International Relations
India-Japan Defence Policy Dialogue
For Prelims: India-Japan Defence Exercises, G-20, QUAD, G-4.
For Mains: Significance, Challenges in India-Japan Relationship.
Why in News?
Recently, the 7th India-Japan Defence Policy Dialogue was co-chaired by Defence Secretary of India and the Vice Minister of Defense for International Affairs of Japan in New Delhi.
What are the Key Details of Dialogue?
- About: The Defence Policy Dialogue is an institutionalized mechanism between India and Japan to discuss bilateral defence cooperation.
- The purpose of the meeting is to discuss a wide range of issues related to defence cooperation between the two countries.
- Highlights of the 7th Dialogue:
- The two countries discussed Service-level exercises and engagements, regional security issues and cooperation in defence equipment & technology.
- The Japanese Vice Minister presented policy updates from their recently released National Security Strategy and National Defense Strategy.
- Both countries appreciated the growing cooperation between the Services through Staff talks and exercises.
- They welcomed the conduct of the inaugural fighter exercise ‘Veer Guardian’ between the Indian Air Force and Japanese Air Self Defence Force in January 2023 in Japan.
- The Defence Secretary emphasized that both the countries should aim to deepen collaboration between the respective defence industries,
- Japanese defence industries were invited for investment in India under the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
- Both sides agreed to diversify cooperation in new and emerging domains like defence space and cyber.
- The two countries discussed Service-level exercises and engagements, regional security issues and cooperation in defence equipment & technology.
How are India's Relations with Japan?
- Defence Cooperation: Japan is one of the few countries with whom India has 2+2 ministerial dialogue
- India and Japan's defence forces also organize a series of bilateral exercises such as:
- JIMEX (naval), Malabar exercise (Naval Exercise), ‘Veer Guardian’ and SHINYUU Maitri (Air Force), and Dharma Guardian (Army).
- India and Japan's defence forces also organize a series of bilateral exercises such as:
- Common Groupings:
- Both India and Japan are members of Quad, G20 and G-4, International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER).
- India-Japan Act East Forum was established in 2017 which aims to provide a platform for India-Japan collaboration under the rubric of India’s “Act East Policy“ and Japan’s "Free and Open Indo-Pacific Strategy”.
- Investment and ODA:
- India has been the largest recipient of the Japanese Official Development Assistance (ODA) Loan for the past decades for.
- Delhi Metro is one of the most successful examples of Japanese cooperation through the utilization of ODA.
- India’s Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) project is funded by a soft loan provided by Japan International Cooperation Agency.
- Japan and India had committed to build a High-Speed Railways in India.
- India has been the largest recipient of the Japanese Official Development Assistance (ODA) Loan for the past decades for.
- Economic Relations: Japan’s bilateral trade with India totaled US$ 20.57 billion during FY 2021-22. India was the 18th largest trading partner for Japan, and Japan was the 12th largest trading partner for India in 2020.
- India-Japan Digital Partnership: Discussion is going on for the “India-Japan Digital Partnership” with a view to enhancing the digital economy through the promotion of joint projects in the area of IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence) and other emerging technologies.
- Japan is looking forward to attracting more highly skilled Indian IT professionals to contribute to the Japanese ICT sector.
- Strategic Clean Energy Partnership: For cooperation in areas such as electric vehicles, storage systems including batteries, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, development of solar energy, hydrogen, ammonia, etc.
- Along with Digital Partnership, it was also announced at the 14th India-Japan Annual Summit
What are the Challenges Related to Defence Cooperation?
- China Factor: While both countries have sought to strengthen their relationship as a counterbalance to China's influence, their approaches to dealing with China have differed.
- India has been more vocal in criticizing China's actions, while Japan has been more cautious in its approach.
- Defence Exports: India is looking to export defence equipment to other countries, which could potentially compete with Japan's own defence exports.
- Influence of US-China Rivalry: The intensification of Chinese-American rivalry contributes to disturbance of regional security in the Indo-Pacific.
Way Forward
- India and Japan are required to transform their military strategy and build on the common interest in preventing the rise of a securing hegemony in the Indo-Pacific (US and China).
- More collaboration and cooperation can prove beneficial to both nations. There is also a huge potential with respect to Make in India.
- Joint ventures could be created by merging Japanese digital technology with Indian raw materials and labour.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The G20 comprises Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, EU, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, UK and USA. Hence Option(a) is correct.


Geography
El Nino
For Prelims: EL Nino, ENSO, Southwest Monsoon Season, Heatwaves, Droughts, WMO.
For Mains: El Nino and its Impact.
Why in News?
Many climate models have forecasted an El Nino in May 2023.
- A record three-year La Nina event ended in March 2023 and currently, the equatorial Pacific Ocean is at normal temperatures, known as the neutral phase.
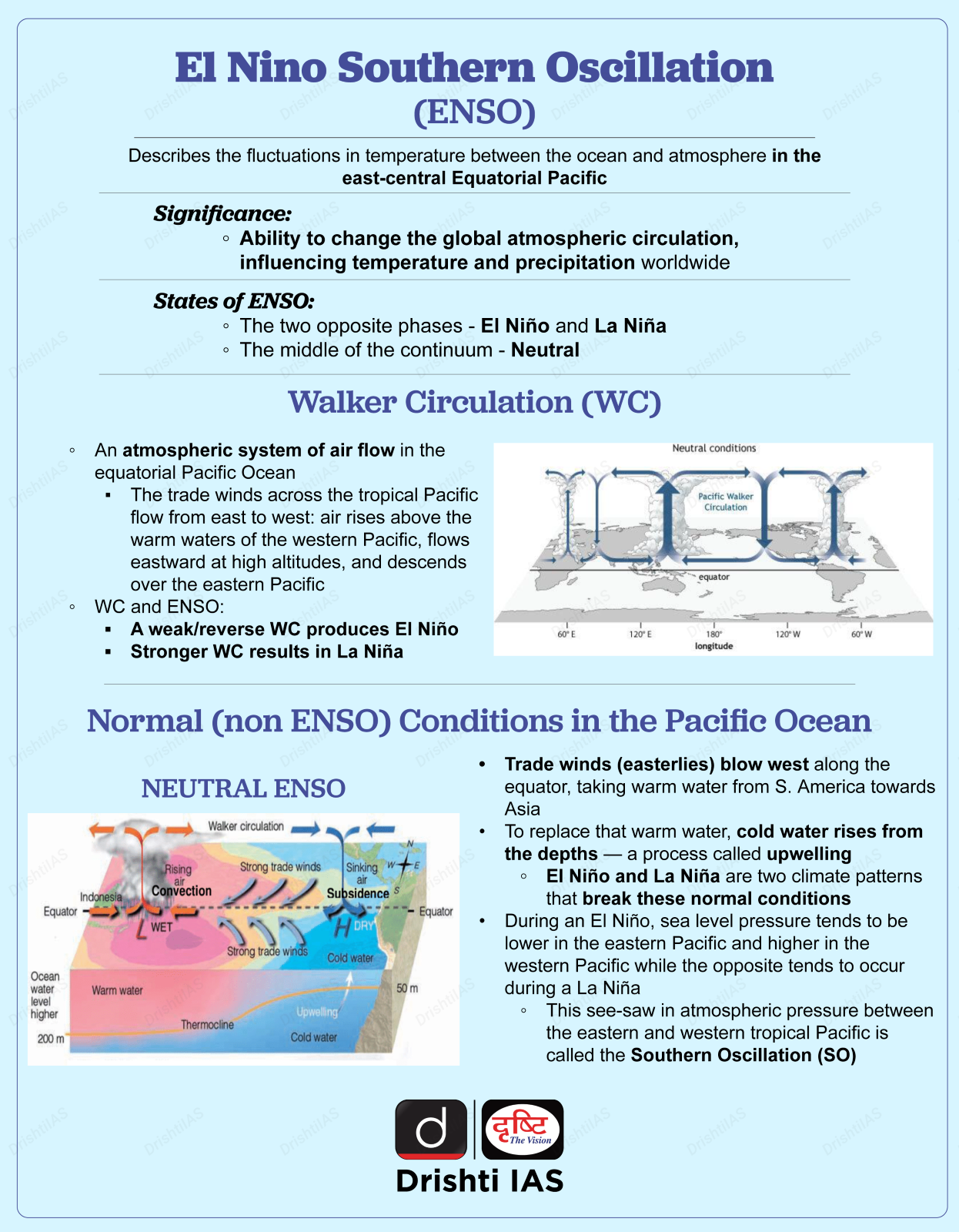
What is El Nino?
- El Nino was first recognized by Peruvian fishermen off the coast of Peru as the appearance of unusually warm water.
- The Spanish immigrants called it El Nino, meaning “the little boy” in Spanish.
- The El Nino is the warmer-than-normal phase of the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) phenomenon, during which there are generally warmer temperatures and less rainfall than normal in many regions of the world, including India.
- During an El Nino event, the Sea Surface Temperatures (SST) in the equatorial Pacific Ocean off the northern coast of South America became at least 0.5 degrees Celsius warmer than the long-term average.
- In the case of a strong El Nino event as occurred in 2015-2016, anomalies can reach as high as 3°C, which is a record.
- The El Nino event is not a regular cycle, they are not predictable and occur irregularly at two- to seven-year intervals.
- Climatologists determined that El Nino occurs simultaneously with the Southern Oscillation.
- The Southern Oscillation is a change in air pressure over the tropical Pacific Ocean.
- Climatologists determined that El Nino occurs simultaneously with the Southern Oscillation.
What do the Climate Models Say About Upcoming El Nino?
- Impact on India:
- Weak Monsoon for India: The development of an El Nino in May or June 2023 may cause weakening of the southwest monsoon season, which brings around 70% of the total rainfall India receives and on which most of its farmers still depend.
- However, sub-seasonal factors such as the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) and monsoon low-pressure systems can temporarily enhance rainfall in some parts as witnessed in the year 2015.
- Hot Temperatures: It may also cause heatwaves and droughts in India and other regions around the world such as South Africa, Australia, Indonesia and the Pacific Islands.
- Weak Monsoon for India: The development of an El Nino in May or June 2023 may cause weakening of the southwest monsoon season, which brings around 70% of the total rainfall India receives and on which most of its farmers still depend.
- Heavier Rainfall in the West: It brings heavy rainfall and flooding to other regions such as California in the United States and could cause bleaching and death of coral reefs.
- Rising Global Average Temp: The El Nino in 2023 and going into 2024 may push the global average temperature towards 1.5°C warmer than the preindustrial average.
- The warming of the oceans is also one of the major impacts of an El Nino event.
- This is when ocean heat content is already at a record high, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- The warming of the oceans is also one of the major impacts of an El Nino event.
- Previous Such Occurrences – Impacts:
- In the 2015-2016, there were widespread heatwaves in India that killed around 2,500 people in each of the years.
- Coral reefs around the world also suffered from bleaching and the sea level rose by 7 millimetres due to thermal expansion.
- The El Nino, along with global warming, had made 2016 the warmest year on record.
- El Nino events of 1982-83 and 1997-98 were the most intense of the 20th century.
- During the 1982-83 event, sea surface temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific were 9-18°C above normal.
- In the 2015-2016, there were widespread heatwaves in India that killed around 2,500 people in each of the years.
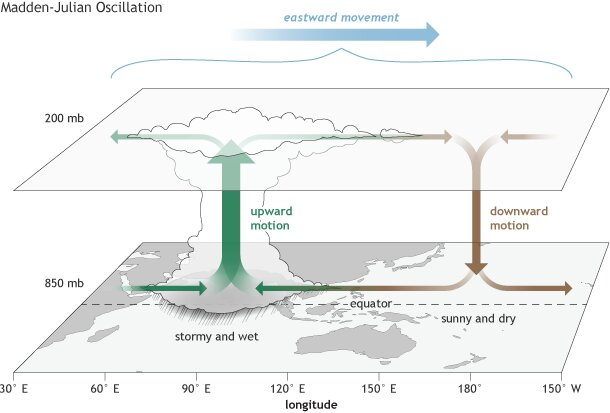
What is MJO?
- The MJO is made up of two parts: an enhanced rainfall phase and a suppressed rainfall phase.
- During the enhanced phase, surface winds converge, causing air to rise and create more rainfall. In the suppressed phase, winds converge at the top of the atmosphere, causing air to sink and leading to less rainfall.
- This dipole structure moves west to east in the Tropics, creating more cloudiness and rainfall in the enhanced phase, and more sunshine and dryness in the suppressed phase.
How does ENSO Affect India?
- The influence of ENSO on India's climate is most pronounced during the monsoon season. During an El Niño event, India experiences below-average rainfall.
- The El Niño also leads to a rise in temperatures, exacerbating heat waves and causing heat-related health issues.
- On the other hand, during a La Niña event, India experiences above-average rainfall.
- This can lead to flooding and landslides, damaging crops and infrastructure. However, La Niña also brings cooler temperatures, which can provide relief from heat waves.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014)


Biodiversity & Environment
5th International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure
For Prelims: ICDRI, CDRI.
For Mains: Disaster Management.
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India, addressed the 5th International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (ICDRI) 2023.
What is ICDRI?
- About:
- ICDRI is the annual international conference of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) in partnership with member countries, organizations and institutions to strengthen the global discourse on disaster and climate-resilient infrastructure.
- Highlights of ICDRI 2023:
- The Prime Minister said that since India is leading the G20 group, the CDRI will be included in many important discussions.
- This means that the solutions discussed in the CDRI will be considered at the highest levels of global policymaking.
- The Prime Minister said that since India is leading the G20 group, the CDRI will be included in many important discussions.
What is CDRI?
- About:
- CDRI is an Independent International Organization consisting of global partnership of national governments, United Nations agencies and programs, multilateral development banks and financing mechanisms, the private sector, and academic and research institutions.
- It aims to increase the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks, thereby ensuring sustainable development.
- It was launched in 2019, at the United Nations Climate Action Summit in New York.
- CDRI is India's second major global initiative after the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- The CDRI Secretariat is based in New Delhi, India.
- CDRI is an Independent International Organization consisting of global partnership of national governments, United Nations agencies and programs, multilateral development banks and financing mechanisms, the private sector, and academic and research institutions.
- Members:
- Since its inception, 31 countries, 6 international organisations and 2 private sector organisations have joined CDRI as members.
- Significance for India:
- CDRI provides a platform for India to emerge as a global leader in climate Action and Disaster Resilience.
- It boosts India's soft power, but more importantly it has wider connotation than just economics, as synergy between disaster risk reduction, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Climate Accord provides for sustainable and inclusive growth.
What are the Initiatives of CDRI?
- Infrastructure for Resilient Island States (IRIS):
- India launched this initiative as a part of the CDRI that would focus on building capacity, having pilot projects, especially in Small Island Developing States or SIDS.
- SIDS face the biggest threat from climate change.
- India’s space agency ISRO will build a special data window for them to provide them with timely information about cyclones, coral-reef monitoring, coastline monitoring etc. through satellite.
- India launched this initiative as a part of the CDRI that would focus on building capacity, having pilot projects, especially in Small Island Developing States or SIDS.
- Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator Fund:
- The Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator Fund is a fund supported by both the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR).
- It is a trust fund that will be managed by the United Nations Multi-Partner Trust Fund Office (UN MPTFO) to help in improving the ability of infrastructure systems to withstand disasters, with a special focus on developing countries and Small Island Developing States (SIDS).


International Relations
Reincarnation in Tibetan Buddhism
For Prelims: Dalai Lama, Tibetan Buddhism, Reincarnation in Buddhism
For Mains: India’s Tibet Policy, India China Relations.
Why in News?
The Dalai Lama has named a US-born Mongolian boy as the 10th Khalkha Jetsun Dhampa, the head of the Janang tradition of Tibetan Buddhism and the Buddhist spiritual head of Mongolia.
- This announcement has brought attention back to the larger question of the Dalai Lama's own reincarnation, which is a civilizational struggle between China and Tibetans over who controls Tibetan Buddhism.
What is the Reincarnation in Tibetan Buddhism?
- Buddhism Schools in Tibet:
- Buddhism became the predominant religion in Tibet by the 9th century AD. Tibetan Buddhism has four major schools: Nyingma, Kagyu, Sakya, and Gelug.
- The Janang school is one of the smaller schools that grew as an offshoot of the Sakya school. The Dalai Lama belongs to the Gelug school.
- History of Reincarnation:
- The cycle of birth, death and rebirth is one of Buddhism's key beliefs, although early Buddhism did not organise itself based on this belief in reincarnation.
- However, Tibet's hierarchical system seemingly emerged in the 13th century, and the first instances of formally recognizing the reincarnations of lamas can be found at this time.
- The Gelug school developed a strong hierarchy and instituted the tradition of succession through reincarnation, with the 5th grand lama of the school being conferred the title of Dalai Lama.
- Reincarnation in Tibetan Buddhism:
- According to Tibetan Buddhist tradition, the spirit of a deceased lama is reborn in a child, which secures a continuous line of succession through successive re-embodiments.
- Several procedures are followed to recognize ‘Tulkus’ (recognised reincarnations), including the predecessor leaving guidance regarding his reincarnation, the prospective child undergoing multiple 'tests', and other oracles and lamas with the power of divination being consulted before the final proclamation is made.
- There are also procedures to iron out disputes, such as making the final decision by divination employing the dough-ball method before a sacred image.
What About India’s Association with the Dalai Lama?
- India and the Dalai Lama have had a long-standing relationship dating back to 1959 when the Dalai Lama fled Tibet and sought refuge in India.
- India has since been the home to the Dalai Lama and the Tibetan government-in-exile, providing them with political asylum, and has supported the Tibetan cause for autonomy from China.
- Over the years, India has taken a diplomatic stance on the Tibetan issue. India has also refused to endorse China's position on the reincarnation of the Dalai Lama, insisting that it is a religious matter that should be decided by the Tibetan people themselves.
- In recent years, India-China relations have been strained, and the Dalai Lama's presence in India has become a contentious issue for China.
Who is Dalai Lama?
- Dalai Lama is a title given by the Tibetan people for the foremost spiritual leader of the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" school of Tibetan Buddhism, the newest of the classical schools of Tibetan Buddhism.
- The 14th and current Dalai Lama is Tenzin Gyatso.
- The Dalai Lamas are believed to be manifestations of ‘Avalokiteshvara’ or Chenrezig, the Bodhisattva of Compassion and the patron saint of Tibet.
- Bodhisattvas are realized beings inspired by a wish to attain Buddhahood for the benefit of all sentient beings, who have vowed to be reborn in the world to help humanity.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With reference to Indian history, who among the following is a future Buddha, yet to come to save the world? (2018)
(a) Avalokiteshvara
(b) Lokesvara
(c) Maitreya
(d) Padmapani
Ans: (c)
Q2. The painting of Bodhisattva Padmapani is one of the most famous and oft-illustrated paintings at (2017)
(a) Ajanta
(b) Badami
(c) Bagh
(d) Ellora
Ans: (a)


Indian Polity
Copyright Act 1957
For Prelims: Copyright Act 1957, Intellectual Property, Performer’s Rights under Copyrights Act.
For Mains: Copyright Act 1957.
Why in News?
Recently, the Bombay High Court has disposed the petitions by an actor, who challenged the sales tax levied on her income from advertisements and performances in award shows.
- The case has raised questions about whether actors hold a Copyright for their performances and whether they are liable to pay sales tax for it.
- It also deals with how Intellectual Property is treated for taxation purposes.
What is the Case about?
- The actor challenged the imposition of a sales tax on her revenue from advertisements and award show performances.
- The tax department argued that she was selling her copyright and thus owed an indirect tax.
- However, the actor argued that, as per Section 2 (d) of the Copyright Act, the producers of the shows are the original creators and possess the respective videos' copyright and she couldn't sell or transfer it adding that she is a ‘performer’ under the law and acquired performer’s rights under section 38 and 38A of Copyright Act.
What are Performer’s Rights?
- The Copyright Act of 1957 has a provision called Section 38 which recognizes "Performer's Rights" for artists, including singers and actors, for their performances in literary works, movies, and songs.
- These rights protect the artist's work for 50 years after the performance. This amendment was made in 2012 to protect artists and ensure they receive royalties for their work.
- These rights cannot be transferred or sold through an agreement, and production houses cannot buy them out.
- This ensures that the artist retains ownership of their work and receives fair compensation for it.
What is the Copyright Act 1957?
- About:
- Copyright is a legal right that protects original works of literature, art, music, films, and computer programs, among others, in India.
- It safeguards expressions of ideas rather than the ideas themselves. The owner of a copyright has exclusive rights to adapt, reproduce, publish, translate, and communicate the work to the public.
- The act has undergone several revisions since it was first passed in 1958. The most recent amendment was in 2012.
- Key Sections:
- Section 2: Deals with various definitions of the work which can be covered under the definition of copyright.
- For example, Section 2(o) deals with literary works, Section 2(h) includes all dramatic works under the definition of copyright protection.
- Section 13: Provides copyright protection to literary works, musical works, dramatic works, cinematographic films, and sound recordings, among others.
- Section 14: Grants the copyright owner a set of exclusive rights such as adapting, reproducing, publishing, translating, and communicating the work to the public.
- No one can exercise these rights unless they have the permission of the copyright owner.
- Section 2: Deals with various definitions of the work which can be covered under the definition of copyright.
Note
- In addition to the act, the Copyright (Amendment) Rules 2021, were brought into effect to bring the copyrights in line with other relevant laws. Under the rules:
- Provisions have been introduced to ensure accountability and transparency in the collection and distribution of royalties.
- The Copyright Board has been merged with the Appellate Board, and the compliance requirements for software registration have been reduced.
- The applicant has the option to file the first 10 and last 10 pages of the source code, or the entire source code if it's less than 20 pages, with no blocked or redacted portions.
- The Central Government has 180 days to respond to an application for registration as a copyright society.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to the ‘National Intellectual Property Rights Policy’, consider the following statements: (2017)
- It reiterates India’s commitment to the Doha Development Agenda and the TRIPS Agreement.
- Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion is the nodal agency for regulating intellectual property rights in India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- According to the Indian Patents Act, a biological process to create a seed can be patented in India.
- In India, there is no Intellectual Property Appellate Board.
- Plant varieties are not eligible to be patented in India.
Which of te statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. In a globalized world, Intellectual Property Rights assume significance and are a source of litigation. Broadly distinguish between the terms—Copyrights, Patents and Trade Secrets. (2014)


Important Facts For Prelims
Invasive Species in Gulf of Mannar Islands
Why in News?
A recent study has revealed that the native vegetation and biodiversity in the Gulf of Mannar are under threat from an alien invasive plant, Prosopis chilensis.
- In addition, the coral reef has been destroyed in several places despite being outlawed for industrial purposes, and human settlements have impacted some islands.
What are Invasive Species?
- About:
- An invasive species is an organism that is not indigenous, or native, to a particular area and causes harm to the native species.
- They are capable of causing extinctions of native plants and animals, reducing biodiversity, competing with native organisms for limited resources, and altering habitats.
- They can be introduced to an area by ship ballast water, accidental release, and most often, by people.
- An invasive species is an organism that is not indigenous, or native, to a particular area and causes harm to the native species.
- About Prosopis Chilensis:
- The Chilean mesquite (Prosopis chilensis (Molina) Stuntz) is a small to medium-sized legume tree and has a shallow and spreading root system.
- It is a common ruderal weed, either growing singly or in groups
- It is found in arid and semi-arid regions with ground water of between 3 and 10 m below the surface.
- It is a drought-resistant plant native to South American countries namely Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru.
- The Chilean mesquite (Prosopis chilensis (Molina) Stuntz) is a small to medium-sized legume tree and has a shallow and spreading root system.
- International Instruments and Programmes on Invasive Species:
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- It was one of the key agreements adopted at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro.
- The Rio de Janeiro Convention on Biodiversity (1992) had also recognised the biological invasion of alien species of plants as the second-worst threat to the environment after habitat destruction.
- Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS) or Bonn Convention (1979):
- It is an intergovernmental treaty that aims to conserve terrestrial, marine and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- It also aims to control or to eliminate already present invasive alien species.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
- It is an international agreement adopted in 1975 that aims to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival.
- It also considers the problems of invasive species when it is involved in trade and threatens the survival of live animals or plants.
- Ramsar Convention (1971):
- The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands.
- It also addresses the environmental, economic and social impact of invasive species on wetlands within their jurisdictions and to take account of the methods of control and solutions for combating invasive species.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
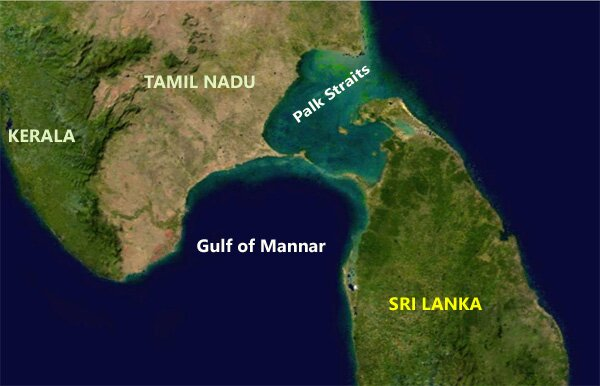
- Gulf of Mannar:
- It is an inlet of the Indian Ocean, between southeastern India and western Sri Lanka.
- It is bounded to the northeast by Rameswaram (island), Adam’s (Rama’s) Bridge (a chain of shoals), and Mannar Island.
- It receives several rivers, including the Tambraparni (India) and the Aruvi (Sri Lanka).
- The gulf is noted for its pearl banks and sacred chank (a gastropod mollusk).
- Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve (GoMBR):
- The GoMBR is home to 21 islands that serve as habitats for coastal birds migrating as far as the Arctic Circle.
- It is India’s first marine biosphere reserve.
- Most of the islands have sand dunes along their coastlines with salt-dominant plant species.
- “Corals, seagrass, and mangroves are among the three unique ecosystems present on the islands
- The GoMBR is home to 21 islands that serve as habitats for coastal birds migrating as far as the Arctic Circle.


Important Facts For Prelims
CBDT Signs 95 Advance Pricing Agreements
Why in News?
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) has entered into a record 95 Advance Pricing Agreements (APAs) in FY 2022-23 with Indian taxpayers.
- This includes 63 Unilateral APAs (UAPAs) and 32 Bilateral APAs (BAPAs).
- This is the maximum number of BAPAs that CBDT has signed in any financial year till date.
- Mutual Agreements with India’s treaty partners namely Finland, the UK, the US, Denmark, Singapore, and Japan led to the signing of the BAPAs.
What is an Advance Pricing Agreement (APA)?
- About:
- The Advance Pricing Agreement (APA) programme in India was launched in 2012 vide the Finance Act, 2012 through the insertion of Sections 92CC and 92CD in the Income-tax Act, 1961.
- APA is an agreement between a taxpayer and tax authority determining the transfer pricing methodology, for pricing the taxpayer’s international transactions for future years.
- Once the APA is sealed, the methodology is to be applied for a certain period of time based on the fulfilment of certain terms and conditions.
- Types:
- An APA can be unilateral, bilateral, or multilateral.
- Unilateral APA: An APA that involves only the taxpayer and the tax authority of the country where the taxpayer is located.
- Bilateral APA (BAPA): an APA that involves the taxpayer, associated enterprise (AE) of the taxpayer in the foreign country, tax authority of the country where the taxpayer is located, and the foreign tax authority.
- Multilateral APA (MAPA): an APA that involves the taxpayer, two or more AEs of the taxpayer in different foreign countries, tax authority of the country where the taxpayer is located, and the tax authorities of AEs.
- An APA can be unilateral, bilateral, or multilateral.
- Significance:
- The APA programme has contributed significantly to the Government of India’s mission of promoting ease of doing business.
- The programme especially benefits cross-border transactions.
- The APA programme has contributed significantly to the Government of India’s mission of promoting ease of doing business.
Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT)
- It is a statutory authority that functions under the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963.
- It is a part of the Department of Revenue in the Ministry of Finance.
- It provides inputs for policy and planning of direct taxes in India and is also responsible for the administration of direct tax laws through the Income Tax Department.
- Direct Taxes include income tax, corporation tax etc.


Important Facts For Prelims
Contamination Concerns over Indian Eye drops in US
Why in News?
US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) have raised concerns over a drug-resistant bacteria strain allegedly linked to eye drops imported from India.
- Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) has written to the USFDA seeking details about the issue.
- Global Pharma Healthcare is recalling EzriCare eye drops from the US market and has halted the Production of ophthalmic (connected with the eye and diseases that affect it) products until the investigation is completed.
- Preliminary Reports by the Healthy ministry in India suggest contamination in the US came from opened bottles; as samples collected from the company were not contaminated.
What is the Status of Indian Pharmaceutical Sector?
- The Indian Pharmaceuticals industry plays a prominent role globally. India ranks 3rd worldwide for production by volume and 14th by value.
- The nation is the largest provider of generic medicines globally, occupying a 20% share in global supply by volume, and is the leading vaccine manufacturer globally.
- India is home to more than 3,000 pharma companies with a strong network of over 10,500 manufacturing facilities as well as a highly skilled resource pool.
Note
- Previously in 2022, the World Health Organisation (WHO) had issued an alert about four Indian-manufactured cough syrups, which are said to be linked to acute kidney injury in children and 66 deaths in the small West African nation of The Gambia.
Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI)
- The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) is the head of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The CDSCO is responsible for approving licenses for specified categories of drugs, such as blood and blood products, IV fluids, vaccines, and sera in India.
- The DCGI is also responsible for setting standards for manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution of drugs and medical devices in India, as well as ensuring uniformity in the enforcement of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act,1940.
- In addition to these responsibilities, the DCGI acts as an appellate authority in case of disputes regarding the quality of drugs and prepares and maintains the national reference standard for drugs. Furthermore, DCGI is the central licensing authority for medical devices that fall under the Medical Device Rules 2017.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Babu Jagjivan Ram

The Prime Minister paid tributes to freedom fighter Babu Jagjivan Ram on his birth anniversary. He was popularly known as Babuji, a national leader, a freedom fighter, a crusader of social justice, a champion of depressed classes and an outstanding Parliamentarian.
He was born on 5th April 1908 in Chandwa in Bihar to a Dalit family. In 1931, he became a member of the Indian National Congress (INC). In 1935, he proposed at a session of the Hindu Mahasabha that drinking water wells and temples be open to untouchables. In 1935, he also appeared before the Hammond Commission at Ranchi and demanded, for the first time, voting rights for the Dalits. When Jawaharlal Nehru formed the provisional government, Jagjivan Ram became its youngest minister.
He died on 6th July 1986 in New Delhi. His memorial at his cremation place is named Samta Sthal (Place of Equality).
Read More: Babu Jagjivan Ram
Sagar Setu App
The Union Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways recently launched the App Version of National Logistics Portal (Marine) - ‘Sagar-Setu’.
The mobile app will ensure data mobility such that approvals & monitoring shall be at the fingertips of port & ministry officials and stakeholders as well.
National Logistics Portal (Marine) is a national maritime single window platform encompassing complete end-to-end logistics solutions to help exporters, importers, and service providers exchange documents seamlessly and transact business. The overarching NLP Marine Vision is to cater to various stakeholders in Government to Government (G2G), Government to Business (G2B) and Business-to-business (B2B) model.
GI Tag for Kathua's 'Basohli Painting'
The world-famous 'Basohli Painting', popular for its miniature art style from Kathua district, Jammu & Kashmir has obtained the Geographical Indication (GI). This is the first time that the Jammu region got a GI tag for handicrafts.
The process for GI-tagging of nine products was initiated by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) in consultation with the Department of Handicrafts and Handloom (J&K) in December 2020.
The products from UT of J&K have been included in the list of 33 products that have received the GI tag recently.
GI is a form of Intellectual Property right that identifies goods originating from a specific geographical location and having distinct nature, quality and characteristics linked to that location.
Read More: Geographical Indication (GI) Tag
UN Statistical Commission
India has been elected to the UN Statistical Commission for a four-year period (beginning on 1 January 2024) in a competitive election. The Commission works under the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC).
The UN Statistical Commission, established in 1947, is the highest body of the global statistical system bringing together the Chief Statisticians from member states from around the world. It is the highest decision-making body for international statistical activities, responsible for setting statistical standards and the development of concepts and methods, including their implementation at the national and international levels.
The Commission consists of 24 member countries (Five members are from African States, four from Asia-Pacific States, four from Eastern European States, four from Latin American and Caribbean States and seven members from Western European and other States) of the United Nations elected by the ECOSOC on the basis of equitable geographical distribution. India has been elected to the Economic and Social Council, one of the six main organs of the United Nations, for the 2022-24 term.
Read More: United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)