Social Justice
NCRB’s Crime in India 2022 Report
For Prelims: National Crime Records Bureau, Cognizable crimes, Sedition, Accidental Deaths & Suicides.
For Mains: State of Crime in India and related issues, Effectiveness of legal frameworks in addressing different types of crimes.
Why in News?
The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) has recently unveiled its annual report titled "Crime in India for 2022," providing a comprehensive overview of crime trends across the nation.
What are the Key Highlights of NCRB’s Crime in India 2022 Report?
- Overall Crime Statistics:
- A total of over 58,00,000 cognizable crimes were registered, comprising both the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and Special & Local Laws(SLL) crimes.
- The registration of cases witnessed a 4.5% decline compared to 2021.
- A total of over 58,00,000 cognizable crimes were registered, comprising both the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and Special & Local Laws(SLL) crimes.
- Crime Rate Decline:
- The crime rate per lakh population dropped from 445.9 in 2021 to 422.2 in 2022.
- This decline is considered a more reliable indicator, considering the impact of population growth on absolute crime numbers.
- The crime rate per lakh population dropped from 445.9 in 2021 to 422.2 in 2022.
- Safest City:
- Kolkata emerged as the safest city in India for the third consecutive year, recording the least number of cognisable offences per lakh population among metropolises.
- Pune (Maharashtra) and Hyderabad (Telangana) secured the second and third positions, respectively.
- Kolkata emerged as the safest city in India for the third consecutive year, recording the least number of cognisable offences per lakh population among metropolises.
- Rise in Cyber Crimes:
- Cybercrime reporting surged by 24.4%, totalling 65,893 cases, a significant surge from 52,974 cases in 2021.
- Cyber fraud constituted the majority of cases (64.8%) of registered cases, followed by extortion (5.5%), and sexual exploitation (5.2%).
- The crime rate under this category rose from 3.9 in 2021 to 4.8 in 2022.
- Suicides and Causes:
- In 2022, India witnessed a significant surge in suicides, totalling over 1.7 Lakh cases, reflecting a concerning increase of 4.2% compared to 2021.
- The suicide rate also rose by 3.3%, calculated as the number of suicides per lakh of the population.
- Major causes included 'Family Problems,' 'Marriage Related Problems,' Bankruptcy and indebtedness, ‘Unemployment and professional issues’ and Illness'.
- Maharashtra reported the highest number of suicides, followed closely by Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, and Telangana.
- Daily wage earners constituted a significant portion, accounting for 26.4% of the total suicides.
- Agricultural workers and farmers were also disproportionately affected, forming a substantial part of the suicide statistics.
- This was followed by unemployed persons, who comprise 9.2% of all suicides reported in India in 2022. Among all suicides reported in the year, over 12,000 were of students.
- Escalating Crimes Against SCs and STs:
- The Crime in India report highlighted an overall increase in crimes and atrocities against Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) persons.
- States like Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Telangana experienced a surge in such cases in 2022.
- Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan persist as key contributors, consistently ranking among the top five states with the highest occurrences of crimes and atrocities against SC and ST communities.
- Other states witnessing elevated levels of such offences include Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Punjab.
- The Crime in India report highlighted an overall increase in crimes and atrocities against Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) persons.
- Crimes Against Women:
- A total of 4,45,256 cases of crime against women were reported in 2022, marking a 4% increase from 2021.
- Dominant categories included 'Cruelty by Husband or His Relatives,' 'Kidnapping & Abduction of Women,' and 'Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage Her Modesty.'
- Crimes Against Children:
- Cases of crimes against children showed an increase of 8.7% compared to 2021.
- A majority of these cases related to kidnapping and abduction (45.7%) and 39.7% were filed under the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act.
- Cases of crimes against children showed an increase of 8.7% compared to 2021.
- Crime against Senior Citizens:
- Cases of crimes against senior citizens rose by 9.3% to 28,545 cases compared to 26,110 cases in 2021.
- A bulk of these cases (27.3%) related to hurt followed by theft (13.8%) and forgery, cheating, and fraud (11.2%).
- Cases of crimes against senior citizens rose by 9.3% to 28,545 cases compared to 26,110 cases in 2021.
- Animal Attacks on the Rise:
- The NCRB report reveals a concerning trend in the number of people dying or getting injured due to animal attacks.
- A significant 19% increase in such incidents was recorded in 2022 compared to 2021.
- Maharashtra reported the highest number of cases, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh followed with varying numbers of reported cases.
- In addition, the number of animal/reptile and insect bites cases also increased by 16.7%.
- The highest number of bite cases were reported from Rajasthan followed by Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh, respectively.
- The NCRB report reveals a concerning trend in the number of people dying or getting injured due to animal attacks.
- Environment-Related Crime:
- The total number of environmental crimes in India decreased by around 18% in 2022, compared to 2021.
- Environment-related offenses include violations under seven acts :
- The Forest Act, 1927, Forest Conservation Act, 1980, The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, The Environmental (Protection) Act, 1986, Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, The Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000, National Green Tribunal Act, 2010.
- Environment-related offenses include violations under seven acts :
- The cases registered for violating the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981 and the Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 have increased by around 42%.
- Violations registered under the Environmental (Protection) Act, 1986 also have increased by around 31%.
- Forest offences increased in four states Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Haryana.
- Wildlife offences increased in five states including Bihar, Punjab, Mizoram, Rajasthan and Uttarakhand.
- Rajasthan, with the maximum number (30%) of wildlife crime cases in the country, recorded a 50% increase in such offenses in 2022 compared to 2021.
- The total number of environmental crimes in India decreased by around 18% in 2022, compared to 2021.
- Offences Against the State:
- Offences against the State exhibited a slight increase in 2022 compared to the previous year.
- There was approximately a 25% rise in cases registered under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA) during this period.
- Conversely, cases under the sedition Section of the IPC experienced a significant decline.
- The decrease in sedition cases may be attributed to the Supreme Court's decision in May 2022 to keep sedition cases in abeyance (hold).
- Offences against the State exhibited a slight increase in 2022 compared to the previous year.
- Rise in Economic Offences:
- Economic offences are categorized into criminal breach of trust, forgery, cheating, fraud (FCF), and counterfeiting.
- FCF accounted for the majority of cases (1,70,901 cases), followed by criminal breach of trust (21,814 cases) and counterfeiting (670 cases).
- The Crime in India report disclosed that government authorities confiscated fake Indian currency notes (FICN) totaling over Rs.342 crore in 2022.
- Economic offences are categorized into criminal breach of trust, forgery, cheating, fraud (FCF), and counterfeiting.
- Crimes Against Foreigners:
- 192 cases registered against foreigners, a 28% increase from 150 cases in 2021.
- 56.8% of victims were from the Asian continent, while 18% were from African countries.
- 192 cases registered against foreigners, a 28% increase from 150 cases in 2021.
- High Chargesheeting Rates:
- States with the highest charge sheeting rates under IPC crimes are Kerala, Puducherry, and West Bengal.
- Chargesheeting rate reflects cases where police reached the stage of framing charges against the accused, out of the total true cases (where a charge sheet was not laid but a final report submitted as true, plus the total cases charge-sheeted).
- States with the highest charge sheeting rates under IPC crimes are Kerala, Puducherry, and West Bengal.
What is the National Crime Records Bureau?
- NCRB was set up in 1986 to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals to assist the investigators in linking the crime to the perpetrators based on the recommendations of the Tandon Committee, National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) Taskforce (1985).
- It is part of the MHA and is headquartered in New Delhi.
- It also acts as a “national warehouse” for the fingerprint records of Indian and foreign criminals, and assists in locating interstate criminals through fingerprint search.
- The NCRB has four divisions: Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS), Crime Statistics, Finger Prints, and Training.
- NCRB Publications:
- Crimes in India, Accidental Deaths and Suicides, Prison Statistics, and Reports on Missing Women and children in India.
- These publications serve as principal reference points on crime statistics not only for police officers but also for criminologists, researchers, media and policymakers not only in India but abroad as well.


Biodiversity & Environment
The Global Climate 2011-2020: WMO
For Prelims: World Meteorological Organization, The Global Climate 2011-2020: A Decade of Acceleration, El Niño event, Greenhouse gases (GHG), Marine Heatwaves, Glaciers.
For Mains: The Global Climate 2011-2020: WMO, Environmental pollution and degradation.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) has published a report titled- The Global Climate 2011-2020: A Decade of Acceleration, concerning the alarming acceleration of climate change and its multifaceted impacts across the planet.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
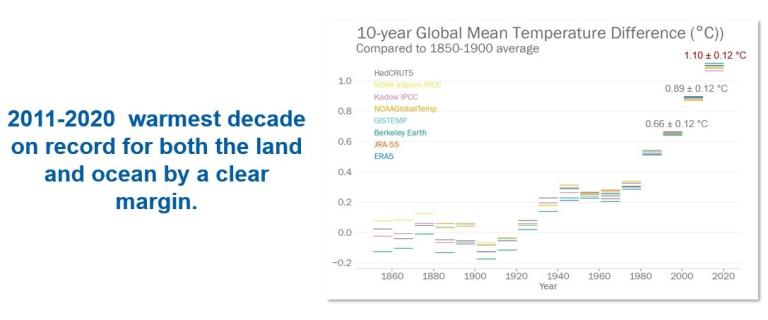
- Temperature Trends:
- The decade 2011-2020 emerged as the warmest on record for both land and ocean.
- Global mean temperature soared to 1.10 ± 0.12 °C above the 1850-1900 average, with each decade since the 1990s surpassing previous ones in warmth.
- Record high temperatures were reported in numerous countries, with 2016 (due to an El Niño event) and 2020 standing out as the warmest years.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
- Atmospheric concentrations of major greenhouse gases (GHG) continued to rise, especially CO2, reaching 413.2 ppm in 2020, primarily due to fossil fuel combustion and land-use changes.
- The decade witnessed an increase in average growth rates of CO2, highlighting the pressing need for sustainable emissions reduction to stabilize the climate.
- Oceanic Changes:
- Ocean warming rates accelerated significantly, with 90% of accumulated heat stored in the ocean. Warming rates doubled in the upper 2000m depth from 2006-2020, impacting marine ecosystems.
- Ocean acidification due to CO2 absorption posed challenges for marine organisms, affecting their shell and skeleton formation.
- Marine Heatwaves and Sea Level Rise:
- Marine Heatwaves increased in frequency and intensity, affecting about 60% of the ocean's surface between 2011 and 2020.
- Global mean sea level rise accelerated to 4.5mm/yr from 2011-2020, mainly due to ocean warming and ice mass loss.
- Glacier and Ice Sheet Loss:
- Glaciers globally thinned by about 1 meter/year between 2011 and 2020, with unprecedented mass loss, affecting water supplies.
- Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets lost 38% more ice compared to 2001-2010, contributing significantly to rising sea levels.
- Arctic Sea Ice Decline:
- Arctic sea ice continued its decline during the summer melt season, with a mean seasonal minimum extent 30% below the 1981-2010 average.
- Ozone Hole and Successes:
- The Antarctic ozone hole diminished in the 2011-2020 period, credited to successful international action under the Montreal Protocol.
- Efforts led to reduced chlorine entering the stratosphere from ozone-depleting substances.
- Impact on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Extreme weather events hindered progress toward SDGs, impacting food security, human mobility, and socioeconomic development.
- Improved early warning systems reduced casualties but economic losses from extreme events escalated.
- The 2011-2020 decade was the first since 1950 when there was not a single short-term event with 10,000 deaths or more.
What are the WMO’s Recommendations for Mainstreaming Action on Climate and Development Goals?
- Enhancing collective resilience against current and future global crises through collaboration and cooperation with international organizations and their partners
- Strengthening science-policy-society interaction to advance synergistic action
- Promoting institutional capacity-building and cross-sectoral and international collaboration at national, institutional, and individual levels, especially for the global South.
- Ensuring policy coherence and coordination among policymakers across sectors and departments for enhancing climate and development synergies at the national, sub-national, and multi-national levels.
What is WMO?
- About:
- It is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 192 Member States and Territories. India is a member.
- It originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which was established after the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Establishment:
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23rd March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology and related geophysical sciences.
- Headquarters:
- Geneva, Switzerland.


Biodiversity & Environment
Coastal Erosion
For Prelims: National Centre for Coastal Research, Marine Pollutions, Coastal processes and Hazards, Coastal Habitats and Ecosystem, Sea Level Rise, Disaster Management , Coastal Zone Management Plans , Flood Management Scheme, Coastal Management Information System
For Mains: Coastal erosion and its Impact on the Coastal Ecosystem.
Why in News?
The Union Minister of State for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change, in a written reply to Lok Sabha, shared insights on shoreline changes across the entire Indian coastline from multi-spectral satellite images and field-surveyed data from 1990 to 2016 conducted by the National Centre for Coastal Research (NCCR).
- NCCR, an attached office of the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, has been mandated to carry out all multidisciplinary research under the central domain: Marine Pollutions, Coastal processes and Hazards, Coastal Habitats and Ecosystem and Capacity Building and Training.
What are the Key Observations of NCCR Regarding Coastal Erosion?
- Some stretches of India’s shoreline are subject to varying degrees of erosion due to natural causes or anthropogenic activities.
- The shoreline analysis suggests that 34% of the coast is eroding, 28% is accreting and 38% is in a stable state.
- The state-wise analysis suggests that in the West Bengal (63%) and Pondicherry (57%) coasts, erosion exceeds more than 50%, followed by Kerala (45%) and Tamil Nadu (41%).
- Odisha (51%) is the only coastal state which is having more than 50% of accretion.
- The receding coastline will cause loss of land/habitat and the livelihood of fishermen in terms of losing the space for parking boats, mending nets and fishing operations.
What Government Measures have been Taken to Combat Coastal Erosion?
- Hazard Line: The Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC) has delineated the hazard line for the entire coast of the country.
- The hazard line is indicative of the shoreline changes, including sea level rise due to climate change.
- This line is to be used by agencies in Coastal States as a tool for Disaster Management including planning of adaptive and mitigation measures.
- Coastal Zone Management Plans: The hazard line features in the new Coastal Zone Management Plans of the coastal States/Union territories approved by the MoEFCC.
- Coastal Regulation Zone Notification, 2019 : MoEFCC has notified Coastal Regulation Zone Notification, 2019 with a view to conserve and protect coastal stretches, marine areas and to ensure livelihood security to the fisher and other local communities.
- The coastal regulations, however, permit setting up of erosion control measures in the coast.
- No Development Zones (NDZ): The notification also provides for NDZ along various categories of coastal areas to protect India’s coastline from encroachment and erosion.
- Flood Management Scheme: This scheme is the Ministry of Jal Shakti, including anti-sea erosion schemes planned and executed by the State Governments with their own resources as per priorities of States.
- The Union Government renders assistance to states which is technical, advisory, catalytic and promotional in nature.
- Coastal Management Information System (CMIS):
- It has been initiated under the Central Sector Plan Scheme "Development of Water Resources Information System".
- CMIS is a data collection activity carried out to collect near shore coastal data which can be used in planning, design, construction and maintenance of site specific coastal protection structures at vulnerable Coastal stretches.
- Coastal Erosion Mitigation: These measures have been taken up at Puducherry and Chellanam in Kerala, which helped in restoration and protection of coastal areas lost at Puducherry and flooding at Chellanam Fishing Village.
- Technical support has been extended to the coastal States in the design of coastal protection measures at vulnerable stretches and preparation of Shoreline Management Plans.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelim:
Q. In India, the problem of soil erosion is associated with which of the following? (2014)
- Terrace cultivation
- Deforestation
- Tropical climate
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
- Soil erosion is a natural process associated with geomorphic processes or agents such as running water, winds, coastal waves and glaciers.
- It occurs in forest lands, arid and semi-arid lands, agricultural lands, construction sites, roadways, disturbed lands, surface mines, glaciated and coastal areas and in areas where natural or geologic disturbances take place. In extreme cases, it may lead to total loss of soil and exposure of the bedrock.
- In India, the problem of soil erosion is most related to deforestation. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Perfectly conducted terrace cultivation captures the water. It is used for the purpose of inhibiting erosion, although extreme heavy rainfall will eventually erode the terrace. Without the terrace, the slope depends entirely on ground cover to prevent erosion. Thus, it can be said that terrace cultivation is a distant and a secondary cause of soil erosion when compared to deforestation. Hence, 1 is not correct.
- Regions in the tropical climate zones suffer the greatest rainfall-related soil erosion. While rainfall provides moisture critical for plant growth, it is also one of the prime causes of soil degradation, referred to as rainfall erosivity, which threatens food and water sustainability. However, tropical climate is not the most important soil erosion causing agent in India because the maximum area under soil erosion comes under subtropical, temperate and alpine climate rather than a tropical climate. Hence, 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Governance
Free of Cost Digital Tools to Marginalized Communities
For Prelims: National Education Policy 2020, PM e-VIDYA, Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA), Digitally Accessible Information System (DAISY), CBSE Podcast- Shiksha Vani, SATHEE portal
For Mains: Significance of government step to provide free of cost digital to marginalized communities.
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of State for Education provided details in a written response in the Lok Sabha about the measures taken by the Government to provide marginalized communities with digital tools at no cost.
- The National Education Policy 2020 calls for investment in digital infrastructure, online teaching platforms and tools, virtual labs, digital repositories, online assessments, technology and pedagogy for online teaching-learning etc.
What Government Initiatives Exist for Providing Digital Tools to Marginalized Communities?
- PM e-Vidhya:
- About:
- A comprehensive initiative called PM e-VIDYA was initiated as part of Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan in 2020.
- It unifies all efforts related to digital/online/on-air education to enable multi-mode access to education.
- The PM eVidya initiative is available to all the students across all the states free of cost.
- Key Components of PM eVidya:
- Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA): DIKSHA is the nation’s digital infrastructure for providing quality e-content for school education in States/Union Territories and QR coded Energized Textbooks for all grades.
- DIKSHA Portal and Mobile App: It has been created by the Ministry of Education as a storehouse of a large number of eBooks and e-Contents created by States/UTs and National level organizations.
- PM e-VIDYA DTH TV Channels: As per the Union Budget announcement for Financial Year 2022-23, the 12 DTH Channels have been expanded to 200 PM e-VIDYA DTH TV Channels to enable all States to provide supplementary education in various Indian languages for classes 1-12.
- CBSE Podcast- Shiksha Vani: The promotion of the extensive utilization of radio, community radio, and the CBSE podcast "Shiksha Vani" is actively encouraged.
- Digitally Accessible Information System (DAISY): Special e-content for visually and hearing impaired developed on DAISY and in sign language on NIOS website/ YouTube.
- Virtual labs and Skilling e-labs: To promote crucial critical thinking skills and to give space for creativity, it has been proposed to establish 750 virtual labs and 75 Skilling e-labs by 2023.
- The Virtual Labs are proposed for Science and Mathematics subjects for Classes 6th – 12th, and Skilling e-labs would provide a simulated learning environment.
- A vertical on Virtual Labs has been created on DIKSHA platform.
- Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA): DIKSHA is the nation’s digital infrastructure for providing quality e-content for school education in States/Union Territories and QR coded Energized Textbooks for all grades.
- About:
- Samagra Shiksha:
- ICT and Digital initiatives component of centrally sponsored scheme of Samagra Shiksha covers Government and Aided schools having classes VI to XII.
- Sathee Portal:
- To assist students preparing for competitive exams across the country, a SATHEE portal has been developed in collaboration with IIT Kanpur.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Mains
Q1. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)
Q2. Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (2021)


Important Facts For Prelims
CCPA Issues Guidelines Safeguarding Against Dark Patterns
Why in News?
The Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA), India's top consumer watchdog, has recently notified guidelines for prevention and regulation of Dark Patterns, 2023.
- These guidelines, issued under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, are designed to protect consumers from deceptive practices employed by online platforms.
What are Dark Patterns?
- Dark patterns, also known as deceptive patterns, refer to strategies employed by websites and apps to make users perform actions they did not intend to or discourage behaviors that are not advantageous for the companies.
- These patterns often exploit cognitive biases and employ tactics such as false urgency, forced actions, hidden costs etc.
What are the Key Guidelines for Prevention and Regulation of Dark Patterns?
- The guidelines prohibit the use of dark patterns to mislead or coerce users.
- The guidelines also urge entities to retain users and drive sales using ethical and consumer-centric approaches.
- These guidelines regarding the dark patterns extend their applicability to all platforms offering goods and services in India, encompassing advertisers and sellers.
- E-commerce players, websites, and apps are subject to the regulatory framework established by these guidelines.
- The CCPA has outlined 13 types of dark patterns in its notification. They are:
- False Urgency: Creating a false sense of urgency or scarcity to induce immediate purchases.
- Basket Sneaking: Inclusion of additional items at checkout without user consent, resulting in higher payments.
- Confirm Shaming: Using fear or shame to nudge users into specific actions for commercial gains.
- Forced Action: Compelling users to take actions requiring additional purchases or sharing personal information.
- Subscription Trap: Making cancellation complex, hiding options, or forcing payment details for free subscriptions.
- Interface Interference: Manipulating the user interface to misdirect users from intended actions.
- Bait and Switch: Deceptively serving an alternate outcome than advertised based on user actions.
- Drip Pricing: Concealing prices upfront, revealing them post-confirmation, or preventing service use unless additional items are purchased.
- Disguised Advertisement: Posing advertisements as other content to trick users into clicking.
- Nagging: Persistent interactions disrupting and annoying users for commercial gains.
- Trick Question: Deliberate use of confusing language to misguide users.
- Saas Billing: Generating recurring payments in a software as a service (SaaS) model.
- Rogue Malwares: Using ransomware or scareware to mislead users into paying for fake malware removal tools.
What is the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)?
- CCPA established under the Consumer Protection Act of 2019, safeguards and defends consumers' rights, issuing guidelines for effective enforcement and enhancement of consumer rights.
- The objective of the CCPA is to promote, protect and enforce the rights of consumers as a class.
- It will be empowered to conduct investigations into violation of consumer rights and institute complaints / prosecution, order recall of unsafe goods and services, order discontinuation of unfair trade practices and misleading advertisements, impose penalties on manufacturers/endorsers/publishers of misleading advertisements.


Important Facts For Prelims
Snakebite Envenoming
Why in News?
Recently, a team of experts from a United Kingdom university have set up a pilot study in Burujhari village in Odisha, India to help it reduce the number of fatalities from Snakebite Envenoming (SE) and will look into solutions like an Early Warning System for snakes.
- India has the biggest burden of deaths due to Snake Bites in the world, with most of the cases in rural India.
- WHO (World Health Organization) formally listed Snakebite Envenoming as a highest-priority Neglected Tropical Disease (NTD) in June 2017.
What is Snakebites Envenoming?
- About:
- SE is a potentially life-threatening disease that typically results from the injection of a mixture of different toxins (venom) following the bite of a Venomous Snake and can also be caused by having venom sprayed into the eyes by certain species of snakes that have the ability to spit venom as a defence measure.
- Snakebite poses a significant daily health risk in rural tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, the Middle East, Asia, Oceania, and Latin America, particularly for the hundreds of millions of people in rural and peri-urban communities reliant on agriculture and subsistence activities for survival
- Impact:
- Many snakebite victims, mostly in developing countries, suffer from long-term complications such as deformities, contractures, amputations, visual impairment, renal complications and psychological distress.
- Deaths from SE:
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 81,410 to 137,880 people around the world die each year because of snakebites.
- WHO’s Roadmap for SE:
- WHO launched its roadmap in 2019 with an aim to halve death and disability from snakebite by 2030.
- In order to create a sustainable market for antivenoms there is a need for a 25% increase in the number of competent manufacturers by 2030.
- WHO has planned a pilot project to create a global antivenom stockpile.
- Integrating snakebite treatment and response into national health plans in affected countries, including better training of health personnel and educating communities.
- WHO launched its roadmap in 2019 with an aim to halve death and disability from snakebite by 2030.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Much before the WHO roadmap was launched, researchers from Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) started community awareness and health system capacity building from the year 2013.
- In alignment with WHO's Snakebite Envenoming Strategy and the United Nations' Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, India ratified a National Action Plan in 2015 to combat this issue.
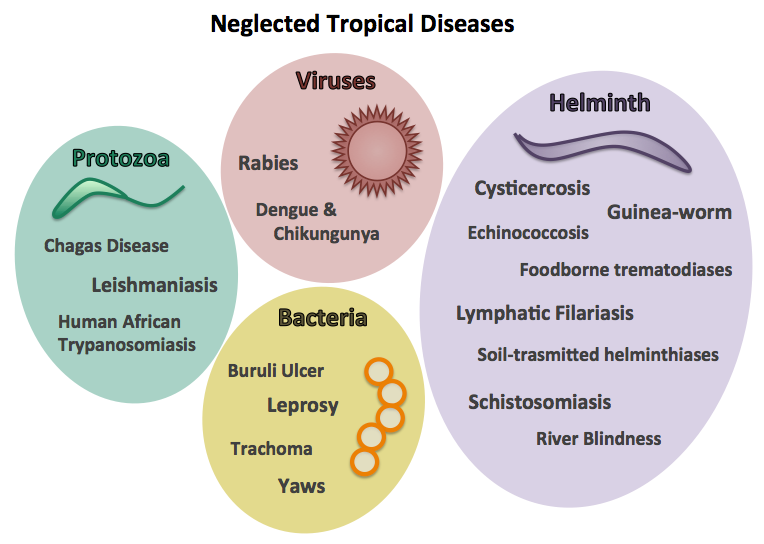
What are Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)?
- NTDs are a group of infections that are most common among marginalized communities in the developing regions of Africa, Asia and the Americas.
- They are caused by a variety of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa and parasitic worms.
- NTDs are especially common in tropical areas where people do not have access to clean water or safe ways to dispose of human waste.
- These diseases generally receive less funding for research and treatment than malaises like tuberculosis, HIV-AIDS and malaria.
- Examples of NTDs are: snakebite envenomation, scabies, yaws, trachoma, Leishmaniasis and Chagas disease etc.


Important Facts For Prelims
Indian Navy Day 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister (PM) of India declared on Indian Navy Day 2023 a government decision to eliminate the colonial military legacy by revealing that designations within the Indian Navy would be revamped to align with Indian cultural roots.
- PM also paid tributes to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, and unveiled a grand statue of the 17th century Maratha king at the coastal fort of Sindhugarh, Maharashtra.
What are the Announcements Made on Navy Day?
- Symbolic Epaulettes and Indigenous Maritime Values:
- The PM mentioned that the epaulettes (ornamental shoulder pieces denoting rank) adorned by Naval officers would now feature the emblem of Shivaji Maharaj's army.
- He connected the Naval flag with the heritage of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, emphasizing the inspiration drawn from the historical figure.
- The PM reiterated Shivaji Maharaj's belief in the power of controlling the seas and credited the Navy for embodying this principle.
- Aligning with the Prime Minister's call to discard the colonial mindset, the Navy adopted a new ensign in 2022 inspired by the legacy of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- Honoring Naval Warriors and India’s Maritime History:
- The PM paid tribute to historical naval warriors like Kanhoji Angre, Mayaji Naik Bhatkar, and Hiroji Indulkar.
- Indian Navy has named its training establishment in Lonavla as INS Shivaji, and the shore-based logistics and administrative hub of the Western Naval Command, Mumbai, as INS Angre — after Kanhoji Angre (1669-1729), the celebrated Maratha naval commander.
What were the Naval Legacies of the Maratha Empire under Shivaji?
- Inspired by conflicts with the Siddis and observing Portuguese naval strength, Shivaji emphasized the need for a robust navy and efficient port system. He strategically constructed coastal forts like Vijaydurg and Sindhudurg to safeguard against adversaries.
- Under Shivaji's leadership, the Maratha navy flourished, establishing strongholds at Kolaba, Sindhudurg, Vijaydurg, and Ratnagiri. Surpassing 500 ships, the Maratha navy successfully thwarted both Portuguese and British advances for over four decades. However, after Shivaji's death in 1680, the Maratha navy weakened, marking a decline in its power and influence.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news? (2018)
(a) An Israeli radar system
(b) India’s indigenous anti-missile program
(c) An American anti-missile system
(d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea.
Ans: (c)
Q. From which one of the following did India buy the Barak anti-missile defence systems? (2008)
(a) Israel
(b) France
(c) Russia
(d) USA
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
One District One Product in PMFME Scheme
The Union Minister of State for Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) in a written reply to Lok Sabha has given information about One District One Product (ODOP).
- The MoFPI has approved ODOP for 713 districts of 35 States and UTs under Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme on the recommendations of respective States / UTs.
- ODOP is an initiative to boost economic growth at the district level by promoting and branding one product from each district of the country.
- ODOP has been approved for all the 36 districts of State of Maharashtra including 20 unique products.
- No ODOP product has been recommended by the State of West Bengal under PMFME Scheme.
Read More: One District One Product' Scheme


Rapid Fire
Fake MGNREGS Job Cards Deleted
Over 10 lakh job cards have been deleted with the reason ‘fake job card’ under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) in the last two financial years 2021-22 and 2022-23.
- As per Section 25 of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005, whoever contravenes the provisions of this Act shall on conviction be liable to a fine which may extend to one thousand rupees.
- The highest number of fake job cards have been deleted in Uttar Pradesh and followed by Madhya Pradesh in 2021-22, and 2022-23.
- MGNREGS was launched by the Ministry of Rural Development to guarantee 100 days of employment in every financial year to adult members of any rural household willing to do public work-related unskilled manual work.
Read More: Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA)