Governance
3 Years of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- 05 Oct 2024
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), DPDP Act, 2023, Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS), National Medical Commission, National Dental Register (NDR).
For Mains: Key Features of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and Related Challenges.
Why in News?
The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) completed its three-year journey on 27th September, aiming to revolutionize the nation's digital healthcare ecosystem by enhancing accessibility, efficiency, and transparency in healthcare.
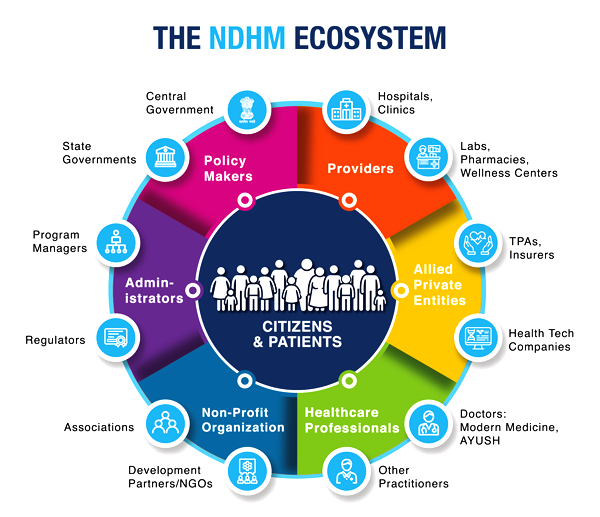
What is Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- About:
- It was launched in 2021 with the aim to provide digital health IDs for all Indian citizens to help hospitals, insurance firms, and citizens access health records electronically when required.
- The National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the implementing Agency of ABDM.
- Key Features of ABDM:
- Unique Health Identifier for Citizens: A unique Health ABHA ID for each individual to securely store and manage health records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): A comprehensive repository of healthcare professionals across modern and traditional systems, enabling connection to India’s digital health ecosystem.
- Health Facility Registries (HFR): A comprehensive repository of public and private health facilities across all systems of medicine, including hospitals, clinics, labs, and pharmacies.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): Facilitates the discovery and delivery of health services, thereby streamlining healthcare interactions and improving service accessibility.
- Data Privacy and Security: In alignment with the DPDP Act, 2023, the ABDM ensures the security, confidentiality, and secure sharing of patient related health information.
- Transparency: It offers individuals access to public and private health services, ensures guideline compliance, and promotes transparency in pricing and accountability.
- Key Initiatives:
- Scan and Share: A QR-code-based OPD registration service allows patients to scan facility QR codes and share their demographic details, minimising queues and reducing data inaccuracies.
- Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): The DHIS encourages hospitals, diagnostic labs, and digital health solution providers to adopt transformative digitization practices through various incentives.
- Microsites for Private Sector Adoption: It is aimed at addressing various challenges in ABDM adoption, especially for private sector providers, has successfully operationalised 106 microsites, surpassing the initial target of 100.
- End to End ABDM Adoption Pilot: The pilot aims to digitise public and private facilities nationwide through comprehensive ABDM adoption, establishing model facilities as benchmarks for future efforts.
- New Portals: The NHA has also developed portals like the National Medical Register (NMC) for the National Medical Commission and the National Dental Register (NDR) for the National Dental Council.
Note:
- National Health Authority (NHA) is the apex body responsible for implementing India’s flagship public health insurance/assurance scheme.
- It was established on 2nd January 2019 under the Society Registration Act, 1860.
What are the Achievements of Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- ABHA ID: By September 2024, over 67 crore ABHA IDs have been created, providing citizens with unique digital health IDs for secure access to and sharing of their health records.
- More than 42 crore health records have been linked to ABHA, allowing seamless access to medical histories and improving healthcare delivery.
- Integration: Over 236 private entities, including labs, pharmacies, and digital solution companies, have integrated with the ABDM ecosystem to support interoperability.
- Public institutions like AIIMS Delhi and AIIMS Bhopal are top performers in generating Scan and Share OPD registrations.
- Leading private healthcare chains have also played a major role in the success of the ABDM.
- National Healthcare Providers Registry (NHPR): The launch of the NHPR has resulted in the registration of 3.3 lakh health facilities and 4.7 lakh healthcare professionals.
- NHPR is a comprehensive repository of registered healthcare professionals and health facilities.
What are the Major Concerns Related to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- Limited Digital Infrastructure:
- Many rural and remote areas suffer from unreliable internet connectivity and low digital literacy, hindering effective engagement with and access to the ABDM.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns:
- The digitization of health records raises concerns about data privacy, cybersecurity, and consent management, highlighting challenges in protecting sensitive health information.
- Cost and Resource Allocation:
- High implementation costs and inadequate government funding for infrastructure, training, and capacity building make it challenging for smaller healthcare facilities and practitioners to adopt the ABDM.
- Regulatory and Legal Framework:
- The evolving regulatory framework for digital health, including unclear data protection laws and patient consent guidelines, creates ambiguity in accountability and responsibility regarding health data ownership and management.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Digital Infrastructure: Investment in enhancing internet connectivity and digital literacy programs in rural and remote areas can be done to ensure equitable access to the ABDM. Collaboration with telecom providers can facilitate the establishment of robust digital networks.
- Enhancing Data Privacy and Security Measures: Developing comprehensive data protection regulations and cybersecurity protocols to address privacy concerns. Implementing strict consent management frameworks will help safeguard sensitive health information and build trust among users.
- Increased Funding and Resource Allocation: Allocating sufficient government resources to support the implementation of ABDM, particularly for smaller healthcare facilities. This includes providing financial assistance for infrastructure development, training programs, and capacity building initiatives.
- Establishing a Clear Regulatory Framework: Creating a coherent and comprehensive regulatory framework that defines data protection laws, patient consent guidelines, and accountability measures. This will clarify responsibilities regarding health data ownership and management, fostering a secure and trustworthy digital health ecosystem.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the key components of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and analyse its potential impact on the Indian healthcare system? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, consider the following statements:
- Private and public hospitals must adopt it.
- As it aims to achieve universal health coverage, every citizen of India should be part of it ultimately.
- It has seamless portability across the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)