Social Justice
Rehabilitation Scheme for Victims of Trafficking
For Prelims: National Crime Records Bureau, Article 23 and 24 of the Constitution of India, Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act, 1956 (ITPA), Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006, United Nations Convention on Transnational Organised Crime , Protection of Children from Sexual offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
For Mains: Status of Human Trafficking in India,Major Causes and Impacts of Human Trafficking.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India, has approved a scheme that aims to provide financial assistance to states and Union Territories to establish protection and rehabilitation homes for victims of trafficking, particularly in states with international borders.
What are the Major Provisions of the Scheme?
- Financial Assistance for Protection and Rehabilitation Homes: The scheme aims to provide financial aid to states and Union Territories in order to establish protection and rehabilitation homes for victims of trafficking.
- These homes will cater to the specific needs of victims, particularly minors and young women, by providing shelter, food, clothing, counseling, primary health facilities, and other essential daily needs.
- Strengthening Anti-Human Trafficking Units (AHTUs): In addition to the establishment of protection and rehabilitation homes, the government has allocated funds from the Nirbhaya Fund to support the strengthening of anti-human trafficking units in every district across all states and Union Territories.
- The funding has been extended to all states and Union Territories, including AHTUS in Border Guarding Forces like the BSF (Border Security Force) and SSB (Sashastra Seema Bal).
- Presently, there are 788 functional AHTUs, including 30 within Border Guarding Forces, across the country.
What is the Status of Human Trafficking in India?
- About:
- Human trafficking is a global issue that affects numerous countries, and India is no exception.
- With its large population, economic disparities, and complex social dynamics, India has become a hotspot for various forms of human trafficking.
- Statistics:
- According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data, 2,189 cases of human trafficking were filed in 2022, involving 6,533 victims.
- Among these victims, 4,062 were female, and 2,471 were male. Notably, 2,877 victims were minors.
- While more underage boys (1,570) were trafficked in 2021 than girls (1,307), the trend was reversed when considering adult victims, with women outnumbering men.
- Certain states have reported higher numbers of human trafficking cases, as indicated by AHTUs:
- Telangana, Maharashtra, and Assam had the highest number of cases registered in their respective AHTUs in 2021.
- These states, due to their geographical locations and other factors, are particularly vulnerable to cross-border trafficking and require special attention and resources.
- India’s neighboring countries often serve as sources for traffickers who exploit women and girls by offering false promises of employment or a better standard of living.
- According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data, 2,189 cases of human trafficking were filed in 2022, involving 6,533 victims.
- Various Forms of Human Trafficking:
- Forced Labor: Victims are coerced or deceived into working under exploitative conditions, including industries like agriculture, construction, domestic work, and manufacturing.
- Sexual Exploitation: Individuals, particularly women and children, are trafficked for commercial sexual exploitation, including prostitution and pornography.
- Child Trafficking: Children are trafficked for various purposes, including child labor, forced begging, child marriage, adoption scams, and sexual exploitation.
- Bonded Labor: People are trapped in a cycle of debt bondage, where they are forced to work to repay a debt that often continues to increase due to exploitative practices.
- Organ Trafficking: Trafficking of organs involves the illegal trade of organs like kidneys, liver, and corneas for transplantation purposes.
- Relevant Laws in India and International Conventions:
- Article 23 and 24 of the Constitution of India.
- Article 23 prohibits human trafficking and begar (forced labour without payment).
- Article 24 forbids employment of children below the age of 14 years in dangerous jobs like factories and mines.
- Indian Penal Code (IPC) Section:
- Section 370 and 370A of IPC provide for comprehensive measures to counter the menace of human trafficking including trafficking of children for exploitation in any form including physical exploitation or any form of sexual exploitation, slavery, servitude, or the forced removal of organs.
- Sections 372 and 373 dealing with selling and buying of girls for the purpose of prostitution.
- Other Legislations:
- The Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act, 1956 (ITPA) is the premier legislation for prevention of trafficking for commercial sexual exploitation.
- There are other specific legislations enacted relating to trafficking in women and children - Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006, Bonded Labour System (Abolition) Act, 1976, Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Act, 1986, Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994,
- Protection of Children from Sexual offences (POCSO) Act, 2012, is a special law to protect children from sexual abuse and exploitation.
- International Convention:
- United Nations Convention on Transnational Organised Crime (UNCTOC) has a Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, especially Women and Children( India has ratified ).
- SAARC Convention on Preventing and Combating Trafficking in Women and Children for Prostitution( India has ratified ).
- Article 23 and 24 of the Constitution of India.
What are the Major Causes and Impacts of Human Trafficking?
- Causes:
- Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, unemployment, and lack of economic opportunities create vulnerability, pushing individuals into desperate situations where they are more likely to be trafficked.
- Gender Inequality and Discrimination: Deep-rooted gender inequalities, discrimination, and violence against women and girls increase their susceptibility to trafficking.
- This includes issues such as dowry-related violence, child marriage, and lack of access to education.
- Political Instability and Conflict: Regions affected by political instability, armed conflict, and displacement provide fertile ground for trafficking, as people are displaced and left vulnerable without protection.
- Corruption and Organized Crime: Widespread corruption within law enforcement agencies, immigration authorities, and judicial systems enables traffickers to operate with impunity, making it difficult to identify, investigate, and prosecute cases effectively.
- Impacts:
- Physical and Psychological Trauma: Trafficking victims endure physical and psychological abuse, violence, and trauma.
- They often suffer from injuries, sexually transmitted infections, malnutrition, and physical exhaustion.
- Moreover, the psychological impact includes anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and a loss of trust in others.
- Violation of Human Rights: Human trafficking fundamentally violates the victims' human rights. It deprives them of their freedom, dignity, and security.
- Economic Exploitation: Trafficked individuals are subjected to harsh working conditions, long hours, and little or no pay.
- In many cases, victims become trapped in debt bondage, where they are forced to work to repay an ever-increasing debt, making escape from exploitation extremely difficult.
- Disruption of Social Fabric: Human trafficking disrupts the social fabric of communities and families.
- It tears apart families as individuals are forcibly separated from their loved ones. This disruption leads to loss of social support networks, and strained relationships within communities.
- Physical and Psychological Trauma: Trafficking victims endure physical and psychological abuse, violence, and trauma.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Legislation and Law Enforcement: There is a need to enact and enforce robust anti-trafficking laws that criminalize all forms of human trafficking and provide adequate penalties for offenders.
- Also, there is a need to enhance training programs for law enforcement agencies, judiciary, and border control officers to identify and respond to trafficking cases effectively.
- Technological Solutions: There is a need to develop advanced data analytics tools and artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze big data sets, identify trafficking trends, and predict potential hotspots.
- Blockchain technology can also be utilised to enhance transparency in supply chains and prevent the use of forced labor in industries prone to trafficking, such as agriculture and garment manufacturing.
- International Collaboration: India can facilitate international collaboration and knowledge exchange platforms to share innovative approaches, best practices, and success stories in combating human trafficking.
- There is also a need to foster partnerships between countries, NGOs, academia, and private sectors to jointly develop and implement innovative solutions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. India’s proximity to the two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What counter-measures should be taken to prevent the same? (2018)


Governance
Global Burden of Unsafe Drinking Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene
For Prelims: WASH , World Health Organization, Sustainable Development Goals
For Mains: Impacts of unsafe WASH practices, Concept of WASH and its importance for public health, Challenges and opportunities in achieving universal access to safe water and sanitation.
Why in News?
According to a new report by the World Health Organization (WHO) titled "Burden of Disease Attributable to Unsafe Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2019 Update," unsafe drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) practices have led to severe consequences, resulting in a significant loss of lives and widespread disease burden.
What are the Impacts of Unsafe WASH Practices?
- Mortality Toll:
- In 2019, unsafe WASH practices caused 395,000 deaths among children under the age of five.
- Breakdown of Deaths:
- 273,000 deaths were attributed to diarrhoea.
- 112,000 deaths were caused by acute respiratory infections.
- Inadequate access to WASH services resulted in at least 1.4 million deaths globally.
- Widespread Disease Impact:
- Diarrhoeal diseases accounted for over a million deaths and 55 million Disability-adjusted life years (DALY).
- DALY is the sum of the number of years of life lost due to premature death and a weighted measure of the years lived with disability due to a disease or injury.
- An estimated 1.5 billion people worldwide are affected by soil-transmitted helminthiases (STH), transmitted through poor sanitation practices.
- STH are transmitted by eggs in human faeces, which in turn contaminate soil in areas where sanitation is poor.
- Inadequate WASH contributes to 10% of the disease burden associated with malnutrition.
- Diarrhoeal diseases accounted for over a million deaths and 55 million Disability-adjusted life years (DALY).
- Global Disparities in WASH Access:
- Currently, 771 million people lack access to safe water globally.
- Approximately 1.7 billion people do not have access to proper sanitation facilities.
- Consequences for Low and High-Income Countries:
- Poor hand hygiene practices led to around 384,000 diarrhoea-related deaths across all age groups in Africa and South-East Asia.
- Even high-income countries, such as the United States, experienced risks, with 33,200 deaths from diarrhoeal diseases and 317,921 deaths from acute respiratory infections in 2019.
What are Unsafe WASH Practices?
- Drinking water from contaminated or untreated sources, such as polluted rivers or stagnant ponds.
- Absence or poor maintenance of toilets, latrines, or sewage systems can result in the improper disposal of human waste.
- Insufficient handwashing with soap, improper food handling practices, and lack of awareness about basic hygiene.
- The practice of defecating in the open, without the use of a toilet or latrine contaminates the environment, water sources, and food.
- Inadequate disposal of solid waste and improper handling of hazardous waste can pollute water sources, contaminate soil, and create breeding grounds for disease-carrying vectors.
What is WASH?
- About:
- WASH is an acronym that stands for the interrelated areas of Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene.
- The WHO WASH Strategy has been developed in response to Member State Resolution (WHA 64.4) and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- It is a component of WHO’s 13th General Programme of Work 2019–2023 which aims to contribute to the health of three billion through multisectoral actions like better emergency preparedness and response; and one billion with Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- It also takes on board the need for progressive realization of the human rights to safe drinking-water and sanitation, adopted by the UN General Assembly in July 2010.
- Importance of Safe WASH:
- Access to clean water, proper sanitation, and hygiene reduces the risk of illness, malnutrition, and mortality.
- Safe WASH facilities contribute to child and maternal health, ensuring safer childbirth practices and preventing child growth and development issues.
- Gender-responsive WASH services empower women and girls, promoting gender equality and dignity.
- Sustainable WASH practices protect water resources, conserve the environment, and mitigate climate change impacts.
- Safe WASH is crucial for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals and creating healthier, more equitable communities.
- Principles of the WHO WASH Strategy:
- Prioritize actions with high public health benefits in WHO-relevant areas.
- Strengthen health sector capacities for safe WASH and outbreak response.
- Align with SDGs on WASH, health, climate, nutrition, and human rights.
- Utilize high-quality science and evidence for WASH norms and procedures.
- Promote incremental improvements in national WASH standards and targets.
- Capitalize on existing regional WASH policy frameworks and targets.
- Stimulate sustainable change through stronger government institutions.
- Engage partners to address health issues in the WASH sector, including healthcare facilities.
- SDGs Linked to WASH:
- Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being - WASH is essential for preventing the spread of diseases and promoting good health.
- Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation - This goal specifically addresses the need for access to clean drinking water and adequate sanitation facilities.
- Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production - WASH is critical to ensure responsible consumption and production of water resources.
- Goal 13: Climate Action - Climate change can impact access to safe drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene, making WASH an important component of climate action.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “To ensure effective implementation of policies addressing the water, sanitation and hygiene needs the identification of the beneficiary segments is to be synchronized with anticipated outcomes.” Examine the statement in the context of the WASH scheme. (2017)


Social Justice
Anaemia and Maternal Health
For Prelims: Anemia and Maternal Health, Anemia, PPH, Anemia Mukta Bharat.
For Mains: Anemia and Maternal Health.
Why in News?
Recently, a study published in The Lancet Journal, titled- Maternal anaemia and the risk of postpartum haemorrhage: a cohort analysis of data from the WOMAN-2 trials, has found that there is a strong link between Anaemia and Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH).
- They used the data from the World Maternal Antifibrinolytic-2 (WOMAN-2) trial. This trial enrolled women with moderate or severe anaemia giving birth vaginally in hospitals in Pakistan, Nigeria, Tanzania, and Zambia.
What is Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)?
- PPH is severe vaginal bleeding after childbirth.
- WHO-defined postpartum haemorrhage (estimated blood loss of at least 500 mL); and calculated postpartum haemorrhage (blood loss of ≥1,000 mL).
- It's a serious condition that can lead to death. Other signs of postpartum hemorrhage are dizziness, feeling faint and blurred vision.
What are the Findings of the Study?
- Anaemia and PPH:
- Mean estimated blood loss was 301 mL for women with moderate anaemia and 340 mL for women with severe anaemia.
- Clinical postpartum haemorrhage occurred in 7.0% of women. The risk of clinical postpartum haemorrhage was 6.2% in women with moderate anaemia and 11.2% in women with severe anaemia.
- This data is based on the trial involving 10,620 women.
- Severe anaemia is associated with seven times higher odds of death or near miss compared to moderate anaemia.
- Anaemia and Pregnancy:
- Worldwide, over half a billion women of reproductive age are anemic.
- Approximately 70,000 postpartum deaths occur annually, mostly in low- and middle-income countries.
- Blood Loss and Shock:
- Lower haemoglobin values associated with increased blood loss and clinical PPH.
- Women with anaemia have reduced oxygen-carrying capacity and are more susceptible to shock.
- Clinical diagnosis of postpartum haemorrhage linked to worse maternal function.
What are the Recommendations of WHO to Reduce PPH?
- It is suggested to use some of the drugs such as oxytocin, oral misoprostol drug etc., to prevent PPH.
- Oxytocin is a commonly recommended medication to stimulate uterine contractions and reduce the risk of excessive bleeding.
- Late cord clamping (performed after 1 to 3 minutes after birth) is recommended for all births while initiating simultaneous essential newborn care.
- Early cord clamping (<1 minute after birth) is not recommended unless the neonate is asphyxiated (baby's brain and other organs do not get enough oxygen and nutrients).
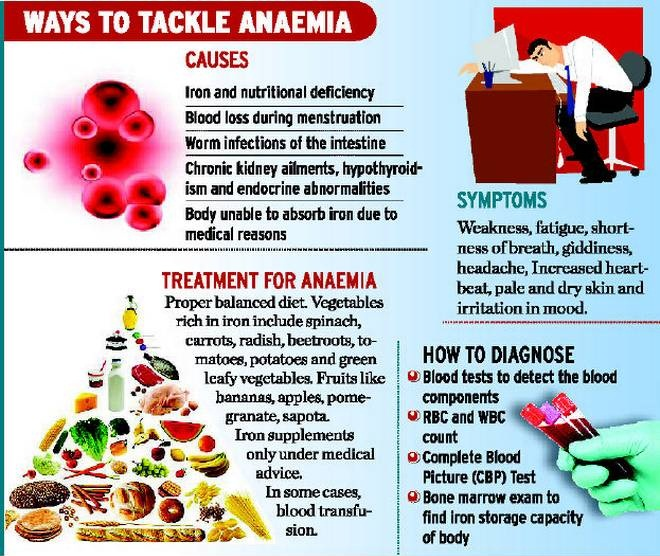
What is Anaemia?
- Anemic Condition:
- It is a condition in which the number of red blood cells or their oxygen-carrying capacity is insufficient to meet physiologic needs, which vary by age, sex, altitude, smoking, and pregnancy status.
- Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anaemia, although other conditions, such as folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin A deficiencies, chronic inflammation, parasitic infections, and inherited disorders can all cause anaemia.
- Status in India:
- The prevalence of anaemia among six groups as per the National Family Health Survey 5 (2019-21), is 25.0% in men (15-49 years) and 57.0% in women (15-49 years), 31.1% in adolescent boys (15-19 yrs), 59.1% in adolescent girls, 52.2% in pregnant women (15-49 years) and 67.1% in children (6-59 months).
What are Government Initiatives to Tackle Anemia?
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat(AMB): It was launched in 2018 as part of the Intensified National Iron Plus Initiative (NIPI) Program for accelerating the annual rate of decline of anaemia from one to three percentage points.
- The target groups for AMB are Children 6-59 months, 5-9 years, Adolescent Girls & Boys of 10-19 years, Women of Reproductive Age (15-49 years), Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers.
- Weekly Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation (WIFS):
- This Programme is being implemented to meet the challenge of high prevalence and incidence of anaemia amongst adolescent girls and boys.
- The intervention under WIFS includes supervised weekly ingestion of Iron Folic Acid (IFA) tablet.
- Operationalization of Blood Bank:
- In District Hospitals and Blood Storage Unit in subdistrict facilities such as Sub-Divisional Hospital/ Community Health Centers is being taken to tackle complications due to severe anaemia.
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA):
- It has been launched to focus on conducting special ANC check up on 9th of every month with the help of medical officers/ OBGYN to detect and treat cases of anaemia.
- Other Steps Taken:
- To control worm infestation biannual deworming with Albendazole is provided.
- Health management information system & Mother Child tracking system is being implemented for reporting and tracking the cases of anaemic and severely anaemic pregnant women.
- Universal screening of pregnant women for anaemia is a part of ante-natal care and all pregnant women are provided iron and folic acid tablets during their ante-natal visits through the existing network of sub-centres and primary health centres and other health facilities as well as through outreach activities at Village Health & Nutrition Days (VHNDs).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt Bharat: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) Only three
d) All four Interventions of Anaemia Mukt Bharat:
Ans: (c)


Indian Polity
Governor’s Powers in Dismissing a Minister
For Prelims: Governor’s Powers in Dismissing a Minister, Article 164, Section 51(1) and 51(5) of the Government of India Act, 1935, Pleasure Doctrine.
For Mains: Governor’s Powers in Dismissing a Minister.
Why in News?
The recent decision of dismissal and suspension of a Minister in Tamil Nadu by the Governor has sparked a Constitutional Controversy. The Governor reversed his decision later and suspended the dismissal order.
What are the Governor’s Powers to Dismiss Ministers?
- Article 164:
- Under Article 164 of the Constitution, the Chief Minister is appointed by the Governor without any advice from anyone. But he appoints the individual Ministers only on the advice of the Chief Minister.
- The Article implies that the Governor cannot appoint an individual Minister according to his discretion. Therefore, the Governor can dismiss a Minister only on the advice of the Chief Minister.
- Reference to the Government of India Act, 1935:
- From Section 51(1) and 51(5) of the Government of India Act, 1935, which governed the colonial rule, the Governor had absolute discretion to choose and dismiss Ministers.
- However, after India gained independence, the Governor's role transformed into that of a constitutional head, acting solely on the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers headed by the Chief Minister.
- Constitutional Limitations on Governor's Discretion:
- The power to choose or dismiss a Minister lies with the Chief Minister, who represents the will of the people.
- B.R. Ambedkar, during the Constituent Assembly debates, unequivocally stated that the Governor has no independent executive functions under the Constitution.
- The inclusion of the "pleasure of the Governor" in Article 164 of the Constitution refers only to the formal act of issuing dismissal orders upon the advice of the Chief Minister.
- The power to choose or dismiss a Minister lies with the Chief Minister, who represents the will of the people.
Note: The pleasure doctrine has been brought into the Constitution of India from the Government of India Act, 1935. Section 51 of the Government of India Act, 1935 confers on the Governor the discretion to choose as well as dismiss the Ministers. But when Article 164 of the Constitution was drafted, the words “chosen”, “dismissal” and “discretion” were omitted. It was a significant omission which makes it abundantly clear that the Constitution did not confer any discretion on the Governor to either choose or dismiss an individual Minister.
What are the Judicial Clarification on Governors Powers?
- In Shamsher Singh and Anr vs State Of Punjab (1974):
- The SC declared that the President and Governor, who hold executive powers under the Constitution, should exercise their formal constitutional powers only with the advice of their Ministers, except in a few exceptional situations.
- Nabam Rebia vs Deputy Speaker (2015):
- The SC has ruled that Governors cannot cause the downfall of elected governments. It reaffirmed the previous ruling in Shamsher Singh and emphasized that the Governor's discretionary powers are limited to the provisions of Article 163(1).
- Article 163(1) states that there shall be a council of Ministers with the Chief Minister at the head to aid and advise the Governor in the exercise of his functions, except in so far as he is by or under this constitution required to exercise his functions or any of them in his discretion.
- The SC has ruled that Governors cannot cause the downfall of elected governments. It reaffirmed the previous ruling in Shamsher Singh and emphasized that the Governor's discretionary powers are limited to the provisions of Article 163(1).
What are the Concerns Related to the Issue of Dismissal of Minister?
- Constitutional Misadventure:
- Removing a Minister is a matter of moral judgment, not a legal requirement. The Governor's decision to dismiss a Minister without the Chief Minister's recommendation is a constitutional misadventure.
- Sets Wrong Precedent:
- This unprecedented and deliberately provocative act of dismissing a Minister of a government without the recommendation of the Chief Minister of the State, may set a precedent and has the potential to destabilise State governments putting the federal system in Jeopardy.
- Collapse of Constitutional System:
- If Governors are allowed to exercise the power of dismissal of individual Ministers without the knowledge and recommendation of the Chief Minister, the whole constitutional system will collapse.
Conclusion
- A legislature should establish clear guidelines for the exercise of powers by the Governor.
- In India, as a parliamentary democracy, the authority of Parliament should be respected, just as the democratically elected State Legislature should have a similar role and importance.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the discretionary powers given to the Governor of a State? (2014)
- Sending a report to the President of India for imposing the President’s rule
- Appointing the Ministers
- Reserving certain bills passed by the State Legislature for consideration of the President of India
- Making the rules to conduct the business of the State Government
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Whether the Supreme Court Judgment (July 2018) can settle the political tussle between the Lt.Governor and elected government of Delhi? Examine. (2018)
Q. Discuss the essential conditions for exercise of the legislative powers by the Governor. Discuss the legality of re-promulgation of ordinances by the Governor without placing them before the Legislature. (2022)


Important Facts For Prelims
Small Finance Banks
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently announced its decision to reject three applications for setting up Small Finance Banks as these applications were found not suitable for granting of in-principle approval to set up SFBs.
- RBI received approximately a dozen applications under the guidelines for 'on-tap' Licensing of Universal Banks and SFBs.
What are Small Finance Banks?
- About:
- SFBs in India are a category of banks established to provide basic banking services and credit facilities to underserved sections of the population, including small business owners, micro and small industries, farmers, and the unorganized sector.
- They are regulated by RBI.
- Example: Capital Small Finance Bank, Ujjivan, Utkarsh etc.
- All prudential norms and regulations of the RBI as applicable to existing commercial banks, including the requirement of maintenance of CRR and SLR are also applicable to SFBs.
- Also, according to RBI, if an SFB aspires to transit into a universal bank, it has to have a satisfactory track record of performance for a minimum period of 5 years.
- SFBs in India are a category of banks established to provide basic banking services and credit facilities to underserved sections of the population, including small business owners, micro and small industries, farmers, and the unorganized sector.
Note:
- On-Tap Licencing: It means that the window for obtaining a bank licence from the RBI is open all year, or that the RBI will accept applications and issue licences to banks at any time.
- CRR and SLR: CRR stands for Cash Reserve Ratio, and SLR stands for Statutory Liquidity Ratio.
- Both CRR and SLR are monetary policy tools used by central banks to regulate and control the availability of credit in the economy.
- Under CRR, the commercial banks have to hold a certain minimum amount of deposit (NDTL) as reserves with the central bank.
- SLR is the minimum percentage of deposits that a commercial bank has to maintain in the form of cash, gold or other securities.
- Eligibility:
- Resident individuals/ professionals (Indian citizens), singly or jointly, each having at least 10 years of experience in banking and finance at a senior level.
- Companies and societies owned and controlled by residents.
- Entities such as microfinance institutions, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), local area banks and payment banks that are controlled by residents can also convert into Small Finance Banks.
- Also, Urban Cooperative Banks(UCBs) desirous of converting to SFB may convert to SFB after ensuring compliance with the guidelines.
- Paid Up Capital Requirement:
- The minimum paid-up voting equity capital for small finance banks shall be Rs.200 crore, except for such small finance banks which are converted from UCBs.
- Mandate:
- Priority Sector Lending: Small Finance Banks have to allocate 75% of their total net credit to priority sector lending, as per the RBI guidelines.
- They will also have to ensure that 50% of their loan portfolio constitutes advances up to Rs 25 lakh.
- The maximum loan size and investment limit exposure to single/ group obligor will be restricted to 10% and 15% of its capita funds, respectively.
- Branch Network: SFBs are required to set up a network of branches in unbanked and underbanked areas, with a particular emphasis on rural and semi-urban regions.
- Initially, they need to have at least 25% of their branches in unbanked rural areas.
- Priority Sector Lending: Small Finance Banks have to allocate 75% of their total net credit to priority sector lending, as per the RBI guidelines.
- Regulation:
- Small Finance Banks are registered as public limited company under Companies Act 2013, and are licensed under section 22 of the Banking Regulation,1949.
- They are primarily governed by Banking Regulation Act,1949 and RBI Act,1934 and other relevant statutes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What is the purpose of setting up of Small Finance Banks (SFBs) in India? (2017)
- To supply credit to small business units
- To supply credit to small and marginal farmers
- To encourage young entrepreneurs to set up business particularly in rural areas.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Scheme for Expansion and Modernization of Fire Services in the States
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India has launched a “Scheme for Expansion and Modernization of Fire Services in the States (SEMFSS)” under the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) for strengthening fire services in the States.
What is the Scheme for Expansion and Modernization of Fire Services in the States?
- About:
- The Scheme finds its origin from the recommendation of the Fifteenth Finance Commission (XV-FC) which allows an allocation of 12.5 % of each of the NDRF and State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) for the Funding Window of Preparedness and Capacity Building.
- Objective:
- The objective of the scheme is to expand and modernize Fire Services in the States with a view that activities for strengthening of fire services at the State-level through preparedness and capacity-building components of the NDRF will be ensured.
- Fund Allocation:
- Out of the total NDRF corpus, an amount of Rs. 5,000 Crore was earmarked for priority "Expanding and Modernization of Fire Services".
- The amount of Rs. 500 crores, out of the total outlay, has been kept for incentivizing the States on the basis of their legal and infrastructure-based reforms.
- Funding Pattern:
- For seeking funds for the projects/proposals under the Scheme, the concerned State Governments shall have to contribute 25% (except for the North-Eastern and Himalayan (NEH) States which shall contribute 10%) of total cost of such projects / proposals from their budgetary resources.
What is the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF)?
- Formation:
- National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF) was renamed as National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) with the enactment of the Disaster Management Act in 2005.
- It is defined in Section 46 of the Disaster Management Act, 2005 (DM Act).
- It is placed in the “Public Account” of Government of India under “reserve funds not bearing interest“.
- Public Accounts: It was constituted under Article 266 (2) of the Constitution. It accounts for flows for those transactions where the government is merely acting as a banker eg. provident funds, small savings etc.
- National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF) was renamed as National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) with the enactment of the Disaster Management Act in 2005.
- Role:
- It is managed by the Central Government for meeting the expenses for emergency response, relief and rehabilitation due to any threatening disaster situation or disaster.
- It supplements the SDRF in case of a disaster of severe nature, provided adequate funds are not available in the SDRF.
- SDRF is the primary fund available with the State governments for responses to notified disasters to meet expenditure for providing immediate relief.
- Financing:
- Financed through the levy of a cess on certain items, chargeable to excise and customs duty, and approved annually through the Finance Bill.


Important Facts For Prelims
SAFF Championship 2023
Why in News?
Recently, India marked a remarkable victory in the South Asian Football Federation (SAFF) Championship 2023 held in Bengaluru, Karnataka, securing their ninth title by defeating Kuwait in a thrilling football match.
What is SAFF Championship?
- About:
- The SAFF Championship is an internationally recognized football tournament that brings together teams from the South Asian subcontinent. Organized by the South Asian Football Federation (SAFF), one of the five sub-confederations under the Asian Football Confederation (AFC).
- SAFF was formed in 1997 by founding Member Associations from Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and SriLanka.
- The SAFF Secretariat currently operates from Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- The SAFF Championship is an internationally recognized football tournament that brings together teams from the South Asian subcontinent. Organized by the South Asian Football Federation (SAFF), one of the five sub-confederations under the Asian Football Confederation (AFC).
- Origin and Evolution:
- Founding members:
- India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, and Maldives.
- Expansion:
- Bhutan joined in 2000, while Afghanistan became a member in 2005 before moving to the Central Asian Football Association (CAFA) in 2015.
- Evolution:
- The South Asian football tournament started as the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) Gold Cup in 1993.
- It was later renamed the South Asian Gold Cup in 1995 and became the SAFF Gold Cup from 1997 to 2005.
- Since 2008, it has been known as the SAFF Championship.
- Founding members:
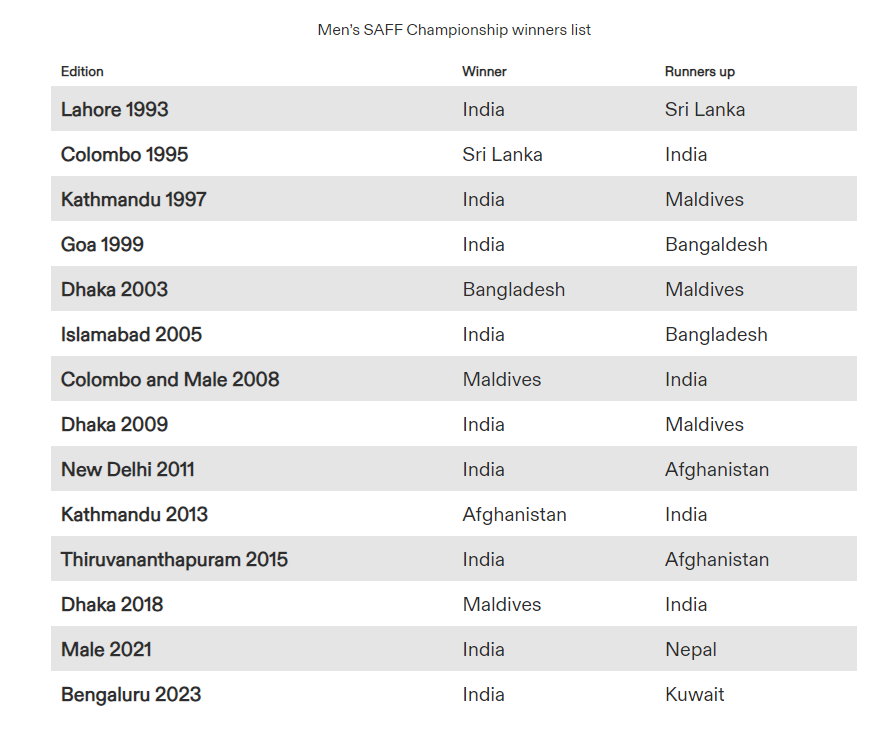
- India's Performance:
- Men's SAFF Championship:
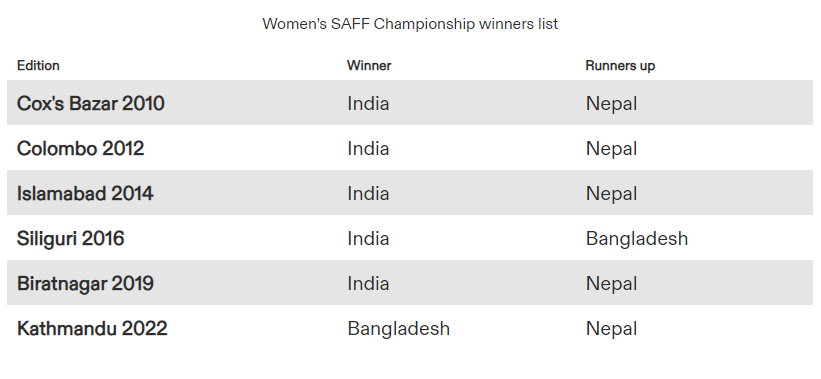
- Women's SAFF Championship:
- India has enjoyed success in the SAFF Championship, winning the inaugural edition in 2010 and subsequently securing victories in 2012, 2014, 2016, and 2019.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Four New Countries Consulted to Join OPEC
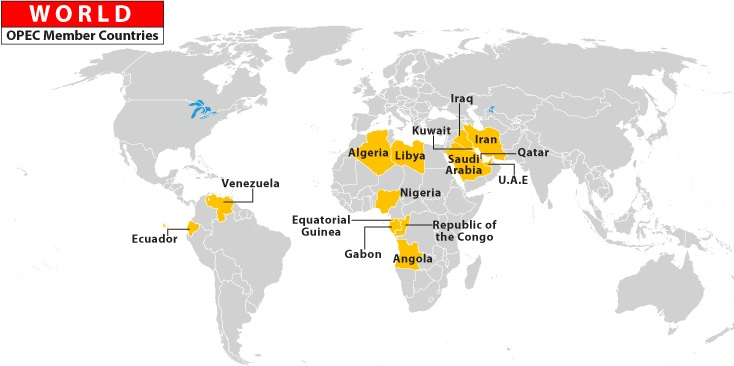
Recently, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) Secretary General announced that discussions are underway with four new countries, namely Azerbaijan, Malaysia, Brunei, and Mexico, to join the organization.
OPEC, which was established in 1960 with founding members Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela, now consists of 13 member states. OPEC produces around 30% of the world's crude oil, with its members accounting for approximately 60% of the global petroleum trade. In 2016, OPEC expanded its alliance by including 10 major oil-producing countries, forming OPEC+.
OPEC+ includes the 13 OPEC member countries along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan, and Sudan. The objective is to coordinate and unify petroleum policies, stabilize oil markets, ensure a steady supply of petroleum to consumers, provide a reliable income for producers, and deliver a fair return on investment in the petroleum industry. The headquarters of OPEC is in Vienna, Austria.
Read more: Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
India Tops Global Charts for Childhood Diabetes and Deaths
A new study published in the journal JAMA Network has revealed that India witnessed the highest number of childhood diabetes cases and deaths globally in 2019. The study highlighted that India also had the highest disability-adjusted life-years (DALY), representing the loss of one year of full health, according to the World Health Organization. Global childhood diabetes cases increased by 39.4% since 1990, with 227,580 cases and 5,390 deaths reported in 2019.
The rise in type 2 diabetes in children is linked to global childhood obesity, unhealthy lifestyles, and parental history of the condition. Childhood diabetes is a condition where a child’s body cannot produce or use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that helps move sugar from the blood into the cells for energy. There are two main types of childhood diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Read more: Type 1 Diabetes, New Injection for Type 2 Diabetes
JIMEX 23
The seventh edition of the bilateral Japan-India Maritime Exercise 2023 (JIMEX 23) is set to take place from 5th to 10th July 2023 in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh.
JIMEX 23 brings together units from the Japan Maritime Self Defence Force (JMSDF) and the Indian Navy. The exercise will involve the participation of various naval assets such as guided missile destroyers, corvettes, submarines, maritime patrol aircraft, and helicopters.
Read more: Japan-India Maritime Exercise, Maritime security
DGCA India and EASA Collaborate for Unmanned Aviation Advancement
The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) India and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) have solidified their collaboration through the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) focused on Unmanned Aircraft Systems and Innovative Air Mobility.
The MoU encompasses licensing of personnel, training, air traffic management, infrastructure, and the establishment of Unmanned Aircraft System Traffic Management (UTM) standards and services.
Read more: Directorate General of Civil Aviation, Unmanned Aircraft Systems