Developments in India-Bangladesh Relations
For Prelims: India-Bangladesh Relations, Bangladesh Liberation War, Russia-Ukraine War, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA), Ganga Waters Treaty.
For Mains: India-Bangladesh Relations, Bilateral, regional, and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, during the visit of Bangladesh Prime Minister to India, the two countries agreed to begin a dialogue on a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) paving the way for broader economic ties between the two neighbouring economies.
- In 2022, both nations concluded a joint feasibility study on a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
What were the Major Outcomes of the Recent Meeting?
- India and Bangladesh have agreed to commence work on a CEPA to enhance economic ties and foster trade and investment between the two nations.
- This agreement seeks to capitalise on the economic complementarity between the two fast-growing economies in South Asia.
- India has agreed to support the construction of an inland container port in Sirajganj, Bangladesh, facilitating better logistics and trade flow.
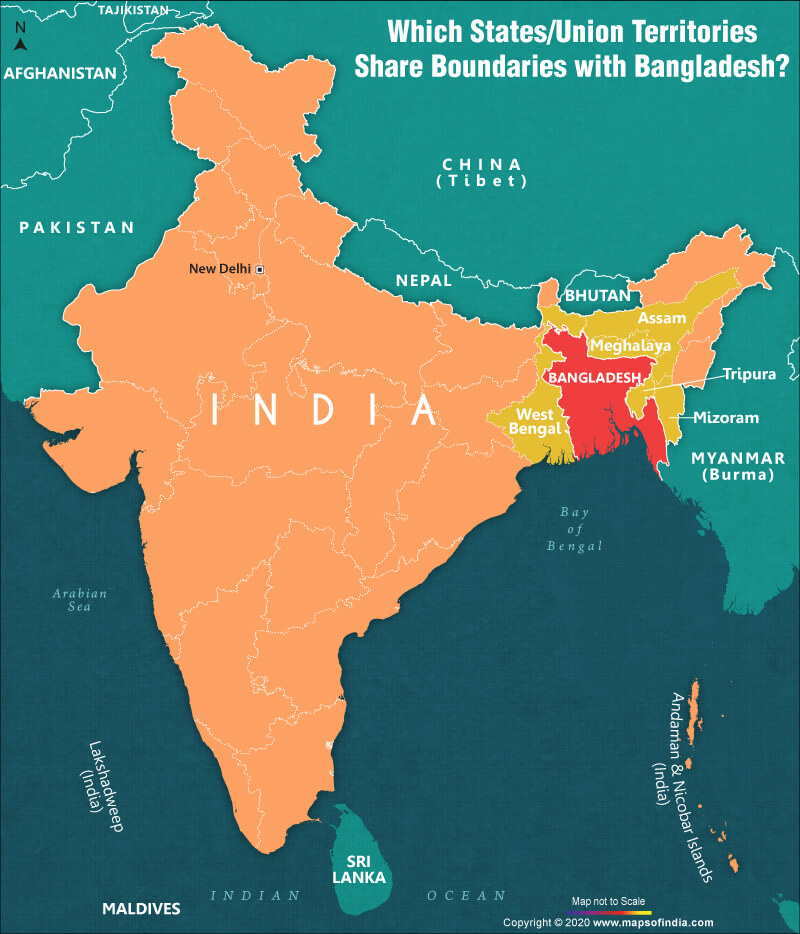
- Both the countries agreed to initiate technical-level talks to renew the 1996 Ganga Water Treaty, focusing on flood management, early warning systems, and drinking water projects. This is significant given the 54 rivers shared between the two nations.
- A maritime cooperation pact was signed, reflecting their shared vision for the Indian Ocean and mutual interests in the Indo-Pacific region. Bangladesh’s decision to join the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative was welcomed by India.
Other Recent Developments in India-Bangladesh Cooperation
- Inauguration of the India-Bangladesh Friendship Pipeline.
- Rehabilitation and operation of pre-1965 rail links between India and Bangladesh.
- Inauguration of Akhaura-Agartala Rail Link in 2023, that connects Bangladesh and the northeast through Tripura. It is the sixth India-Bangladesh cross-border rail link.
- The BIMSTEC Master Plan for Transport Connectivity connects major transport projects in India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand, thereby establishing a shipping network.
- Operationalisation of the Maitree Super Thermal Power Plant.
- Cargo facility for India’s northeastern States through the Khulna-Mongla Port.
- Mongla Port has been connected by rail for the first time.
- Cultural exchanges and cooperation through centres like the Indira Gandhi Cultural Centre.
- Bangladesh annually benefits from Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) training courses and scholarships for higher education in India.
How have been the Ties Between India-Bangladesh?
- Historical Ties:
- The foundation of India’s relationship with Bangladesh was laid in the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War. India provided critical military and material support to assist Bangladesh in its fight for independence from Pakistan.
- Despite this, relations worsened within a few years due to military regimes, anti-India sentiment but stability returned with a change in regime in 1996 along with a treaty on Ganga water sharing.
- India and Bangladesh also successfully resolved long-pending issues, like the Land Boundary Agreement (LBA) in 2015 and a maritime dispute over territorial waters.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Bilateral trade between India and Bangladesh has grown steadily over the last decade.
- Bangladesh is India's biggest trade partner in South Asia and India is the second biggest trade partner of Bangladesh in Asia.
- India is Bangladesh's largest export destination in Asia, with approx USD 2 billion of Bangladeshi exports to India in FY 2022-23.
- Since 2010, India has extended Lines of Credit to Bangladesh worth over USD 7 billion.
- Energy:
- In the energy sector, Bangladesh imports nearly 2,000 megawatts (MW) of electricity from India.
- In 2018, Russia, Bangladesh and India signed a memorandum on cooperation in the implementation of the Rooppur Nuclear power plant project, Bangladesh's first nuclear power reactor.
- Defence and Multilateral Cooperation:.
- Bilateral Exercises:
- Exercise Sampriti (Army)
- Exercise Bongo Sagar (Navy)
- Platforms for Regional Cooperation:
- Bilateral Exercises:
What are the Challenges and Potential Solutions in India-Bangladesh Relations?
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the major challenges in India-Bangladesh relations. Suggest measures to address these issues to enhance bilateral cooperation and regional stability. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
- River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Analyze internal security threats and transborder crimes along Myanmar, Bangladesh and Pakistan borders including Line of Control (LoC). Also discuss the role played by various security forces in this regard. (2018)
Regulating Facial Recognition Technology in India
For Prelims: Facial Recognition Technology, Right to Information, Biometric Technology, Artificial Intelligence
For Mains: Facial Recognition Technology, Need for Governance of FRT in India, Its Implication and Uses, Challenges in FRT.
Why in News?
Recently, the NITI Aayog, the premier public policy think-tank of the Government of India, has called for comprehensive policy and legal reforms to regulate the use of Facial Recognition Technology (FRT) in the country.
- This step is considered a major development amid growing worries about privacy, transparency, and accountability.
What are the Proposals to Regulate the Use of FRT in India?
- Status of Regulation in India:
- Currently, there is absence of any comprehensive legal framework present to regulate the use of Facial Recognition Technology (FRT) in India.
- Need For Regulating FRT:
- Multifaceted Challenges: FRT presents distinct challenges compared to other technologies due to its ability to capture and process sensitive biometric data remotely. Existing regulations might not adequately address these specific concerns.
- Ensuring Responsible Development: The objective is to create a comprehensive governance framework that can ensure the responsible development and deployment of FRT in India.
- This is crucial to mitigate the risks and ethical concerns associated with the use of FRT, such as privacy violations, algorithmic bias, and abuse of surveillance powers.
- International Thought Leadership: Proactive regulation will allow India to emerge as a global thought leader on FRT governance, shaping international discourse and policies.
- Promoting Public Trust: Effective regulation will build public trust in the technology and facilitate its widespread adoption across various sectors.
- Balancing Innovation and Safeguards: The reforms seek to strike a balance between promoting FRT innovation and putting in place necessary safeguards to protect individual rights and societal interests.
- Key Proposals:
- Standardising Liability:
- Establishing a legal framework that imposes liability and defines the extent of damages for harms caused by FRT malfunctions or misuse. This would incentivise responsible development and deployment.
- Ethical Oversight:
- Creating an independent ethical committee with diverse expertise to oversee FRT implementation. This committee would address issues of transparency, accountability, and potential bias within the algorithms.
- Transparency in Deployment:
- Mandating clear and transparent guidelines on the deployment of FRT systems. This would include informing the public about the use of FRT in specific areas and obtaining consent where necessary.
- Legal Compliance:
- Ensuring FRT systems comply with the Supreme Court's established legal principles in its judgment given in Justice K. S. Puttaswamy (Retd) Vs Union of India case.
- These principles include legality (adherence to existing laws), reasonability (proportionality to the objective), and proportionality (balancing the need for security with individual rights).
- Standardising Liability:
What is Facial Recognition Technology?
- About:
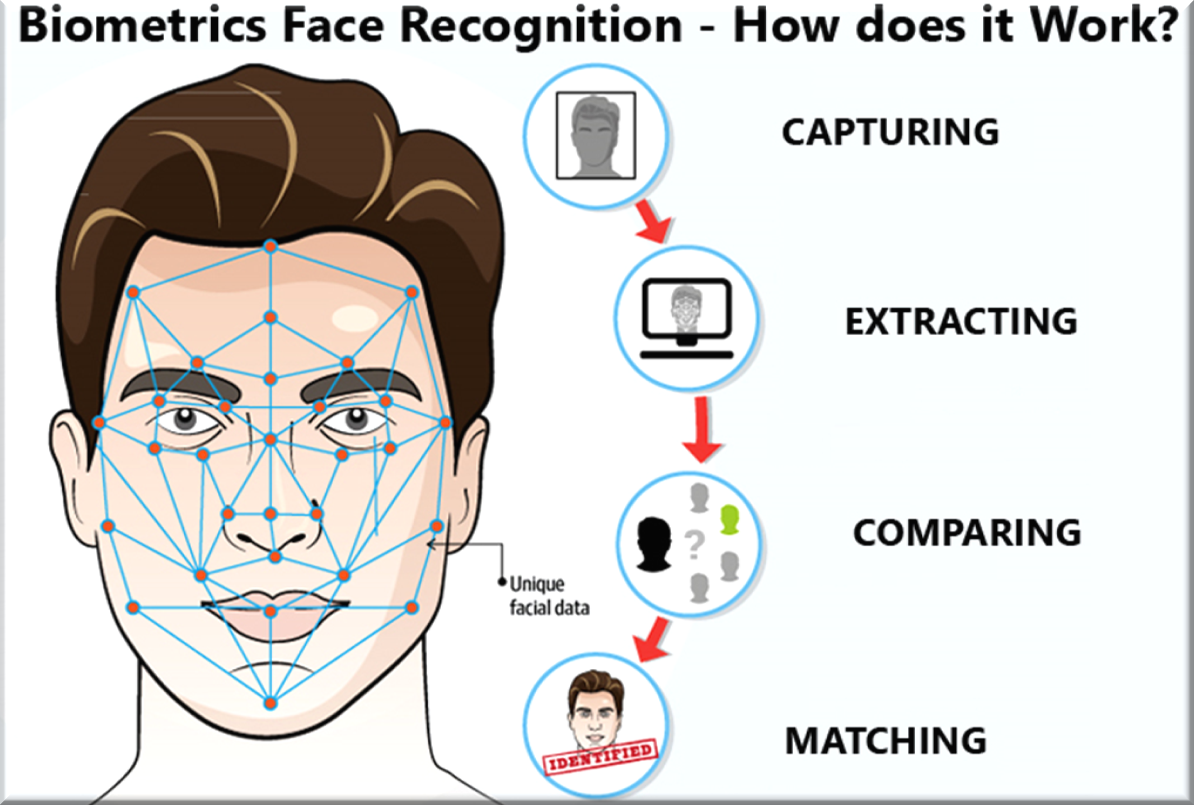
- Facial recognition is an algorithm-based technology which creates a digital map of the face by identifying and mapping an individual’s facial features, which it then matches against the database to which it has access.
- In the Automated Facial Recognition System (AFRS), the large database (containing photos and videos of peoples’ faces) is used to match and identify the person.
- Image of an unidentified person, taken from CCTV footage, is compared to the existing database using Artificial Intelligence technology, for pattern-finding and matching.
- Working:
- The facial recognition system works primarily by capturing the face & its features through the camera and then using various kinds of software to reconstruct those features.
- The captured face along with its features is stored into a database, which can be integrated with any kind of software that may be used for security purposes, banking services, etc.
- Uses:
-
Verification:
- The facial map is obtained for the purpose of matching it against the person’s photograph on a database to authenticate their identity. For example, it is used to unlock phones.
- Identification:
- The facial map is obtained from a photograph or video and then matched against the entire database to identify the person in the photograph or video. For example, law enforcement agencies usually procure FRT for identification.
-
What are the Concerns Regarding the Use of FRT Technology?
- Inaccuracy, Misuse and Privacy Concerns: FRT's limitations include misidentification, particularly across racial and gender demographics. This can lead to wrongful disqualification of legitimate candidates.
- The widespread use of FRT for surveillance and data collection can clash with the objectives of data privacy and protection, even in the presence of a legal framework.
- Racial and Gender Biases: Studies reveal disparities in FRT accuracy based on race and gender, potentially excluding deserving candidates and reinforcing societal biases.
-
Exclusion from Essential Services: Failures in biometric authentication, such as under the Aadhaar system, have led to the exclusion of individuals from accessing essential government services.
- Absence of Data Protection Laws: The lack of comprehensive data protection laws makes FRT systems vulnerable to misuse, with inadequate safeguards for the collection, storage, and use of biometric data.
- Ethical Concerns: It also raises ethical questions about the balance between public safety and individual rights, as well as the potential for misuse and abuse of the technology. There are concerns about the erosion of anonymity and the potential for FRT to be used for social control and suppression of dissent.
FRT Regulation in Other Countries
- European Union (EU): Apart from the General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) and the Data Protection Directive, the EU has an AI Act which aims to create a risk-based compliance framework, categorising FRT systems as “high risk” and subjecting them to the strictest compliance requirements.
- UK, US, Canada, and Australia: In these countries, the regulation of FRT is mainly governed by their respective data protection and privacy laws.
Way Forward
- Robust Legal Framework: Establish dedicated laws or regulations governing FRT deployment by both public and private actors. These laws should clearly define lawful purposes for FRT use, emphasise proportionality, and establish clear lines of accountability.
- Ethical Oversight and Governance: There is a need for creation of independent ethical oversight committees to assess the ethical implications of FRT deployments, prescribe codes of practice, and ensure compliance.
- Transparency and Data Protection: Make public disclosure of FRT deployments mandatory for both government and private entities and aligning FRT governance with India's upcoming data protection framework to ensure robust data protection safeguards.
- Addressing Bias: There is a need to develop clear guidelines promoting fair and non-discriminatory use of FRT, particularly in high-stakes applications.
- Global Leadership: Actively participate in international discussions on FRT governance to shape global standards. Leverage India's position as a technological leader to champion responsible AI development on the world stage.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the major concerns associated with the deployment of Facial Recognition Technology (FRT) systems and suggest measures to ensure transparency, accountability and address potential biases. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q. The identity platform ‘Aadhaar’ provides open “Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)”. What does it imply? (2018)
- It can be integrated into any electronic device.
- Online authentication using iris is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q1. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
Q2. What are the areas of prohibitive labour that can be sustainably managed by robots? Discuss the initiatives that can propel the research in premier research institutes for substantive and gainful innovation. (2015)
Q3. “Human beings should always be treated as ‘ends’ in themselves and never as merely ‘means’.” Explain the meaning and significance of this statement, giving it’s implications in the modern techno-economic society. (2014)
FATF’s Mutual Evaluation Report on India
For Prelims: FATF (Financial Action Task Force), Money Laundering (ML), Terrorist Financing (TF), G20, JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile) Trinity Terrorism, Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City),foreign direct investment (FDI).
For Mains: Challenges, Initiatives, Problem of Money Laundering (ML), Terrorist Financing (TF) for India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) issued a Mutual Evaluation Report (MER) on India, approved during their plenary session in Singapore. The MER report specifically assessed India's efforts in combating Money Laundering (ML), Terrorist Financing (TF) and proliferation financing.
What are the Highlights of the MER Report on India?
- Regular Follow-Up Category:
- India has been classified into the 'regular follow-up' category, joining Russia, France, Italy, and the UK, also designated in this category.
- Under the 'regular follow-up' category, India is required to submit a progress report on recommended actions by October 2027.
- FATF categorises member countries into four groups: regular follow-up, enhanced follow-up, grey list, and black list.
- Regular follow-up is the top category amongst 4 and only 5 countries in G20 including India have been placed in regular follow-up after the Mutual evaluation report.
- India has achieved strong results and a high level of technical compliance, yet it must address delays related to prosecutions for money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Digital Economy Through JAM Trinity:
- India's transition to a digital economy, facilitated by the JAM (Jan Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile) Trinity and stricter cash transaction regulations, has successfully mitigated risks associated with ML, TF, and proceeds from crimes such as corruption and organised crime.
What is the Significance of the MER Report on the Indian Economy?
- Enhanced Global Financial Reputation:
- The positive FATF evaluation demonstrates India's robust financial system, boosting international confidence. This could support initiatives like the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City) in attracting more international financial institutions.
- This improved reputation can lead to better credit ratings, potentially lowering borrowing costs for Indian entities in global markets.
- Increased Foreign Investment:
- A trustworthy financial system is likely to attract more foreign direct investment (FDI). In sectors like fintech and e-commerce, where financial integrity is crucial, companies like Amazon and Walmart have already made significant investments in India.
- Expansion of Digital Payment Systems:
- The report's endorsement supports the global expansion of India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI). This could lead to wider acceptance of UPI in international markets as UPI is already operational in countries like Singapore and UAE, with plans for expansion to more nations.
- Boost to India's Fintech Industry:
- The positive evaluation could accelerate the growth of India's Fintech sector. Fintech companies like Paytm and PhonePe could find it easier to expand internationally. It may attract more venture capital and encourage innovation in areas like blockchain and digital currencies.
- Enhanced Remittance Flows:
- With improved financial systems, remittances from Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) could become more efficient and cost-effective and can increase the volume of remittances, which are a significant contributor to India's foreign exchange.
What is Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing (ML/TF)?
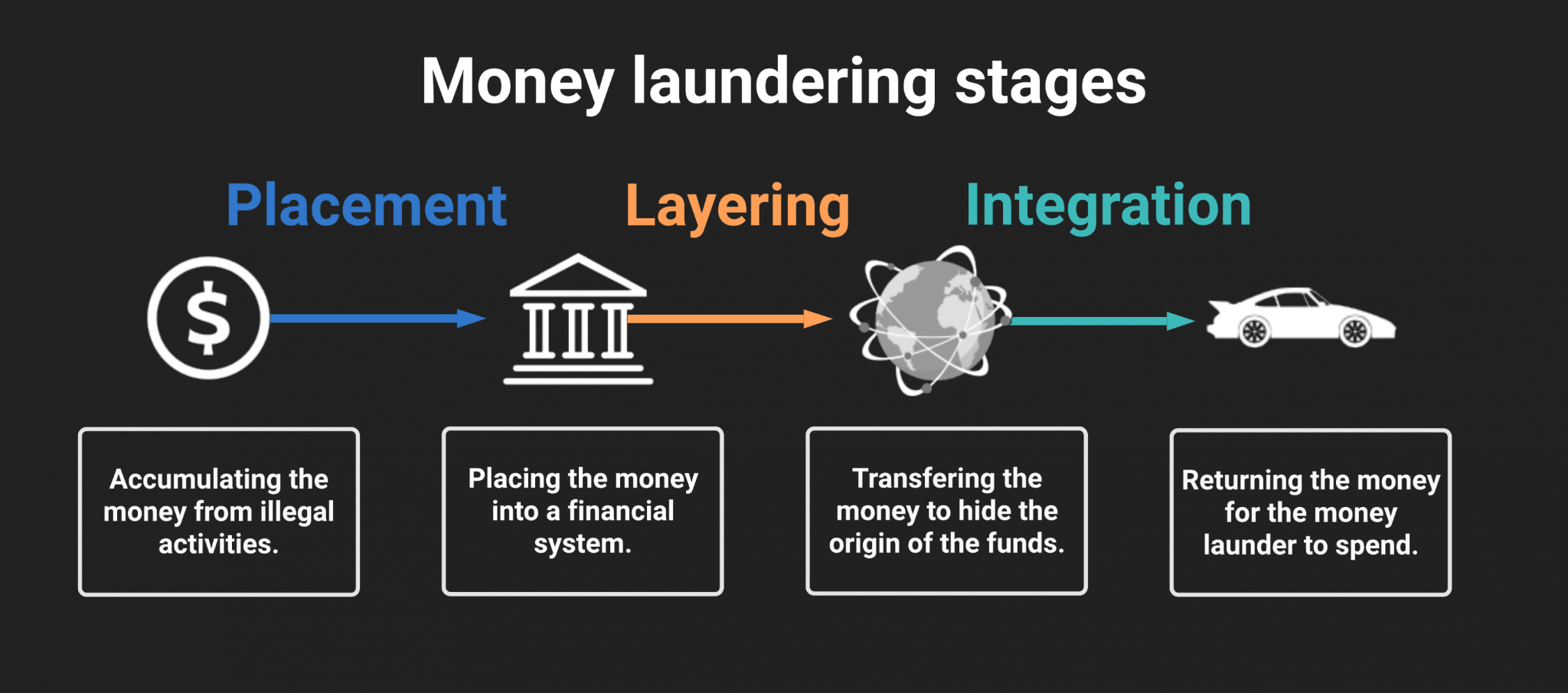
- Money Laundering (ML):
- Money laundering is concealing or disguising the identity of illegally obtained proceeds so that they appear to have originated from legitimate sources.
- It is frequently a component of other, much more serious, crimes such as drug trafficking, robbery or extortion. According to the IMF, global Money Laundering is estimated between 2 to 5% of World GDP.
- Terrorism Financing (TF):
- Terrorism financing is the act of providing financial support to terrorists or terrorist organisations to enable them to carry out terrorist acts or to benefit any terrorist or terrorist organisation.
- While funds may come from criminal activities, they may also be derived from legitimate sources, for example, through salaries, revenue from legitimate business or donations including through non-profit organisations.
- There are generally three stages in terrorism financing: raising, moving and using funds.
What are the Concerns and Suggestions Suggested by FATF for India?
| Concerns | Suggestions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
What are India's Efforts to Combat ML/TF?
- Effort At National Level:
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA): It was enacted in 2002 and provides a comprehensive legal framework to combat money laundering in India.
- Enforcement Directorate (ED): ED is the principal agency responsible for enforcing PMLA in India. It investigates and prosecutes cases of money laundering.
- Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND): It was established in 2004, FIU-IND is the central national agency responsible for receiving, processing, analysing, and disseminating information relating to suspect financial transactions to enforcement agencies.
- Banking Regulations: The RBI and other financial regulators have implemented stringent guidelines for banks and financial institutions to prevent money laundering and ensure KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance.
- Effort At Global Level:
-
United Nations Conventions: India has ratified various UN Conventions related to combating terrorism and money laundering, such as the UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) and its protocols.
-
Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements: India engages with Interpol, and the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) to align its efforts with global standards and participate in capacity-building programs to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
-
|
Drishti Mains Questions: Assess India's progress in enhancing its anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing regime. What key challenges and measures should India prioritise to effectively address these identified issues? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (2021)
India Won the 2024 T20 World Cup
Why in News?
Recently, India secured their first ICC title since the 2013 Champions Trophy by winning the ICC T20 World Cup in Barbados.
- This victory was seen as the end of a drought in major ICC tournaments.
How has the Journey of the T20 World Cup been Over the Years?
- About:
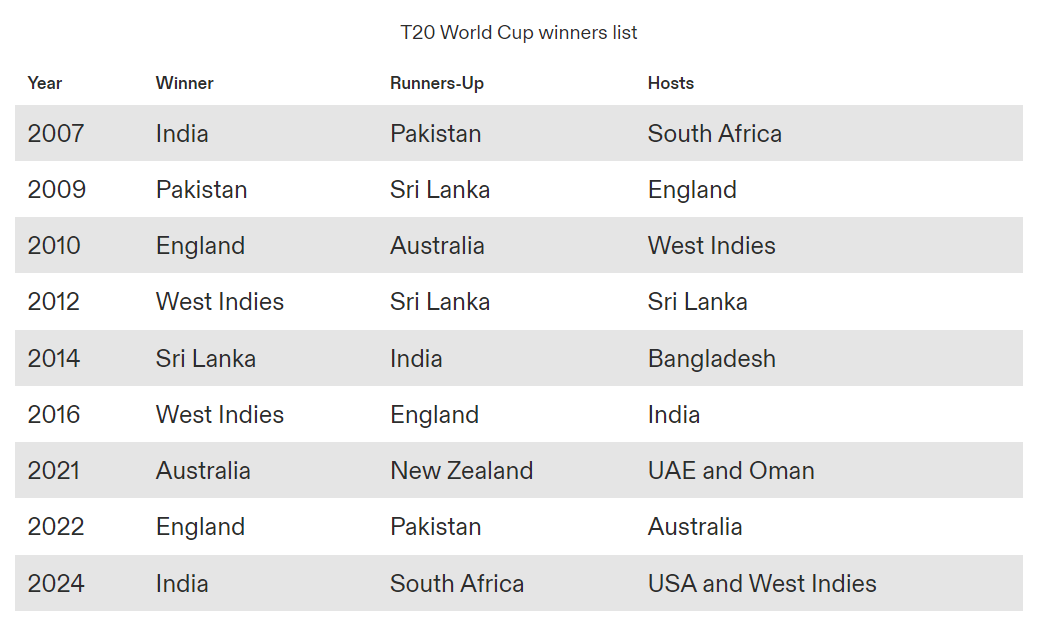
- The T20 World Cup, first played in 2007, is an international cricket championship, usually held once every two years.
- While the T20 World Cup began as a 12-team competition in 2007, it was expanded to 16 teams from the 2014 edition.
- The 2024 edition had 20 sides competing in four groups.
- India’s Journey Over the Years:
- India won the first men’s Twenty20 World Cup in South Africa, defeating Pakistan in the final led by MS Dhoni.
- India finished runners-up in 2014, losing to Sri Lanka in the final.
- Winners:
-
Teams to win two T20 WCs
- India (2007 & 2024)
- West Indies (2012 & 2016)
- England (2010 & 2022)
- With the 2022 victory, England became the first team to simultaneously hold both men’s World Cups - the 2019 ODI World Cup and the 2022 T20 World Cup.
-
- Individual Feats of 2024 Cup:
- India’s Virat Kohli is the leading run-getter in the T20 World Cup history with 1292 runs in 35 matches, since his debut in 2012.
- Bangladesh all-rounder Shakib Al Hasan is the top wicket-taker in the T20 World Cup, recording 50 scalps in 43 matches between 2007 and 2024.
- Key Highlights of the 2024 T20 Final:
- Player of the Match: Virat Kohli
- Player of the Tournament: Jasprit Bumrah
- Most wickets in a T20 WC Edition:
- 17 - Arshdeep Singh (IND, 2024)
- 17 - Fazalhaq Farooqi (AFG, 2024)
- Lowest Economy Rate in a T20 WC Edition:
- 4.17 - Jasprit Bumrah (2024)
- Only the 3rd time a team won the T20 WC final while defending the target after India in 2007 and West Indies in 2012.
- India became the first team to win a T20 World Cup by being unbeaten through the tournament.
- Post World Cup win, three Indian players namely, Virat Kohli, Rohit Sharma, and Ravindra Jadeja have announced their retirement from T20 internationals.
- BCCI, the cricket governing body of India has announced Rs 125 crore prize money for Team India after the T20 World Cup win.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000: (2021)
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far.
- Roger Federer received this award maximum number of times compared to others.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
National Security Council
Why in News?
Deputy National Security Adviser (NSA) Rajinder Khanna has been appointed as the additional NSA. This is the first time the additional NSA post has been filled, a position that has always existed but remained vacant until now.
- Additionally, Intelligence Bureau special director T.V. Ravichandran has been appointed as deputy NSA.
- The NSA acts as secretary of National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS), which is one of Three-tier Structure of National Security Council (NSC).
What is the Organisational Structure of the National Security Council?
- Establishment: The NSC was established in 1998 by the government of then Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee following nuclear tests by India and Pakistan. It is the apex body for national security management in India.
- Prior to the formation of the NSC, the functions related to national security were carried out by the Principal Secretary to the Prime Minister.
- It operates under a three-tier structure i.e. Strategic Policy Group (SPG), National Security Advisory Board (NSAB) and National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS).
- Three-tier Structure of NSC:
-
Strategic Policy Group (SPG): The SPG is chaired by the Cabinet Secretary, consisting of serving senior officials responsible for policy-making and for follow up action in matters concerning national security.
-
It includes the Chiefs of the Armed Forces, the Intelligence Bureau and the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW). Its main task is to make policy recommendations to the NSC.
-
-
National Security Advisory Board (NSAB): It includes senior retired officials, academics, and experts from civil society.
-
It provides long-term analysis and policy recommendations on national security issues to the NSC, covering areas like Internal and External Security, Foreign Affairs, Defence, Science & Technology, and Economic Affairs.
-
- National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS): It is overseen by the Prime Minister, operates with NSA as its secretary, and serves as the apex body for all matters concerning internal and external security.
-
- Heads: The NSC is headed by the Prime Minister of India. The NSA acts as the secretary of the NSC and also as the primary advisor to the prime minister. The headquarters of the NSC is located in New Delhi.
- Ajit Doval is the current NSA, serving a third term. He is the longest-serving NSA in India’s history, with a tenure of over 10 years. Brajesh Mishra served as the country’s first NSA.
- The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC) in India appoints top government positions. It is chaired by the Prime Minister and the Minister of Home Affairs.
- The committee processes proposals for senior government appointments and makes decisions on positions such as the National Security Advisor.
- NSC Members: Besides the NSA, it includes Deputy NSA and additional NSA, Ministers of Defence, External Affairs, Home Affairs, and Finance of the Government of India, and the Vice Chairman of the NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India). Additional officials may be invited to monthly meetings as needed.
CCPA and Pendency of Cases
Why in News?
Recently, the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) imposed a penalty of Rs. 3 lakh on an advertisement by an Edtech platform that was found to be "false and misleading" under Section 21 of the Consumer Protection Act.
What is the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)?
- About:
- CCPA is the regulatory body established under Section 10 of the Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2019, it regulates matters related to consumer rights violations and unfair trade practices.
- The act empowers the CCPA to prevent false or misleading advertisements and ensure consumer rights are protected.
- It operates under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- CCPA is the regulatory body established under Section 10 of the Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2019, it regulates matters related to consumer rights violations and unfair trade practices.
- Section 21 of CPA Act:
- Section 21 of CPA, 2019 grants the CCPA the power to issue directions and penalties against false or misleading advertisements. It provides definition of Misleading Advertisement, Powers of the CCPA and Penalties (imprisonment of up to 2 years and a fine of up to Rs. 10 lakh).
- Benefits to Consumers:
- Informed Consumers: CCPA empowers informed consumer decisions by deterring deceptive marketing.
- Transparent Ads: CCPA interventions promote truthful advertising practices.
- Trustworthy Claims: CCPA discourages misleading claims, boosting consumer trust.
- Fair Competition: It ensures competition based on product merit, not deceptive claims.
Case Study
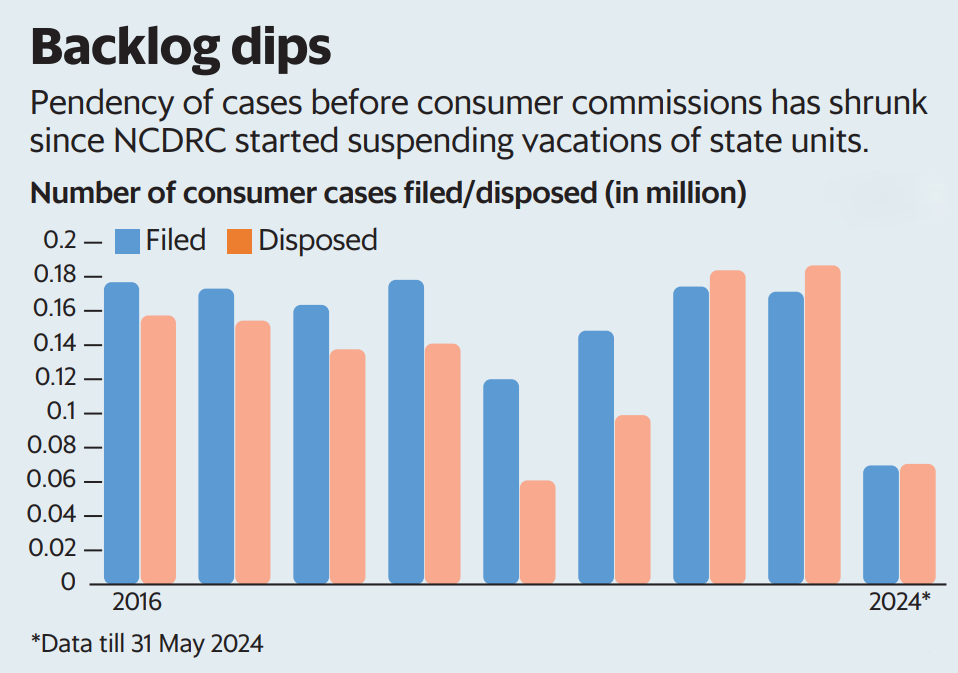
Reducing Pendency in Consumer Courts through Suspension of Vacations:
- National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) and state consumer commissions have worked to clear the backlog of pending cases by suspending the traditional summer vacation practices.
- Background:
-
Since the CCPA's inception (July 2020), 415,104 cases have been filed, and 440,971 cases have been disposed of, indicating a positive trend.
-
However, 555,000 cases are pending before consumer commissions as of December 2022.
-
-
-
Addressing the Backlog:
-
In 2022, the NCDRC started suspending summer vacations for state consumer commissions.
- The NCDRC cited the provisions of the CCPA, which state that all commissions must follow the holiday schedule prescribed by the state government, and there is no provision for a summer vacation in any state office.
-
- Impact and Outcomes:
-
In 2022, the NCDRC received 3,420 cases and resolved 4,138 cases, compared to 2,449 cases received and 2,011 cases resolved in 2021.
- In 2023, the NCDRC received 5,276 cases and resolved 6,422 cases, further reducing the backlog.
- As of May 2024, consumer commissions have resolved 70,576 cases, while 69,615 cases have been filed, indicating a positive trend in clearing the backlog.
- The introduction of e-courts has also contributed to the increased efficiency of the consumer dispute redressal process.
-
Note:
- Consumer forums are categorised into District, State, and National levels. According to the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, complaints can be filed based on the value of the claim.
- District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (DCDRC) for claims up to Rs 50 lakh.
- State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (SCDRC) for claims between Rs 50 lakh and Rs 2 crore
- National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) for claims above Rs 2 crore.
What are the Initiatives for Consumer Protection?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q.1 With reference to ‘consumers’ rights/privileges under the provisions of law in India, which of the following statements is/are correct ? (2012)
- Consumers are empowered to take samples for food testing.
- When a consumer files a complaint in any consumer forum, no fee is required to be paid.
- In case of death of consumer, his/her legal heir can file a complaint in the consumer forum on his/ her behalf.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: c
DBS Brain Implant Surgery for Epilepsy Treatment
Why in News?
Recently, a UK-based teenager has become the first person in the world to be fitted with a brain implant device to help bring his epileptic seizures under control.
- The Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) device was inserted in his skull which reduced his daytime seizures by 80%.
What is Epilepsy Disorder?
- About Epilepsy:
- It is a central nervous system (neurological) disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behaviour, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness.
- Causes:
- It is caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
- The disease has no identifiable cause in nearly 50% of the cases. However, head trauma, tumours in the brain, some infections like meningitis, or even genetics can lead to epilepsy.
- It’s more common in young children and older adults. It occurs slightly more in males than in females.
- Available Treatment of Epilepsy:
- Anti-seizure Medications: These are the first line of treatment, aiming to control seizure frequency and severity..
- Ketogenic diet: A high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet can be remarkably effective, particularly in children with medication-resistant epilepsy.
- Epilepsy Surgery: Doctors can carry out brain surgery to remove a portion of the brain where the seizures originate.
- Corpus Callosotomy: In this surgical procedure doctors remove the corpus callosum (a part that connects both halves of the brain) that will not allow abnormal electrical signals to travel from one half of the brain to another, preventing abnormal electrical discharges from spreading and causing seizures.
Note
- Epilepsy has been recognised by the World Health Organisation (WHO) as a neurological disorder.
- According to a 2022 Lancet study, the prevalence of epilepsy in India ranges from 3 to 11.9 cases per 1,000 people.
- Despite the availability of several anti-seizure medications, approximately 30% of the patients remain resistant to treatment.
What is the DBS Brain Implant Technology to Treat Epilepsy?
- About:
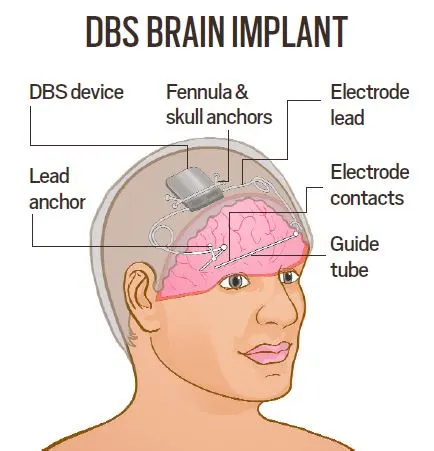
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) involves implanting a medical device with electrodes that deliver mild electrical currents to specific brain regions linked to seizures.
- DBS is considered for patients with medication-resistant epilepsy, where traditional medications haven't controlled seizures.
- Unlike surgery that removes brain tissue, DBS offers a more targeted approach with potentially fewer side effects.
- Working:
- The device is a neurostimulator that delivers constant electrical impulses to the brain to disrupt or block abnormal seizure-causing signals in the brain.
- Two electrodes were inserted deep into the brain, reaching the thalamus, a relay station for motor and sensory information. The electrodes are connected to the neurostimulator device.
- The device can be recharged wirelessly using a headphone.
- Advantages:
- Effective Seizure Control: It helps reduce seizure frequency by around 40% in some patients.
- Alternative for Complex Epilepsy: It offers a viable alternative for patients with epilepsy originating from multiple brain regions, where surgery is difficult or impractical.
- Treatment-Resistant Cases: It can be a valuable option when traditional interventions like medications and dietary modifications have failed to achieve adequate seizure control.
- Limitations:
- DBS is not a guaranteed cure.
- It can be expensive with a total cost can reach around Rs 17 lakh.
- DBS success rates are lower compared to well-established surgical approaches. Brain surgery can achieve seizure freedom in nearly 90% of suitable cases.
- NeuraLink (American neurotechnology company): Neuralink's brain implant aims to help people with traumatic injuries control computers using only their thoughts.
- It aims to significantly enhance human abilities by addressing conditions like Parkinson's Disease.
- Brainoware: It integrates brain organoids with microelectrodes and can be used to study human brain development and brain-related diseases.
Read more: Epilepsy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. Consider the following statements:
- Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperms of a prospective parent.
- A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage.
- Human induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Havaldar Adbul Hamid
Recently, the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) chief visited the village Dhamupur in Ghazipur, Uttar Pradesh, the native village of 1965 war hero Abdul Hamid.
- He released two books- 'Mere Papa Paramvir' on Hamid and 'Bharat ka Musalman'.
- Abdul Hamid was a soldier in the 4th Grenadiers in the Indian Army who fought and died during the Battle of Asal Uttar in the 1965 India-Pakistan war.
- Asal Uttar is situated in Punjab near the India-Pakistan border.
- The Battle of Asal Uttar was one of the largest tank battles fought during the 1965 war, where the Pakistani 1 Armoured Division's offensive was decimated by the Indian forces.
- The battle resulted in the loss of 97 Patton tanks for the Pakistani Army, and the surrender of an entire Pakistani armoured regiment.
- Hamid was deployed near Chima village. On 10th September 1965, he destroyed 3 Pakistani tanks and disabled a 4th one but was killed in the process.
- Hamid was awarded the Param Vir Chakra, India's highest gallantry award, posthumously for his bravery.
- The site of his death is now part of a war memorial, with a captured Pakistani Patton tank standing as a tribute.
Read More: Kargil Vijay Diwas
Certificates of Deposit
Recently, the Clearing Corporation of India released data that revealed that Commercial banks have mobilised Rs 1.45 trillion through Certificates of Deposit (CDs) to strengthen their balance sheets.
Certificates of Deposit (CDs):
- A CD is a negotiable, unsecured money market instrument offered by banks and credit unions that provides an interest rate premium in exchange for the customer agreeing to leave a lump-sum deposit untouched for a predetermined period.
- In other words, it pays a fixed interest rate on money held in banks for an agreed-upon period.
- CDs can be issued by scheduled commercial banks and All-India Financial Institutions (FIs) to individuals (including NRIs), corporations, companies, trusts, funds, associations, etc.
- A minimum amount of a CD should be Rs.1 lakh and thereafter permits multiples of it.
- The maturity period of CDs issued by banks ranges from 7 days to one year, while for FIs this limit is from 1 year to upto 3 years from the date of issue.
Clearing Corporation of India (CCIL):
- Established in 2001, it provides reliable clearing and settlement services in the Money and Government Securities markets.
Read more: Banking Sector: Opportunities and Challenges
International Conference on Steel Slag Road
Recently, the 1st International Conference on Steel Slag Road was organised by CSIR in New Delhi.
- NITI Aayog released the guidelines for the utilisation of steel slag in road construction.
Steel Slag Road Technology:
- It uses steel slag (metal waste) from steel production, to create stronger and more durable roads.
- The process involves removing impurities and metal content from the slag and using it as an aggregate for road construction.
- This processed steel slag has high strength, hardness, abrasion resistance, skid resistance, and drainage capacity, making it ideal for road building. It is eco-friendly, cost-effective and durable.
- Every year in India, approximately 1.8 billion tonnes of natural aggregates are needed for construction and maintenance projects. This demand can be partially met by using processed steel slag aggregates as a substitute.
- India's First Steel Slag Road was built at Surat.
Read more: Steel Slag Road Technology, Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR)
New Nanocomposite for Cleaning Organic Waste
Recently, a new metal oxide nanocomposite has been developed by researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) that can be used as sustainable technologies for cleaning up the environment.
- These new composites use photocatalysis for the decomposition of pollutants.
- Photocatalysts are materials that change the rate of a chemical reaction on exposure to light.
- In the presence of light, they generate electron-hole pairs that degrade pollutants into harmless by-products.
- Metal oxide photocatalysis ( eg. Titanium Dioxide, Zinc Oxide, And Tungsten Trioxide), due to its high surface area and stability, offers a sustainable solution for removing organic pollutants from water bodies.
- These new photocatalytic metal oxides can be used for the degradation of organic pollutants in the dyes and pharmaceutical sectors.
- The nanocomposite (a combination of two or more materials, of which at least one is a nanomaterial) can be used in catalysis, energy storage, sensors, optoelectronics, biomedical fields, coatings, and renewable energy production.
- Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST), located in Guwahati, is an autonomous institution of the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
Read more: Ratification of 7 Persistent Organic Pollutants, Role of Nanomaterials in Solving Environmental Issues `