World's Largest Grain Storage Plan in Cooperative Sector
For Prelims: Cooperative sector, Food security, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Inter-Ministerial Committee, Food Corporation of India, District Central Cooperative Banks, Union Budget 2023-24.
For Mains: Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has given its approval for the establishment of the "world's largest grain storage plan in the cooperative sector" with an outlay of around Rs 1 lakh crore.
- The initiative aims to curb crop damages, prevent distress sales by farmers, and bolster the country’s food security.
What are the Major Highlights Related to Grain Storage Plan?
- About:
- The plan focuses on the creation of godowns and other agricultural infrastructure at the level of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to strengthen food security, reduce wastage, and empower farmers.
- This ambitious project aims to converge eight ongoing schemes of three ministries to address the shortage of agricultural storage infrastructure in India.
- Ministry of Cooperation will implement a pilot project in at least 10 selected districts.
- The plan focuses on the creation of godowns and other agricultural infrastructure at the level of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) to strengthen food security, reduce wastage, and empower farmers.
- Inter-Ministerial Committee:
- An Inter-Ministerial Committee (IMC) will be constituted under the chairmanship of the Minister of Cooperation, with the participation of the Ministers of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, and Food Processing Industries, along with the concerned secretaries.
- Rationale:
- The Ministry of Cooperation has developed the grain storage plan to leverage the strength of cooperatives and transform them into successful business enterprises, aligning with the vision of "Sahakar-se-Samriddhi" (Cooperation for Prosperity).
- The plan focuses on establishing agri-infrastructure, including warehouses, custom hiring centres, and processing units, at the PACS level.
- India has over 1,00,000 PACS with a vast membership base of more than 13 crore farmers.
- Given their significant role in the agricultural and rural landscape, the plan seeks to empower PACS by creating decentralised storage capacity and other necessary infrastructure.
- This transformation will enhance the economic viability of PACS and contribute to the growth of the Indian agricultural sector.
- Benefits:
- Addressing Infrastructure Shortage: The plan aims to establish godowns at the level of PACS to alleviate the shortage of agricultural storage infrastructure in the country.
- Diversification of PACS Activities: PACS will be empowered to undertake various activities, including functioning as procurement centres for state agencies or the Food Corporation of India (FCI), serving as fair price shops, and setting up custom hiring centres and common processing units.
- This diversification will enhance the incomes of farmer members.
- Reduction of Food Grain Wastage: By creating decentralised storage capacity at the local level, the plan aims to reduce grain wastage, contributing to improved food security.
- Preventing Distress Sale: The plan provides farmers with various options, preventing distress sale of crops and enabling them to realise better prices for their produce.
- Cost Reduction: The establishment of storage facilities at the PACS level will significantly reduce transportation costs of food grains to procurement centres and fair price shops.
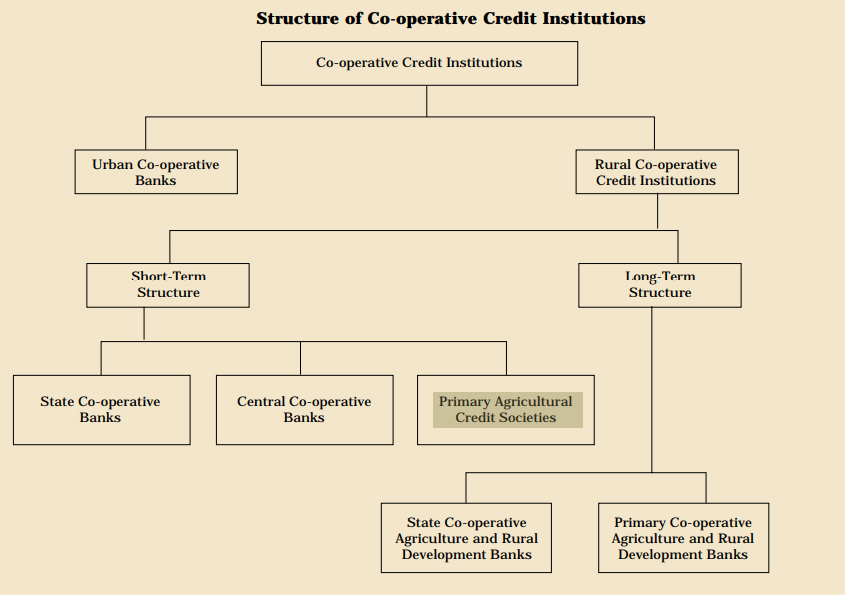
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies?
- PACS constitute the lowest tier of the Short-Term Cooperative Credit (STCC) structure in the country, headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Credit from the SCBs is transferred to the District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs), which operate at the district level. The DCCBs work with PACS, which deal directly with farmers.
- The first PACS was established in 1904. They are involved in short term lending. At the start of the cropping cycle, farmers avail credit to finance their requirement of seeds, fertilisers etc.
- The Union Budget 2023-24 has announced Rs 2,516 crore for computerisation of 63,000 PACS over the next five years, with the aim of bringing greater transparency and accountability in their operations and enabling them to diversify their business and undertaking more activities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. In the villages itself no form of credit organisation will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural finance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural finance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (2014)
Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee: UNEP
For Prelims: Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee, UNEP, UNEA, Minamata Convention, Plastic Pollution, EPR.
For Mains: Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee.
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has gathered in Paris, France, for the second meeting of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-2).
- The first session of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-1) concluded in Uruguay in 2022.
- INC-2 aimed to set the stage for negotiations on the substance of a global deal to end plastic pollution to edge closer to protecting ecosystems, species and humanity from the grave impacts of the linear plastics economy.
What are the Key Highlights of INC-2 Meeting?
- The primary agenda of INC-2 was to adopt the rules of procedure. The rules govern various aspects such as the negotiation process, decision-making procedures (consensus or voting), and the entities authorized to make decisions.
- During the previous INC-1 meeting, a part of Rule 37, stating "each member shall have one vote," was kept in brackets, indicating unresolved disagreement.
- The bracketed part now includes provisions from the Minamata Convention, allowing regional economic integration organizations (such as the European Union) to vote on behalf of their member states. However, the member states must be present during voting or as part of the committee.
- India has consistently insisted on bracketing Rule 38, which states, “The Committee shall make every effort to reach agreement on all matters of substance by consensus.
- If all efforts to reach consensus have been exhausted and no agreement has been reached, the decision shall, as a last resort, be taken by a two-thirds majority of the representatives of Members who are present and voting.”
- The formation of the OEWG (Open-Ended Working Group) has delayed the start of discussions in the contact groups on substantive matters.
- In UNEA resolution 5/14, the assembly mandated an ad hoc open-ended working group (OEWG) to lay the groundwork for negotiations.
What is the Intergovernmental Negotiation Committee (INC)?
- About:
- The INC was established in February 2022, at the 5th session of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA-5.2).
- A historic resolution (5/14) was adopted to develop an international legally binding instrument on plastic pollution, including in the marine environment with the ambition to complete the negotiations by the end of 2024.
- Need:
- The rapidly increasing levels of plastic pollution represent a serious global environmental issue that negatively impacts the environmental, social, economic and health dimensions of sustainable development.
- In the absence of necessary interventions, the amount of plastic waste entering aquatic ecosystems could nearly triple from some 9–14 million tonnes per year in 2016 to a projected 23–37 million tons per year by 2040.
- Objective:
- Under the legally binding agreement, countries will be expected to develop, implement and update national action plans reflecting country-driven approaches to contribute to the objectives of the instrument.
- They will be expected to promote national action plans to work towards the prevention, reduction and elimination of plastic pollution and to support regional and international cooperation.
What is the United Nations Environment Assembly?
- It is the governing body of the UN Environment Programme.
- It is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on the environment.
- The Assembly is made up of the 193 UN Member States and convenes every two years to advance global environmental governance.
- It was created in June 2012, during the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, also referred to as RIO+20.
What are the Initiatives to tackle Plastic Pollution?
- Indian:
- Global:
Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan Launched
For Prelims: GOBARdhan Scheme, Biogas/Compressed Biogas, Mission LiFE,
For Mains: Significance and Benefits of GOBARdhan, Waste to Energy
Why in News?
Recently, the Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan was launched as a part of the Government of India's initiative to convert waste to wealth and promote a circular economy.
What are the Key Features of the Portal?
- About:
- The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti, has developed the portal to facilitate the setting up of Biogas/Compressed Biogas (CBG) plants.
- Objectives and Scope:
- The portal acts as a one-stop repository for assessing investment and participation in the Biogas/CBG sector at the pan India level.
- It streamlines the process of setting up CBG/Biogas plants
- Enrollment:
- Any government, cooperative, or private entity intending to set up a Biogas/CBG/Bio CNG plant in India can enroll in the portal and obtain a registration number.
- The registration number enables access to various benefits and support from the Ministries and Departments of the Government of India.
- States are advised to prioritize the registration of their CBG/Biogas plant operators on the portal to avail existing and upcoming support from the Union Government.
- Any government, cooperative, or private entity intending to set up a Biogas/CBG/Bio CNG plant in India can enroll in the portal and obtain a registration number.
- Benefits:
- Stakeholder Participation:
- The launch of the portal demonstrates cooperative federalism, with stakeholders from central Ministries, line departments of the Centre and States collaborating on its development and deployment.
- The Union Minister of Jal Shakti emphasizes the significant achievements in waste to wealth generation through more than 650 GOBARdhan plants and the unified registration portal.
- Ease of Doing Business:
- The portal ensures ease of doing business and attracts greater investment from private players in the Biogas/CBG sector.
- Aligns with Climate Action Goals:
- It aligns with India's climate action goals, promotes clean energy, rural employment, improved health outcomes, and contributes to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Govt. of India’s Mission LiFE.
- Strengthen Supply Chain:
- The Union Government aims to strengthen the CBG/Biogas supply chain through biomass aggregation, grid pipeline connectivity, organic farming practices, research and development, and continuous engagement with stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Participation:
What is GOBARdhan Initiative?
- About:
- Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan (GOBARdhan) is a crucial umbrella initiative of the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India.
- In 2018, the government launched this scheme as a national priority project under the Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen-Phase II program.
- Objective:
- To support villages safely manage their cattle waste, agricultural waste and in long run all organic waste.
- To support communities convert their cattle and organic waste to wealth using decentralized systems.
- Promote environmental sanitation and curb vector borne diseases through effective disposal of waste in rural areas.
- Convert organic waste, especially cattle waste to biogas and fertilizer for use in rural areas.
- Potential Benefits:
- Effective biodegradable waste management.
- Reduction of GHG emission.
- Reduction in import of crude oil.
- Employment opportunity for the local community.
- Boost to entrepreneurship.
- Additional income for farmers/ local village community from organic waste.
- Promotion of organic farming.
- Models of Scheme:
- Individual Household:
- This model can be adopted by households which have three (3) or more cattles. The biogas and slurry generated from the plants are used for cooking and as manure by the households.
- Community:
- The Biogas plants can be constructed for a minimum number of households (5 to 10). The plants can be operated and managed by GP/SHGs.
- The gas generated will be supplied to households/restaurants / institutions and slurry can be used by the community as organic manure in agriculture or sold to farmers.
- Cluster:
- In this model, individual Biogas plants are installed in number of households in a village/ group of villages.
- The biogas generated is used by the households and the slurry is collected at a common place, separated to solid and liquid parts and then fortified and sold as biofertilizers.
- Commercial CBG:
- CBG plants can be set up by Entrepreneurs / Cooperative Societies/ Gaushalas etc.
- The raw biogas produced is compressed and can be used as vehicular fuel and / or sold to industries.
- The slurry generated is converted into organic manure / bio-fertilizer and can be sold to farmers.
- Individual Household:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What are the impediments in disposing the huge quantities of discarded solid waste which are continuously being generated? How do we remove safely the toxic wastes that have been accumulating in our habitable environment? (2018)
Third Employment Working Group Meet
For Prelims: Indian G20 Presidency, Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Gig and platform economy, United Nations.
For Mains: International Labour Organization.
Why in News?
The Indian G20 Presidency is organising the third Employment Working Group (EWG) meeting at the International Labour Organization (ILO) headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- This meeting, which aligns with the ILO's annual International Labour Conference, brings together delegates from G20 member countries, guest countries, and international organizations including International Labour Organization (ILO), Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), International Social Security Association (ISSA), World Bank (WB).
What are the Major Highlights of the Meet?
- Priority Areas:
- The Indian Presidency has identified three priority areas for the EWG in 2023:
- Addressing Global Skill Gaps: This area focuses on developing strategies to bridge the skill gaps prevalent in the global workforce and enhance employability.
- Gig and Platform Economy and Social Protection: Discussions centre around ensuring social protection for workers in the gig and platform economy, considering the evolving nature of work.
- The gig and platform economy refers to a modern work arrangement where individuals perform short-term, freelance, or on-demand tasks or services through digital platforms or apps.
- It is characterised by the temporary and flexible nature of work, facilitated by online platforms that connect service providers (often referred to as gig workers) with customers or clients.
- Sustainable Financing of Social Protection: This area emphasises the importance of sustainable financing models to support social protection initiatives and provide safety nets for workers.
- The Indian Presidency has identified three priority areas for the EWG in 2023:
- Phases of the Meet:
- The EWG meeting is organised in four different phases in different cities in India.
- The first phase was held in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, in February 2023.
- The second phase was held in Guwahati, Assam, in April 2023.
- The third phase is being held in Geneva from 31st May to 2nd June 2023.
- The fourth and final phase will be held in Indore, Madhya Pradesh in July 2023.
- The EWG meeting is organised in four different phases in different cities in India.
What is an Employment Working Group?
- About:
- The Employment Working Group (EWG) is a forum established within the G20 framework to address issues related to employment, labour markets, and social policies.
- It serves as a platform for G20 member countries and relevant international organisations to engage in discussions, share experiences, and develop policy recommendations on employment-related matters.
- Purpose:
- The main purpose of the EWG is to promote inclusive and sustainable economic growth by fostering job creation, improving labour market outcomes, and ensuring social protection for workers.
What is the International Labour Organization?
- About:
- The ILO is one of the international knowledge partners of the Ministry of Labour and Employment that provides technical expertise to the EWG.
- The ILO is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards.
- Founded in October 1919 (Treaty of Versailles) under the League of Nations, it is the first and oldest specialised agency of the UN.
- Members:
- The ILO has a tripartite structure that brings together representatives of governments, employers and workers from its 187 member states.
- India is a founder member of the International Labour Organization.
- The ILO has a tripartite structure that brings together representatives of governments, employers and workers from its 187 member states.
- International Labour Conference:
- The ILO also hosts an annual International Labour Conference in Geneva that sets the International labour standards and the broad policies of the ILO.
- It is often referred to as an International Parliament of Labour.
- The ILO also hosts an annual International Labour Conference in Geneva that sets the International labour standards and the broad policies of the ILO.
- Means of Action:
- The principal means of action in the ILO is the setting up of the International Labour Standards in the form of Conventions and Recommendations.
- Conventions are international treaties and are instruments, which create legally binding obligations on the countries that ratify them.
- Recommendations are non-binding and set out guidelines orienting national policies and actions.
- The principal means of action in the ILO is the setting up of the International Labour Standards in the form of Conventions and Recommendations.
- Achievements:
- Received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1969.
- For improving peace among classes
- Pursuing decent work and justice for workers
- Providing technical assistance to other developing nation
- Received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1969.
- Major Reports Released by ILO:
UPSC Previous Year Questions:
Q. International Labour Organization’s Conventions 138 and 182 are related to (2018)
(a) Child Labour
(b) Adaptation of agricultural practices to global climate change
(c) Regulation of food prices and food security
(d) Gender parity at the workplace
Ans: a
Appointment of Vice-Chancellors of State Universities
For Prelims: Governors, vice-chancellors, President, University Grants Commission, Central Universities
For Mains: Issues over appointment of the vice chancellors of state universities and way forwards.
Why in News?
A tussle between the Chief Minister of West Bengal and Governor came to the fore over the appointment of 10 senior professors as interim Vice-Chancellors (VC) of state-run universities.
- The Education Minister of West Bengal urged the professors to refuse the appointments and is seeking legal opinion.
What is the Role of Governor and President in the Universities?
- State Universities:
- In the state universities, the Governor of the state is the ex-officio chancellor of the universities in that state.
- While as Governor he functions with the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers, as Chancellor he acts independently of the Council of Ministers and takes his own decisions on all University matters.
- According to the University Grants Commission (UGC) Regulations, 2018, the VC of a university, in general, is appointed by the Visitor/Chancellor, from a panel of three to five names recommended by the duly constituted Search cum Selection Committee.
- Where there is a conflict between the State University Act and the UGC Regulations, 2018 to the extent State legislation is repugnant, the UGC Regulations, 2018 shall prevail.
- According to Article 254(1), if any provision of a state law is repugnant to a provision in a law made by the Parliament, which the Parliament is competent to enact, or with any existing law regarding any matter in the Concurrent List, then the Parliamentary law would prevail over the State law.
- Where there is a conflict between the State University Act and the UGC Regulations, 2018 to the extent State legislation is repugnant, the UGC Regulations, 2018 shall prevail.
- Central Universities:
- Under the Central Universities Act, 2009, the President of India shall be the Visitor of a central university.
- With their role limited to presiding over convocations, Chancellors in central universities are titular heads, who are appointed by the President in his capacity as Visitor.
- The Vice Chancellor is appointed by the Visitor from panels of names picked by search and selection committees formed by the Union government.
- A visitor is empowered to call for a set of fresh names in case of dissatisfaction with the given panel.
- The Act adds that the President, as Visitor, shall have the right to authorize inspections of academic and non-academic aspects of the universities and to institute inquiries.
What is the Role of Vice-Chancellor?
- As per the constitution of the University, the Vice- Chancellor (VC) is considered the ‘Principal Academic and Executive Officer of the University’.
- As head of the University, he/she is expected to function as a ‘bridge’ between the executive and the academic wing of the university.
- It is to facilitate this expected role that universities are always in search of persons with values, personality characteristics and integrity in addition to academic excellence and administrative experience.
- The reports of the Radhakrishnan Commission (1948), Kothari Commission (1964-1966), Gnanam Committee (1990) and Ramlal Parikh Committee (1993) have highlighted the importance of the role of VC in maintaining the quality and relevance of universities, in addition to its growth and development, keeping in view, the much-needed changes from time to time.
- He shall be the ex-officio Chairman of the Court, Executive Council, Academic Council, Finance Committee and Selection Committees and shall, in the absence of the Chancellor preside at any convocation of the university for conferring degrees.
- It shall be the duty of the Vice-Chancellor to see that the provisions of the Act, Statutes and Ordinances and Regulations are fully observed, and he should have the power necessary for the discharge of this duty.
What are the Tussles between CMs of several Indian States and Governors over Appointment of VC?
- Recently, the Tamil Nadu Assembly passed two Bills that seek to transfer the Governor’s power in appointing Vice-Chancellors (VC) of 13 state universities to the state government.
- A bill from West Bengal seeking to make the chief minister the chancellor of all state-run universities, replacing the governor, was passed by the assembly in 2022 (still Pending for Assent of Governor).
- Maharashtra, Karnataka, Jharkhand and Rajasthan, state laws underline the need for concurrence between the state and the Governor.
Way Forward
- The time may have come for all States to reconsider having the Governor as the Chancellor.
- However, they should also find alternative means of protecting university autonomy so that ruling parties do not exercise undue influence on the functioning of universities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to the Legislative Assembly of a State in India, consider the following statements: (2019)
- The Governor makes a customary address to Members of the House at the commencement of the first session of the year.
- When a State Legislature does not have a rule on a particular matter, it follows the Lok Sabha rule on that matter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
- Article 176(1) of the Constitution of India enjoins that the Governor shall address both the Houses assembled together at the commencement of the first Session after each general election to the Assembly and at the commencement of the first session of each year and inform the Legislature of the causes of its Summons. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Article 208 deals with the Rules of Procedure in State Legislatures. It states that:
- (1) A House of the Legislature of a State may make rules for regulating subject to the provisions of this Constitution, its procedure and the conduct of its business.
- (2) Until rules are made under clause (1), the rules of procedure and standing orders in force immediately before the commencement of this Constitution with respect to the Legislature for the corresponding Province shall have effect in relation to the Legislature of the State subject to such modifications and adaptations as may be made therein by the Speaker of the Legislative Assembly, or the Chairman of the Legislative Council, as the case may be.
- So, in case, when there is no rule on a particular subject in the State Legislature, under a convention since colonial times, state legislatures follow the rules of the Lok Sabha. Hence, statement 2 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- No criminal proceedings shall be instituted against the Governor of a State in any court during his term of office.
- The emoluments and allowances of the Governor of a State shall not be diminished during his term of office.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Article 361 of the Indian Constitution provides certain immunities to the President of India and the Governor of the States:
- No criminal proceedings whatsoever shall be instituted or continued against the President, or the Governor of a State, in any court during his term of office. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- No process for the arrest or imprisonment of the President, or the Governor of a State, shall issue from any court during his term of office.
- No civil proceedings against the President, or the Governor, shall be instituted during his term of office in any court in respect of any act done by him in his personal capacity. However, after giving two months’ notice, civil proceedings can be instituted against him during his term of office in respect of his personal acts done before or after entering the office.
- Article 158 states that the emoluments and allowances of the Governor shall not be diminished during his term of office. Hence, statement 2 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Whether the Supreme Court Judgment (July 2018) can settle the political tussle between the Lt. Governor and elected government of Delhi? Examine. (2018)
Q. Discuss the essential conditions for exercise of the legislative powers by the Governor. Discuss the legality of re-promulgation of ordinances by the Governor without placing them before the Legislature. (2022)
PM SVANidhi Scheme
For Prelims: PM SVANidhi Scheme, Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, Urban Local Bodies
For Mains: Microfinance, its Significance and the Related Initiatives.
Why in News?
Over 46.54 lakh small working capital loans have been disbursed to street vendors under the Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM-SVANidhi) in the three years since it was launched on June 1, 2020.
- A total of 46,54,302 loans had been disbursed. Out of those loans, about 40% (18,50,987) have been repaid so far.
What are the Key Features of the PM-SVANidhi?
- About:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme i.e., fully funded by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs with the following objectives:
- To facilitate working capital loan;
- To incentivize regular repayment; and
- To reward digital transactions
- Introduction of 3rd term loan of up to ₹50,000 in addition to 1st & 2nd loans of ₹10,000 and ₹20,000 respectively.
- The loans would be without collateral.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme i.e., fully funded by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs with the following objectives:
- Lending Agencies:
- Microfinance Institutions, Non-Banking Financial Company, Self Help Groups have been allowed due to their ground level presence and proximity to the urban poor including the street vendors.
- Eligibility:
- States/Union Territories (UTs):
- The Scheme is available for beneficiaries belonging to only those States/UTs which have notified Rules and Scheme under Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014.
- Beneficiaries from Meghalaya, which has its own State Street Vendors Act may, however, participate.
- States/Union Territories (UTs):
- Street Vendors:
- The Scheme is available to all street vendors engaged in vending in urban areas.
- Earlier the Scheme was available to all street vendors engaged in vending on or before March 24, 2020.
- The Scheme is available to all street vendors engaged in vending in urban areas.
- Benefits of Early Repayment:
- Interest Subsidy:
- On timely/early repayment of the loan, an interest subsidy of 7% per annum will be credited to the bank accounts of beneficiaries through direct benefit transfer on a six monthly basis.
- Credit Limits Extension:
- The scheme provides for the rise of the credit limit on timely/ early repayment of loans i.e. if a street vendor repays the installments on time or earlier, he or she can develop his or her credit score that makes him/her eligible for a higher amount of term loan.
- No-Penalty on Early Repayment:
- There will be no penalty on early repayment of loan.
- Early repayment (or resettlement) is a clearance of debt or loan before the scheduled time.
- Many banks and lenders charge penalties for repaying loans early.
- Interest Subsidy:
- E-governance:
- Encourage Digital Transactions:
- The scheme incentivises digital transactions by the street vendors through monthly cash back.
- Transparency:
- In line with the vision of leveraging technology to ensure effective delivery and transparency, a digital platform with web portal/ mobile app is being developed to administer the scheme with end-to-end solution.
- This platform will integrate the web portal/ mobile app with UdyamiMitra portal of SIDBI for credit management and PAiSA portal of MoHUA to administer interest subsidy automatically.
- In line with the vision of leveraging technology to ensure effective delivery and transparency, a digital platform with web portal/ mobile app is being developed to administer the scheme with end-to-end solution.
- Financial Inclusion:
- It will help in integrating the vendors into the formal financial system.
- Encourage Digital Transactions:
- Focus on Capacity Building:
- MoHUA in collaboration with State Governments will launch a capacity building and financial literacy programme of all the stakeholders and Information, Education and Communication (IEC) activities throughout the country
- Role of Urban Local Bodies (ULBs):
- ULBs will play a pivotal role in the implementation of the scheme by ensuring to target the beneficiary and reaching to them in an efficient manner.
Who is a Street Vendor/hawker?
- Any person engaged in vending of articles, goods, wares, food items or merchandise of daily use or offering services to the public in a street, footpath, pavement etc., from a temporary built up structure or by moving from place to place.
- The goods supplied by them include vegetables, fruits, ready-to-eat street food, tea, pakodas, breads, eggs, textile, apparel, artisan products, books/ stationary etc. and the services include barber shops, cobblers, pan shops, laundry services etc.
- Around 49.48 lakh street vendors have been identified in India.
- Uttar Pradesh has the maximum at 8.49 lakh, followed by Madhya Pradesh at 7.04 lakh.
- Delhi has only 72,457 street vendors.
- No street vendor has been identified in Sikkim.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (2021)
Q. How has globalization led to the reduction of employment in the formal sector of the Indian economy? Is increased informalization detrimental to the development of the country? (2016)
India's Transformation: Morgan Stanley's Report
Why in News?
A recent report by Morgan Stanley (global financial services firm) highlights the significant changes that have taken place in India over the past decade.
- The report challenges the skepticism surrounding India's potential and emphasizes the transformative reforms implemented in recent years.
- Morgan Stanley counters global opinions of India's underperformance. It emphasizes India's growth as the second-fastest-growing economy and top-performing stock market.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Significant Growth Drivers:
- Supply-Side Policy Reforms:
- Bringing corporate tax at par with other countries.
- Acceleration of infrastructure investment.
- Formalization of the Economy:
- Rising collection of Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- Implementation of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code.
- Introduction of flexible inflation targeting.
- Focus on foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Government support for corporate profits.
- Digitalizing Social Transfers.
- Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act .
- Multi-year high sentiment among multinational corporations (MNCs).
- India’s 401(k) Moment.
- Supply-Side Policy Reforms:
Note:
India’s 401(k) Moment:
- India’s 401(k) moment is the term used by Morgan Stanley to describe moment refers to the increase in household savings and investments in financial assets, inspired by the US 401(k) retirement savings plan.
- This shift reflects a change in household preferences from physical assets like gold and real estate to financial assets like equities and bonds.
- Key financial assets involved in India's 401(k) moment include mutual funds, insurance, and pension schemes.
- Economic Indicators:
- Manufacturing and capital spending as a percentage of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) have consistently risen.
- Export market share is projected to double to 4.5% by 2031(from 2021 level).
- Lower volatility in inflation and shallower interest rate cycles has impacted consumption patterns.
- Future Outlook:
- Anticipated rise in manufacturing and capital spending in GDP.
- Expected broad-based gains in goods and services exports.
- Per capita income is projected to increase and implications for discretionary consumption.
- It is expected to clock in at $5,200 within the next decade.
- Structural transformation contributing to a narrower current account deficit (CAD).
- Doubling of profits in GDP, resulting in strong earnings growth.
- Implications on Stock Market:
- There is a possibility of higher valuations for domestic shares, which could lead to increased investment opportunities.
- The demand for stocks within India is expected to remain strong, contributing to sustained growth in the market.
- India's reduced dependence on global capital flows may contribute to a more stable stock market, with less vulnerability to international market fluctuations.
- The stock market may become less influenced by changes in oil prices and the US recession.
- India's beta to emerging markets falling to 0.6, which is a consequence of reduced dependence on global capital market flows.
Note:
- Beta:
- Beta is a measure of systematic risk, also known as market risk or non-diversifiable risk. It quantifies how sensitive a stock's returns are to changes in the broader market.
- A beta of 1 indicates that the stock tends to move in line with the market, while a beta greater than 1 suggests the stock is more volatile than the market.
- A beta less than 1 indicates the stock is less volatile than the market.
- Anticipated Key Risks:
- Global recession.
- Sharp rise in commodity prices and supply outages.
- Shortages in skilled labor supply.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the context of finance, the term “beta” refers to (2023)
(a) the process of simultaneous buying and selling of an asset from different platforms
(b) an investment strategy of a portfolio manager to balance risk versus reward
(c) a type of systemic risk that arises where perfect hedging is not possible
(d) a numeric value that measures the fluctuations of a stock to changes in the overall stock market
Ans: (d)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Electronics Repair Services Outsourcing (ERSO)
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India has recently introduced the Electronics Repair Services Outsourcing (ERSO) Pilot initiative with the ambitious goal of establishing India as the Repair Capital of the World. The primary objective of this initiative is to position India as the most appealing destination for repairing Information and Communication Technology (ICT) products on a global scale.
The ERSO industry is projected to contribute up to USD 20 billion in revenue to India within the next five years, while also creating numerous employment opportunities. The pilot project, which will be conducted in Bengaluru, is scheduled to last for three months. Notably, this initiative aligns with Mission LiFE, which is dedicated to promoting global environmental sustainability. By facilitating affordable and dependable repair services for ICT products, the ERSO initiative aims to extend the lifespan of devices worldwide.
Fiscal Deficit Target Narrows To 6.4%
In the financial year 2022-23, the Centre's fiscal deficit decreased to 6.4% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), as estimated in the budget announcement made in February. The government aims to further reduce the fiscal deficit to 5.9% of the GDP in the current financial year 2023-24. During 2022-23, as part of devolution of taxes, the central government transferred ₹9.48 lakh crore to the State governments, showing an increase of ₹50,015 crore compared to the previous year (2021-22). In FY2023, the government witnessed a healthy growth of 15.2% in net tax revenues, despite a 17.8% contraction in non-tax revenues.
Fiscal deficit is the difference between the government's total expenditure and its total revenue (excluding borrowings). It is an indicator of the extent to which the government must borrow in order to finance its operations and is expressed as a percentage of the country's GDP.
Read More: Fiscal Deficit
GDP Expanded 6.1% in 2022-23 Last Quarter
India's GDP(Gross Domestic Product) growth accelerated to 6.1% in the January to March 2023 quarter, lifting the economy’s uptick in 2022-23 to 7.2% from the 7% estimated earlier. India's 6.1% GDP growth was the fastest among major economies in the fourth quarter.
Gross Value Added (GVA) in the economy is reckoned to have risen 7% in 2022-23, compared to 8.8% in 2021-22, with manufacturing GVA growth sliding to just 1.3% from 11.1% a year ago, despite a 4.5% rebound in the final quarter after six months of contraction.
Only three of eight broad economic activity segments recorded a higher GVA growth than in 2021-22, with the agricultural GVA growing 4%, up from 3.5% in the previous year. Consumption remained on lower side despite positive surprises in several sectors, especially in the last quarter of the year.
The higher-than-expected GDP growth in 2022-23 could temper growth expectations for 2023-24, which the government and central bank expect to be around 6.5%.
Read More: GDP and GVA
Regional Office of the Universal Postal Union (UPU) in New Delhi
The establishment of a Regional Office of the Universal Postal Union (UPU) in New Delhi has been approved by India's Union Cabinet. This decision allows India to actively engage in multilateral organizations within the postal sector, with a specific focus on South-South and Triangular cooperation. India will contribute staff and provide the necessary office setup for the UPU's regional office, which will be responsible for carrying out development cooperation and providing technical assistance in the region. The office will undertake various projects aimed at enhancing the capacity, efficiency, and quality of postal services, as well as advancing postal technology, e-commerce, and trade promotion. Through this initiative, India aims to expand its diplomatic presence, strengthen relationships with other countries, especially in the Asia-Pacific region, and enhance its participation in global postal forums.