Governance
Health Initiatives in Union Budget 2025-26
For Prelims: Union Budget 2025-26, Economic Survey (ES) 2024-25, Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs), Basic Customs Duty (BCD), Indirect Tax, Health Insurance, Gig Workers, E-Shram portal, Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM), PM Matru Vandana Yojana, Child Nutrition, Anganwadi, Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme, National Tele Mental Health Programme, WHO, Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2022-23, FSSAI, Chemotherapy.
For Mains: Health Initiatives in Union budget 2025-26, Concerns regarding ultra-processed foods (UPFs), establishment of cancer day-care centers.
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2025-26 has allocated around Rs 1 lakh crore for the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The share of health in the FY26 budget increased marginally to 1.97% from 1.9% in FY25 but overall health allocation remained below 2% of the budget.
- The Economic Survey (ES) 2024-25 and Union budget 2025-26 recommended and announced a number of measures to promote health in the country.
- Among several announcements, the major one is the establishment of Daycare Cancer Centers.
Note: The National Health Policy 2017 recommends that the health expenditure be increased from 1.15% (2017) of the GDP to 2.5% of the GDP by 2025.
What are the Measures Recommended and Announced to Promote Health?
- Taxing UPFs: The ES 2024-25 proposed a ‘health tax’ on ultra-processed foods (UPFs) to curb their consumption, citing links to obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
- The high consumption of UPF is a key reason for India being the diabetic capital of the world, with over 101 million affected.
- Cancer Care Expansion: The government plans cancer care centers in every district by FY 2026 and 200 new Daycare Cancer Centers by FY 2025-26 for localized chemotherapy and treatment.
- Life-Saving Drug Exemptions: The budget exempts 36 life-saving drugs from Basic Customs Duty (BCD), reducing costs, while Patient Assistance Programmes (PAPs) run by pharma firms will continue providing free medicines duty-free.
- BCD is an indirect tax levied on all the goods and commodities imported to India.
- PAPs assist those without health insurance by covering full medication costs or offering discounts on medicines.
- AB PM-JAY for Gig Workers: AB PM-JAY has been expanded to cover nearly 1 crore gig workers, who will be registered on the e-Shram portal with ID cards for healthcare access.
- Health Infrastructure and Manpower: The budget allocated Rs 4,200 crore for Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) to enhance healthcare facilities and set up five skill centers to train 3,00,000 healthcare professionals annually to meet global healthcare demands.
- Women and Child Healthcare: PM Matru Vandana Yojana will expand maternal health programs, with increased funding for child nutrition and vaccinations.
- More Anganwadi centers will be upgraded with digital tracking systems.
- Pharmaceutical Research: The government allocated Rs 2,445 crore for the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme to boost pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Mental Health and Telemedicine: The National Tele Mental Health Programme received funding to expand mental healthcare services across India.
- Medical Tourism: The government plans to simplify visa procedures for medical tourists to boost India’s medical tourism market that is valued at USD 7.56–USD 10.4 billion in 2024.
- The "Heal in India" initiative was launched in 2023 to promote medical tourism.
Note:
- A 2023 WHO report showed India's UPF spending surged from USD 900 million in 2006 to USD 37.9 billion in 2019, with a 13.7% growth in retail sales (2011–2021).
- The Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2022-23 found UPFs make up 9.6% of rural and 10.64% of urban household food budgets.
- Countries like Brazil, Canada, Chile, France, Mexico, Israel, Peru, the UK, and Uruguay use the Nutrient Profile Model for labeling and marketing restrictions of UPFs.
- The NPM rates foods based on their nutrients to identify healthy options and those that may harm health.
- Denmark introduced a tax on saturated fats as early as 2011, while Mexico levied surcharges on sugary drinks and junk food.
What ES 2024-25 Recommended to Reduce Consumption of UPFs?
- Clear Regulations: It recommended stricter FSSAI regulations, including clear UPF definitions, and labeling standards.
- Stronger Monitoring: Implement stricter monitoring of branded products to ensure compliance with health standards and prevent misleading claims.
- Enhanced Consumer Protection: Strengthen laws to address aggressive marketing, particularly targeting children and adolescents.
- Higher Taxation: Consider imposing higher taxes on heavily marketed UPFs to discourage consumption and fund public health initiatives.
- Consumer Awareness: Launch educational campaigns, especially for children, about the health risks of UPFs, including obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases.
What is a Daycare Cancer Center?
- About: A Daycare Cancer Center is a cancer clinic offering chemotherapy in a day facility for patients who need quick treatments and don't require overnight hospital stays.
- The government plans to establish 200 centers by 2025-26 across India’s 759 district hospitals.
- Objective: It aims to enhance district-level cancer care, easing the burden on metropolitan hospitals, and is vital for rural populations facing high treatment costs and long travel distances.
- Significance: The centers will offer chemotherapy, medications, biopsies, and complication management to improve cancer care accessibility.
- Concerns:
- Lack of Service Clarity: Concerns exist about the absence of advanced treatments like radiotherapy, which requires high investment in equipment.
- Infrastructure Issues: Many district hospitals lack biopsy services, and some medical colleges don’t offer cancer treatment, raising doubts about their ability to manage these centers.
- Trust Issues: Patients may be reluctant to trust district-level centers for cancer treatment, preferring established hospitals like AIIMS.
- Workforce Shortages: Concerns exist about attracting trained oncologists to smaller districts, which may require competitive salaries and incentives.
- Public Health Impact: Cancer cases are rising in India, with one in nine people expected to develop it.
- The centers will ease the growing patient load and improve treatment accessibility, particularly in rural areas.
Conclusion
The Union Budget 2025-26 introduces key health measures, including cancer care expansion and taxation on ultra-processed foods (UPFs), to address rising health concerns. While the initiatives aim to improve accessibility and affordability, challenges like infrastructure, workforce, and public trust remain significant hurdles to overcome.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the significance of the proposed cancer day-care centers and the challenges involved in their implementation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Aspartame is an artificial sweetener sold in the market. It consists of amino acids and provides calories like other amino acids. Yet, it is used as a low-calorie sweetening agent in food items. What is the basis of this use? (2011)
(a) Aspartame is as sweet as table sugar, but unlike table sugar, it is not readily oxidized in human body due to lack of requisite enzymes
(b) When aspartame is used in food processing, the sweet taste remains, but it becomes resistant to oxidation
(c) Aspartame is as sweet as sugar, but after ingestion into the body, it is converted into metabolites that yield no calories
(d) Aspartame is several times sweeter than table sugar, hence food items made with small
quantities of aspartame yield fewer calories on oxidation
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q. Why is nanotechnology one of the key technologies of the 21st century? Describe the salient features of Indian Government’s Mission on Nanoscience and Technology and the scope of its application in the development process of the country. (2016)


Governance
State of India’s Digital Economy (SIDE) Report 2024
For Prelims: State of India’s Digital Economy (SIDE) Report 2024, Digital India, BharatNet , Open Network for Digital Commerce, 5G rollout, Skill India Digital Hub, India’s Atma Nirbhar Bharat vision, Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission.
For Mains: Key Drivers of India’s Digital Growth, Key Issues Associated with India’s Digital Growth.
Why in News?
The State of India’s Digital Economy (SIDE) Report 2024, published by the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER) and based on a study by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), provides a comprehensive analysis of India’s digital economy.
What are the Key Highlights of State of India’s Digital Economy Report 2024?
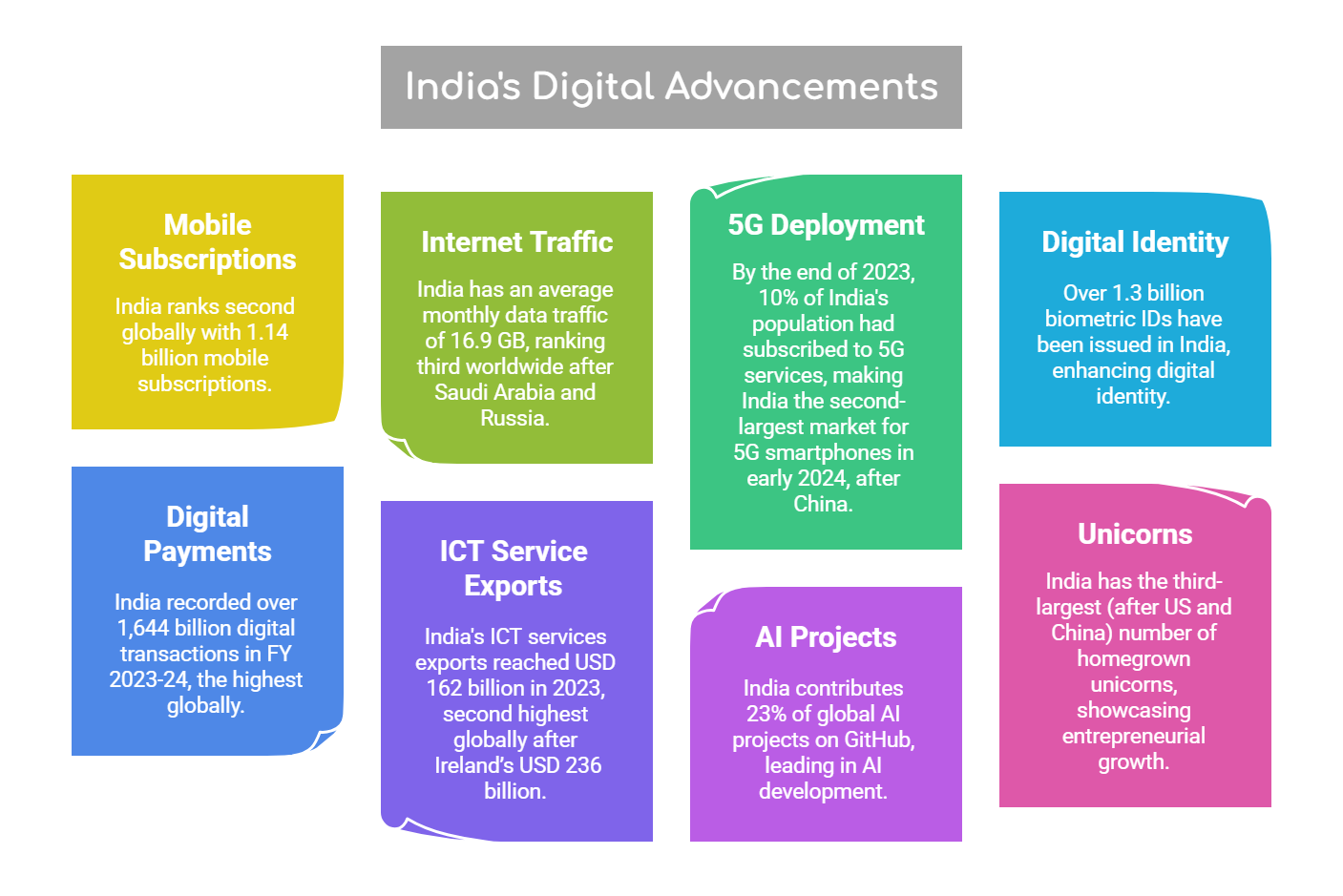
- India's Digital Economy Standing: India is the 3rd largest digitalized (behind the US and China) economy in the world in terms of economy-wide digitalisation.
- It ranks 12th among G20 nations in terms of digitalisation of individual users, indicating lower average user digitalisation.
- Contribution of Digital Economy: In 2022-23, the digital economy contributed 11.74% to GDP, with projections to rise to 13.42% by 2024-25.
- It employs 2.55% of the workforce with productivity 5 times higher than the overall economy.
- Future Projection: By 2029-30, the digital economy is expected to contribute one-fifth (20%) of GDP, surpassing agriculture and manufacturing.
- Sectoral Breakdown: The traditional ICT sector is the largest contributor to the digital economy, while new digital industries, including Big Tech and platforms, account for nearly 2% of GVA.
- State-Level Disparities: Richer states like Karnataka, Maharashtra, Telangana, Gujarat, and Haryana exhibit higher digitalisation levels compared to poorer states.
CHIPS (Connect-Harness-Innovate-Protect-Sustain):
- The CHIPS (Connect-Harness-Innovate-Protect-Sustain) framework, introduced in the SIDE 2024, offers a comprehensive approach to measuring digitalization, focusing on outcomes and risks.
- Unlike traditional indices that emphasize internet access, the CHIPS framework includes 5 pillars (Connect, Harness, Innovate, Protect, Sustain) and 50 indicators, enabling comparisons at both national and sub-national levels.
What are the Key Drivers of Digital Economy Growth in India?
- Expanding Digital Infrastructure: India’s digital infrastructure is bridging urban-rural divides and fueling a vibrant digital economy.
- Initiatives like BharatNet are providing high-speed internet to rural areas, while the 5G rollout is enhancing digital adoption, e-governance, e-commerce, fintech and IT services especially in underserved regions.
- Programs like Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) are enabling small businesses to enter the digital marketplace.
- Rising Smartphone Penetration: Affordable smartphones and low-cost data have positioned India as a mobile-first economy, enhancing access to online education, digital payments, and entertainment.
- Domestic manufacturing incentives are supporting India's Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Global Capability Centers (GCCs): India hosts 55% of the world’s GCCs, which provide essential services like IT support, R&D, and business process management.
- Start-Up Ecosystem and Innovation: India’s startup ecosystem is a major driver of digital innovation. Initiatives like Start-Up India and strong funding have helped tech startups address unique market needs.
- In 2024, Indian startups raised USD 30.4 billion in funding, despite global economic challenges.
- Digital Financial Inclusion: Programs such as UPI and Jan Dhan accounts are transforming financial inclusion in India, especially in rural areas.
- UPI processed Rs 23.49 lakh crores across 16.58 billion transactions in October 2024.
What are the Key Issues Associated with India’s Digital Growth?
Read more: Navigating India’s Digital Growth
What Steps can be taken to Strengthen and Secure the Digital Landscape in India?
Read more: Navigating India’s Digital Growth
Conclusion
India’s digital economy is a key driver of economic growth and employment. The digitalization of traditional sectors, along with the rise of digital platforms, is transforming industries and creating new job opportunities. With growing digital literacy, adoption of emerging technologies, and expanding employment prospects, India is well-positioned to lead in digital transformation, ensuring sustainable and inclusive growth.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2022)
- Aarogya Setu
- CoWIN
- DigiLocker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)


Governance
Revamping Digital Infrastructure in India
For Prelims: Artificial intelligence, IndiaAI Mission, Large Multimodal Models, Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), sustainable development, Aadhaar, UPI
For Mains: Challenges and Mitigation of India’s Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), IndiaAI Mission, Boosting AI innovation and startups, AI ecosystem in India
Why in News?
India's digital infrastructure has evolved rapidly, contributing 11.74% to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2022-23 and projected to reach 20% of GVA by 2029-30.
- To further accelerate this growth, Union Budget 2025-26 has sanctioned Rs 2,000 crore for the IndiaAI Mission to develop AI infrastructure and skill-building programs.
What are the Key Achievements in India’s Digital Infrastructure Growth?
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI): UPI was launched in 2016, it now powers 49% of global real-time transactions (ACI Worldwide Report 2024).
- Digital transactions rose from Rs 707.93 crore (2016) to Rs 23.24 lakh crore (2024), with participating banks increasing from 35 to 641. It has expanded to 7 countries, including the UAE, Singapore, and France.
- Internet Infrastructure:
- Telephone connections increased from 933 million (2014) to 1,188.70 million (2024).
- Internet connections grew from 25.15 crore (2014) to 96.96 crore (2024), an increase of 285%.
- Broadband penetration rose by 1,452% from 6.1 crore (2014) to 94.92 crore (2024).
- BharatNet, launched in 2011 to provide affordable high-speed internet to Gram Panchayats has connected 2.14 lakh Gram Panchayats by 2025 with 6.92 lakh km of optical fiber cable laid, and 1.04 lakh Wi-Fi hotspots installed.
- Telephone connections increased from 933 million (2014) to 1,188.70 million (2024).
- Aadhaar: Aadhaar, launched in 2009, serves as a digital identity framework, linking biometric and demographic data. It has enabled direct benefit transfers, financial inclusion, and reduced corruption.
- By March 2023, 136.65 crore Aadhaar cards were issued. Aadhaar face authentication crossed 100 crore transactions (Jan 2025), and E-KYC transactions grew from 0.01 crore (2014) to 1,470.22 crore (2023).
- DigiLocker & UMANG: DigiLocker launched in 2015, provides secure access to digital documents, reducing reliance on physical records.
- As of February 2025, it has 46.52 crore users, with yearly signups rising from 9.98 lakh (2015) to 2025.07 lakh (2024).
- UMANG app, launched to integrate e-Gov services, has 7.34 crore registered users in 2024, up from 0.25 lakh (2017).
- ONDC & GeM: ONDC (launched in 2022) promotes fair e-commerce competition, benefiting MSMEs. By December 2024, it expanded to 616+ cities, with 7.64 lakh sellers and 154.4 million orders.
- GeM, launched in 2016, streamlines government procurement with Rs 4.09 lakh crore GMV in FY 2024-25, supporting 1.6 lakh buyers and 22.5 lakh sellers, fostering transparency and efficiency for small enterprises.
- BHASHINI: BHASHINI has enhanced digital access in 22+ Indian languages, facilitating 100 million+ inferences monthly and has over 500,000 app downloads, promoting inclusive digital governance and bridging linguistic divides.
What is IndiaAI Mission?
- About: The IndiaAI Mission is a flagship initiative launched by the Government of India aimed at creating a comprehensive AI ecosystem to foster innovation, research, and development in AI.
- Objective: It aims to build a robust AI ecosystem by establishing high-performance computing infrastructure, enhancing data quality and AI models, promoting indigenous AI technologies, and fostering innovation in sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- It also focuses on supporting AI startups, attracting talent, and ensuring ethical AI practices.
- Budgetary Allocation: Rs 2,000 crore has been allocated for 2025-26, which is nearly a fifth of the scheme’s total outlay.
- Key Components:
- AI Center of Excellence: It aims at integrating AI technologies into the curriculum to enhance educational outcomes. The Union Budget 2024-25 allocates Rs 500 crore for this.
- Additionally, 3 AI centers in agriculture, health, and sustainable cities, announced in 2023, will continue to receive support.
- IndiaAI Innovation Centre
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative
- IndiaAI FutureSkills
- IndiaAI Startup Financing
- Safe & Trusted AI
- AI Center of Excellence: It aims at integrating AI technologies into the curriculum to enhance educational outcomes. The Union Budget 2024-25 allocates Rs 500 crore for this.
Conclusion
India’s digital infrastructure has significantly boosted economic growth, governance efficiency, and financial inclusion. To sustain this progress and achieve a 'Viksit Bharat' by 2047, the focus must shift to enhancing cybersecurity, expanding 5G, and promoting digital literacy. Leveraging its digital capabilities, India can drive sustainable development, improve service delivery, and empower citizens in the digital era.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the objectives and key components of the IndiaAI Mission? How does it aim to transform India's AI landscape? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2022)
Q. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)


Social Issues
Mental Health at Workplace and Economic Productivity
For Prelims: Economic Survey 2025, World Health Organization (WHO), Annual Survey of Industries (ASI)
For Mains: Impact of informal Work on Mental Health, Impacts of Poor Mental Health, Steps Taken by the Government, steps that can be taken to Improve Mental Health
Why in News?
The Economic Survey 2025 highlighted the significant impact of workplace culture, working hours, and lifestyle on mental health and worker productivity.
- It stressed the urgent need for improved workplace conditions and healthier lifestyles to boost employee well-being, which in turn, can enhance economic growth.
What are the Key Factors Affecting Mental Health?
- Workplace Culture: A positive workplace culture boosts mental well-being. The survey finds that employees with good relationships with managers and colleagues report 33% higher mental well-being scores.
- A sense of purpose at work further enhances well-being.
- Workload Management: Excessive workloads negatively impact mental health. Employees with manageable workloads report 27% greater mental well-being than those overwhelmed by work.
- Long working hours (55-60 per week) increase stress and anxiety.
- Impact of Remote Work: While remote work offers flexibility, fully remote employees report 17% lower mental well-being scores than those in-office or in hybrid models.
- Social interaction at work is crucial for mental health.
- Lifestyle Choices and Mental Well-being:
- Dietary Choices: Individuals who avoid ultra-processed and packaged foods report better mental well-being.
- Physical Activity: Lack of exercise is linked to higher stress levels and lower productivity.
- Social Media Usage: Excessive social media consumption is correlated with declining mental health.
- Family Ties: Strong family relationships contribute significantly to better mental well-being.
Increase in Self-Employed Workers as per Economic Survey 2024-25
- Rise in Self-Employment: The proportion of self-employed workers increased from 52.2% (2017-18) to 58.4% (2023-24).
- Sectoral Trends: Agriculture remains dominant in employment, rising from 44.1% to 46.1% during the same period.
- Decline in Regular Jobs: The share of salaried employment fell from 22.8% in 2017-18 to 21.7% in 2023-24.
- Casual employment also declined from 24.9% to 19.8%, indicating a shift toward structured self-employment.
- Unemployment Reduction: The unemployment rate (15+ age group) declined from 6% (2017-18) to 3.2% (2023-24).
- Formal Sector Growth: Net additions to EPFO subscriptions more than doubled, rising from 61 lakh (2018-19) to 1.31 crore (2023-24), with 61% of new payroll additions from youth (<29 years).
What are the Key Implications of Poor Mental Health on the Economy?
- Lost Productivity: Mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety contribute to reduced work efficiency, absenteeism, and presenteeism (working while unwell).
- As per WHO, globally, depression and anxiety lead to a loss of 12 billion work days annually, amounting to an economic cost of nearly USD 1 trillion.
- In India, this translates to a loss of approximately Rs 7,000 per affected worker per day.
- As per WHO, globally, depression and anxiety lead to a loss of 12 billion work days annually, amounting to an economic cost of nearly USD 1 trillion.
- Absenteeism and Turnover: Mental health conditions can result in higher rates of sick days, early departures, and increased job turnover, further disrupting workflow and incurring costs associated with recruitment and training replacements.
- Economic Survey 2024-25 noted that individuals with poor mental well-being lose about 15 working days per month, compared to 2-3 days for healthier individuals.
- Increased Healthcare Expenditure: Poor mental health leads to higher healthcare costs due to frequent medical visits, hospitalizations, and long-term treatment, increasing the burden on public health infrastructure, diverting resources from other critical areas.
- Decline in Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Poor mental health hampers creativity, risk-taking, and decision-making, slowing technological and business advancements, especially in high-performance sectors facing stress and burnout.
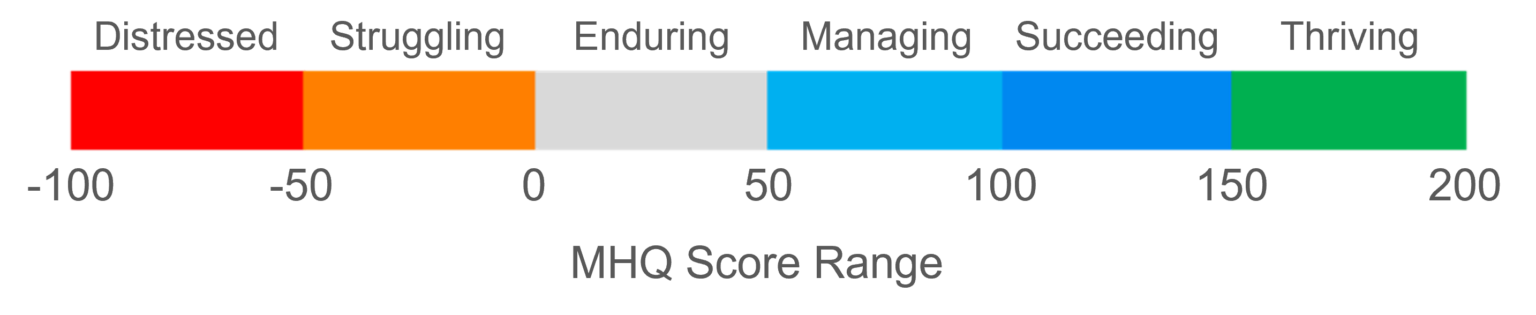
Mental Health Quotient (MHQ)
- MHQ is a standardized measure assessing mental well-being and cognitive functioning.
- The evaluation is based on self-reported responses to a standardized questionnaire, assessing mental well-being across key domains like emotional resilience, cognitive function, social well-being, and risk factors.
- The MHQ score ranges from -100 to +200, assessing overall mental well-being. Higher scores indicate better mental health
What are Suggestions Provided by Economic Survey 2024-25?
- Workplace Reforms: Foster a supportive work culture by improving interpersonal relationships, reducing workplace stress, and promoting a sense of purpose.
- Implement work-hour regulations to prevent burnout and enhance productivity.
- Flexible Work Models: Encourage hybrid work policies to balance flexibility and social interaction, mitigating the negative effects of full remote work.
- Health and Lifestyle Interventions: Employers and the government should promote healthy eating, physical activity, and digital detox to improve mental well-being.
- Awareness and Mental Health Programs: Implement large-scale mental health awareness initiatives, counseling services, and employee assistance programs to support workplace well-being.
- Policy and Legislative Measures: Strengthen occupational health policies by integrating mental health considerations into labor laws, ensuring workplaces adopt mental health-friendly practices.
Conclusion
The Economic Survey 2024-25 highlights mental well-being as a national priority. A healthy workforce is key to productivity, resilience, and economic growth. Prioritizing workplace mental health through supportive policies will strengthen India’s path to becoming a global economic powerhouse.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. In order to enhance the prospects of social development, sound and adequate health care policies are needed particularly in the fields of geriatric and maternal health care. Discuss.(2020)
Q. Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
International Big Cat Alliance
Why in News?
The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) officially became a treaty-based intergovernmental organization and international legal entity on 23rd January 2025 with headquarters in India.
What is the International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA)?
- Origins: IBCA was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2023 during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger, and was formally approved by the Union Cabinet in February 2024.
- Implementation: IBCA established through the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- It functions as a global platform to share conservation expertise, fund conservation initiatives, and create a repository of technical knowledge.
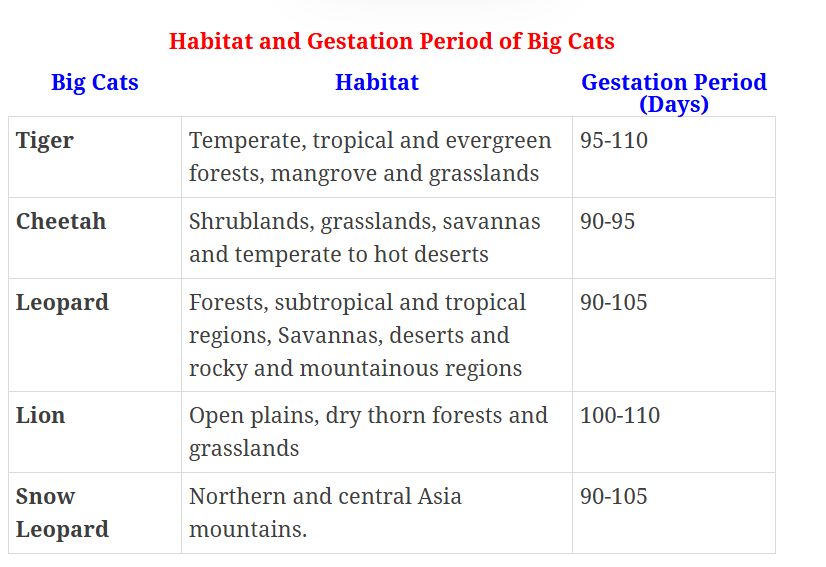
- Objective: The initiative’s main objective is the conservation of seven major big cat species: the Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma.
- Membership: The Republic of Nicaragua, Kingdom of Eswatini, Republic of India, Federal Republic of Somalia, and Republic of Liberia have ratified the IBCA framework agreement.
- Membership is open to all United Nations member states, including range countries where these species naturally occur and non-range countries interested in supporting big cat conservation.
- Need for IBCA: Big Cats are under threat due to habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and human-wildlife conflicts.
- Conservation at a global scale is required to halt population decline and reverse negative trends.
- Funding: India has committed Rs. 150 crore (2023-2028) in support to the IBCA and is exploring additional funding through bilateral, multilateral, and donor organizations.
- Role in Conservation Efforts:
- Collaborative Conservation Platform: IBCA creates a global network of conservationists, policymakers, researchers, and governments.
- Facilitates sharing of best practices in habitat management, anti-poaching strategies, and ecological restoration.
- Financial and Technical Assistance: Acts as a common funding pool for conservation projects worldwide.
- Provides technical know-how and scientific research to under-resourced nations.
- Strengthening Existing Agreements & Initiatives: Works alongside CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species), CMS (Convention on Migratory Species), and other wildlife protection treaties.
- Aims to support national and regional big cat conservation programs.
- Climate Change Mitigation & Ecological Security: Conservation of apex predators like big cats ensures healthy ecosystems, biodiversity preservation, and climate resilience.
- Restoration of forests and grasslands through IBCA initiatives will aid in carbon sequestration and climate adaptation.
- Collaborative Conservation Platform: IBCA creates a global network of conservationists, policymakers, researchers, and governments.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- The NTCA, a statutory body under the MoEFCC, was established in 2005 following the Tiger Task Force's recommendations and gained legal status under Section 38L of the Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act, 2006.
- Objectives: Grants statutory authority to Project Tiger, ensures federal accountability in tiger reserve management and addresses local livelihood concerns around tiger reserves.
Conservation Efforts for Big Cats in India
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only.
- Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only.
- One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2024)
- Lions do not have a particular breeding season.
- Unlike most other big cats, cheetahs do not roar.
- Unlike male lions, male leopards do not proclaim their territory by scent marking.
Which of the statements given above are correct 2
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 2
Ans: (a)
Q. Consider the following: (2012)
- Black-necked crane
- Cheetah
- Flying squirrel
- Snow leopard
Which of the above are naturally found in India?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Maharashtra Mandates Marathi Language Use
Why in News?
Maharashtra has mandated the use of Marathi language in all official communication across government, semi-government, local self-government bodies, and government-aided offices.
- The Marathi Language Policy, approved in 2024, recommends the use of Marathi in all public affairs.
Note:
- Marathi was designated as the official language of Maharashtra in 1960.
- In 2024, Marathi achieved the status of a classical language.
- India has 2 official Languages (Hindi and English) and 22 Scheduled Languages as per the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India.
- It includes Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu.
- Part XVII of the Indian constitution deals with the official languages in Articles 343 to 351.
Mandatory Regional Languages in Other Indian States
- Tamil Nadu: Tamil is mandatory for government communication, and passing a Class 10 Tamil exam is required for government jobs.
- Karnataka: Kannada is compulsory in government offices and business signboards, with a law mandating 60% of signboard space in Kannada.
- Jharkhand: Jharkhand mandated knowledge of regional and tribal languages for government jobs, requiring candidates to score at least 30% in languages like Mundari, Santhali, Ho, or Kurukh.
- West Bengal: Encourages hiring candidates fluent in Bengali for government jobs.
What are the Key Constitutional Provisions Related to Official Language?
- Article 345: Article 345 of the Constitution states that a state legislature can choose one or more languages to be used for official purposes.
- This includes the language or languages already spoken in the state, or Hindi.
- Article 347: Article 347 of the Constitution deals with the recognition of languages spoken by a section of a state's population.
- It allows the President to officially recognize such languages if a substantial portion of the state's population requests it.
- This provision allows the inclusion of regional languages into the official framework of the state, ensuring linguistic inclusivity.
- Article 350A: Article 350A of the Constitution requires states to provide adequate facilities for instruction in the mother tongue for children from linguistic minority groups. This applies to primary education.
- Article 351: Article 351 of the Constitution provides for the promotion of the spread of Hindi as a link language without overriding the linguistic rights of states to promote their official languages.
Committees and Commissions Related to Languages of Union
- The Official Languages Commission (1955): It was established under the Chairmanship of B.G. Kher, that examined the issue of the use of Hindi and English as the official language of the Union and made recommendations for the transition to Hindi.
- Parliamentary Committee of Official Language (1976): The Parliamentary Committee of Official Language (1976) recommends replacing English with Hindi in institutions and Central services exams.
- However, these proposals have not been fully implemented due to resistance, especially from non-Hindi speaking states.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements:(2021)
- 21st February is declared to be the International Mother Language Day by UNICEF.
- The demand that Bangla has to be one of the national languages was raised in the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to India, the terms ‘HaIbi, Ho and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
(a) dance forms of Northwest India
(b) musical instruments
(c) pre-historic cave paintings
(d) tribal languages
Ans: (d)
Q3. Which one of the following was given classical language status recently? (2015)
(a) Odia
(b) Konkani
(c) Bhojpuri
(d) Assamese
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
Jal Jeevan Mission Extended Till 2028
Union Budget 2025-26 has extended the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) till 2028 with the aim of benefiting the remaining (20%) rural households.
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)
- About: The JJM was launched in 2019 with the aim to provide drinking tap water supply to every rural household by 2024, targeting 55 liters per person per day.
- Progress: In 2019, only 3.23 crore (17%) of rural households had tap water connections.
- As of 2024, it covered 15 crore households (80% of rural India).
- Focus: The extension of the Mission will focus on improving the quality of infrastructure and ensuring the operation and maintenance of rural piped water supply systems, with a strong emphasis on public participation.
- Memorandums of Understanding (MoUs): New MoUs will be signed with states and union territories to ensure the sustainability and citizen-centric water service delivery.
- Impact of JJM:
- Time Savings: WHO estimates JJM will save over 5.5 crore hours daily, primarily for women, spent collecting water.
- Health Benefits: JJM could prevent nearly 400,000 deaths from diarrheal diseases and save 14 million Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs).
- Child Mortality Reduction: Research suggests safe water could reduce child mortality by 30%, saving 136,000 lives annually.
Read More: Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)


Rapid Fire
Breach of Parliamentary Privileges
Formal notices of breach of parliamentary privilege were filed against some MPs following their comment on the President address.
- Breach of Parliamentary Privilege: A breach of privilege occurs when someone disregards or attacks the privileges, rights, or immunities of a member or the House itself.
- About Parliamentary Privilege: Parliamentary privileges and immunities are special rights granted to MPs and MLAs to ensure their effective functioning without external interference.
- Sources:
- Constitution i..e, Article 105, Article 122, Article 194, and Article 212.
- Parliamentary Conventions (based on British parliamentary practices as of 1947).
- Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business (Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha)
- Judicial Interpretations (Supreme Court and High Court rulings)
- Statutory Laws (laws enacted by Parliament) (Currently, there is no act of the Parliament defining parliamentary privileges).
- Parliamentary Privilege Includes:
- Individual Privileges: Freedom of Speech, Immunity from Legal Proceedings, Freedom from Arrest etc.
- Collective Privileges: Secret Sittings, Inquiry Powers, Judicial Immunity etc.
- Under Article 87, the President addresses both Houses of Parliament at the start of the first session after each general election and at the commencement of the first session of each year.
Read More: Parliamentary Privileges and Immunities


Rapid Fire
India Won ICC Under-19 Women’s T20 World Cup 2025
India won the International Cricket Council (ICC) Under-19 Women’s T20 World Cup 2025, defeating South Africa in Malaysia.
- It is organised by the ICC, it features national women's under-19 teams competing in the Twenty20 format.
- First Edition: The inaugural ICC Under-19 Women’s T20 World Cup was held in 2023, with South Africa as the host. India won the maiden title, defeating England.
- ICC: It is the global governing body for cricket, responsible for overseeing 108 members (including India) and managing the sport worldwide.
- Enforces the ICC Code of Conduct and playing conditions, and appoints match officials for international matches.
- ICC plays a crucial role in combating corruption and match-fixing through its Anti-Corruption Unit, ensuring the integrity of the sport.
- Formats of Cricket: The ICC recognizes three main formats of cricket at the international level (Test matches, One-Day Internationals (ODIs), and Twenty20 Internationals (T20Is)).
- Test cricket: The oldest format (since 1877), lasting five days with two innings per team.
- ODIs: Introduced in 1971, these 50-over matches blend technique, speed, and skill.
- T20Is: Introduced in 2005, T20Is are the newest, shortest (usually competed in three hours) and fastest form of cricket, with each team playing 20 overs.
Read more: India Won the 2024 T20 World Cup


Place in News
Haiti
Haiti faces a surge in gang violence, with over 5,600 deaths in 2024. The United Nations (UN) highlighted human rights violations and corruption exacerbating the crisis.
- It is driven by political instability, corruption, weak governance, economic hardship, impunity, and the flow of illegal arms, compounded by widespread displacement.
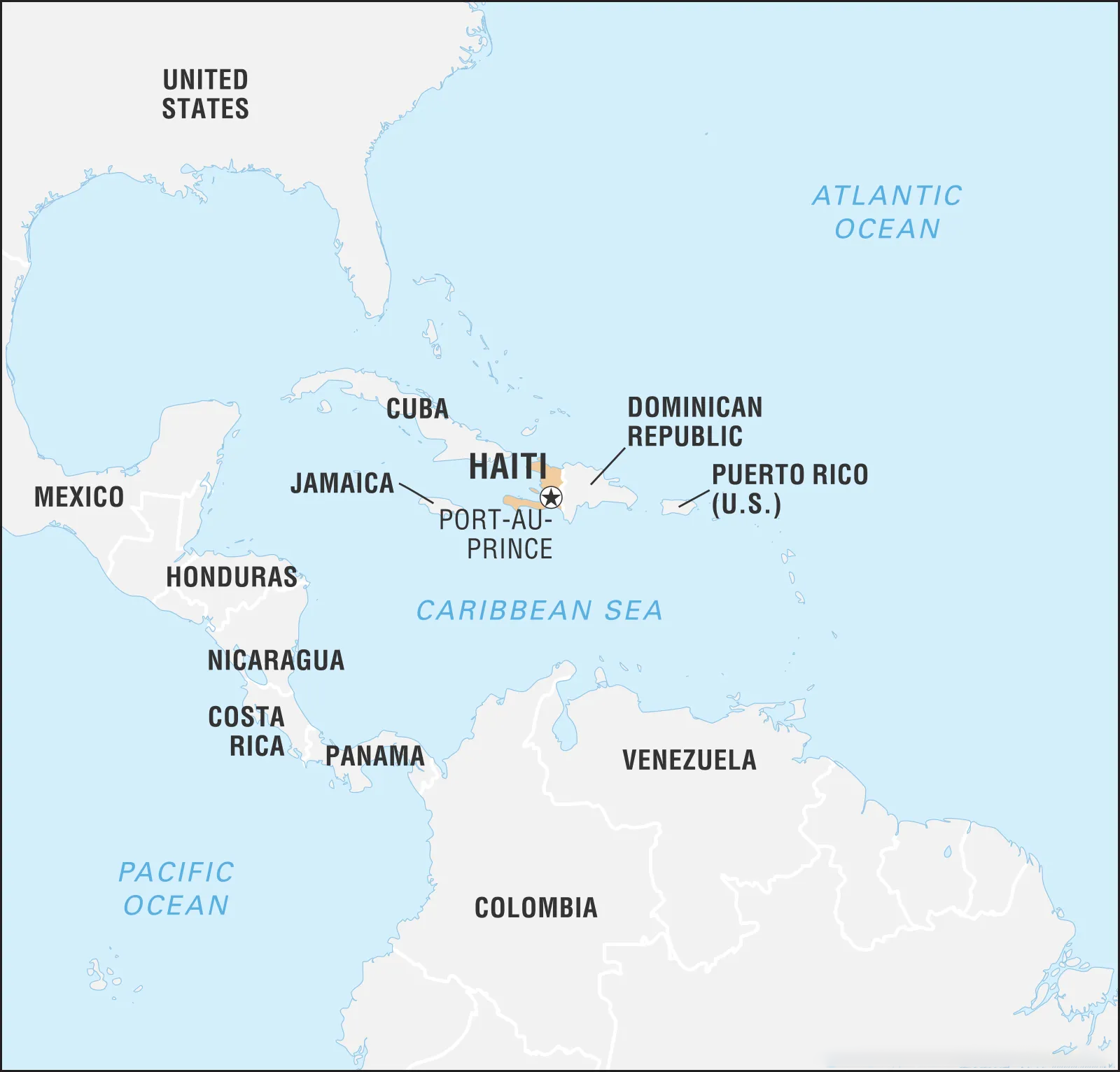
Haiti:
- Location: Between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean.
- It occupies the western third of Hispaniola Island, bordered by the Dominican Republic to the east, Jamaica to the west, and Cuba to the northwest.
- Official Languages: French and Haitian Creole
- Historical Significance: World’s first independent Black-led republic, after over 200 years of Spanish rule and more than 100 years of French rule.
India-Haiti Relations:
- India and Haiti maintain friendly relations and diplomatic ties were established in 1996.
- In 1995, India sent a 140-member CRPF troop to Haiti on a UN peace mission.
- India has been offering assistance to Haiti under the ITEC programme.
Read More: Assasination of Haiti’s President



 _Framework.png)