Indian Society
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India Report 2021: NCRB
- 30 Aug 2022
- 8 min read
For Prelims: National Crime Records Bureau, Reports of NCRB, National and Sectoral Data
For Mains: Population and Associated Issues, Key Findings of the NCRB Report, Reports of NCRB, Functions of NCRB
Why in News?
Recently, the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released the “Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India Report 2021.”
- The report tabled figures for “Crime Against Women”, “Suicide” and “Crime Rates”.
What are the Report’s findings for Crime Against Women?
- National Figures:
- The rate of crime against women (number of incidents per 1 lakh population) increased from 56.5% in 2020 to 64.5% in 2021.
- 31.8%: Cruelty by husband or his relatives
- 20.8%: Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage her Modesty
- 17.6%: Kidnapping and Abduction
- 7.40%: Rape
- The rate of crime against women (number of incidents per 1 lakh population) increased from 56.5% in 2020 to 64.5% in 2021.
- State:
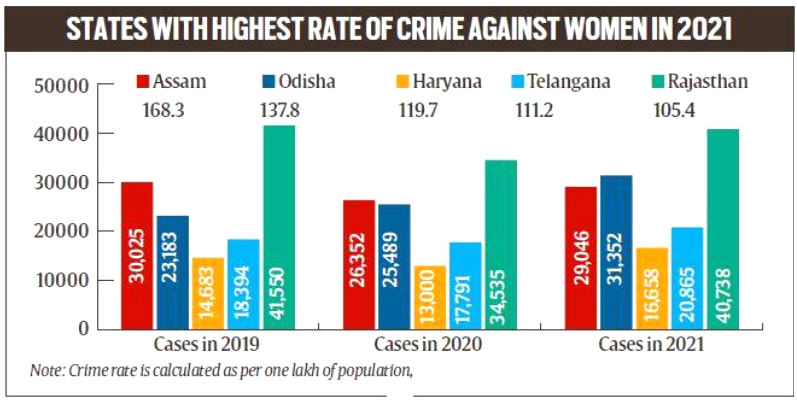
- The highest rate of crime against women in 2021 was registered in Assam 168.3% followed by Odisha, Haryana, Telangana and Rajasthan.
- Rajasthan showed a marginal decrease in the actual number of cases while the three other states (Odisha, Haryana and Telangana) marked an increase.
- In terms of actual number of cases registered in 2021, UP tops the list followed by Rajasthan, Maharashtra, West Bengal and Odisha.
- Nagaland stood out with the lowest number of crimes against women registered in the past three years.
- The highest rate of crime against women in 2021 was registered in Assam 168.3% followed by Odisha, Haryana, Telangana and Rajasthan.
- Union Territories:
- Among Union Territories, Delhi had the highest rate of crime against women in 2021 at 147.6%.
- Cities:
- Jaipur had the highest rate at over 194%, followed by Delhi, Indore and Lucknow.
- Chennai and Coimbatore (Both in Chennai) had the lowest rate.
- In actual numbers among these cities, Delhi topped in 2021 (13,892) followed by Mumbai, Bengaluru and Hyderabad.
- Jaipur had the highest rate at over 194%, followed by Delhi, Indore and Lucknow.
- Domestic Violence & Dowry Deaths:
- Only 507 cases were registered in the country under the Domestic Violence Act in 2021 — 0.1% of the total cases of crime against women.
- The highest number of cases (270) were filed in Kerala.
- 6,589 cases of dowry deaths were registered in 2021 with the highest number of such deaths registered in UP and Bihar.
- Only 507 cases were registered in the country under the Domestic Violence Act in 2021 — 0.1% of the total cases of crime against women.
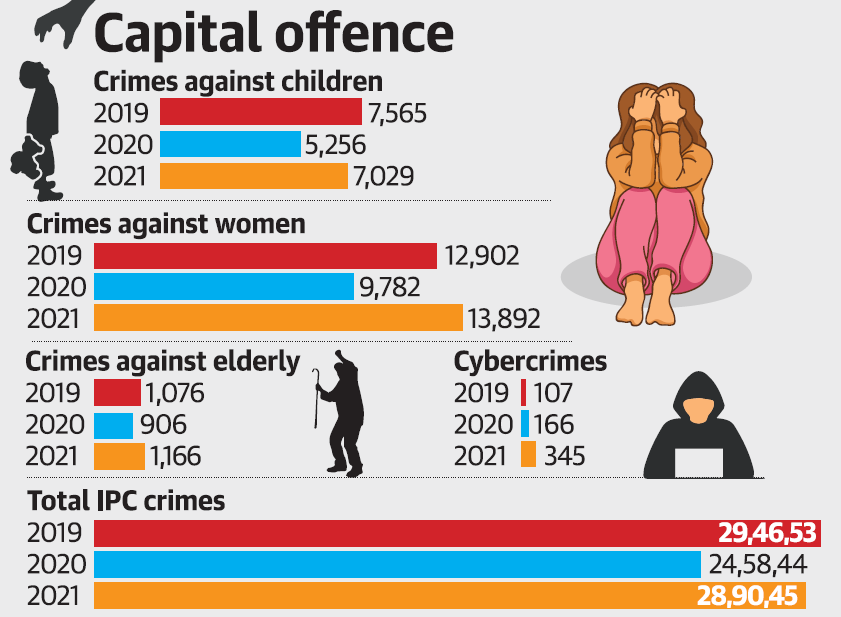
What are the Report’s findings for Suicide Rate?
- Daily Wager:
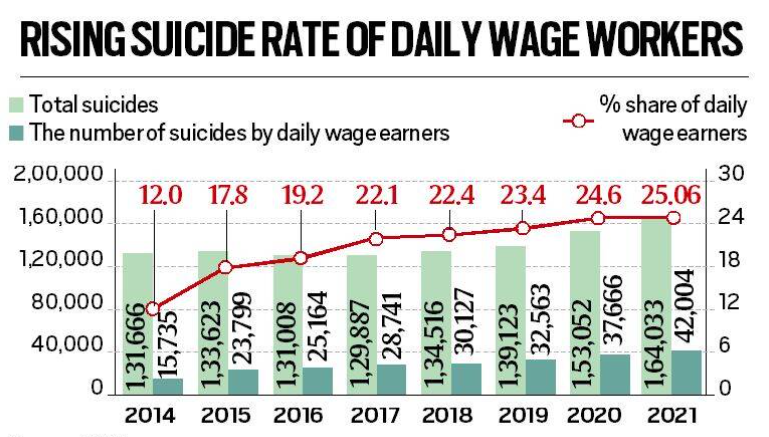
- Daily wage earners remained the largest profession-wise group among suicide victims in 2021, accounting for 42,004 suicides (25.6%).
- The share of daily wagers death by suicide has crossed the quarter mark for the first time.
- At the national level, the number of suicides increased by 7.17% from the years 2020 to 2021.
- However, the number of suicides in the daily wage group rose by 11.52% during this period.
- Farming Sector:
- The overall share of “Persons engaged in farming sector” among the total recorded suicides stood at 6.6% during 2021.
- Profession Wise Distribution:
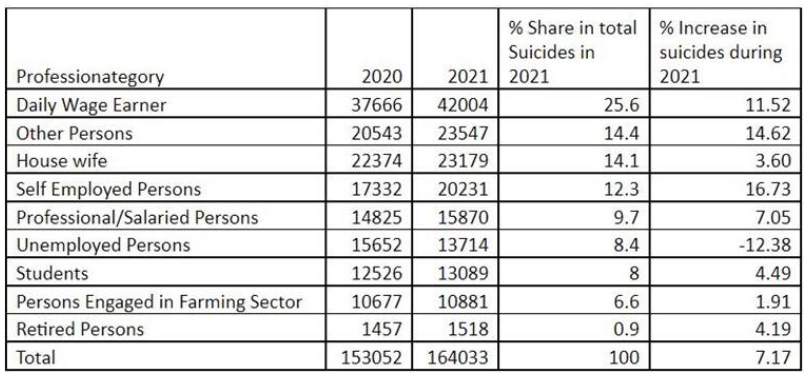
- The highest increase of 16.73% was recorded by “self-employed persons”.
- The “unemployed persons” group was the only one that saw a decline in suicides, with the number dipping by 12.38% from 15,652 in 2020 to 13,714 suicides in 2021.
- Reasons for Suicide:
- 33.2%: Family Problems (other than marriage related problems)
- 4.8%: Marriage Related Problems
- 18.6%: Illness
- State:
- Maharashtra topped the country in terms of the number of suicides reported in 2021 followed by Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh.
- Maharashtra contributed 13.5% to the total number of suicides registered across the country in 2021.
- Maharashtra topped the country in terms of the number of suicides reported in 2021 followed by Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh.
- Union Territories:
- Delhi recorded the highest number of 2,840 suicides.
What are the Report’s findings for Crime Rates?
- About:
- Registered violent crimes such as rape, kidnapping, crimes against children and robberies increased again across India in 2021.
- Pandemic-related restrictions led to a decline in these severe offences in 2020.
- Murders, which did not come down even in 2020, continued to increase last year too.
- Registered violent crimes such as rape, kidnapping, crimes against children and robberies increased again across India in 2021.
- Crime Wise Data:
- Rape cases:
- Increased by 13% (28,046 in 2020)
- Rajasthan had the highest rate of rape for 2021 at 16.4% and topped in actual numbers with 6,337 cases registered in 2021.
- Kidnapping:
- Rose by 20% (84,805 in 2020)
- Murder:
- Increased to 29,272 cases in 2021 from 29,193 in 2020
- Uttar Pradesh registered the highest number of murders followed by Bihar and Maharashtra.
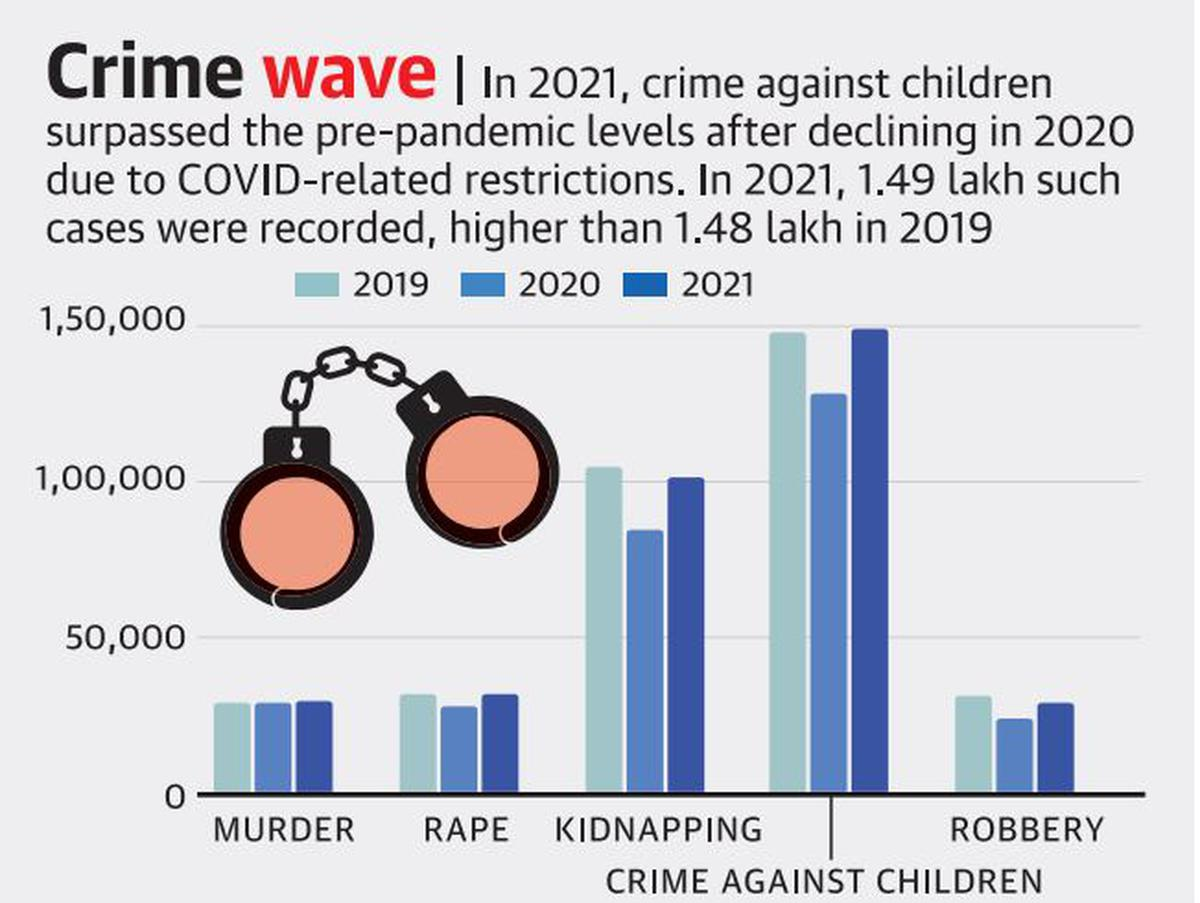
- Crime Against Children:
- Crime against children surpassed the pre-pandemic levels after declining in 2020 due to Covid-related restriction.
- In 2021, 1.49 lakh such cases were recorded, higher than 1.48 lakh in 2019.
- Sikkim has the highest rate of sexual offences against children followed by Kerala, Meghalaya, Haryana and Mizoram.
- Rape cases:
- Covid-19 Violations Dips:
- The decline in overall crimes in 2021 can be attributed to a sharp decrease in cases registered under “disobedience to order duly promulgated by a public servant (Section 188 of IPC).
- Such cases were registered mainly over violations of COVID-19 norms. They were also recorded under ‘Other IPC Crimes’ and ‘Other State Local Acts.’
- The number of cases filed under Section 188 of the IPC has almost halved from 6.12 lakh cases in 2020 to 3.22 lakh in 2021.
- The decline in overall crimes in 2021 can be attributed to a sharp decrease in cases registered under “disobedience to order duly promulgated by a public servant (Section 188 of IPC).
What is the National Crime Records Bureau?
- About:
- NCRB, headquartered in New Delhi, was set-up in 1986 under the Ministry of Home Affairs to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Task Force (1985).
- Functions:
- The Bureau has been entrusted to maintain National Database of Sexual Offenders (NDSO) and share it with the States/UTs on regular basis.
- NCRB has also been designated as the Central Nodal Agency to manage technical and operational functions of the ‘Online Cyber-Crime Reporting Portal’ through which any citizen can lodge a complaint or upload a video clip as evidence of crime related to child pornography, rape/gang rape.
- The responsibility of implementation of the Inter-operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS) has also been given to the NCRB.
- ICJS is a national platform for enabling integration of the main IT system used for delivery of Criminal Justice in the cuntry.
- It seeks to integrate the five pillars of the system viz Police (through Crime and Criminal Tracking and Network Systems), e-Forensics for Forensic Labs, e-Courts for Courts, e-Prosecution for Public Prosecutors and e-Prisons for Prisons.
- Major Publications:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. Why do some of the most prosperous regions of India have an adverse sex ratio for women? Give your arguments. (2014)