Infographics
Biodiversity & Environment
Conference on Human-Wildlife Conflict
For Prelims: Human-Wildlife Conflicts, International Union for Conservation of Nature, FAO, UNDP.
For mains: Issues of Human-Wildlife Conflict and Solutions.
Why in News?
Recently, the International Conference on Human-Wildlife Conflict and Coexistence was held in Oxford, the United Kingdom, which has brought hundreds of activists from 70 countries to discuss solutions to address Human-Wildlife Conflicts.
- The Conference was organized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the UN Development Programme and several other organizations together.
What does the Conference Aim at Achieving?
- Facilitate dialogue and peer-to-peer learning across sectors and actors on the topic for partnerships and collaboration across people and institutions working on human-wildlife conflict.
- Generate interdisciplinary and shared understanding of the latest insights, technologies, methods, ideas, and information from the field of human-wildlife conflict, coexistence and interactions.
- Mainstream human-wildlife conflict as one of the top global priorities in biodiversity conservation and the Sustainable Development Goals for the next decade, catalysing opportunities for working together on national, regional or global policies and initiatives.
- Identify and develop a collective way forward for addressing knowledge and implementation gaps for effective efforts to reduce and manage human-wildlife conflict.
What is the Need for this Conference?
- Human-wildlife conflicts across the world are a major challenge to conservation of species, making coexistence with nature difficult and hinders biodiversity protection.
- Conflict-related killing affects more than 75% of the world’s wild cat species, according to the United Nations Environment programme (UNEP).
- It will provide a platform for experts from the fields of “ecology, animal behaviour, psychology, law, conflict analysis, mediation, peacebuilding, international development, economics, anthropology and others, to understand human-wildlife conflict through various viewpoints, learn from each other, and build new links and collaborations.
- Effective management of human-wildlife interactions is prescribed in Target 4 of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework agreed at the UN Biodiversity Conference in December 2022.
What is Human-Animal Conflict?
- About:
- Human-animal conflict refers to situations where human activities, such as agriculture, infrastructure development, or resource extraction, come into conflict with wild animals, leading to negative outcomes for both humans and animals.
- Implications:
- Economic Losses: Human-animal conflict can result in significant economic losses for people, especially farmers and livestock herders. Wild animals can destroy crops, damage infrastructure, and kill livestock, leading to financial hardship.
- Threats to Human Safety: Wild animals can pose a threat to human safety, especially in areas where people and wildlife coexist. Attacks by large predators such as lions, tigers, and bears can result in serious injury or death.
- Ecological Damage: Human-animal conflict can have a negative impact on the environment. For example, when humans kill predators, it can lead to an increase in prey populations, which can then cause ecological imbalances.
- Conservation Challenges: Human-animal conflict can also pose a challenge to conservation efforts, as it can lead to negative perceptions of wildlife and make it difficult to implement conservation measures.
- Psychological Impacts: Human-animal conflict can also have psychological impacts on people, especially those who have experienced attacks or property damage. It can lead to fear, anxiety, and trauma.
- Government Measures:
- The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: This act provides the legal framework for the activities, Prohibition of hunting, Protection and management of wildlife habitats, Establishment of protected areas etc.
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002: India is a part of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity. The provisions of the Biological Diversity Act are in addition to and not in derogation of the provisions in any other law relating to forests or wildlife.
- National Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016): It focuses on strengthening and enhancing the protected area network, on the conservation of Endangered wildlife and their habitats, on controlling trade in wildlife products and on research, education, and training.
- Project Tiger: Project Tiger is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme of the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC) launched in 1973. It provides havens for tigers in the country’s national parks.
- Project Elephant: It is a centrally sponsored scheme and was launched in February 1992 for the protection of elephants, their habitats and corridors.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC): (2017)
- TRAFFIC is a bureau under United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
- The mission of TRAFFIC is to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC), the wildlife trade monitoring network, is a joint program of World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) and IUCN – the International Union for Conservation of Nature. It was founded in 1976. It is not a bureau under UNEP. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- TRAFFIC works to ensure that trade in wild plants and animals is not a threat to the conservation of nature. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- TRAFFIC focuses on leveraging resources, expertise and awareness of the latest globally urgent species trade issues such as tiger parts, elephant ivory and rhino horn. Large scale commercial trade in commodities like timber and fisheries products is also addressed and linked to work on developing rapid results and policy improvements. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Biodiversity & Environment
Salt Marshes Succumb to Sea Level Rise
For Prelims: Salt marshes, carbon sink, coastal ecosystem.
For Mains: Importance of salt marshes in the coastal ecosystem, threats and conservation methods, Ecosystems under threat.
Why in News?
For the past 50 years, researchers from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) have monitored the vegetative cover of the Great Sippewissett Marsh in Falmouth, Massachusetts, to examine the effects of increased nitrogen levels on the marsh grass species there.
- But a recent study suggests that by the turn of the century, more than 90% of these biologically productive ecosystems could be lost to sea level rise.
What are Salt Marshes?
- About:
- Salt marshes are coastal wetlands that are regularly flooded and drained by tides. They are unique ecosystems that are situated between land and sea, and they consist of a mixture of grasses, sedges, rushes, and other plants that can tolerate high levels of salt.
- Characteristics:
- Salt marshes are marshy because the soil may be composed of deep mud and peat. Peat is made of decomposing plant matter that is often several feet thick.
- Salt marshes smell like sulfurous rotten-egg smell. Because salt marshes are frequently submerged by tides and contain a lot of decomposing plant material, oxygen levels in the peat can be extremely low—a condition called hypoxia.
- Hypoxia is caused by the growth of bacteria which produce the sulfurous rotten-egg smell that is often associated with marshes and mud flats.
What are the Advantages of Salt Marshes?
- Salt marshes have long been considered one of the most productive and biologically diverse ecosystems on the planet. They serve as a vital habitat for numerous species of fish, birds, and other wildlife.
- Salt marshes are the “ecological guardians of the coast” that maintain healthy fisheries, coastlines and communities.
- They provide shelter, food and nursery grounds for more than 75% of coastal fisheries species including shrimp, crab and many finfish.
- Salt marshes also protect shorelines from erosion by creating a buffer against wave action and by trapping soils.
- Salt marshes reduce the flow of flood water and absorb rainwater. By filtering runoff and excess nutrients, salt marshes also help to maintain water quality in coastal bays, sounds and estuaries.
- Salt marshes are also important carbon sinks, meaning they absorb and store large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This helps to mitigate the impacts of climate change by reducing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
What are the Threats to Salt Marshes?
- Despite their numerous advantages, salt marshes are facing a number of threats that could put their survival at risk. One of the most significant of these threats is sea level rise.
- As sea levels continue to rise due to climate change, salt marshes are at risk of being submerged and disappearing entirely.
- Another threat to salt marshes is the introduction of excess nitrogen, which can alter the balance of plant species and lead to a loss of biodiversity. This excess nitrogen can come from a variety of sources, including fertilizer runoff from agricultural fields and urban areas.
- Anthropogenic activities, such as the construction of seawalls and other structures along the coast, can also prevent salt marshes from migrating landward in response to rising sea levels.
- This can lead to a phenomenon known as “coastal squeeze,” where the marshes are squeezed between rising seas and man-made barriers.


Governance
Lokayukta
For Prelims: Lokayukta, Chief Minister’s Distress Relief Fund (CMDRF), Ombudsman, Administrative Reforms Commission, Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act in 2013.
For Mains: Issues Related to Lokayukta in India.
Why in News?
The Kerala Lokayukta, has referred a case related to alleged nepotism and anomalies in the Chief Minister’s Distress Relief Fund (CMDRF) to a three-member full bench for investigation.
What is Lokayukta?
- About:
- The Lokayukta is the Indian Parliamentary Ombudsman, executed into power, through and for, each of the State Governments of India.
- It is an anti-corruption authority. The object of Lokayukta system in a state is to make investigation of grievances, allegations against public servants.
- Origin:
- The origin of the Lokayukta can be drawn to the Ombudsman in Scandinavian countries.
- In India, the Administrative Reforms Commission, (1966-70), had recommended the creation of the Lokpal at the Centre and Lokayukta in the states.
- Before the passing of the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act in 2013, several states in India passed laws for creating the Institution of 'Lokayukta'.
- Maharashtra was first in this respect with its Lokayukta body established in 1971.
- Appointment:
- The lokayukta and upalokayukta are appointed by the Governor of the state. While appointing, the governor in most of the states consults (a) the chief justice of the state high court, and (b) the leader of Opposition in the state legislative assembly.
- Tenure:
- In most of the states, the term of office fixed for lokayukta is of 5 years duration or 65 years of age, whichever is earlier. He is not eligible for reappointment for a second term.
- Issues Related to Lokayukta:
- No Clear Legislation:
- The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act 2013 only has one section on Lokayukta, which mandates that states must pass the Lokayukta Act within one year and there is no information about their makeup, powers, or other features.
- States, in fact, have complete autonomy over how their own Lokayuktas are appointed, how they work, and under what conditions they serve.
- Delay in Resolution:
- One of the major challenges faced by the Lokayukta is the delay in the investigation and resolution of complaints.
- The Lokayukta is also dependent on the state government for funding and infrastructure, which can lead to interference and lack of independence.
- No Clear Legislation:
Way Forward
- Strengthening the Lokpal and Lokayukta Act: The Lokpal and Lokayukta Act should be amended to provide more powers to the Lokayukta, such as the power to investigate and prosecute cases of corruption against all public servants, including the Chief Minister and the judiciary.
- Ensure Adequate Resources and Staffing: The Lokayukta offices across the country need to be adequately staffed and resourced to enable them to effectively carry out their mandate.
- Enhance Accountability and Transparency: The Lokayukta should be made more accountable and transparent in its functioning. It should regularly publish reports on its activities, investigations, and outcomes.


International Relations
Promoting India's Culture through Foreign Students
For Prelims: Awards of Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR), Indian Tourism Development Corporation, All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE).
For Mains: India’s Soft power diplomacy, Functions of Indian Council for Cultural Relations.
Why in News?
The Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) plans to expand India's cultural footprint globally by utilising the experiences of foreign students studying in India.
- This "soft power diplomacy" is meant to spread the India story when students go back to their home countries.
What are the Initiatives of ICCR To Expand India’s Cultural Footprints?
- The ICCR will start E-3 or Exit Engagement Evenings with foreign students 3 to 4 months before they finish their courses in various Central and State universities, institutes, and agricultural colleges of the country.
- After the engagement evenings, the students are sure to go back and promote Indian heritage and aspects of its unique culture.
- The engagements would also include visits to places of national importance. The ICCR has zeroed in on the Khadi Commission, the Indian Tourism Development Corporation, and the Department of AYUSH to hold these evenings with the students.
- The ICCR has also launched a website called the India Alumni Portal in April 2022 as a platform to connect with foreign students around the world who have studied in India.
What is the Current Status of Foreign Students Enrolling in India?
- The number of foreign students enrolled in Indian higher education institutions was 48,035 in 2020-21, a marginal dip from 49,348 in 2019-20, according to the latest All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) brought out by the Ministry of Education.
- People from more than 160 countries visit India to study, with Nepal, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, the U.S., the UAE, Bhutan, Sudan, Nigeria, Tanzania, and Yemen being the countries from which the majority of the students came.
What are the Functions of Indian Council for Cultural Relations?
- About:
- The ICCR is an autonomous organisation of the Government of India under the Ministry of External Affairs.
- It was established in 1950 with the aim of promoting Indian culture and its values abroad and fostering cultural exchanges between India and other countries.
- Functions:
- Organising cultural festivals, performances, exhibitions, and lectures in India and abroad.
- Granting scholarships to foreign students to study in India.
- Offering courses in Indian music, dance, yoga, and languages.
- ICCR has been assigned the responsibility of facilitating the celebration of the International Day of Yoga by Indian Missions/Posts abroad since 2015.
- Collaborating with international organisations, cultural institutions, and foreign governments to promote cultural exchanges.
- Awards:
- Distinguished Indologist Award, World Sanskrit Award, Distinguished Alumni Award – Citation and Plaque and Gisela Bonn Award.


Biodiversity & Environment
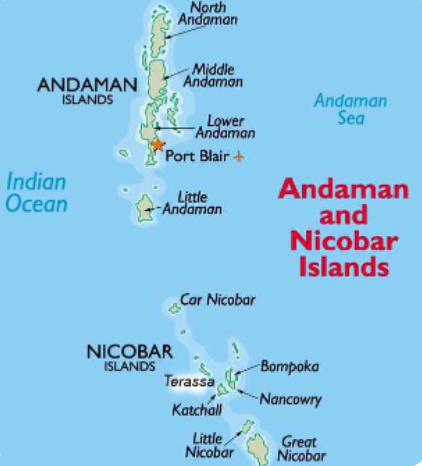
Internet Connectivity in Andaman and Nicobar Islands
For Prelims: Chennai-Andaman & Nicobar Islands (CANI), Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF), Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups, Coral reefs, Submarine Optical Fibre Cable (OFC).
For Mains: Significance of ANI for India, Recent Developmental Plans for ANI, Challenges Related to ANI.
Why in News?
Port Blair has seen significant improvements in Internet Connectivity since August 2020, when the Chennai-Andaman & Nicobar Islands (CANI) cable was inaugurated.
- However, Andaman & Nicobar Islands (ANI) is currently encountering a number of challenges that necessitate the adoption of an objective viewpoint in order to ensure the comprehensive and enduring progress of ANI towards inclusivity and sustainability.
What are the Recent Developments in Internet Connectivity in ANI?
- The undersea cable between the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Chennai, i.e., CANI, connecting the Union Territory to the global Internet, has seen a reasonable level of interest from telecom operators.
- The Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) provided information that telecom operators have purchased over 70 GBPS of bandwidth for internet connectivity in Andaman and Nicobar Islands (ANI).
- Airtel and BSNL account for the lion’s share of the purchased bandwidth, with 60 GBPS being allocated to the two telcos. Airtel even launched 5G services in Port Blair.
What is the Significance of ANI for India?
- About:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a group of islands at the southeastern edge of the Bay of Bengal.
- They are part of the union territory of India and are situated approximately 1,400 km from the Indian mainland.
- Significance:
- Treasure of Tribes: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are home to 5 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups: Great Andamanese, Jarwas, Onges, Shompens and North Sentinelese.
- Strategic Location: They give India a commanding position over the Sea Lines of Communication (SLOCs) and the considerable traffic that flows to and fro between the Indian and Pacific Oceans through the Malacca Strait.
- Space for Maritime Partners: India's key maritime partners such as the US, Japan, Australia and France acknowledge and recognise the strategic location of the Andaman and Nicobar.
- These islands not only provide India with a key maritime space but also carry significant potential in shaping the strategic and military dynamics of the Indian Ocean region.
- Recent Developmental Plans for ANI:
- Japan’s Overseas Development Assistance: Japan approved a USD 265 crore grant aid for ANI development projects in 2021.
- NITI Aayog’s Project for Great Nicobar: It includes an international container transhipment terminal, an airport, a power plant, and a township.
- NITI Aayog’s Proposal for Little Andaman: The plan calls for the development of a new greenfield coastal city to compete with Singapore and Hong Kong.
What are the Challenges Related to ANI?
- Unsustainable Development: Andaman and Nicobar have become a major tourist attraction, and this has resulted in many development projects being initiated in this region.
- While at one side it will transform the islands substantially, it would also cause loss of ecological stability.
- Developmental activities are also impacting the coral reefs in the area, which are already under threat from warming oceans, and are of enormous ecological importance.
- Environmentalists have also flagged the loss of mangroves on the island as a result of the development project.
- Geological Volatility: The Andaman and Nicobar island's groups lie in a seismically highly active zone. Due to this, the region is prone to a number of natural disasters.
- For instance, in 2004 an earthquake and accompanying tsunami devastated large parts of the island chain.
- Nicobar and Car Nicobar (northernmost Nicobar Island) lost almost one-fifth of its population and close to 90% of its mangroves.
- For instance, in 2004 an earthquake and accompanying tsunami devastated large parts of the island chain.
- Geo-Political Instability: Andaman and Nicobar Islands are part of the Indo-Pacific geopolitical theatre, where China is actively trying to expand its influence, potentially posing a threat to India's blue economy and maritime security.
- Encroachment in Tribal Space: While PVTGs are accorded the highest level of protection by local administration, they still face numerous challenges due to encroachment into their areas in the name of development, and lack of effective rehabilitation program.
Way Forward
- Sustainable Island Development Framework: Infrastructure and developmental projects in Andaman and Nicobar will no doubt aid India’s strategic and maritime capabilities, but such development should not come at the cost of the exploitation of the ecosystem that the Andaman and Nicobar offers.
- Prior to any development activity in this region, an Environmental and Social Impact Assessment should be made mandatory.
- A Sustainable Island Development framework is not only important for the Andaman and Nicobar but should also be applicable to other Indian islands as well.
- Developing Island Security Model: There is a need for India to invest in capacity building in maritime security and incentivize research, to develop an Island Security Model, and to equip its Navy with the latest technology to track any infiltration attempt.
- Revitalising Linking Projects: There is a need to revitalise the plan of linking the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to the mainland through Submarine Optical Fibre Cable (OFC).
- Submarine Cable will also assist A&N in providing cheaper and better connectivity and all of Digital India's advantages, especially in improving online education, telemedicine, banking and online trading.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following have coral reefs? (2014)
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Gulf of Kachchh
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q3. In which one of the following places is the Shompen tribe found? (2009)
(a) Nilgiri Hills
(b) Nicobar Islands
(c) Spiti Valley
(d) Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and its partners successfully demonstrated a precise landing experiment for a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) at the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR), Chitradurga, Karnataka.
- An Indian Air Forces (IAF) Chinook helicopter was used to drop the RLV-TD from a 4.5 km altitude and ISRO executed the landing experiment of the RLV-TD as planned.
What is ISRO’s RLV Project?
- About:
- According to ISRO, the series of experiments with the winged Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstration (RLV-TD) are part of efforts at “developing essential technologies for a fully reusable launch vehicle to enable low-cost access to space”.
- In the future, this vehicle will be scaled up to become the first stage of India’s reusable two-stage orbital (TSTO) launch vehicle.
- Features and Application:
- ISRO’s RLV-TD looks like an aircraft. It consists of a fuselage, a nose cap, double delta wings, and twin vertical tails.
- The RLV-TD will be used to develop technologies like hypersonic flight (HEX), autonomous landing (LEX), return flight experiment (REX), powered cruise flight, and Scramjet Propulsion Experiment (SPEX).
- Significance:
- With the costs acting as a major deterrent to space exploration, a reusable launch vehicle is considered a low-cost, reliable, and on-demand mode of accessing space.
- By using RLVs the cost of a launch can be reduced by nearly 80% of the present cost.
- With the costs acting as a major deterrent to space exploration, a reusable launch vehicle is considered a low-cost, reliable, and on-demand mode of accessing space.
- Other Previous Experiment:
- ISRO had earlier demonstrated the re-entry of its winged vehicle RLV-TD in the HEX mission in May 2016.
- In HEX, the vehicle landed on a hypothetical runway over the Bay of Bengal. Precise landing on a runway was an aspect not included in the HEX mission.
- The LEX mission achieved the final approach phase that coincided with the re-entry return flight path exhibiting an autonomous, high speed (350 kmph) landing.
- Other Agencies Using RLV or Partial RLV:
- Reusable space vehicles have been in existence for a long time with NASA space shuttles carrying out dozens of human space flight missions.
- SpaceX has been demonstrating partially reusable launch systems with its Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets since 2017.
- SpaceX is also working on a fully reusable launch vehicle system called Starship.
Conclusion
The successful landing experiment of the RLV-TD programme marks a significant milestone in India’s space technology development. The RLV-TD is an important step towards achieving low-cost access to space, and its successful implementation will benefit India’s space program in the future.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Seed Bank at Asola Bhatti Sanctuary
Why in News?
A ‘seed bank for native plant species found in the Aravallis region is gradually taking shape at a nursery at the Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary, after a few years of efforts at collecting seeds from across Delhi and other states.
What is the Project?
- About:
- The project, which started in 2015, is being implemented jointly by the Forest Department and the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS).
- The nursery at Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary is growing more than 100 species of native grasses, plants, and trees, and provides saplings for plantation by agencies in the city.
- Aim:
- The aim of the seed bank is to supply native saplings for the city and reintroduce species that have become rare or hard to locate.
- The seed bank also aims to create awareness around the trees that are disappearing in Delhi, have these trees available for people to be able to grow them, and map where they are.
- The plan is to raise production to around 10 lakh saplings every year.
What is Seed Bank?
- About:
- Seed banks are important repositories of plant genetic resources.
- They store seeds of different plant varieties, which are conserved to maintain their genetic diversity and to preserve their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Seed banks also serve as important resources for research, agriculture, and conservation.
- India’s Seed Bank:
- India has established its own seed storage facility at Chang La in Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir.
- It has been built jointly by the Defence Institute of High-Altitude Research (DIHAR) and the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR) in 2010 under the aegis of Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It stores over 5,000 seed accessions (one accession consists of a set of seeds of a particular species collected from different geographical and demographic locations).
- India has established its own seed storage facility at Chang La in Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir.
- World’s Largest Seed Vault:
- Svalbard Global Seed Vault or Doomsday Vault is the world’s largest seed storage facility situated at Norway.
Asola-Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary
- Asola-Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary covering 32.71 sq. km area on the Southern Delhi Ridge of Aravalli hill range on Delhi-Haryana border lies in Southern Delhi as well as northern parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts of Haryana state.
- It is also part of the Sariska-Delhi Wildlife Corridor, which runs from the Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan to Delhi Ridge.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of food and nutritional security of India, enhancing the ‘Seed Replacement Rates’ of various crops helps in achieving the food production targets of the future. But what is/are the constraint/constraints in its wider/greater implementation? (2014)
- There is no National Seeds Policy in place.
- There is no participation of private sector seed companies in the supply of quality seeds of vegetables and planting materials of horticultural crops.
- There is a demand-supply gap regarding quality seeds in case of low value and high volume crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- In 2002, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare rolled out National Seed Policy, which envisioned development of new and improved varieties of plants, timely availability of quality seeds, the compulsory registration of the seeds, creation of infrastructure facilities, quality assurance, promotion of seed industry, abolition of licensing for seed dealers, facility for import of the best quality seeds, encouragement for export of seeds and creation of Seed Banks And National Seed Grid. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- As per the seed policy, private seed production agencies were involved in the supply of quality seeds of vegetables and planting materials of horticultural crops. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Seed Replacement Rate (SRR) is the percentage of area sown out of the total area of crop planted in the season by using certified/quality seeds other than the farm saved seed.The Planning Commission in its mid term appraisal of the 10th Five Year Plan (2002-07) pointed out that SRR remained within 2-10% in certain states for certain crops, which was below the targeted SRR of 33%. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- According to the Success Report 2018-19 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, India has achieved 33% SRR for self pollinated crops with improvement in the production of High Yielding Variety (HYV) seed.
- Therefore, as per 2002-2007 data, option (b) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
New Butterfly Species Discovered in Kerala
Why in News?
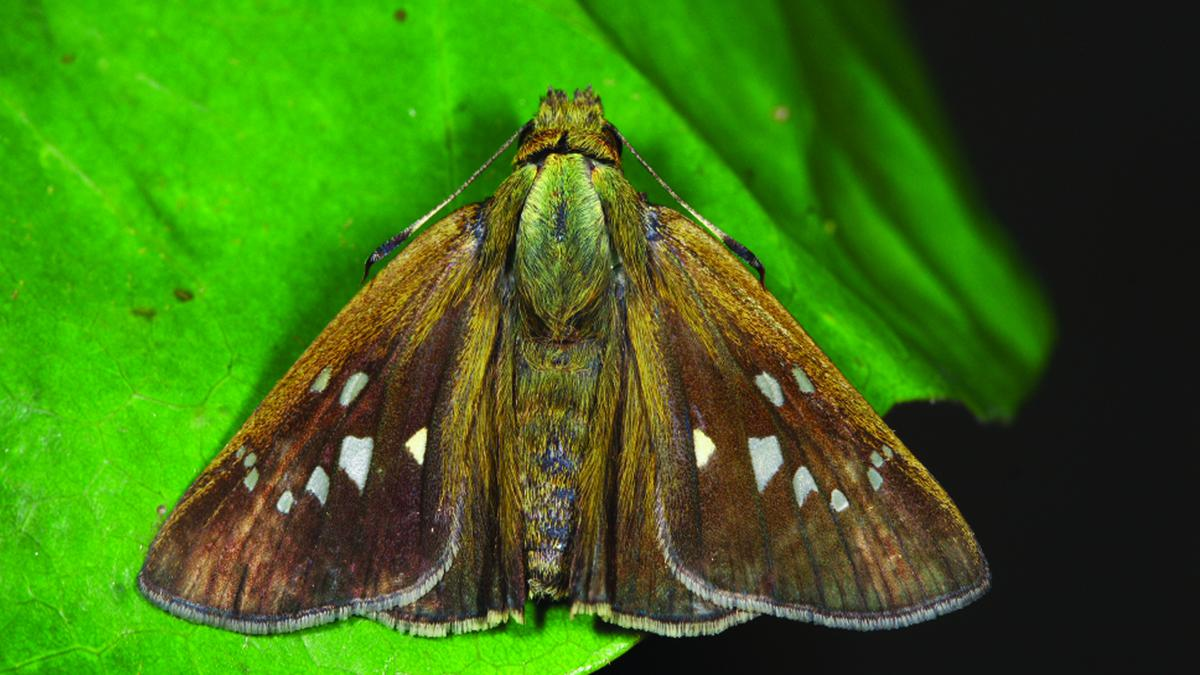
Recently, a butterfly subspecies (Caltoris bromus sadasiva) from the fringes of Akkulam and Vembanad lakes in Kerala has been discovered.
What are the Key Points Related to the Discovery?
- About: It belongs to the skipper butterfly family of Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies).
- It is the first documented subspecies of the Bromus swift ( Caltoris bromus) butterfly in the Western Ghats and Peninsular India.
- Number of Butterfly Species: The discovery of Caltoris bromus sadasiva brings the count of butterfly species in the Western Ghats to 336 and the count of skipper butterflies to 83, with the last skipper butterfly discovery being almost 75 years ago.
- Caltoris: Caltoris, an Indo-Australian genus has over 15 species distributed across south-east Asia. Caltoris bromus, one of them, has two other subspecies Caltoris bromus bromus and Caltoris bromus yanuca.
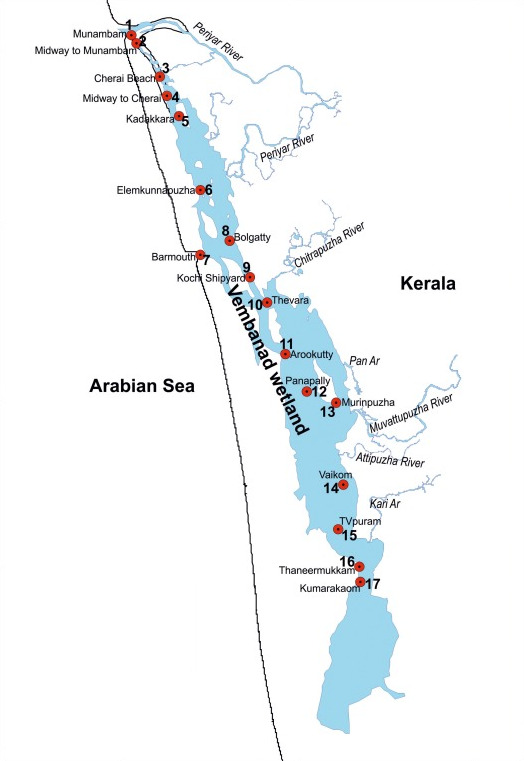
What are the Key Facts about Vembanad Lakes?
- This is the largest lake in Kerala and the longest Lake in India.
- Vembanad Lake is also known as Vembanad Kayal, Vembanad Kol, Punnamada Lake (in Kuttanad) and Kochi Lake (in Kochi).
- The lake has its source in four rivers, Meenachil, Achankovil, Pampa and Manimala.
- It is separated from the Arabian Sea by a narrow barrier island and is a popular backwater stretch in Kerala.
- In 2002, it was included in the list of wetlands of international importance, as defined by the Ramsar Convention.
- It is the second-largest Ramsar site in India only after the Sundarbans in West Bengal.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Recently, for the first time in our country, which of the following States has declared a particular butterfly as State Butterfly? (2016)
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Karnataka
(d) Maharashtra
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Maharashtra became the first State in the country to have a ‘State Butterfly’. It declared the Blue Mormon (Papilio polymnestor) as the State Butterfly.
- It is the second largest butterfly in India after the Troides minos commonly known as the Southern Birdwing.
- It is found only in Sri Lanka, Western Ghats of Maharashtra, South India and coastal belts of the country.
- It has velvet and black wings with bright blue spots. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q2. In which of the following regions of India are you most likely to come across the ‘Great Indian Hornbill’ in its natural habitat? (2016)
(a) Sand deserts of northwest India
(b) Higher Himalayas of Jammu and Kashmir
(c) Salt marshes of western Gujarat
(d) Western Ghats
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Great Indian Hornbills are large and wide-ranging birds and most species are dependent on tropical forest habitats that contain large and tall trees.
- India has nine Hornbill species, of which four are found in the Western Ghats – Indian Grey Hornbill (endemic to India), Malabar Grey Hornbill (endemic to the Western Ghats), Malabar Pied Hornbill (endemic to India and Sri Lanka) and endangered Great Indian Hornbill.
- India also has one species that has one of the smallest ranges of any Hornbill – the Narcondam Hornbill, found only on the island of Narcondam in Andaman Sea. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Autism Awareness Day
Autism, also known as an autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a developmental disorder that affects a broad range of people, is typically diagnosed in early childhood and can impact individuals throughout their lives. Those with autism may experience social difficulties and display repetitive behavior patterns or speech, as well as other behavioral issues. And those with this condition may require different levels of care and support. To raise awareness of autism and promote acceptance and support for those affected by the condition, the United Nations established World Autism Awareness Day on April 2. The first World Autism Awareness Day was observed in 2008.
The theme for World Autism Awareness Day 2023 is "Contribution of Autistic Individuals at Home, at Work, in the Arts, and Policymaking." The day serves as an opportunity to increase public understanding of autism and encourage individuals, communities, and organizations to take action to support people with autism. Right of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 of India deal with rights of people with disabilities including autism.
Read more: Autism Spectrum Disorder
India-Bangladesh Friendship Pipeline
The India-Bangladesh Friendship Pipeline (IBFP) was inaugurated by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi and Bangladesh Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina in a virtual mode. The pipeline, with a capacity to transport 1 million Metric Ton Per Annum (MMTPA) of High-Speed Diesel (HSD) to Bangladesh, is the second cross-border energy pipeline between India and its Neighbours. While IBFP is the first cross-border energy pipeline between India and Bangladesh. This pipeline will further strengthen their relationship, enhancing connectivity and people-to-people linkages between the two sides. And enhance ongoing energy cooperation between the two countries and will further growth in Bangladesh, especially in the agriculture sector.
Read more: India Bangladesh Relations
Bastille Day Parade
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi was invited to France for the Bastille Day parade. Since80, the French military parade known as the Bastille Day military parade, also referred as the 14 July military parade, has been performed on the morning of July 14 in Paris. This day is marked as France's National Day. It is celebrated with a mixture of solemn military parades and easygoing dancing and fireworks.
Mahavir Jayanti
Recently, on The Vice President, Shri Jagdeep Dhankhar has greeted the people of the nation on the occasion of Mahavir Jayanti. It is an auspicious day for the followers of Jainism as it marks the birth anniversary of Lord Mahavira, who was the last Tirthankara of Jainism. Lord Mahavira was born on the 13th day of the bright half of the moon in the month of Chaitra. As per the Gregorian calendar, it is usually celebrated in the month of March or April. On Mahavir Jayanti, A procession is held with the idol of Lord Mahavira called the Rath Yatra, and the statue is given a ceremonial bath called abhisheka. Devotees recite Jain prayers or stavans in praise of the Lord.
Mahavira's teachings revolved around the principles of ahimsa, Satya, brahmacharya, and aparigraha. He emphasized the importance of non-violence, truth, non-stealing, chastity, and non-attachment, which were later compiled into Jain Agamas. His teachings were simple and easy to understand as they were in Prakrit, a language that ordinary people could comprehend. It is believed that Lord Mahavira passed away at the age of 72 and attained moksha or liberation from the cycle of birth and death at Pavapuri near modern-day Rajgir in Bihar. The celebration of Mahavir Jayanti is an opportunity for people to reflect on these principles and strive to lead a more ethical and spiritual life.
Read more: Mahavir Jayanti
Cope India Exercise
The Air Forces of India and the U.S. are set to conduct the Cope India exercise from April 10 to 21 at the Kalaikunda airbase in West Bengal, with Japan as an observer. Cope India Exercise is a bilateral combined training session involving the Indian Air Force (IAF) and the US Air Force (USAF). Cope India started out as a fighter-training drill in 2004. The most recent iteration of the practice took place in 2019. The exercise has developed to include, in addition to fighter-training exercises, subject matter expert exchanges, air mobility training, airdrop training, and large-force exercises.
Other joint defense drills between India and the US include Yudh-Abhyas (Military Exercise), Vajra Parhar, and Dharma Guardian with Japan. And a Trilateral Maritime Exercise Malabar is scheduled between the navies of India, Japan, and the USA.
Read more: India - US Relations.