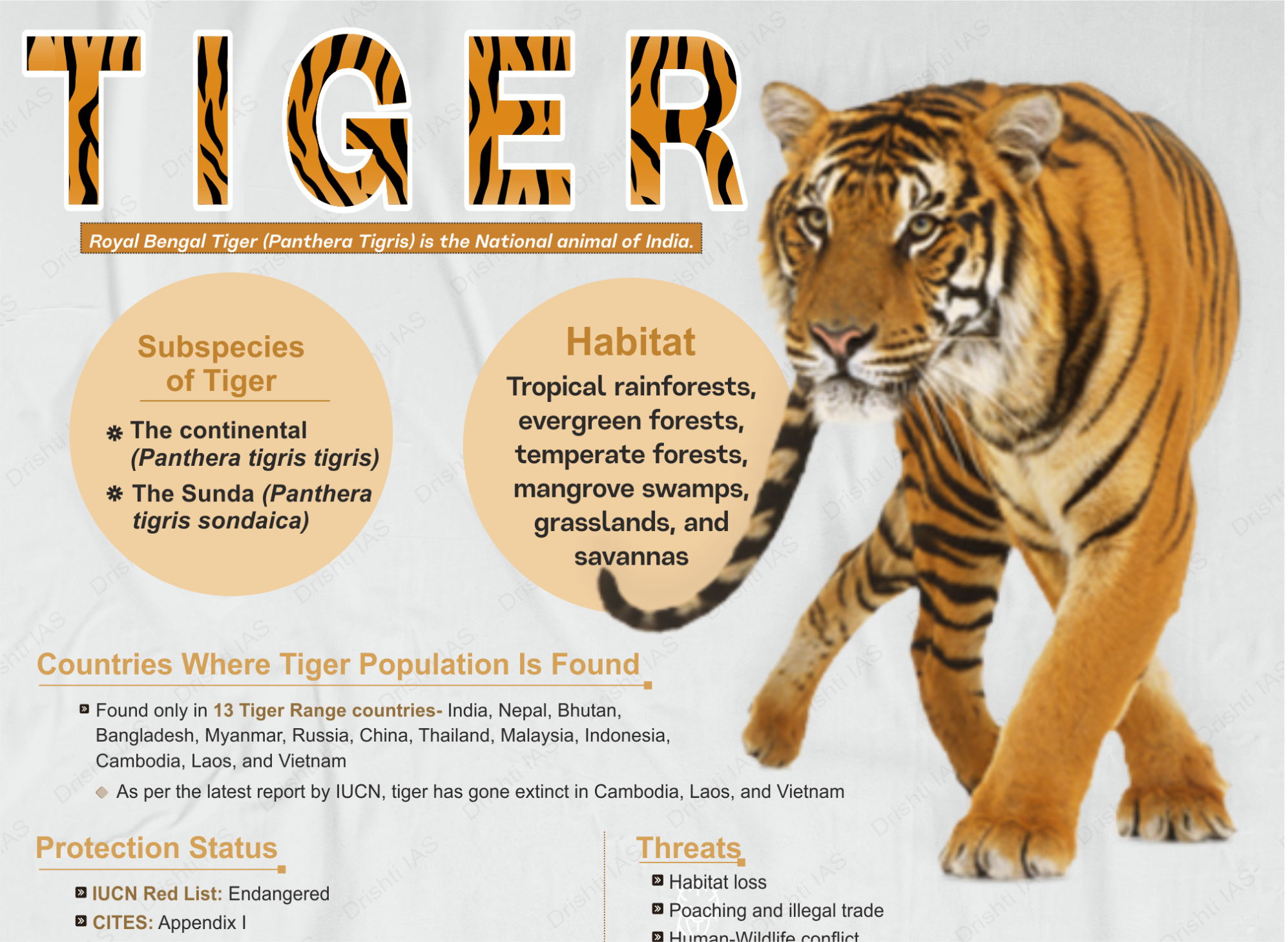
Project Tiger:
- About:
- Project Tiger is a wildlife conservation initiative in India that was launched in 1973.
- The primary objective of Project Tiger is to ensure the survival and maintenance of the tiger population in their natural habitats by creating dedicated Tiger Reserves.
- Starting with only nine reserves covering 9,115 sq. km, the project marked a paradigm shift in wildlife conservation efforts.
- Method of Tiger Census:
- The unreliable pug-mark method of the first tiger census in 1972 gave way to more accurate techniques like the camera-trap method.
- Growth Rate in Tiger Population:
- The first tiger census, in 1972, used the unreliable pug-mark method to count 1,827 tigers.
- As of 2022, the tiger population is estimated at 3,167-3,925, showcasing a growth rate of 6.1% per year.
- India is now home to three-quarters of the world’s tigers.
- Tiger Reserve:
- In 1973, Project Tiger began with nine reserves covering 9,115 sq. km. By 2018, it had grown to 55 reserves in different states, totalling 78,135.956 sq. km or 2.38% of India's land area.
Wildlife (Protection) Act,1972:
- The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 provides a legal framework for the protection of various species of wild animals and plants, management of their habitats, regulation, and control of trade in wild animals, plants, and products made from them.
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act (WLPA), 1972 laid the groundwork for tiger conservation. It established National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries, segregating rights in favour of State governments and introducing the concept of Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH).
- The amendment to WLPA in 2006 led to the creation of the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and a comprehensive tiger conservation plan.
- This marked a departure from the earlier fortress conservation approach, acknowledging the inseparable link between tiger protection, forest conservation, and the well-being of local communities.
Tiger Task Force:
- In 2005, the formation of the Tiger Task Force, prompted by concerns about tiger conservation, emphasized the necessity for a reassessment. The task force pointed out flaws in the existing strategy that heavily depended on weapons, guards, and fences.
What is the Recognition of Forest Rights Act, 2006?
- The enactment of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 recognized the customary and traditional forest rights in communities.
- This empowered Gram Sabhas to democratically manage forest resources and biodiversity within their boundaries.
- Critical Wildlife Habitat (CWH):
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA) introduced a 'Critical Wildlife Habitat' (CWH), similar to the Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH) under the Wildlife Protection Act (WLPA).
- However, a key difference was that once a CWH was notified, it couldn't be redirected for non-forestry purposes. This particular clause was insisted upon by Adivasi movements during negotiations.
- Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH) cover 42,913.37 sq. km, or 26% of the area under National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries.
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA) introduced a 'Critical Wildlife Habitat' (CWH), similar to the Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH) under the Wildlife Protection Act (WLPA).
- The Gram Sabhas were given the authority to safeguard, preserve, and oversee the forest, wildlife, and biodiversity within their customary boundaries.
Conclusion
The journey from Project Tiger in 1973 to creation of the NTCA by 2006 amendments reflects India's commitment to tiger conservation and sustainable coexistence. The integration of community empowerment, recognition of forest rights, and a nuanced approach to wildlife protection showcase a holistic paradigm in wildlife conservation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006? (2021)
(a) Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
(b) Ministry of Panchayati Raj
(c) Ministry of Rural Development
(d) Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The definition of “Critical Wildlife Habitat” is incorporated in the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
- For the first time in India, Baigas have been given Habitat Rights.
- Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change officially decides and declares Habitat Rights for Primitive and Vulnerable Tribal Groups in any part of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Governance
Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhuyday Yojana
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhuyday Yojana, Centrally Sponsored Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana, Babu Jagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana, Scheduled Caste (SC)
For Mains: Schemes for welfare for STs, Safeguards for STs, Government Initiatives
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment highlighted the Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhuyday Yojana (PM-AJAY) is a comprehensive scheme amalgamating three Centrally Sponsored Schemes, including Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY), Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP), and Babu Jagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana (BJRCY).
- This initiative, launched in the fiscal year 2021-22, aims to uplift Scheduled Caste (SC) communities by generating employment opportunities through skill development, income-generating schemes, and various initiatives.
What are the Key Highlights of the PM-AJAY?
- Objectives:
- Reduce poverty in the SC communities by the generation of additional employment opportunities through skill development, income-generating schemes and other initiatives.
- To increase literacy and encourage enrolment of SCs in schools and higher educational institutions by providing adequate residential facilities in quality institutions, in the aspirational districts/SC majority blocks and elsewhere in India.
- Components of PM-AJAY:
- Development of SC-Dominated Villages into an “AdarshGram”: This component was formerly known as Pradhan Mantri AdarshGram Yojana (PMAGY) and the objective of this component is to ensure integrated development of SC-majority villages.
- Provide adequate infrastructure for socio-economic development needs.
- Target improvement in identified socio-economic indicators (Monitorable indicators).
- The monitorable indicators are distributed across 10 domains. These domains encompass crucial aspects such as Drinking water and Sanitation, Education, Health and Nutrition, Social Security, Rural Roads and Housing, Electricity and Clean fuel, Agricultural Practices, Financial Inclusion, Digitization, and Livelihood and Skill Development.
- Eliminate disparity between SC and non-SC population.
- Ensure completion of education up to at least the secondary level for all SC children.
- Address factors leading to maternal and infant mortality.
- Eliminate the incidence of malnutrition, especially among children and women.
- Achievements:
- Under the Adarsh Gram Component, a total of 1834 villages have been Declared as Adarsh Gram during the current FY2023-24.
- ‘Grants-in-aid’ for District/State-level Projects:
- This component was formerly known as Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Caste Sub Plan.
- The scheme aims at the socio-economic development of SCs through grants for the following types of projects:
- Comprehensive Livelihood Projects: Such projects which create an entire eco-system for producing sustainable income, or social advancement to the SCs only shall be taken up. The projects should preferably be a combination of two or more of the following:
- Skill Development: Skilling courses as per norms of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship. Related facilities and infrastructure for conducting Skill Development Activities conducted by the Government. Skill Development Institutions can also be funded.
- Grants for Creation/Acquisition of Assets for Beneficiaries/Households: No standalone individual asset distribution is allowed under the scheme. If the project involves acquiring or creating assets crucial for livelihoods, beneficiaries can receive financial assistance for loans, up to Rs. 50,000 or 50% of the asset cost, whichever is less, per beneficiary/household.
- Infrastructure development: Development of infrastructure related to the project and also Hostels and residential schools.
- Special Provisions:
- Upto 15% of the total Grants exclusively on viable income-generating economic development schemes/programmes for SC Women.
- Upto 30% of the total Grants utilized for infrastructure development
- Atleast 10% of the total funds for skill development
- Promote SC Women Cooperatives engaged in the production and marketing of consumer goods and services.
- Achievements:
- During the FY 2023-24, the perspective plan for 17 states has been approved under the Grant-in-aid component.
- Construction of Hostels in Higher Educational Institutions:
- It enables and encourages SC students to attain quality education and reduce dropout rate, Implemented through the State Governments, UT Administrations and central and State Universities/Institutions
- The cost norms for construction/expansion of hostels will be as under:
- North Eastern Region: Rs.3.50 lakh per inmate.
- Northern Himalayan Regions: Rs.3.25 lakh per inmate.
- Gangetic Plains & Lower Himalayan Region: Rs3.00 lakh per inmate.
- 100% Central assistance for hostels for boys ’hostels as well– earlier it was cost sharing with the State.
- The cost norms for construction/expansion of hostels will be as under:
- It enables and encourages SC students to attain quality education and reduce dropout rate, Implemented through the State Governments, UT Administrations and central and State Universities/Institutions
- Achievements:
- During the FY 2023-24, a total of 15 new hostels have been sanctioned.
- Development of SC-Dominated Villages into an “AdarshGram”: This component was formerly known as Pradhan Mantri AdarshGram Yojana (PMAGY) and the objective of this component is to ensure integrated development of SC-majority villages.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. In 2001, RGI stated that Dalits who converted to Islam or Christianity are not a single ethnic group as they belong to different caste groups. Therefore, they cannot be included in the list of Scheduled Castes (SC) as per Clause (2) of Article 341, which requires a single ethnic group for inclusion. (2014)
Q. Whether the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) can enforce the implementation of constitutional reservation for the Scheduled Castes in the religious minority institutions? Examine. (2018)


Social Justice
Global Risks Report 2024: WEF
For Prelims: World Economic Forum (WEF), Extreme Weather Conditions, Generative AI, Climate change.
For Mains: Global Risks Report 2024: WEF, Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has released the Global Risk Report 2024, highlighting some of the most severe risks we may face over the next decade, against a backdrop of rapid technological change, economic uncertainty, a warming planet and conflict.
- The report is based on a survey of nearly 1,500 experts, industry leaders and policymakers.
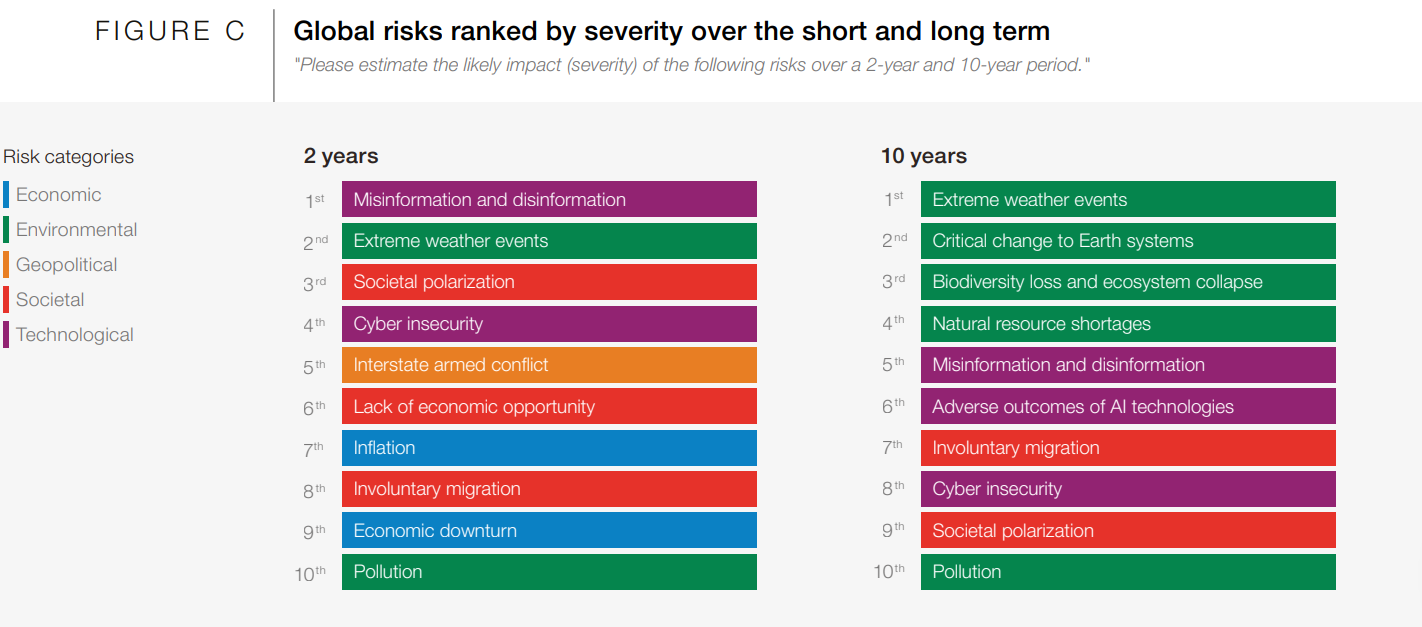
What are the Key Highlights of the Global Risk Report 2024?
- Deteriorating Global Outlook:
- Various global events in 2023, including lethal conflicts, Extreme Weather Conditions, and societal discontent, have contributed to a predominantly negative outlook.
- AI Powered Misinformation and Disinformation:
- Misinformation and disinformation are listed as the most severe risks over the next two years, highlighting how rapid advances in technology also are creating new problems or making existing ones worse.
- It is concerning that the boom in Generative AI chatbots like ChatGPT means that creating sophisticated synthetic content that can be used to manipulate groups of people won't be limited any longer to those with specialized skills.
- AI-powered misinformation and disinformation is emerging as a risk just as billions of people in a slew of countries, including large economies like the United States, Britain, Indonesia, India, Mexico, and Pakistan, are set to head to the polls in 2024 and next.
- Structural Forces Shaping Global Risks:
- There are four structural forces shaping global risks over the next decade: Climate change, Demographic Bifurcation, Technological Acceleration, and Geostrategic shifts.
- These forces represent longer-term shifts in the global landscape, and their interactions will contribute to uncertainty and volatility.
- Environmental Risks at the Forefront:
- Environmental risks, particularly extreme weather, dominate the risk landscape over all time frames.
- Concerns about climate change, biodiversity loss, and critical changes to Earth systems are evident, with potential irreversible consequences.
- Economic Strains and Inequality:
- The cost-of-living crisis and economic risks such as Inflation and economic downturn are significant concerns for 2024.
- Economic uncertainty will disproportionately affect low- and middle-income countries, leading to potential digital isolation and worsening societal and environmental impacts.
- Security Risks and Technological Advances:
- Interstate armed conflict is identified as a new entrant into the top risk rankings over the next two years.
- Technological advances, especially in artificial intelligence, pose security risks as they enable non-state actors to access disruptive tools, potentially leading to increased conflict and crime.
- Geopolitical Shifts and Governance Challenges:
- A deeper divide between global powers, especially between the Global North and South, may lead to challenges in international governance.
- The growing influence of states in the Global South, combined with geopolitical tensions, could reshape security dynamics and impact global risks.
What are the Recommendations?
- Localized strategies leveraging investment and regulation can reduce the impact of those inevitable risks that we can prepare for, and both the public and private sector can play a key role to extend these benefits to all.
- Single breakthrough endeavors, grown through efforts to prioritize the future and focus on research and development, can similarly help make the world a safer place.
- The collective actions of individual citizens, companies and countries may seem insignificant on their own, but at critical mass they can move the needle on global risk reduction.
- Even in a world that is increasingly fragmented, cross-border collaboration at scale remains critical for risks that are decisive for human security and prosperity.
What is Global Risk?
- Global risk is defined as the possibility of the occurrence of an event or condition which, if it occurs, would negatively impact a significant proportion of global gross domestic product, population or natural resources.
- The Global Risks Report is an annual study published by the World Economic Forum ahead of the Forum’s Annual Meeting in Davos, Switzerland.
What is the World Economic Forum?
- About:
- The WEF is a Swiss nonprofit foundation established in 1971, based in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Recognized by the Swiss authorities as the international institution for public-private cooperation.
- Mission:
- Committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas.
- Founder and Executive Chairman: Klaus Schwab.
- Some major reports published by WEF are:
- Energy Transition Index.
- Global Competitiveness Report.
- Global IT Report
- WEF along with INSEAD, and Cornell University publishes this report.
- Global Gender Gap Report.
- Global Travel and Tourism Report.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Q2. Who among the following is the founder of World Economic Forum? (2009)
(a) Klaus Schwab
(b) John Kenneth Galbraith
(c) Hobert Zoellick
(d) Paul Krugman
Ans (a)
Q3. The Global Competitiveness Report is published by the (2019)
(a) International Monetary Fund
(b) United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
(c) World Economic Forum
(d) World Bank
Ans: (c)


Indian Polity
Selection of Tableaux on the Republic Day
For Prelims: Republic Day Parade, Selection of Tableaux on the Republic Day, Ministry of Defence, Viksit Bharat, Bharat-Loktantra ki Matruka, Constitution Day.
For Mains: Selection of Tableaux on the Republic Day, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Defence has proposed a rollover plan for the States and Union Territories (UTs) to showcase their tableaux in the Republic Day Parade.
- It comes after a few states’ governments have criticized the central government for not allowing it to be a part of the 2024 Republic Day Parade Tableaux.
Which States/Union Territories have been Selected for the Republic Day Parade?
- 16 States and UTs have been selected for the 2024 Republic Day Parade, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Jharkhand, Ladakh, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh.
- The MoD has included a provision for States and Union Territories that are not selected for the Republic Day parade to showcase their tableaux at the Bharat Parv.
- The Government of India organizes the six-day mega event “Bharat Parv” from January 26-31, as part of the Republic Day celebrations. This alternative event takes place at the historic Red Fort.
- The Government has finalized a rotational plan to ensure that every State and Union Territory gets an opportunity to present their tableaux at the Republic Day parade within a three-year cycle (2024-2026).
- The rotational system, agreed upon by 28 States, intends to provide fair opportunities to all regions, mitigating accusations of political bias and fostering a more inclusive celebration.
What is the Selection Process of Tableaux?
- Ministry Responsible for Conducting Parade:
- The Ministry of Defence (MoD) is responsible for conducting the parade and coordinating arrangements with States and other agencies.
- Preparations for the ceremony, which has become synonymous with national pride and patriotism, begin months in advance. This process includes the selection and shortlisting of tableaux.
- The Ministry of Culture collaborates with the MoD in the selection process, given the cultural and artistic nature of the tableaux, supporting in the evaluation and promotion of cultural displays.
- Selection and Shortlisting:
- There is a standard procedure for selecting parade participants. Every year, months ahead of the event, the MoD invites States, UTs and departments to submit sketches or designs for tableaux on a broad theme.
- For instance, the theme of 2024 is ‘Viksit Bharat’ (Developed India) and ‘Bharat-Loktantra ki Matruka’ (India-Mother of Democracy).
- The sketch or design must be simple, colourful, easy to comprehend and avoid statistical data and unnecessary details.
- Additionally, the Ministry shares basic guidelines that must be included in the proposal like the use of eco-friendly material and technology.
- Writing or use of logos on the tableaux is not allowed except for the name of State/UT presenting, which can be in Hindi in the front, English at the back and in the regional language on the sides of the tableau.
- There is a standard procedure for selecting parade participants. Every year, months ahead of the event, the MoD invites States, UTs and departments to submit sketches or designs for tableaux on a broad theme.
- Committee of Experts:
- The MoD constitutes a committee of experts from the fields of arts, culture, painting, sculpture, music, architecture, and choreography, among others, to screen proposals.
- The expert committee, consisting of renowned artists recommended by IGNCA (Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts) and ICCR (Indian Council for Cultural Relations), selected the tableaux of 16 States and UTs for the year 2024 parade after four rounds of meetings.
- In the first phase, the panel carries out a basic evaluation and suggests modifications in the sketch or design.
- Once the designs are approved post any modifications, participants present a three-dimensional model of the proposed tableau to the panel.
- These are examined by experts for final selection. Only shortlisted candidates are informed about the next round.
- The MoD constitutes a committee of experts from the fields of arts, culture, painting, sculpture, music, architecture, and choreography, among others, to screen proposals.
What is Republic Day?
- India became Independent on 15th August, 1947 which is celebrated as Independence Day.
- Republic Day is celebrated as the day when India acquired a written Constitution and became an independent republic.
- The term ‘Republic’ indicates that India has an elected head called the President.
- The Constitution of India was adopted by the Constituent Assembly on 26th November 1949 and came into effect on 26th January 1950.
- 26th November is observed as Constitution Day.
- 26th January was chosen to be observed as the Republic Day because it was on this day in 1930 when the Indian National Congress (INC) declared Purna Swaraj or Indian independence from the British regime.
- During INC’s Lahore session of December 1929, Purna Swaraj resolution was passed. The session was presided over by Jawaharlal Nehru.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What was the exact constitutional status of India on 26th January 1950? (2021)
(a) A Democratic Republic
(b) A Sovereign Democratic Republic
(c) A Sovereign Secular Democratic Republic
(d) A Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Discuss each adjective attached to the word ‘Republic’ in the ‘Preamble’. Are they defendable in the present circumstances? (2013)


Economy
World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024
For Prelims: International Labour Organisation’s (ILO), Unemployment, Labor Market, G20 countries, Informal Work.
For Mains: World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024.
Why in News?
Recently, the International Labour Organisation’s (ILO) has released the World Employment and Social Outlook: Trends 2024 report, which highlighted that Global Unemployment rate is set to increase in 2024 and growing inequalities and stagnant productivity are causes for concern.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Resilience Amid Deteriorating Economic Conditions:
- Despite deteriorating economic conditions, global labor markets have shown surprising resilience, with improvements in both the unemployment rate and the jobs gap rate (the number of persons without employment who are interested in finding a job).
- Global Unemployment Trends:
- The global unemployment rate stood at 5.1% in 2023, a modest improvement from 2022.
- However, the report projects a worsening Labor Market outlook, with an additional two million workers expected to be looking for jobs in 2024, raising the global unemployment rate to 5.2%.
- Uneven Recovery:
- The recovery from the pandemic is uneven, with new vulnerabilities and multiple crises eroding prospects for greater social justice.
- Differences persist between higher and lower income countries, both in terms of unemployment rates and jobs gap rates.
- While the jobs gap rate in 2023 was 8.2% in high-income countries, it stood at 20.5% in the low-income group.
- Similarly, while the 2023 unemployment rate persisted at 4.5% in high-income countries, it was 5.7% in low-income countries.
- Income Inequality Widening:
- Income inequality has widened, and Disposable Incomes have declined in the majority of G20 countries.
- Disposable income is net income. It's the amount left over after taxes.
- The erosion of real disposable income is seen as a negative factor for aggregate demand and a more sustained economic recovery.
- Income inequality has widened, and Disposable Incomes have declined in the majority of G20 countries.
- Working Poverty Persists:
- Despite quickly declining after 2020, the number of workers living in extreme poverty (earning less than USD 2.15 per person per day in purchasing power parity terms) grew by about 1 million in 2023.
- The number of workers living in moderate poverty (earning less than USD3.65 per day per person in PPP terms) increased by 8.4 million in 2023.
- Working poverty is likely to persist as a challenge.
- Informal Work Rates Remain High:
- Rates of Informal Work are expected to remain static, accounting for around 58% of the global workforce in 2024.
- Labor Market Imbalances:
- The return to pre-pandemic labor market participation rates has varied between different groups.
- Women's participation has bounced back quickly, but a gender gap still persists, especially in emerging and developing nations.
- Youth unemployment rates and the NEET (Not in Employment, Education, or Training) category remain high, posing challenges for long-term employment prospects.
- Productivity Growth Slowed:
- After a brief post-pandemic boost, labor productivity has returned to the low levels seen in the previous decade.
- Productivity growth has continued to slow despite technological advances and increased investment, with barriers including skills shortages and the dominance of large digital monopolies.
- Outlook Uncertain and Structural Concerns:
- The imbalances observed are not simply part of pandemic recovery but may be structural. Workforce challenges pose a threat to both individual livelihoods and businesses.
- Falling living standards, weak productivity, persistent inflation, and greater inequality undermine efforts to achieve Social Justice and sustainable recovery. The report emphasizes the need to address these challenges effectively and quickly.
- Positive Real Wages:
- Real wages in India and Turkey are "positive" compared to other G20 countries, but the available data refer to 2022 relative to 2021. This implies that, despite global challenges, wage increases in India have managed to outpace inflation, contributing to an improvement in real wages.
- The other G20 countries saw real wages fall; the declines were particularly pronounced in Brazil (6.9%), Italy (5%) and Indonesia (3.5%).
What is the International Labour Organisation?
- About:
- It was created in 1919, as part of the Treaty of Versailles that ended World War I, to reflect the belief that universal and lasting peace can be accomplished only if it is based on social justice.
- It became a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1946.
- It is a tripartite organization, the only one of its kind bringing together representatives of governments, employers and workers in its executive bodies.
- It was created in 1919, as part of the Treaty of Versailles that ended World War I, to reflect the belief that universal and lasting peace can be accomplished only if it is based on social justice.
- Members:
- India is a founding member of the ILO with a total 187 member States.
- In 2020 India assumed the Chairmanship of the Governing Body of ILO.
- Headquarter:
- Geneva in Switzerland.
- Awards:
- In 1969, ILO received the Nobel Peace Prize for improving fraternity and peace among nations, pursuing decent work and justice for workers, and providing technical assistance to other developing nations.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. International Labour Organization’s Conventions 138 and 182 are related to (2018)
(a) Child Labour
(b) Adaptation of agricultural practices to global climate change
(c) Regulation of food prices and food security
(d) Gender parity at the workplace
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Vaccine Drive to Fight Cervical Cancer
Why In News?
The Indian Government intends to initiate a three-phase vaccination drive against human papillomavirus (HPV) for girls aged 9-14, aiming to mitigate the risk of cervical cancer.
- The vaccine also offers protection against the HPV strains that cause cancer of the anus, vagina and oropharynx. Additionally, it also protects against the HPV strains that are responsible for genital warts.
Note
The Serum Institute of India in 2023 launched an indigenous HPV vaccine known as CERVAVAC.
What is Cervical Cancer?
- About:
- Cervical cancer develops in a woman's cervix. It is the 4th most common type of cancer among women, globally and 2nd most common among women in India.
- India contributes the largest share of the global cervical cancer burden; nearly 1 in every 4 deaths globally due to cervical cancer (as per The Lancet study).
- Almost all cervical cancer cases (99%) are linked to infection with high-risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV) , an extremely common virus transmitted through sexual contact.
- Effective primary (HPV vaccination) and secondary prevention approaches (screening for and treating precancerous lesions) will prevent most cervical cancer cases.
- When diagnosed, cervical cancer is one of the most successfully treatable forms of cancer, as long as it is detected early and managed effectively.
- India accounts for about a fifth of the global burden for cervical cancer, recording about 1.25 lakh cases and about 75,000 deaths each year.
- Cervical cancer develops in a woman's cervix. It is the 4th most common type of cancer among women, globally and 2nd most common among women in India.
- Types of Strain:
- Persistent infections with certain high-risk HPV strains lead to nearly 85% of all cervical cancers.
- At least 14 HPV types have been identified as oncogenic (potential to cause cancer).
- Among these, HPV types 16 and 18, considered to be the most oncogenic, have been found to be responsible for about 70% of all cervical cancer cases globally.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to (2016)
(a) immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Mission Indradhanush is an immunization scheme launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, GoI on 25th December, 2014.
- Depicting seven colours of the rainbow, it aimed to cover all those children by 2020 who are either unvaccinated, or are partially vaccinated against seven vaccine preventable diseases which include diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio, tuberculosis, measles and hepatitis B.
- The mission is technically supported by WHO, UNICEF, Rotary International and other donor partners.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Natural Pathogenic Fungi to Save Eucalyptus Forests
Why in News?
Recently, scientists have found a natural remedy to protect eucalyptus forest plantations from a pest, eucalyptus snout beetle, which is known to cause serious damage to eucalypts.
- The researchers have managed to collect a naturally occurring pathogenic fungi and characterized it to turn it into a biopesticide for controlling beetle populations.
- Eucalyptus (evergreen tree) wood is a crucial material for paper pulp production.
What is Eucalyptus Snout Beetle?
- Eucalyptus snout beetle (Gonipterus platensis) is a leaf-feeding beetle that is a major defoliator of eucalypts, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- The pest is indigenous to Australia but occurs in many countries throughout the world where eucalypts are grown.
- It can cause damage over vast areas as it has a great flight capability and gets transferred with transport of forest products.
- The beetle feeds on leaves, buds and shoots, resulting in stunted growth and deflation and causing heavy losses.
How can Fungi Control the Eucalyptus Snout Beetle?
- In the recent research, the scientists collected the fungi from naturally infected beetles in eucalyptus forest plantations and characterized them to develop a bio-pesticide for controlling the beetle.
- The fungi belong to the genera Beauveria and Metarhizium, which are known to infect and kill insects.
- Beauveria pseudobassiana and Metarhizium brunneum were the most virulent fungi.
- B bassiana was highly effective both by contact and ingestion, with a mortality rate of 100%.
- The fungi could be used to develop a bio-pesticide for sustainable forestry using integrated pest management.
- The fungi is developed by treating insecticidal activity, UV-B radiation tolerance among other parameters to ensure that recovered fungi are suitable to produce bio-insecticide and mass production and commercialisation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following organisms: (2013)
- Agaricus
- Nostoc
- Spirogyra
Which of the above is/are used as biofertilizer/biofertilizers?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
- Biofertilizers are products containing carrier based (solid or liquid) living microorganisms which are agriculturally useful in terms of nitrogen fixation, phosphorus solubilisation or nutrient mobilization to increase the productivity of soil or crop.
- Classification of biofertilizers based on microorganism:
- Bacterial Biofertilizers: Rhizobium, Azospirilium, Azotobacter, Phosphobacteria, Nostoc, etc. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Fungal Biofertilizers: Mycorrhiza
- Algal Biofertilizers: Blue Green Algae (BGA) and Azolla.
- Actinomycetes Biofertilizer: Frankia.
- Agaricus is an edible fungus and is commonly known as mushroom. It is a saprophytic fungus found growing on soil humus, decaying litter on forest floors, in the fields, lawns, wood logs and manure piles. Hence, 1 is not correct.
- Spirogyra is a large genus of freshwater green algae found in shallow ponds, ditches and amongst vegetation at the edges of large lakes, generally growing free-floating. It is valued for human consumption, and is known as an important source of natural bio-active compounds for antibiotic, antiviral, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic purposes. Hence, 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q. Lichens, which are capable of initiating ecological succession even on a bare rock, are actually a symbiotic association of (2014)
(a) algae and bacteria
(b) algae and fungi
(c) bacteria and fungi
(d) fungi and mosses
Ans: (b)
- Lichen is not a single organism. Rather, it is a symbiosis between different organisms – a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium. Cyanobacteria are sometimes referred to as ‘blue-green algae’, though they are quite distinct from the algae.
- Lichens are amongst the first organisms to colonize the barren surfaces (e.g., road cuttings, rock outcrops and volcanic ash) and prepare these areas for later plants by trapping moisture and windblown organic debris and then contributing to the organic deposits when they themselves die and decay.
Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Rapid Fire
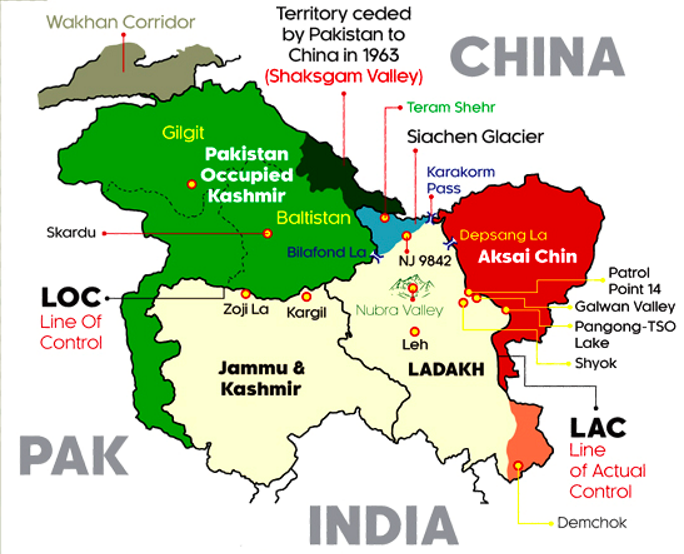
Indian Army Eyes Upgraded 'Pup Tents' for Icy Heights Along LAC
Army Plans insulated 'Pup Tents' for Troops on Icy Line of Actual Control (LAC) Heights at -50°C.
- The pup tents are meant for soldiers deployed in extreme cold weather conditions, such as in eastern Ladakh, Sikkim and Siachen glacier.
- The Line of Actual Control (LAC) is the border that divides the territories of India and Aksai Chin(China occupied Indian Territory).
- It is divided into three sectors: the eastern sector which spans Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim (1346 km), the middle sector in Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh (545 km), and the western sector in Ladakh (1597 km).
Read More: India-China Conflict


Rapid Fire
Gangireddu Melam
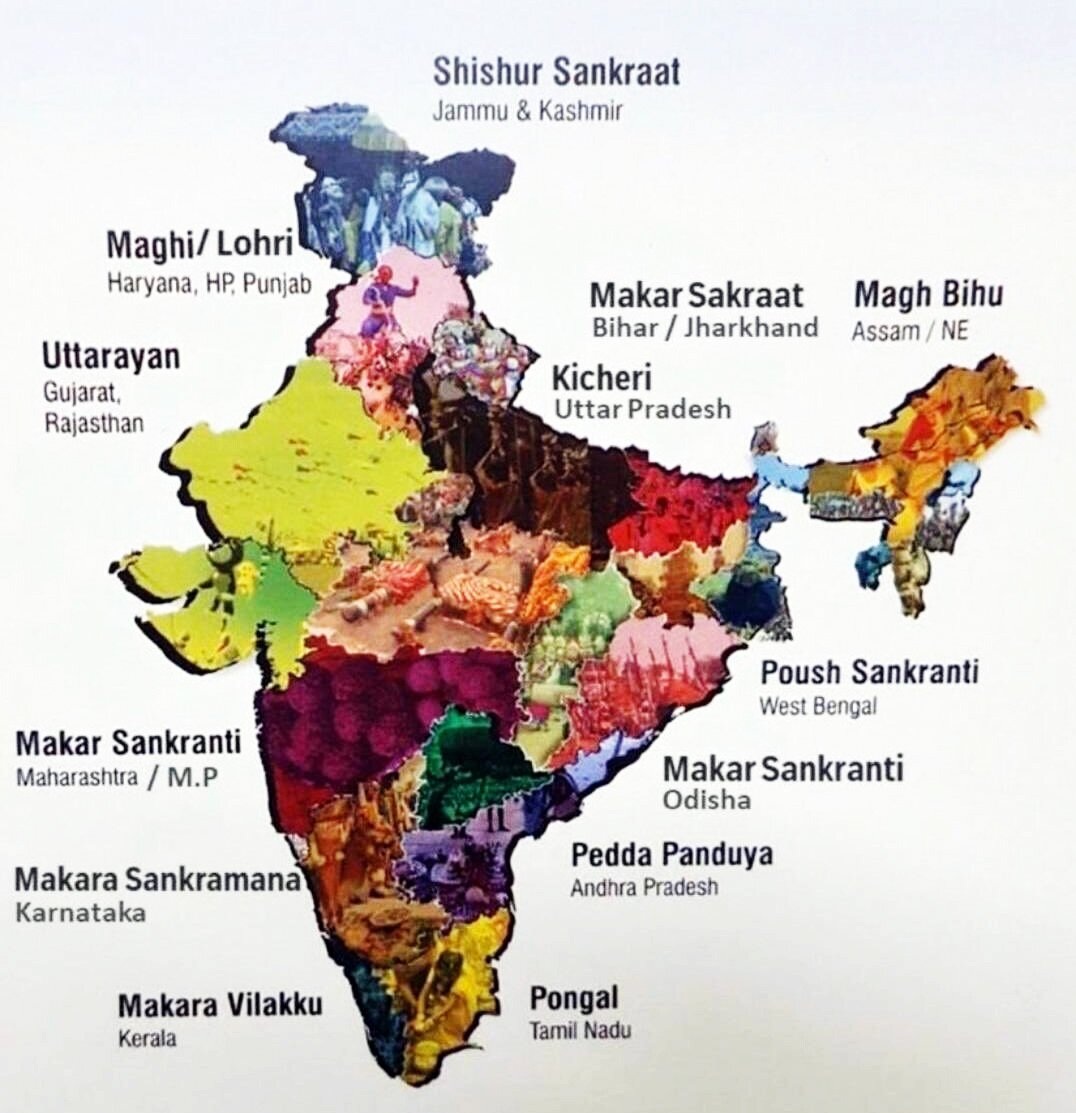
Gangireddu Melam, a traditional folk performance associated with the Sankranti harvest festival in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
- The bulls, adorned with colorful flowers and garments is the central motif of the dance. The performance also incorporates elements of local folklore and storytelling, showcasing the region's rich cultural heritage.
- The harvest festival of 'Sankranti' is celebrated in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana for three days as Bhogi, Sankranti, and Kanuma.
- Sankranti marks the first day of the sun's transit into the Makara, marking the end of the winter solstice and the start of longer days.
- Sankranti is celebrated in various parts of the country with different names:
Read more: Winter Solstice, Sankranti


Rapid Fire
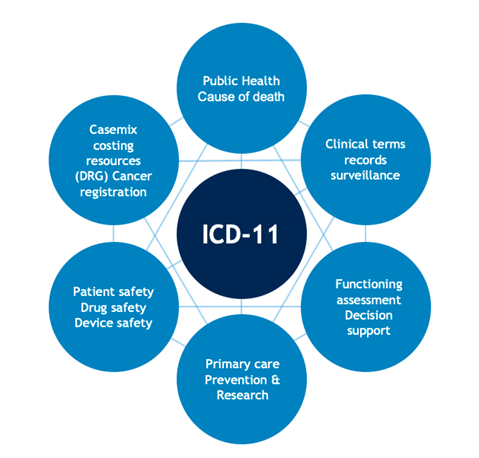
ICD 11 TM Module 2 Launch: Global Integration of Ayush Medicine
The World Health Organisation(WHO) has officially unveiled the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 11, Traditional Medicine Module 2, marking the commencement of its implementation phase.
- This module incorporates data and terminology from Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani Medicine into the WHO ICD-11 classification, indexing the terminology as codes.
- The Ministry of AYUSH, in collaboration with the WHO, has classified diseases from Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani systems under the TM-2 module.
- WHO stated that including traditional medical terminologies in ICD-11 establishes a vital link between traditional medicine and global standards.
Read more: International Classification of Diseases, Global Center for Traditional Medicine


Rapid Fire
Indian of the Year Award 2023
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Science & Technology presented the "Indian of the Year Award" for 2023 to Team Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in the category of 'Outstanding Achievement.'
- The award recognized ISRO's contribution to space exploration, particularly highlighting the historic soft landing of Chandrayaan-3 on the Moon's uncharted South Polar region.
- The remarkable growth of the private space sector was also highlighted in the event, with 190 startups and over Rs. 1,000 crore invested in the current financial year 2023-24.
Read more: India's Space Endeavors