Infographics
Indian Economy
Lab-Grown Diamonds
Prelims: Lab-Grown Diamonds, Naturally Occurring Diamonds, Allotrope of Carbon, HPHT Method, CVD Method.
Mains: Lab-Grown Diamonds and its Significance
Why in News?
The Ministry of Finance (MoF) in its 2023-24 Union Budget has put special emphasis on Laboratory-Grown Diamonds (LGD).
- Scientists working at a General Electric research laboratory in New York are credited with the creation of the world’s first-ever LGD in 1954.
What are Laboratory-Grown Diamonds?
- About:
- LGD are manufactured in laboratories, as opposed to naturally occurring diamonds. However, the chemical composition and other physical and optical properties of the two are the same.
- Naturally occurring diamonds take millions of years to form; they are created when carbon deposits buried within the earth are exposed to extreme heat and pressure.
- Manufacturing:
- They are mostly manufactured through two processes, High Pressure,High Temperature (HPHT) method or Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) method.
- Both HPHT and CVD methods of growing diamonds artificially begin with a seed, a slice of another diamond.
- In the HPHT method, the seed, along with pure graphite carbon, is exposed to temperatures around 1,500 degrees Celsius and extremely high pressure.
- In the CVD method, the seed is heated to around 800 degrees Celsius inside a sealed chamber filled with a carbon-rich gas. The gas sticks to the seed, gradually building the diamond.
- Applications:
- They are used for industrial purposes in machines and tools and their hardness and extra strength make them ideal for use as cutters.
- Pure synthetic diamonds are used in electronics as a heat spreader for high-power laser diodes, laser arrays and high-power transistors.
- Significance:
- The environmental footprint of a diamond grown in a laboratory is much lesser than that of a naturally occurring diamond.
- According to a report by Diamond Foundry, an environmentally conscious LGD manufacturer, it takes ten times more energy to extract a natural diamond from the earth than it takes in creating one above the ground.
- Open-pit mining, one of the most common methods of mining naturally occurring diamonds, involves moving tonnes of earth and rock to extract these precious stones.
What is the Scenario of India’s Diamond Industry?
- India is the world’s largest cutting and polishing center for diamonds, accounting for over 90% of polished diamond manufacturing globally. This is attributed to factors such as the easy availability of high skilled labour, cutting-edge technology, and lower costs involved.
- Surat in Gujarat is a global hub for diamond manufacturing.
- The US is the biggest market for cut and polished diamonds, with China a close second.
- India contributes 19% of the total diamond exports in the world.
- The UAE is also the largest export destination for Indian gold jewellery, accounting for over 75% of the South Asian country’s jewellery exports.
- India’s overall exports of gems and jewellery in November 2022 were USD 2.43 billion, up 2.05 % from the same year-ago period.
What are the Government Initiatives to Promote Lab-Grown Diamond?
- The 2023 Union Budget promises to reduce the basic customs duty on seeds used in the manufacture of lab-grown diamonds in a bid to popularise their production in India— the duty on seeds for rough LGDs will be reduced from 5% to nil.
- A five-year research grant will also be provided to one of the Indian Institute of Technologies (IITs) for research and development in the field of LGDs.
- MoF has also proposed the creation of new tariff lines to help in better identification of a number of products, including synthetic diamonds. The aim of the move is to help facilitate trade as well as to have clarity on availing concessional import duty.


Governance
The Concern of South Indian States on Delimitation
For Prelims: Delimitation, Delimitation Commission, Lok Sabha.
For Mains: Indian Constitution, Issues Faced by Southern States Due to Lack of Seats in Lok Sabha & Recommendations, Statutory Bodies, Delimitation Process.
Why in News?
As the Country is preparing for the next census, it is observed that the delimitation of Lok Sabha seats along with a smaller share of central funds to states on the basis of the population can be unfair to Southern states, which have implemented family planning programs more effectively than the states in North India.
- The argument is that Southern states should be recognized and rewarded for their efforts to control population growth, rather than being penalized for their success. The national delimitation exercise has, however, raised concerns about the unequal representation of states in the Lok Sabha.
What is Delimitation?
- About:
- Delimitation means the act or process of fixing limits or boundaries of territorial constituencies in a country to represent changes in population.
- The Delimitation Commission Act was enacted in 1952.
- Once the Act is in force, the Union government sets up a Delimitation Commission.
- Delimitation Commissions have been set up four times — 1952, 1963, 1973 and 2002 under the Acts of 1952, 1962, 1972 and 2002.
- The first delimitation exercise was carried out by the President (with the help of the Election Commission) in 1950-51.
- Hisory:
- The last delimitation exercise that changed the state-wise composition of the Lok Sabha was completed in 1976 and done on the basis of the 1971 census.
- The Constitution of India mandates that the allocation of seats in the Lok Sabha should be based on the population of each state so that the ratio of seats to population is as close as possible to being equal across all states. It is intended to ensure that each person's vote carries roughly the same weight, regardless of which state they live in.
- However, this provision meant that states that took little intersst in population control could end up with a greater number of seats in Parliament.
- To avoid these consequences, the Constitution was amended during Indira Gandhi’s Emergency rule in 1976 to suspend delimitation until 2001. Another amendment postponed this until 2026. It was hoped that the country would achieve a uniform population growth rate by this time.
- Need:
- To provide equal representation to equal segments of a population.
- Fair division of geographical areas so that one political party doesn’t have an advantage over others in an election.
- To follow the principle of “One Vote One Value”.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Under Article 82, the Parliament enacts a Delimitation Act after every Census.
- Under Article 170, States also get divided into territorial constituencies as per Delimitation Act after every Census.
What is Delimitation Commission?
- Appointment:
- The Commission is appointed by the President of India and works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India.
- Composition:
- Retired Supreme Court judge
- Chief Election Commissioner
- Respective State Election Commissioners
- Functions:
- To determine the number and boundaries of constituencies to make the population of all constituencies nearly equal.
- To identify seats reserved for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, wherever their population is relatively large.
- Powers:
- In case of a difference of opinion among members of the Commission, the opinion of the majority prevails.
- The Delimitation Commission in India is a high-power body whose orders have the force of law and cannot be called in question before any court.
How Delimitation is Being Unfair to the Southern States?
- Development:
- The economic situation of Southern states has improved dramatically since the turn of the 21st century. Prior to the 1990s, Northern states were outperforming Southern states in terms of income and poverty levels.
- However, the Southern states have seen a significant increase in their economic performance in recent years, which has led to a significant reduction in poverty and an increase in income levels.
- This economic turnaround has had a significant impact on the region and has helped to drive growth and development in the Southern states.
- The combined Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of just three States — Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu is greater than 13 States in the East.
- The economic situation of Southern states has improved dramatically since the turn of the 21st century. Prior to the 1990s, Northern states were outperforming Southern states in terms of income and poverty levels.
- Educational and Health Outcomes:
- The previous Annual Status of Education Reports (ASER) data suggests that southern regions have performed better in terms of children being enrolled in schools and having better learning outcomes compared to their northern counterparts.
- Further, a higher proportion of graduates in the southern States indicates the greater prevalence of a specific set of skills.
- For instance, in 2011, only 5% of Uttar Pradesh’s population was graduated, while in Tamil Nadu, nearly 8% of its population was graduated.
- During the Covid-19 pandemic, Tamil Nadu has 314 testing centres for a population of 78.8 million as of December 2021 and Uttar Pradesh has only 305 Covid testing centres for a population of 235 million, which is clearly inadequate.
- Governance Factor:
- If the educational and health outcomes are better in the southern States, this also implies that the ability to discern and the quality of decision-making must be significantly better there.
- The expectation for better public services and high civic activism in southern states suggests that the electorate there is more likely to vote for better governance compared to the north.
- Advantages for the North:
- Based on the population patterns, the existing distribution of parliamentary constituencies across the States is tilted in favour of populous States such as Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, while southern States like Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Karnataka have a lesser number of seats.
- If delimitation occurs, Southern states will face a decrease in the number of seats allocated to them, compared to the northern states, during the next delimitation process.
- Hence, during the electoral representation, it should be kept in mind that it is not the number of people, but their quality that should be the deciding factor.
What are the Issues in this Regard?
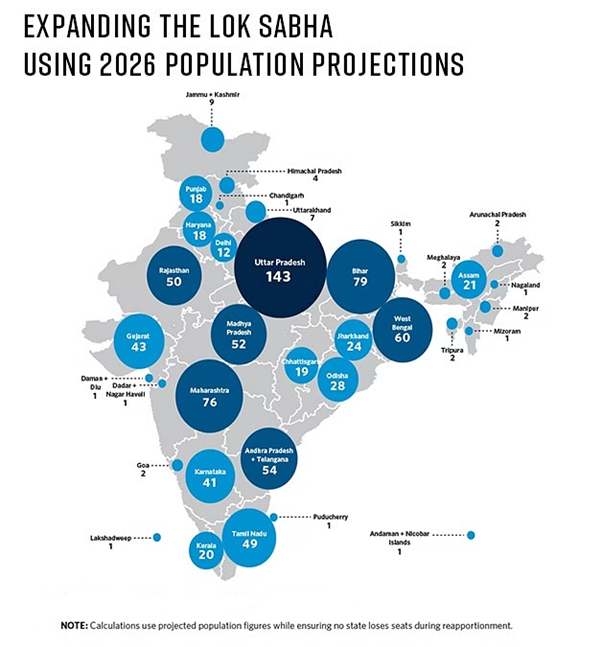
- Inadequate Representation: According to the 2019 research paper India’s Emerging Crisis of Representation, if the delimitation is carried out according to the 2031 Census (the earliest scheduled after 2026), Bihar and Uttar Pradesh alone would gain as many as 21 seats in total, while Tamil Nadu and Kerala together will lose 16 seats.
- Affecting the Reservations for SCs/ STs: The scheduled delimitation and reallocation of seats may result in not only a loss of seats for southern states but also an increase in power for political parties with their base of support in the north. This could potentially lead to a shift of power toward the north and away from the south.
- The exercise will also affect the division of seats reserved for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (SC/ST) in each state.
- Inadequate Funding: After the 15th Finance Commission used the 2011 Census as a basis for its recommendation, concerns were raised about southern states losing funding and representation in parliament.
- Previously, the 1971 Census was used as the base for funding and tax devolution recommendations to states.
- Demographic Dividend: In 1976, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, during the Emergency, suspended the revision of seats until after the 2001 Census. In 2001, the Parliament extended this freeze until the next decennial census after 2026, scheduled for 2031 as per the Constitution (84th Amendment) Act, 2001.
- Therefore, if Lok Sabha seats are reallocated after 2031, legislators and policy makers will have to factor in demographic and political changes in the country over the past 60 years.
What are the Recommendations?
- Establishment of a Robust Plan: Making a firm commitment to reallocating resources after 2031 without any further delays due to political or policy challenges. It would provide certainty and stability for southern states in terms of funding and representation.
- Increase in Number of Seats: The advantage of increasing the number of seats in the Lok Sabha is that Members of Parliament (MPs) would represent smaller constituencies. This would lead to more efficient governance as administrative agencies would not be burdened by a large population, allowing for faster and more effective decision making.
- Increasing the number of seats is seen as a more politically feasible option as it is easier for politicians to agree to adding seats in certain areas or states, rather than giving up seats in areas where they have more power.
- To Maintain Existing Position: Increasing the total number of seats in Parliament could be considered to ensure that no state loses the seats it currently has. This proposal may be under consideration by the Union government.
- Adequate Representation: Reports suggest that the architects of the new Lok Sabha, being built as part of the Central Vista project, have been asked to plan for at least 888 seats in the lower house.
- This would allow for adequate representation for all states and prevent any state from losing its current number of seats.


Governance
State-wide Crackdown on Child Marriages
For Prelims: Raising Legal Age of Marriage for Women, Child Marriage, Jaya Jaitly Committee, Protection of Children From Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006, International Conventions Related to Child Marriage.
For Mains: Issues with Minimum Marriage Ages.
Why in News?
Over the last few days, the Assam government has arrested over 2,000 men in a campaign against child marriages that have taken place in the state.
- The police will retrospectively book people who participated in child marriage in the last seven years and the focus will especially be on “mullahs, kazis, and pujaris” conducting these marriages. The arrests come in the backdrop of growing debate on the minimum age of marriage of Muslim women.
Under What Law are the Arrests Being Made?
- The men who married girls below 14 years of age would be booked under the Protection of Children From Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act and those marrying girls between the age of 14 and 18 years would be booked under the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006.
- POCSO Act:
- The POCSO Act, of 2012 criminalises sex between a minor and an adult. The law does not recognize a minor’s consent as valid.
- Sexual assault under POCSO is a non-bailable, cognisable offence. This means that the police can make an arrest without warrant.
- So, a presumption of sexual assault is being made in cases of child marriage involving minor girls below the age of 14.
- Sexual assault, that is not penetrative, carries a minimum imprisonment of three years that may extend to five years with a fine.
- Under Section 19, the Act imposes a “mandatory reporting obligation” which requires every person who suspects or has knowledge of a sexual offence being committed against a child must report it to the police or the Special Juvenile Police Unit. Failure to do so will result in imprisonment, a fine, or both.
- PCMA, 2006:
- It says that child marriages are illegal but not void. They are voidable at the minor's choice if he/she petitions the court to declare the marriage null and void.
- The Act stipulates 18 years as the minimum marriageable age for women, while for men it is 21 years.
- The Act punishes child marriage with rigorous imprisonment which may extend to two years or with a fine which may extend to one lakh rupees or both.
- The punishment also extends to anyone who performs, conducts, directs, or abets any child marriage.
- It says that child marriages are illegal but not void. They are voidable at the minor's choice if he/she petitions the court to declare the marriage null and void.
- POCSO Act:
What is the Debate on Muslim Age of Marriage?
- Under Muslim personal laws, the marriage of a bride who has attained puberty is considered.
- Puberty is presumed, in the absence of evidence, on completion of the age of fifteen years.
- This gap between Muslim personal law and special legislation prohibiting child marriages or sexual activity of minors puts a shadow on criminality in such marriages.
What are the Personal Laws of Other Religions?
- The Hindu Succession Act of 1956 lays out guidelines for property inheritance among Hindus, Buddhists, Jains and Sikhs.
- The Parsi Marriage and Divorce Act of 1936 lays out rules to be followed by the Parsis according to their religious traditions.
- The Hindu Marriage Act of 1955 codified laws related to marriage among Hindus.
What is the Central Government’s Stand?
- At the time of India’s independence, the minimum marriageable age stood at 15 years for females and 18 years for men.
- In 1978, the government increased it to 18 for girls and 21 for men.
- In 2008, the report of the Law Commission the minimum marriageable age for both men and women should be 18 years of age.
- In 2020, the Jaya Jaitly Committee was established by the Ministry of Women & Child Development which also recommended the same in light of factors like reproductive health, education, etc.
- In 2021, the Central government sought to introduce the Prevention of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill 2021, to raise the manageable age for women across all religions, from 18 to 21 years.
- As per the Union Minister for Women and Child Development this Amendment will apply to all communities in the country and once enacted, will supersede existing marriage and personal laws.
Note
- Along with the Indian laws and constitutional provisions modern international laws and conventions do mandate countries to stipulate a minimum legal age for marriage. But child marriages continue to have religious sanctions in large parts of India.
- Some of the conventions are:
- The United Nations (UN) Convention on Consent to Marriage (1962)
- Minimum Age for Marriage and Registration of Marriages (1962)
- The UN Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (1979)
- The Beijing Declaration (1995)
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016).


Social Issues
Increasing Cases of Suicides in Educational Hubs
For Prelims: National Crime Records Bureau, Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India Report, World Mental Health Day.
For Mains: Status of Suicides in India , Factors that Increase Suicide Risk, Related Initiatives to Reduce Suicides.
Why in News?
The National Crime Records Bureau’s (NCRB’s) Accidental Deaths and Suicide in India (ADSI) report 2021 shows student suicides had gone up drastically during the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021 and have been steadily rising in the last five years.
What is the Current Status of Suicides in Students?
- Over 13,000 students died by in 2021 in India at the rate of more than 35 every day, a rise of 4.5% from the 12,526 deaths in 2020 with 864 out of 10,732 suicides being due to "failure in examination" according to the latest data as per NCRB’s ADSI report 2021.
- Since 1995, the country lost the highest number of students to suicides in 2021, while nearly 2 lakh of them have died by suicide in the past 25 years.
- The death by suicide of students has increased by 32.15% since 2017, when 9,905 students died by suicide.
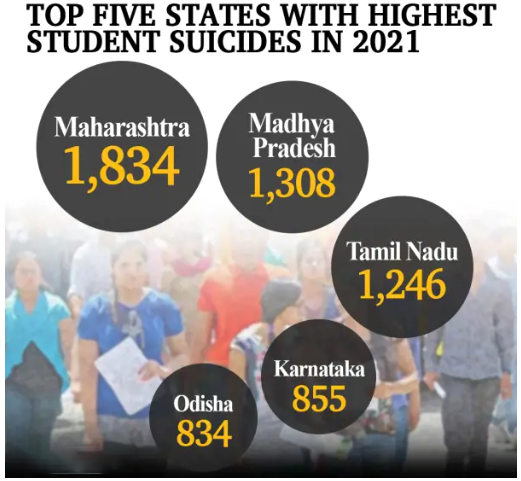
- Maharashtra had the highest number of student suicides in 2021 with 1,834, followed by Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- The report also showed the percentage of women student suicide was at a five-year low of 43.49%, while men student suicides made up 56.51% of the total student suicides.
- In 2017, 4,711 women students died by suicide, while in 2021 such deaths increased to 5,693.
- Since 1995, the country lost the highest number of students to suicides in 2021, while nearly 2 lakh of them have died by suicide in the past 25 years.
- As per Ministry of Education, 122 students from IITs, NITs, central universities and other central institutions died by suicide over 2014-21.
- 68 of 122 belonged to the scheduled castes (SC), scheduled tribes (ST) or other backward classes (OBC).
- Suicides are a growing concern in Kota, India, a hub for engineering and medical entrance exams preparation.
- As of January 2023, 22 students have died in Kota since 2022 and around 121 have died since 2011.
What are the Factors that Increase Suicide Risk?
- Academic Pressure:
- High expectations from parents, teachers and society can lead to excessive stress and pressure to perform well in exams.
- This pressure to succeed can be overwhelming for some students, leading to feelings of failure and hopelessness.
- Mental Health Issues:
- Mental health problems such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder can contribute to student suicides.
- These conditions can be exacerbated by stress, loneliness, and lack of support.
- Mental health problems such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder can contribute to student suicides.
- Isolation and Loneliness:
- Many students in educational hubs come from far away and live away from their families and friends.
- This can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness, which can be particularly difficult to deal with in an unfamiliar and competitive environment.
- Financial Concerns:
- Financial difficulties, such as not being able to afford tuition fees or living expenses, can create a great deal of stress and worry for students.
- This can lead to feelings of hopelessness and desperation.
- Cyber Bullying:
- Cyber bullying and online harassment are becoming increasingly common and can contribute to student suicides.
- Cyber bullying can take many forms, such as harassment, cyberstalking, or bullying through social media.
- Cyber bullying and online harassment are becoming increasingly common and can contribute to student suicides.
- Substance Abuse:
- Substance abuse and alcohol abuse can contribute to student suicides. Substance abuse can lead to mental health problems, financial difficulties, and legal issues, all of which can be overwhelming for students.
- Relationship Problems:
- Relationship problems, such as break-ups, family conflicts, and friendship issues can also contribute to student suicides.
- These problems can be particularly difficult to deal with for students who are far from home and have limited support.
- Lack of Support:
- Many students in educational hubs are reluctant to reach out for help when they are struggling.
- This can be due to stigma surrounding mental health problems or a fear of being judged.
- This lack of support can lead to feelings of hopelessness and desperation.
- Many students in educational hubs are reluctant to reach out for help when they are struggling.
What can be Done to Prevent Suicides?
- Improved Mental Health Services:
- Providing students with access to mental health services and resources such as counseling services, support groups, and psychiatric services can help prevent suicides.
- Also, schools and universities must train teachers, staff, and students in mental health first aid .
- Providing students with access to mental health services and resources such as counseling services, support groups, and psychiatric services can help prevent suicides.
- Embracing Positive Attitude towards Mental Health:
- Positive attitudes towards mental health and help-seeking must also be promoted through open discussions about mental health and suicide.
- Focus on Overall Personality Development:
- By taking a holistic approach to personality development, educational institutions can create a supportive and inclusive environment that helps students thrive both academically and emotionally, and can play a critical role in preventing suicides.
- Encouraging Participation in Sports:
- Sports can play a role in preventing suicides in educational hubs by providing a positive outlet for stress and emotions, as well as increase self-esteem and confidence.
- Addressing the Socio-economic Issues:
- Socio-economic factors such as poverty, homelessness, and unemployment should be addressed to improve students' overall well-being and reduce stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Stricter Cyber Bullying Policies:
- Implementing stricter cyber bullying policies and cracking down on online harassment can help reduce the risk of student suicides.
- This may include monitoring social media sites, providing education about cyber bullying, and taking legal action against cyber bullies.
- Implementing stricter cyber bullying policies and cracking down on online harassment can help reduce the risk of student suicides.
- Substance Abuse Prevention Programs:
- Implementing substance abuse prevention programs can help reduce the risk of student suicides.
- This may include educating students about the dangers of substance abuse, providing support for those struggling with addiction, and taking steps to reduce access to drugs and alcohol.
- Implementing substance abuse prevention programs can help reduce the risk of student suicides.
- Building Positive Relationships:
- Encouraging students to build positive relationships and connections, offering relationship counseling services, and encouraging students to reach out for help can help reduce the risk of suicide.
- Family Support:
- Providing students with support from their families can help reduce the risk of suicide.
- This may include offering support and resources for families, and encouraging students to maintain contact with their families.
- Providing students with support from their families can help reduce the risk of suicide.
What are Related Initiatives to Reduce Suicides?
- Global Initiatives:
- World Suicide Prevention Day (WSPD): Observed on 10th of September every year, WSPD was established in 2003 by the International Association for Suicide Prevention (IASP) in conjunction with the WHO. It focuses attention on the issue, reduces stigma and raises awareness among organizations, government, and the public, giving a singular message that suicide can be prevented.
- “Creating hope through action” is the triennial theme for the WSPD from 2021 - 2023. This theme is a reminder that there is an alternative to suicide and aims to inspire confidence and light in all of us.
- World Mental Health Day: 10th October is celebrated as World Mental Health Day, every year. The overall objective of World Mental Health Day is to raise awareness of mental health issues around the world and to mobilize efforts in support of mental health.
- The theme of World Mental Health Day 2022 is “Making Mental Health & Well-Being for All a Global Priority”.
- World Suicide Prevention Day (WSPD): Observed on 10th of September every year, WSPD was established in 2003 by the International Association for Suicide Prevention (IASP) in conjunction with the WHO. It focuses attention on the issue, reduces stigma and raises awareness among organizations, government, and the public, giving a singular message that suicide can be prevented.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Mental Healthcare Act (MHA), 2017:
- MHA 2017 aims to provide mental healthcare services for persons with mental illness.
- KIRAN:
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has launched a 24/7 toll-free helpline “KIRAN” to provide support to people facing anxiety, stress, depression, suicidal thoughts and other mental health concerns.
- Manodarpan Initiative:
- Manodarpan is an initiative of the Ministry of Education under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- It is aimed to provide psychosocial support to students, family members and teachers for their mental health and well-being during the times of Covid-19.
- Manodarpan is an initiative of the Ministry of Education under Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- National Suicide Prevention Strategy:
- Announced in 2023, National Suicide Prevention Strategy is the first of its kind in the country, with time-bound action plans and multi-sectoral collaborations to achieve reduction in suicide mortality by 10% by 2030.
- The strategy is in line with the World Health Organisation’s South East-Asia Region Strategy for suicide prevention.
- Its objectives are:
- The strategy broadly seeks to establish effective surveillance mechanisms for suicide within the next three years.
- It seeks to establish psychiatric outpatient departments that will provide suicide prevention services through the District Mental Health Programme in all districts within the next five years.
- It also aims to integrate a mental well-being curriculum in all educational institutions within the next eight years.
- It envisages developing guidelines for responsible media reporting of suicides, and restricting access to means of suicide.
- Announced in 2023, National Suicide Prevention Strategy is the first of its kind in the country, with time-bound action plans and multi-sectoral collaborations to achieve reduction in suicide mortality by 10% by 2030.
- Mental Healthcare Act (MHA), 2017:


Science & Technology
Google’s Bard: AI Generative Chatbot
Prelims: LaMDA, ChatGPT, Generative Artificial Intelligence.
Mains: Google’s Bard: AI Generative Chatbot, ChatGPT
Why in News?
Google will soon unveil its new AI chatbot Bard in response to Microsoft’s ChatGPT.
What is Bard?
- About:
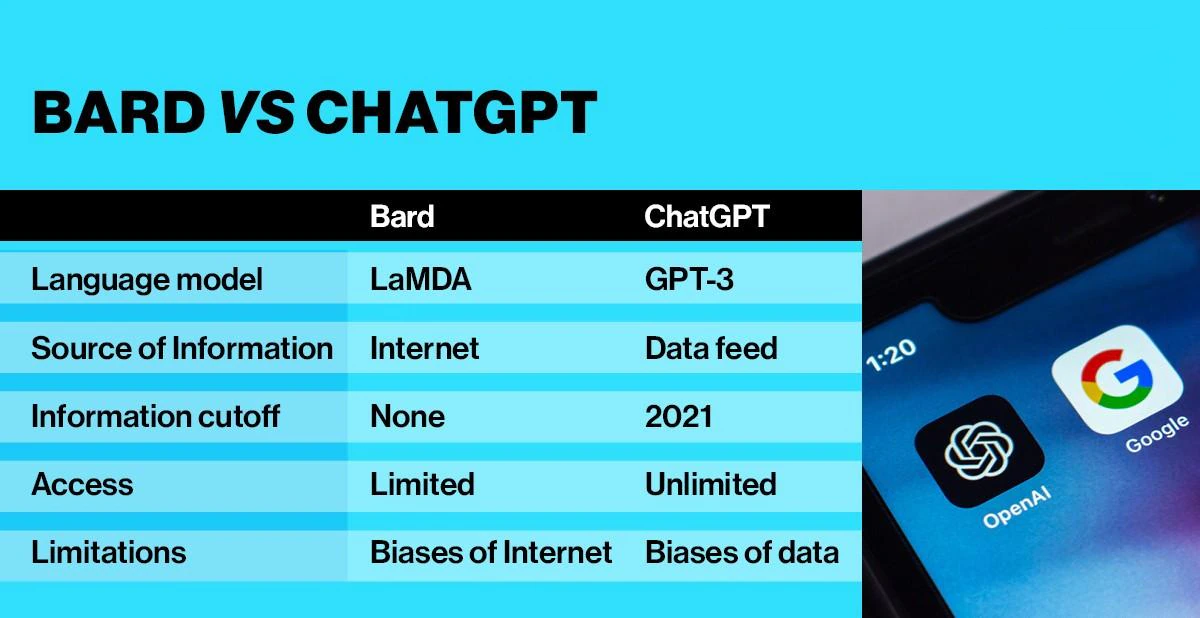
- Bard is based on the Language Model for Dialogue Application (LaMDA), Google’s own conversational AI chatbot.
- It will give in-depth, conversational and essay-style answers just like ChatGPT does right now.
- However, the model is currently a “lightweight” version of LaMDA, and the one being “requires significantly less computing power, enabling it to scale to more users.
- Features:
- It is built on Transformer technology, which is also the backbone of ChatGPT and other AI bots.
- Transformer technology was pioneered by Google and made open source in 2017.
- Transformer technology is a Neural Network Architecture, which is capable of making predictions based on inputs and is primarily used in natural language processing and computer vision technology.
- The architecture determines how the network processes information and influences its accuracy and efficiency in solving a particular problem. Common architectures include feedforward networks, recurrent networks, and convolutional neural networks.
- It is built on Transformer technology, which is also the backbone of ChatGPT and other AI bots.
How is ChatGPT different from Bard?
- ChatGPT has impressed with its ability to respond to complex queries — though with varying degrees of accuracy — but its biggest shortcoming perhaps is that it cannot access real-time information from the Internet.
- But Microsoft just unveiled a new version of Bing that's powered by ChatGPT which is a significant improvement of the version of ChatGPT.
- ChatGPT’s language model was trained on a vast dataset to generate text based on the input, and the dataset, at the moment, only includes information until 2021.
- Whereas, for questions where there might not be a clear-cut answer, Bard will synthesise a response that reflects differing opinions.
- For example, the question, “Is it easier to learn the piano or the guitar?” would be met with “Some say the piano is easier to learn, as the finger and hand movements are more natural. Others say that it’s easier to learn chords on the guitar.”
What are the Concerns of AI-Based Generative Chatbots?
- The text generation software from Google and OpenAI, while fascinating and eloquent, can be extremely prone to inaccuracies, experts have pointed out.
- The ability to search the Internet in real-time, including content such as hate speech and racial and gender biases and stereotyping, could lead to problems, and take the sheen off these new products.
- Even with natural language processing, they may not fully comprehend a customer's input and may provide incoherent answers.
- Many chatbots are also limited in the scope of queries that they are able to respond to.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)


Governance
Decline in Budgetary Allocation for Ministry of Minority Affairs
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram, Education Scheme for Minorities, USTTAD
For Mains: Welfare Schemes related to Minorities, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Budgetary allocation for the Union Ministry of Minority Affairs decreased by 38% in 2023-24 compared to 2022-23.
Where did Budgetary Allocations Decline the Most in Minority Affairs?
- The major decline was in the allocation for pre-matric scholarships, free coaching for minorities, skill development and livelihoods programmes (including USTTAD scheme, Nai Manzil and Scheme for Leadership Development of Minority Women) .
- Also, allocation for the Umbrella Programme for Development of Minorities, which includes the Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram and Education Scheme for Madrasas and Minorities, fell from ₹1810 crore to ₹610 crore, which is a dip of 66.2% in allocation.
What are the Major Schemes in India for the Welfare of Minorities?
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme, Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme, Merit-cum-Means based Scholarship Scheme: For educational empowerment of students, through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode.
- Naya Savera- Free Coaching and Allied Scheme: The Scheme aims to provide free coaching to students/candidates belonging to economically weaker sections of minority communities for preparation of entrance examinations of technical/ professional courses and competitive examinations.
- Padho Pardesh: Scheme of interest subsidy to students of economically weaker sections of minority communities on educational loans for overseas higher studies.
- Nai Roshni: Leadership development of women belonging to minority communities.
- Seekho Aur Kamao: It is a skill development scheme for youth of 14 - 35 years age group and aiming at improving the employability of existing workers, school dropouts etc.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK): It is a Scheme designed to address the development deficits of the identified Minority Concentration Areas.
- The areas of implementation, under PMJVK, have been identified on the basis of minority population and socio-economic and basic amenities data of Census 2011 and will be known as Minority Concentration Areas.
- USTTAD (Upgrading the Skills and Training in Traditional Arts/Crafts for Development): Launched in May 2015 aims to preserve the rich heritage of traditional skills of indigenous artisans/craftsmen.
- Under this scheme HunnarHaats are also held all over the country to provide a nation-wide marketing platform to Minority artisans & entrepreneurs and to create employment opportunities.
- Prime Minister-Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PM Vikaas): New PM Vikas has been added to the Ministry of Minority Affairs' Budget in 2023.
- It is a skilling initiative focussing on the skilling, entrepreneurship and leadership training requirements of the minority and artisan communities across the country.
- The scheme is intended to be implemented in conjunction with the ‘Skill India Mission’ of the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship and through integration with the Skill India Portal (SIP).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1 In India, if a religious sect/community is given the status of a national minority, what special advantages it is entitled to? (2011)
- It can establish and administer exclusive educational institutions.
- The President of India automatically nominates a representative of the community to Lok Sabha.
- It can derive benefits from the Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q.2 In India, which of the following review the independent regulators in sectors l ike telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.? (2019)
- Ad Hoc Committees set up by the Parliament
- Parliamentary Department Related Standing Committees
- Finance Commission
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission
- NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q.3 With reference to the Parliament of India, which of the following Parliamentary Committees scrutinises and reports to the House whether the powers to make regulations, rules, sub-rules, by-laws, etc., conferred by the Constitution or delegated by the Parliament are being properly exercised by the Executive within the scope of such delegation? (2018)
(a) Committee on Government Assurances
(b) Committee on Subordinate Legislation
(c) Rules Committee
(d) Business Advisory Committee
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Keoladeo National Park
Why in News?
The Rajasthan Government has proposed to construct a zoo inside Keoladeo National Park, a World Heritage Site popularly known as Bharatpur bird sanctuary, to display a range of wetland species.
- The purpose of this zoo, called Wetland ex-situ Conservation Establishment (WESCE), is to display a range of wetland species, including rhinos, water buffaloes, crocodiles, dolphins and exotic species.
What is the Purpose of WESCE?
- The WESCE aims to rejuvenate the biodiversity of Keoladeo National Park, thereby boosting its outstanding universal values.
- The WESCE plan is part of the ambitious Rajasthan Forestry and Biodiversity Development Project (RFBDP) for which Agence Française de Développement (AFD), the overseas development arm of the French government, has agreed to fund up to Rs 12 crore over eight years.
- Several facilities are planned inside Keoladeo National Park, including,
- A breeding and reintroduction centre for locally extinct species (otters, fishing cats, blackbucks, hog deer, etc).
- An aquarium for indigenous species like Gangetic Dolphin, crocodiles; enclosures for the display of large wetland species like Indian Rhino, Water Buffalo, Barasingha (swamp deer); etc.
What are the Key Points of Keoladeo National Park?
- About:
- Keoladeo National Park is a wetland and bird sanctuary located in Bharatpur, Rajasthan. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most important bird-watching areas in the world.
- Chilika Lake (Orissa) and Keoladeo National Park (Rajasthan) were recognized as the first Ramsar Sites of India in 1981.
- Currently, Keoladeo National Park and Loktak Lake (Manipur) are in Montreux record.
- It is known for its rich avian diversity and abundance of waterbirds. The park is home to over 365 species of birds, including several rare and threatened species, such as the Siberian crane.
- Different species from far-flung areas of the northern hemisphere visit the Sanctuary for breeding. The Siberian crane is one of the rare species that can be spotted here.
- Keoladeo National Park is a wetland and bird sanctuary located in Bharatpur, Rajasthan. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most important bird-watching areas in the world.
- Fauna:
- Animals such as Jackals, Sambar, Nilgai, wild cats, hyenas, wild boar, porcupine and mongoose can be found in the region.
- Flora:
- The principal vegetation types are tropical dry deciduous forest dominated by Acacia nilotica intermixed with dry grassland.
- River:
- Gambhir and Banganga are two rivers that flow through this National Park.
What are Protected Areas in Rajasthan?
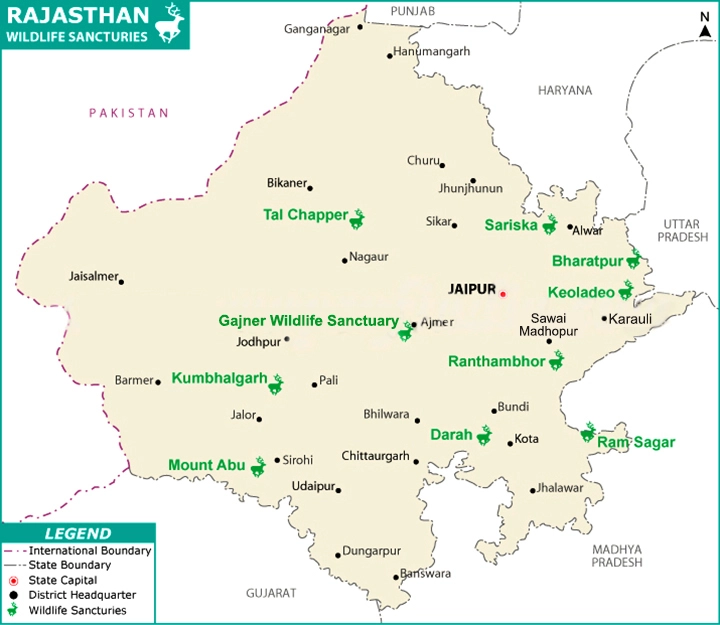
- Tiger Reserves:
- Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (RTR) in Sawai Madhopur
- Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR) in Alwar
- Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve (MHTR) in Kota
- National Park:
- Desert National Park, Jaisalmer
- Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Sajjangarh wildlife sanctuary, Udaipur
- National Chambal Sanctuary (on tri-junction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2014)
| Wetlands | Confluence of Rivers | |
| 1. | Harike Wetlands | Confluence of Beas and Satluj/Sutlej |
| 2. | Keoladeo Ghana | Confluence of Banas National Park and Chambal |
| 3. | Kolleru Lake | Confluence of Musi and Krishna |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Hajj Pilgrimage
Why in News?
The ministry of Minority Affairs has announced a new Haj policy under which the application forms have been made available for free and the package cost per pilgrim has been reduced by Rs 50,000.
- The reduction of Rs 50,000 comes primarily in the form of relaxation of norms for foreign currency – earlier a Haj pilgrim had to submit the equivalent of 2,100 Saudi Riyal, amounting to approximately Rs 44,000, that was submitted to the Haj Committee for foreign exchange.
What is Hajj Pilgrimage?
- The Hajj is a religious pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia that is mandatory for all able-bodied Muslims who can afford it. It is one of the Five Pillars of Islam and is considered a central part of Muslim religious life.
- Five Pillars:
- Shahada (Faith): The declaration of faith in the oneness of God and the acceptance of Muhammad as God's prophet.
- Salah (Prayer): Performing the five daily prayers facing the Kaaba in Mecca.
- Zakat (Charity): Giving a portion of one's wealth to those in need.
- Sawm (Fasting): Fasting during the month of Ramadan.
- Hajj (Pilgrimage): Making a pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca at least once in a lifetime if one is physically and financially able.
- Five Pillars:
- The Hajj takes place during the Islamic month of Dhu al-Hijjah and involves several rituals.
- Dhu al-Hijjah is the twelfth and final month of the Islamic calendar. It is considered one of the most sacred months in the Islamic year and is seen as a time of renewal, spiritual growth, and reflection, and is considered an important time to strive for greater closeness with God.
- Participating in the Hajj is seen as a way to demonstrate one's devotion to God and to earn spiritual merit, and it is a source of great pride and inspiration for many Muslims.
How is Hajj Pilgrimage Promoted by India?
- Ministry of Minority Affairs is the nodal ministry to conduct Haj pilgrimage in India.
- Haj pilgrimage for the Indian Pilgrims is conducted either through Haj Committee of India (HCoI), which is a statutory organization under the administrative control of Ministry of Minority Affairs or through the Haj Group Organisers (HGOs) dully approved by Ministry.
- Also, the Hajj pilgrimage is promoted by various religious organizations, Islamic cultural centers, and other government agencies.
- India signed the Haj 2023 bilateral agreement with Saudi Arabia. According to the agreement, a total of 1,75,025 Indian Haj pilgrims will be able to perform Haj, reportedly the highest in history.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
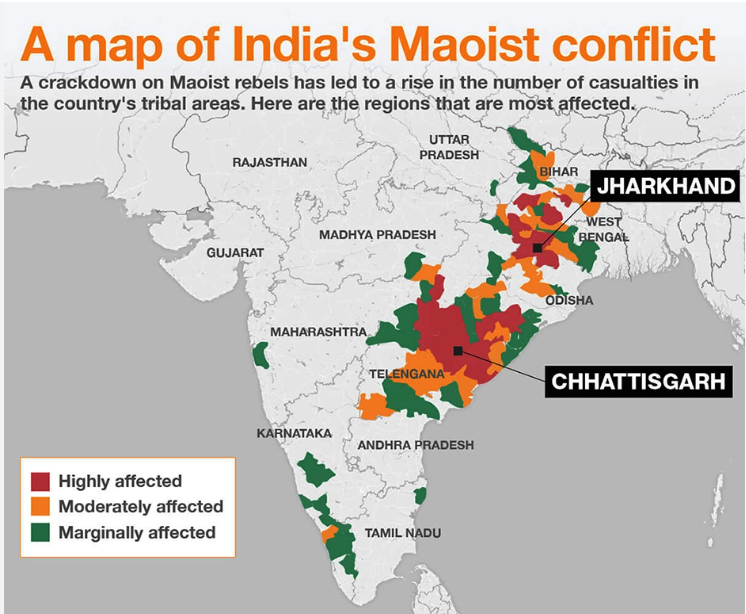
Record Decline in LWE Related Violence
The Union Home Minister in a meeting said that for the first time in 4 decades, the number of deaths of civilians and security forces in Left Wing Extremism (LWE) came down under 100 in 2022. Violence related to LWE had come down by 76% in 2022 as compared to 2010.
LWE organizations are the groups that try to bring change through violent revolution. They are against democratic institutions and use violence to subvert the democratic processes at the ground level.
The MHA’s policy to deal with LWE is a three-pronged approach – strategy to curb extremist violence with ruthless approach, better coordination between Centre and states, and eliminating support for LWE through public participation in development.
As part of the goal to ensure all-round development in LWE affected areas; construction of 11,811 km of roadways had been completed to improve road connectivity, 2,343 mobile towers had been installed during the last 8 years, 245 Eklavya Model Residential Schools had been sanctioned in 90 LWE-affected districts and 121 of them were now functional.
Read More - Left Wing Extremism
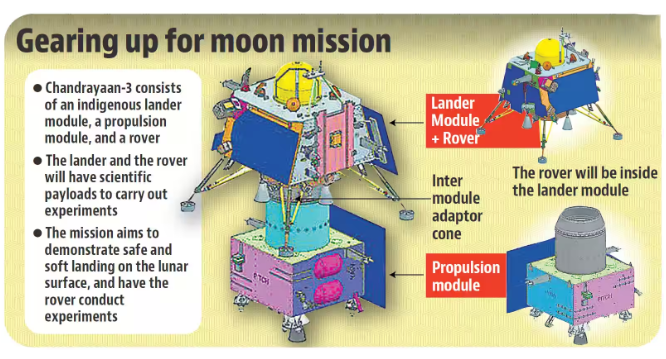
Possible Landing Sites for Chandrayaan 3
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has finalised the coordinates of three possible landing sites for its third lunar mission – Chandrayaan-3 – expected to be launched later in 2023. The prime landing site for Chandrayaan-3 lies between Manzius U and Boguslawsky M craters on the moon. The moon’s southern polar region is of particular interest to scientists because there’s a possibility of finding water ice.
Chandrayaan programme, also known as the Indian lunar exploration programme, is an ongoing series of outer space missions by ISRO.
Chandrayaan-1 was launched in 2008 and was successfully inserted into lunar orbit. Chandrayaan-2 was successfully launched and inserted into lunar orbit in 2019, but its lander crash-landed on the moon’s surface when it deviated from its trajectory while attempting to land in Sept 2019. Chandrayaan-3 will be launched by Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM3) rocket from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
Other upcoming ISRO missions for 2023 include - Aditya-L1, India’s first dedicated scientific mission to study the sun, and Gaganyaan’s uncrewed ‘G1’ mission.
Read More - Chandrayaan-3
India Seeks Armed Predator Drones from US
The Indian armed forces are seeking 18 armed Predator MQ 9A drones from the US. The Predator armed drones can fly up to 50,000 feet for up to 24 hours and carry an option of Hellfire air-to-ground missiles for high-value targets or air-to-air missiles to bring down aerial enemy targets.
Of these 18 drones from the US, 6 drones will be provided to each of the three services.
The Indian Navy already has two General Atomics-manufactured Sea Guardian (MQ 9B) drones for maritime domain awareness on lease from the US. Currently, the navy is the leading service in armed drone acquisition and deployment.
The National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO) (an electronic and spatial intelligence organisation) will also soon acquire 8 Indian-manufactured Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) drones for border surveillance. The MALE drones have been built with the help of Israel in a joint venture in Gujarat.
Both China and Pakistan have the Wing Loong II armed drones in their arsenals, therefore, the acquisition of these surveillance and predator drones is significant from India’s security perspective.
Read More - Atma Nirbhar India in Defence Production, India-Us Defence Ties
Steps Towards Prison Reforms
Rajasthan has adopted an open prison model where convicts stay on community land without high walls or strict surveillance. The move has promoted a reformative form of punishment and succeeded in transforming the lives of inmates. The state has opened 40 such camps.
Under the system, Prisoners who have served 1/3rd of their sentences are eligible to shift to the open jails. In these open camps, each inmate can stay with 3 family members, some are also established at gaushalas to enable the inmates to work at the cow shelters.
As minimum-security facilities, open prisons require 92.4% less staff compared to closed jails and the cost incurred per prisoner is only ₹500/month.
In another significant move, Tihar jail is installing AI-powered CCTV cameras to monitor inmates and fight crime. The premises will also have a real-time grievance redressal system and optical fibre network. Tihar jail is the largest prison complex of South Asia. With a capacity to house 5,200 inmates, it has 12,762 prisoners at present. The overcrowding has made monitoring inmates difficult leading to commitment of many crimes from inside the jail.
Read More - Need for Prison Reforms