International Relations
India-Sri Lanka Fishing Dispute
For Prelims: Palk Bay, International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL), UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), Katchatheevu, High Seas, Palk Strait, Seaweed Farming.
For Mains: India-Sri Lanka fishing dispute, its implications and way forward.
Why in News?
The Sri Lankan Navy arrested some Indian fishermen for fishing in Palk Bay (Sri Lankan waters), reigniting the India-Sri Lanka fishing dispute.
- In 2024, Indian fishermen arrested in Sri Lanka crossed 500 for the first time in a decade (2014: 787 arrests).
What are the Key Issues in the India-Sri Lanka Fishing Dispute?
- Recurrent Arrests: Indian fishermen with their trawlers often in search of fishes stray into Sri Lankan waters due to engine failures or sudden weather changes.
- The destruction of fishing vessels, continued boat confiscation after fishermen's release, and heavy fines by Sri Lankan authorities remain recurring issues between both nations.
- Violation of IMBL: Indian fishermen claim historical fishing rights beyond the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) based on traditional practices that lead to arrests of Indian fishermen in areas close to the IMBL.
- The Palk bay is equally divided between India and Sri Lanka by the IMBL, but fishing rights remain contested.
- The IMBL (as per UNCLOS) is an official boundary separating territorial waters, defining maritime jurisdiction, and regulating fishing, resource use, and naval activities.
- Depletion of Fish Stocks: Overfishing on the Indian side of the IMBL forces Indian fishermen into Sri Lankan waters, which Sri Lanka views as “poaching,” posing security risks and threatening local livelihoods.
- Bottom-Trawling: Sri Lanka opposes ecologically destructive bottom trawling employed by Indian fishermen, and seeks a sustainable solution to protect their waters from over-exploitation.
- Bottom trawling drags weighted nets along the seabed, damaging marine habitats like coral reefs and sponges.
- Sri Lanka’s National Security Concerns: Sri Lanka alleges that Indian trawlers intrude regularly in a coordinated manner and fears Tamil militant groups may re-emerge using fishing vessels.
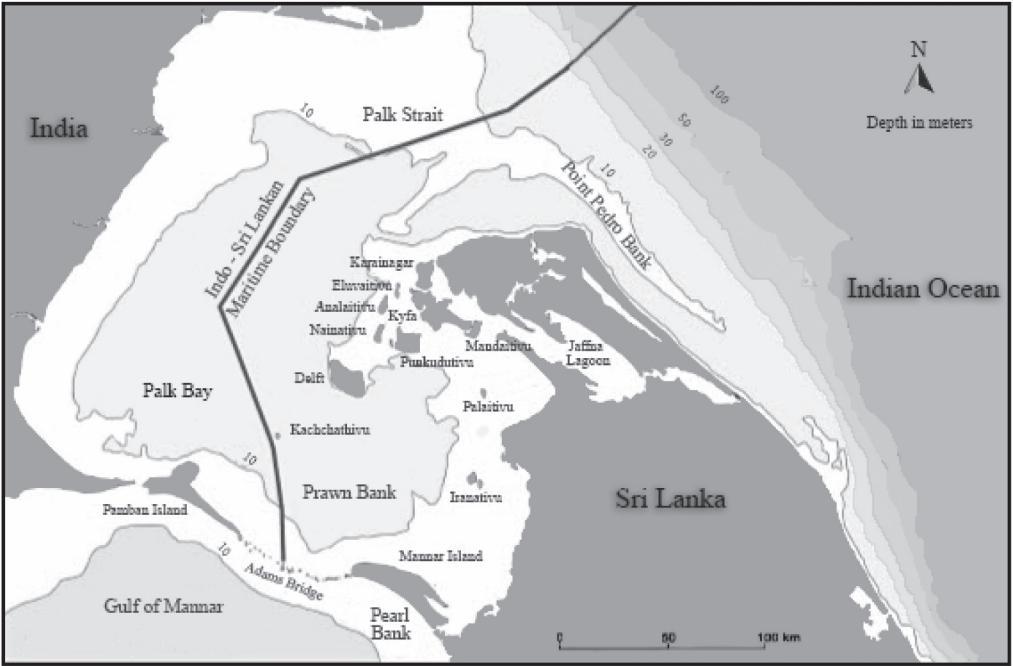
- Katchatheevu Island Dispute: Katchatheevu, a 285-acre islet in the Palk Strait, was ceded to Sri Lanka in 1974.
- Indian fishermen can only use Katchatheevu for drying nets and resting, and Tamil Nadu politicians periodically demand its return to India.
Note: Due to depletion of fisheries stock in Indian and Sri Lankan waters, Indian fishermen are venturing into the High seas. They are now also being arrested in Maldivian waters and by the British Navy near Diego Garcia for allegedly crossing the maritime boundary.
What are International Laws on Freedom of Fishing?
- UN Fish Stocks Agreement (UNFSA, 1995): States should either become members, or they should agree to apply the conservation and management measures established by Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs) to access fishery resources.
- RFMOs are international bodies responsible for managing and conserving fish stocks in specific ocean regions.
- UNCLOS, 1982: Article 87 of UNCLOS limits fishing freedom on the high seas, making it illegal for vessels from States that fail to meet its conditions.
- E.g., Considering due regard for the interests of other States in their exercise of the freedom of the high seas.
Palk Bay
- About: Palk Bay is a narrow water body between southern India and northern Sri Lanka, and is rich in biodiversity, due to monsoon-driven nutrient inflow.
- Boundaries: The southern boundary is marked by the Pamban Strait, Rameswaram Island, and Adam’s Bridge (Rama Setu).
- The northeastern boundary is the Palk Strait that connects the Palk Bay to the Bay of Bengal.
- Palk Bay Fishing Conflict: Following the end of the Sri Lankan civil war in 2009, fishing disputes escalated, reaching their peak in 2013 due to overfishing and bottom trawling by Indian fishers.
Click Here to Read: India and Sri Lanka Relations
What are the Implications of Indo-Sri Lanka Fishing Conflict?
- Livelihood Issues: Sri Lanka Navy's arrests of Indian fishers distress their families, while sea conflicts have caused fatalities and missing fishers, heightening risks for fishing communities.
- Enforcement Challenges: The enforcement cost for patrolling the IMBL has risen, straining resources.
- Smuggling Concerns: The Indian Coast Guard and Sri Lanka Navy struggle to differentiate between genuine fishers and smugglers making IMBL vulnerable to smuggling.
- Political Ramifications: Allegations against the Sri Lanka Navy’s actions in the Palk Bay have fueled diplomatic tensions between the two nations.
- E.g., Political tensions have influenced India’s support for UN resolutions on Sri Lanka’s human rights record.
- Environmental Impact: Bottom trawling harms fish breeding, depletes stocks, and damages the seafloor, with recovery taking thousands of years.
- Economic Consequences: Overfishing has reduced fishery resources and fishers' income, with Sri Lanka losing an estimated USD 730 million annually due to Indian poaching.
Way Forward
- Enforcing Maritime Regulations: Enhanced patrolling and surveillance of IMBL can help prevent illegal fishing activities.
- A dedicated Joint Working Group (JWG) should be established to ensure continuous dialogue and problem-solving mechanisms.
- Alternative Livelihood Programs: Tamil Nadu should offer alternative livelihoods like marine tourism, seaweed farming, and inland aquaculture for fishers facing restrictions.
- Joint Marine Resource Management: A regional fisheries management authority should be established to regulate fishing activities and prevent overexploitation of marine ecosystems.
- Sustainable fishing like catch limits and quotas can ensure fish populations recover quickly and release fish fingerlings can compensate for depleting resources.
- Deep-Sea Fishing: The Indian government should enhance funding, training, and incentives to ensure higher adoption of deep-sea fishing by Indian fishers.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the key issues involved in the Indo-Sri Lanka fishing dispute and suggest measures for a sustainable resolution. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Elephant Pass, sometimes seen in the news, is mentioned in the context of the affairs of which one of the following? (2009)
(a) Bangladesh
(b) India
(c) Nepal
(d) Sri Lanka
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. ‘India is an age-old friend of Sri Lanka.’ Discuss India's role in the recent crisis in Sri Lanka in the light of the preceding statement. (2022)
Q. In respect of India-Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. (2013)


Social Justice
International Day of Women and Girls in Science
For Prelims: International Day of Women and Girls in Science (IDWGS), Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), Department of Science and Technology, Vigyan Jyoti Programme, GATI program.
For Mains: Representation of Women in Science and Associated Government Initiatives.
Why in News?
The year 2025 marks the 10th anniversary of the International Day of Women and Girls in Science (IDWGS), observed annually on 11th February.
- This day promotes the full and equal participation of women and girls in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM).
What is the Status of Women in STEM?
- Global Scenario:
- Women in STEM: According to UN data, globally, women remain underrepresented in STEM education and careers, constituting only 35% of STEM graduates.
- Between 1901 and 2024, only 26 out of 650 Nobel laureates in Physics, Chemistry, and Physiology or Medicine have been women.
- Indian Scenario:
- Women in Research: Government data presented in Lok Sabha (2024) shows women comprise only 18.6% of the scientific workforce.
- STEM Enrolment: Women constitute 43% of STEM students in higher education.
- Declining Representation: Their presence significantly drops at higher research levels and leadership positions in scientific institutions.
What are India's Initiatives Related to STEM?
- National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations
- Vigyan Jyoti
- Gender Advancement for Transforming Institutions (GATI)
- WISE-KIRAN Scheme
- BioCARe Fellowship:
- It supports women scientists in biotechnology and allied fields to build successful research careers.
- Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) at Women’s Universities
- TBIs have been established at IGDTUW (Delhi), SPMVV (Tirupati), and iTBI at DTU to promote women-led innovation and gender inclusivity in entrepreneurship.
What are the Challenges Related to Women in STEM?
- Workforce Dropout & Societal Barriers: Women in STEM face career discontinuity due to caregiving responsibilities, rigid work policies, and re-entry challenges. Cultural stereotypes further discourage their participation, widening the gender gap in science.
- Workplace Barriers: Gender biases, lack of mentorship, and underrepresentation in decision-making roles restrict career growth. Women face lower access to research funding and leadership positions.
- Institutional Barriers: Lack of gender-sensitive policies such as maternity benefits, flexible work arrangements and limited gender data access hinder women's retention and equity in STEM.
Way Forward
- Gender-Inclusive Policies: Implement gender-sensitive hiring, leadership quotas, and research grants for women scientists. Promote flexible work policies and family support programs in scientific institutions.
- Leadership & Mentorship: Establish mentorship networks and encourage women in leadership roles in academia, research, and policymaking.
- Workplace Equity: Implement transparent evaluation and promotion systems to ensure equal pay and recognition for women.
- Women Entrepreneurship: Strengthen NIDHI, BioCARe, and Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) to support women-led startups in science and technology.
- Global Collaboration: Adopt successful models from countries with higher women representation in STEM, ensuring global partnerships and exchange programs for women researchers.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Examine the factors hindering women's participation and empowerment in STEM fields in India. Propose effective policy interventions to promote gender-inclusive growth in science and technology. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Q. Two of the schemes launched by the Government of India for Women’s development are Swadhar and Swayam Siddha. As regards the difference between them, consider the following statements: (2010)
- Swayam Siddha is meant for those in difficult circumstances such as women survivors of natural disasters or terrorism, women prisoners released from jails, mentally challenged women etc., whereas Swadhar is meant for holistic empowerment of women through Self Help Groups.
- Swayam Siddha is implemented through Local Self Government bodies or reputed Voluntary Organizations whereas Swadhar is implemented through the ICDS units set up in the states.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.1 “Empowering women is the key to control population growth”. Discuss. (2019)
Q.2 Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalization on women in India? (2015)
Q.3 Male membership needs to be encouraged in order to make women’s organization free from gender bias. Comment. (2013)


Indian Polity
Bills on Parliamentary Sittings and POCSO Act, 2012
For Prelims: Private members’ Bill, Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha, Article 85, Article 174, National Crime Records Bureau
For Mains: Reforms in Parliamentary Functioning, Issues Related to Children, Implementation of POCSO and child welfare laws
Why in News?
Private members’ Bills were introduced in the Rajya Sabha, focusing on mandating a minimum number of parliamentary sittings, and amending the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
What are the Two Bills Introduced in Parliament?
On Parliamentary Sittings
- Objective: The two separate bills were proposed in Rajya Sabha to mandate a minimum of 100-120 parliamentary sittings per year, with lost hours due to disruptions compensated in extended sessions to enhance productivity, and improve government accountability.
- The General Purposes Committee of the Lok Sabha, 1955 explored the idea of a fixed parliamentary calendar, while the 2002 National Commission on Constitutional Review recommended minimum sittings of 100 days for Rajya Sabha and 120 days for Lok Sabha.
- Current Scenario of Parliamentary Sittings: The first Lok Sabha (1952-1957), under Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru, had an average of 135 sittings per year, whereas the 17th Lok Sabha (2019-2024) sat for only 55 days annually, the lowest in history.
- Constitutional Provisions: The Constitution does not mandate a fixed number of sessions or sitting days.
- However, Article 85 (Parliament) the President summons each House as needed, ensuring no more than six months between sessions. The President can also prorogue or dissolve the Lok Sabha.
- Article 174 (State Legislatures) the Governor has powers to summon, prorogue, and dissolve the Legislative Assembly, ensuring a maximum six-month gap between sessions.
Bill Regarding Amending the POCSO Act, 2012
- Objective: The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (Amendment) Bill, 2024, introduced, aims to make the POCSO Act more victim-centric and improve its implementation.
- Provisions of Bill: POCSO (Amendment) Bill, 2024 mandates a 24-hour reporting rule, requiring police or the special juvenile police unit to present the child before the Child Welfare Committee and report the case to the Special Court (or Sessions Court, if unavailable).
- It strengthens victim support by ensuring timely compensation and structured procedures.
- It calls for enhanced stakeholder training, including police, educational institutions, and child care personnel, for better implementation.
- Need for the Amendment: According to NCRB data, POCSO cases have increased by 94% since 2017, with over 2 lakh registered cases as of May 2024.
- Lack of structured compensation procedures leads to long delays for victims.
- There is a shortage of Special Public Prosecutors trained for POCSO cases, affecting the sensitivity and efficiency in handling child sexual abuse cases.
- Many cases are not reported or delayed due to fear, stigma, or lack of awareness.
- A key gap in the POCSO Act, 2012 is the lack of "support persons" for victims, with 96% of cases lacking necessary support.
- These support persons, either individuals or organizations, help guide survivors through the legal process and ensure their well-being.
- Minors aged 16-18 engaging in consensual sexual activity may be charged under POCSO, leading to legal consequences like prolonged detention and the potential denial of bail.
- Additionally, the insufficient designation of POCSO courts further delays justice, as not all districts have these specialized courts.
- Lack of structured compensation procedures leads to long delays for victims.
POCSO Act, 2012
- The POCSO Act, 2012 is a law aimed at addressing the sexual exploitation and abuse of children.
- The POCSO Act recognizes that both boys and girls can be victims of sexual abuse, and the crime is punishable regardless of the gender of the victim. It defines a child as any person below the age of 18 years.
- It mandates that the identity of child victims must be kept confidential, with no media disclosures about the victim’s name, address, or family details.
- The Act mandates that individuals with knowledge of or reasonable suspicion of child abuse must report it to the relevant authorities.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Evaluate the need for a minimum number of parliamentary sittings in the context of India's legislative accountability. Q. What challenges are faced in the implementation of the POCSO Act, 2012, suggest measures to address? |
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are envisaged by the Right against Exploitation in the Constitution of India?(2017)
- Prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour
- Abolition of untouchability
- Protection of the interests of minorities
- Prohibition of employment of children in factories and mines
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016)


Important Facts For Prelims
Antibiotics Resistance
Why in News?
Widespread antibiotic use in healthcare has fueled drug-resistant bacteria, with antimicrobial resistance (AMR) causing about 1.2 million deaths globally in 2021.
- Indian hospitals report a 13% mortality rate in infections caused by drug-resistant bacteria.
What is Antibiotics Resistance?
- About Antibiotics: Antibiotics treat bacterial infections in humans and animals by killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth and multiplication.
- They target bacterial structures or processes, ensuring minimal impact on human cells.
- Working of Antibiotics: Bacterial cells have a protective cell wall made of peptidoglycan. Its two key components are Glycans and Peptides.
- Antibiotics like Penicillin weakens bacterial cell walls by disrupting peptide crosslinks, leading to bacterial death.
- Development of Antibiotics Resistance: Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria mutate or gain resistance genes, making infections harder to treat.
- Bacteria evolve resistance through various mechanisms like:
- Producing enzymes like penicillinase against Penicillin, which break down antibiotic molecules.
- Modifying their own structures to evade the antibiotic’s effects.
- Bacteria evolve resistance through various mechanisms like:
- New Survival Strategy: A new study found that bacteria can compensate for lost functions, enhancing resilience and making antibiotic resistance harder to combat.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India? (2019)
- Genetic predisposition of some people
- Taking incorrect doses of antibiotics to cure diseases
- Using antibiotics in livestock farming
- Multiple chronic diseases in some people
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q.What is the importance of using Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in India? (2020)
- These vaccines are effective against pneumonia as well as meningitis and sepsis.
- Dependence on antibiotics that are not effective against drug-resistant bacteria can be reduced.
- These vaccines have no side effects and cause no allergic reactions.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Restructuring Skill India Programme
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved the continuation and restructuring of the Skill India Programme (SIP) by integrating 3 flagship schemes- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0), Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS), and Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme into a composite Central Sector Scheme till March 2026.
What is the Skill India Programme?
- About:
- The Skill India Programme (SIP) is a skill development initiative launched in 2015 under the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
- Over 2.27 crore people have benefited so far from these schemes including rural youth, women, and marginalized communities.
- All the courses and certifications under the Skill India Program are aligned with the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF) and integrated with DigiLocker & National Credit Framework (NCrF), ensuring formal recognition and seamless transition into employment and higher education.
- Objective:
- The programme aimed to train 40 crore individuals by 2022 across various skill sectors through key initiatives, including:
- National Skill Development Mission (NSDM)
- National Policy for Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (2015)
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- Skill Loan Scheme
- The programme aimed to train 40 crore individuals by 2022 across various skill sectors through key initiatives, including:
- Key Components of Restructured SIP:
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0):
- It provides short-term training, reskilling, and upskilling.
- 400+ new courses introduced in emerging technologies like AI, 5G, cybersecurity, green hydrogen, and drone technology.
- Focus on international mobility and on-the-job training (OJT) by recognition of prior learning and equipping Indian workers with globally recognized skills.
- It aligns with PM Vishwakarma, PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana, National Green Hydrogen Mission, and NAL JAL Mitra, ensuring cross-sector impact.
- Target Beneficiaries: Individuals aged 15-59 years.
- Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (PM-NAPS):
- PM-NAPS aims to enhance apprenticeship training across industries.
- Provides 25% of the stipend (up to Rs 1,500 per apprentice per month) through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) for apprentices.
- Expands apprenticeship opportunities in AI, robotics, blockchain, green energy, Industry 4.0.
- Special focus on small establishments, MSMEs, aspirational districts, and the North-East Region.
- Target Beneficiaries: Individuals aged 14 to 35 years.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) Scheme:
- The JSS scheme is a community-driven vocational training initiative aimed at empowering women, rural youth, and economically weaker sections in the 15-45 age group through low-cost, flexible skilling programs.
- It is linked with initiatives like PM JANMAN and Understanding of Lifelong Learning for All in Society (ULLAS) for inclusive skilling.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana 4.0 (PMKVY 4.0):
Government Initiatives Related to Skill Development
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
Edible Oil Imports and SAFTA Agreement
Why in News?
The Solvent Extractors’ Association of India (SEA) has raised concerns over the massive influx of refined Edible Oil (soybean and palm) from Nepal to India, citing a misuse of the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) agreement’s duty-free import provisions.
Note: Established in 1963, SEA represents India’s solvent extraction industry, including processors, exporters, refiners, and traders. It operates independently as a private body.
- Solvent extraction is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids.
What is the Edible Oil Scenario in India’s Economy?
- Edible Oil and Oil Seeds: India, one of the largest oilseed producers, contributes 5-6% to global production, with an estimated 39.66 million tonnes in 2023-24.
- Major oilseeds include Groundnut, Soybean, Sunflower, Mustard, Sesame, Niger, and Safflower.
- India's vegetable oil economy is the world's fourth largest after the USA, China and Brazil.
- The edible oil industry contributes significantly to agriculture and trade, with oilseed and oil meal exports valued at Rs 29,587 crore in 2023-24.
- In 2022-23, India imported 16.5 million tonnes (MT) of edible oils, with domestic production fulfilling only 40-45% of the country’s requirements, relying on imports for 57% of consumption.
- Major Edible Oils in India:
- Traditional oils: Groundnut, mustard/rapeseed, sesame, safflower, linseed, niger seed, castor, Soybean, and sunflower.
- Plantation-based oils: Coconut, oil palm (grown in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andaman and Nicobar).
- Non-conventional oils: Rice bran oil, cottonseed oil.
- Forest-based oils: Collected from tree and forest sources, mainly in tribal regions.
- Government Initiatives: The country aims to reduce import dependency through initiatives like the National Mission on Oilseeds and Oil Palm (NMOOP), aiming to boost oilseed production from 39 to 69.7 million tonnes by 2030-31, meeting 72% of edible oil demand.
- Concerns: SEA is concerned about rising refined edible oil imports from Nepal, after India raised import duties on edible oils in 2024, Nepalese refiners started importing large amounts of crude oil and exporting refined oil to India at lower prices through SAFTA impacting Indian refiners and oilseed farmers.
- SEA Recommendations: India should restrict duty-free edible oil imports from SAFTA nations that don't produce oilseeds and amend SAFTA to prevent agro-commodity dumping.
- Introduce a Minimum Import Price (MIP) (protects farmers from predatory import pricing) based on the Minimum Support Price (MSP) of oilseeds.
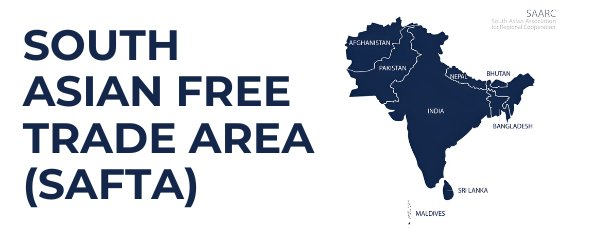
South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)
- About: SAFTA is the free trade arrangement of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
- Came into force in 2006, succeeding the 1993 SAARC Preferential Trading Arrangement.
- Members: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- SAFTA Provisions: SAFTA's trade liberalization policy ensures a gradual reduction of tariffs to 0–5% on traded goods.
- LDCs (Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Nepal) receive special treatment, such as a longer implementation period for tariff reductions, greater exemptions from trade restrictions.
- Safeguard Measures allow temporary suspension to protect domestic industries.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The quantity of imported edible oils is more than the domestic production of edible oils in the last five years.
- The Government does not impose any customs duty on all the imported edible oils as a special case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
TROPEX-25
The Indian Navy's Theatre Level Operational Exercise (TROPEX) 2025 is being conducted in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) over a duration of 3 months (Jan - Mar 2025).
- About TROPEX: It is the Indian Navy's biennial and largest maritime exercise that strengthens joint operations against maritime threats with participation from the Army, Air Force, and Coast Guard.
- Objective: Validate the Indian Navy’s warfighting skills and ensure an integrated response to conventional, asymmetric, and hybrid maritime threats posed by countries like China.
- China, the world's largest navy with over 360 warships and submarines, deploys 7-8 naval vessels and spy ships in the IOR at all times.
- Phases: It includes Harbour and Sea Phases, featuring combat operations, cyber & electronic warfare, live weapon firings, and Amphibious Exercise (AMPHEX).
- Objective: Validate the Indian Navy’s warfighting skills and ensure an integrated response to conventional, asymmetric, and hybrid maritime threats posed by countries like China.
Read More: Securing India's Interests in the Indian Ocean Region


Rapid Fire
National Commission for Safai Karamcharis
The Union Cabinet has extended the National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK) for three years until 31st March 2028.
National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK)
- Established: 1994 under the NCSK Act, 1993; became a non-statutory body in 2004 under the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- Structure: Chairperson (MoS rank), Vice-Chairperson, 5 members (including 1 woman).
- Mandate:
- Recommends policies for welfare and rehabilitation of Safai Karamcharis.
- Monitors implementation of schemes and laws like The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers Act, 2013.
- Investigates grievances and policy lapses.
- Ensures Rs 30 lakh compensation for sewer deaths, Rs 10-20 lakh for disabilities (SC ruling, 2023).
- Working: Field visits, grievance redressal, policy reviews, suo-motu actions, meetings, and reports to the ministry.
Schemes for Sanitation Workers:
- NAMASTE scheme: Aimed at profiling of Septic Tanks Workers, provide occupational safety training, protective kits, and health insurance (AB-PMJAY),
- National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC): Offers concessional loans and financial aid for the socio-economic upliftment of Safai Karamcharis and their families.
Read More: National Commission for Safai Karamcharis


Rapid Fire
Campaign to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the Annual Nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) Campaign for Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) elimination.
- Lymphatic Filariasis: LF (elephantiasis), is a neglected tropical disease caused by parasitic filarial worms ( like Wuchereria bancrofti) and transmitted by mosquitoes.
- Leads to lifelong disabilities like lymphoedema (swollen limbs) and hydrocele (scrotal swelling).
- Morbidity Management & Disability Prevention (MMDP) services (hygiene, skin care, and hydrocele surgeries) help prevent severe disability.
- MDA Campaign: Covers 111 endemic districts in 13 states, aiming to protect over 17.5 crore people and eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis by 2027.
- The MDA campaign ensures supervised administration of anti-filarial medicines in LF-endemic areas, using Double (Diethylcarbamazine Citrate and Albendazole) and Triple Drug Regimen (Ivermectin, DEC, and Albendazole)
- MDA aims to stop LF transmission by eliminating filarial parasites from the bloodstream, preventing mosquito transmission.
- The medication is not for children under 2, pregnant women, or seriously ill individuals.
- India’s MMDP Services: Integrated into Ayushman Arogya Mandir (AAM), with hydrocelectomy (remove a hydrocele) covered under National Health Mission and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana.
- In 2024, nearly 50% of hydrocele surgeries were done in endemic states.
Read more: Lymphatic Filariasis


Rapid Fire
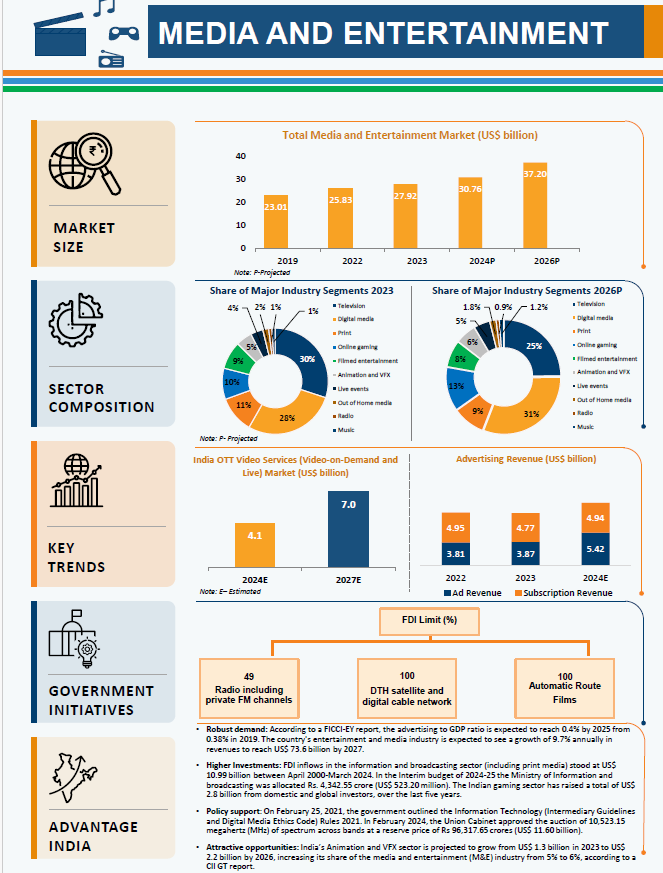
WAVES 2025 and Creative Economy
The Prime Minister chaired a virtual meeting of WAVES (World Audio Visual & Entertainment Summit) to amplify India's creative media and economy.
WAVES:
- WAVES is a global summit for the media and entertainment (M&E) industry, organized by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- The summit aims to bring together industry leaders, stakeholders, and innovators to address challenges, explore prospects, and promote global trade, thereby influencing the future of the sector.
- The summit launched the "Create in India Challenge," aimed at fostering innovation and creativity in India's creative and media economy.
Creative Economy (Orange Economy):
- The creative economy is a knowledge-based sector involving the creation, production, and distribution of creative goods and services.
- It includes industries like advertising, architecture, arts, fashion, film, music, photography, publishing, R&D, and software.
- India's creative industry is valued at USD 30 billion and employs nearly 8% of the country's working population. In 2023, India had over 100 million content creators.
India's Media and Entertainment (M&E):
- India's M&E industry, the world's fifth-largest (1st is US), is projected to grow to USD 44.2 billion by 2028.
Read More: Create in India Challenge to Boost Creators' Economy