Mangroves in India
For Prelims: International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem, UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Indian State Forest Report 2021, Sundarbans, Royal Bengal tiger, Irrawady Dolphin, MISHTI (Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes), Sustainable Aquaculture In Mangrove Ecosystem (SAIME) initiative.
For Mains: Significance of Mangroves, Challenges Related to Mangroves in India
Why in News?
On the International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem, West Bengal, which is home to approximately 40% of India's mangrove forests, unveiled plans to establish a dedicated 'Mangrove Cell' to streamline mangrove management efforts.
International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem
- The International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem is celebrated every year on 26 July and aims to raise awareness of the importance of mangrove ecosystems as “a unique, special and vulnerable ecosystem” and to promote solutions for their sustainable management, conservation and uses.
- This International Day was adopted by the General Conference of the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2015.
What is the Status of Mangroves in India?
- About:
- Mangroves are a unique type of coastal ecosystem found in tropical and subtropical regions. They are dense forests of salt-tolerant trees and shrubs that thrive in intertidal zones, where land meets the sea.
- These ecosystems are characterized by their ability to withstand harsh conditions, such as saline water, tidal fluctuations, and muddy, oxygen-poor soils.
- Characteristics:
- Mangroves exhibit Viviparity mode of reproduction, where seeds germinate within the tree before falling to the ground. This is an adaptive mechanism to overcome the challenge of germination in saline water.
- Some mangrove species secrete excess salt through their leaves, while others block the absorption of salt at their roots.
- Mangrove plants have special roots like prop roots and pneumatophores, which help impede water flow and provide support in the challenging tidal environment.
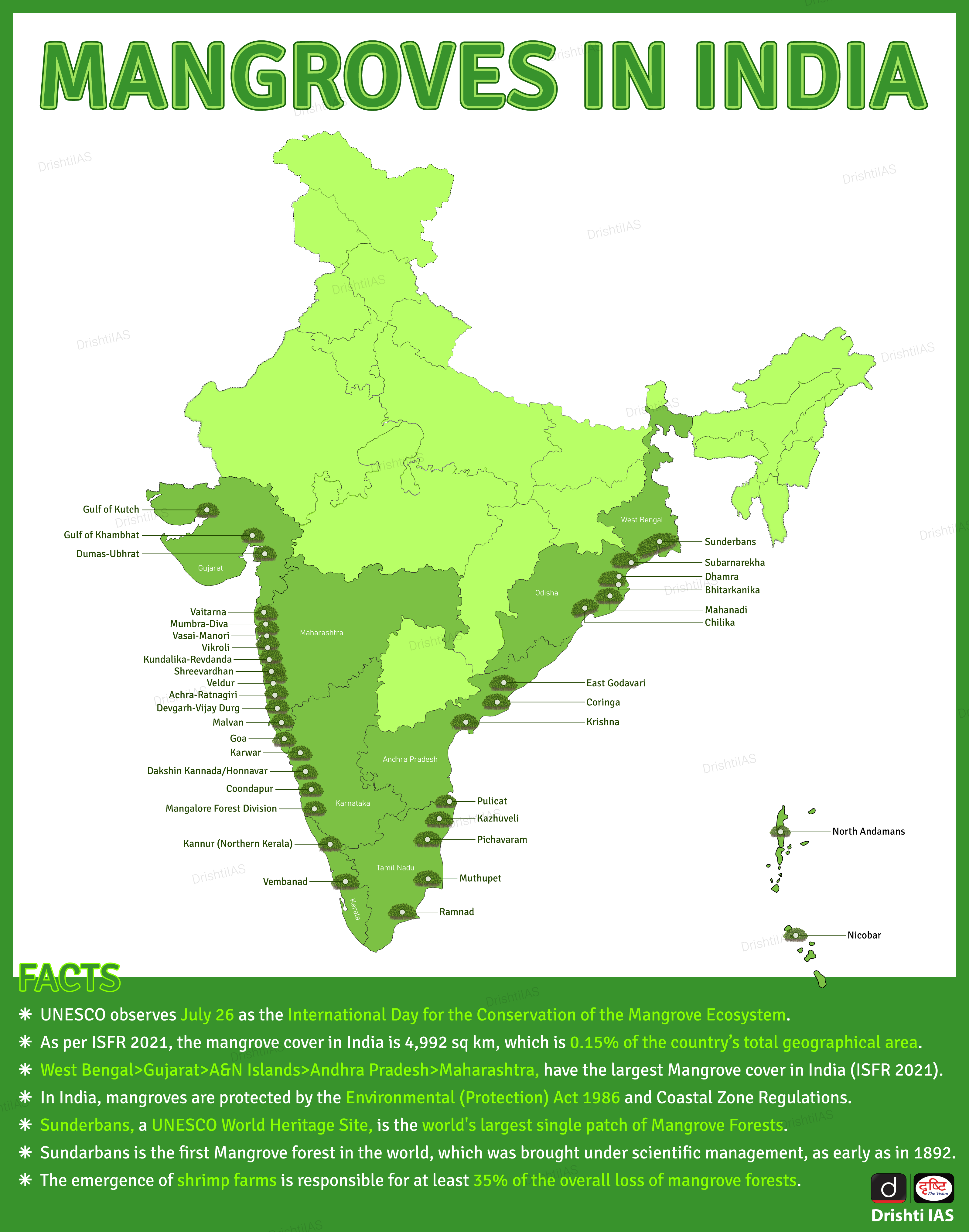
- Mangrove Cover in India:
- According to the Indian State Forest Report 2021, Mangrove cover in India is 4992 sq. Km which is 0.15% of the country's total geographical area.
- Sundarbans in West Bengal are the largest mangrove forest regions in the world. It is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Besides the Sundarbans, the Andamans region, the Kachchh and Jamnagar areas in Gujarat too have substantial mangrove cover.
- Significance:
- Biodiversity Conservation: Mangroves provide a unique habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, serving as breeding, nursery, and feeding grounds for numerous marine and terrestrial organisms.
- For example, sundarban hosts the Royal Bengal tiger, Irrawady Dolphin, Rhesus macaque, Leopard cats, Small Indian civet.
- Coastal Protection: Mangroves act as natural buffers against coastal erosion, storm surges, and tsunamis.
- Their dense root systems and tangled network of prop roots stabilize shorelines and reduce the impact of waves and currents.
- During hurricanes and cyclones, mangroves can absorb and dissipate a significant amount of energy, protecting inland areas and human settlements from devastating damage.
- Carbon Sequestration: Mangroves are highly efficient carbon sinks, sequestering large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass and sediments.
- Fisheries and Livelihoods: Mangroves support fisheries by providing nursery areas for fish and shellfish, enhancing fishery productivity and contributing to livelihood and local food security.
- Water Quality Improvement: Mangroves act as natural filters, trapping and removing pollutants and excess nutrients from coastal waters before they reach the open ocean.
- Their role in purifying water contributes to the health of marine ecosystems and helps maintain the balance of fragile coastal ecosystems.
- Tourism and Recreation: Mangroves offer recreational opportunities such as eco-tourism, birdwatching, kayaking, and nature-based activities, which can promote sustainable economic growth for local communities.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Mangroves provide a unique habitat for a wide variety of plant and animal species, serving as breeding, nursery, and feeding grounds for numerous marine and terrestrial organisms.
- Challenges:
- Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation: Mangroves are often cleared for various purposes, including agriculture, urbanization, aquaculture, and infrastructure development.
- Such activities lead to the fragmentation and loss of mangrove habitats, disrupting their ecosystem functioning and biodiversity.
- The conversion of mangroves into shrimp farms and other commercial uses is a significant concern.
- Climate Change and Sea Level Rise: Rising sea levels due to climate change pose a significant threat to mangroves.
- Climate change also brings about extreme weather events, such as cyclones and storms, which can cause severe damage to mangrove forests.
- Pollution and Contamination: Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and improper waste disposal contaminate mangrove habitats.
- Heavy metals, plastics, and other pollutants adversely affect the flora and fauna of these ecosystems.
- Lack of Integrated Management: Often, mangroves are managed in isolation, without considering their interconnectedness with adjacent ecosystems like coral reefs and seagrass beds.
- Integrated management approaches that consider the broader coastal ecosystem are necessary for effective conservation.
- Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation: Mangroves are often cleared for various purposes, including agriculture, urbanization, aquaculture, and infrastructure development.
- Government Initiatives Related to Mangrove Conservation:
Way Forward
- Drone Monitoring and AI: Employ drone technology equipped with high-resolution cameras and AI algorithms to monitor mangrove health and detect illegal activities such as encroachment or illegal logging.
- This approach can help in efficient and timely surveillance over vast areas.
- Mangrove Adoption Program: Launch a public-driven initiative where individuals, corporates, and institutions can "adopt" a patch of mangroves.
- Participants would be responsible for the maintenance, protection, and restoration of their adopted area, fostering a sense of ownership and collective responsibility.
- Mangrove Research and Development: Invest in research to explore novel applications of mangroves, such as phytoremediation to clean polluted water or developing new medicines from mangrove plant extracts.
- This could lead to innovative ways to leverage mangroves' unique properties for sustainable development.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following regions of India has a combination of mangrove forest, evergreen forest and deciduous forest? (2015)
(a) North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
(b) South-West Bengal
(c) Southern Saurashtra
(d) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss the causes of depletion of mangroves and explain their importance in maintaining coastal ecology. (2019)
Space Debris
For Prelims: Space Debris, Indian Space Research Organization, China’s Long March 5B rocket, Kessler Syndrome, Project NETRA, Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee.
For Mains: Challenges in Managing Space Debris and Way Forward.
Why in News?
Recently, ISRO’s (Indian Space Research Organization) Rocket Debris was found on the shores of Western Australia.
- In November 2022, large fragments of China’s Long March 5B rocket plunged uncontrolled into the south-central Pacific Ocean. These fragments were stages of the rocket used to deliver the third and final module of the Tiangong space station.
- In May 2021, a large chunk of a 25-tonne Chinese rocket fell into the Indian Ocean.
What is Space Debris?
- About:
- Space debris refers to man-made objects in Earth's orbit that no longer serve a useful purpose.
- This includes defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments of debris from collisions or other events.
- Threats from Space Debris:
- Threat to Marine Life:
- Even when falling into the oceans, which is more likely since 70% of the earth’s surface is ocean, large objects can be a threat to marine life, and a source of pollution.
- Threat for Operational Satellites:
- The floating space debris is a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- This overpopulation of space with objects and debris is referred to as Kessler Syndrome.
- The floating space debris is a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- Reduction of Orbital Slots:
- The accumulation of space debris in specific orbital regions can limit the availability of desirable orbital slots for future missions.
- Space Situational Awareness:
- The increasing amount of space debris makes it more challenging for satellite operators and space agencies to accurately track and predict the orbits of objects in space.
- Threat to Marine Life:
What are the Challenges in Tackling Space Activities?
- More Satellite Launches by Various Countries:
- Countries like the United States, China, India, and Japan are actively engaged in space activities, including manned missions, lunar exploration, and resource exploitation.
- Satellite launches have exponentially increased in the past decade, with 210 launches in 2013, 600 in 2019, 1,200 in 2020, and 2,470 in 2022.
- Valuable metals in asteroids and planets have attracted international interest in the absence of an agreed international framework on space resource exploration that poses challenges in dealing with space activities.
- Countries like the United States, China, India, and Japan are actively engaged in space activities, including manned missions, lunar exploration, and resource exploitation.
- Coordination and Space Traffic Management:
- The current coordination of space traffic is fragmented, with different countries and regional entities employing varying standards and practices.
- This lack of coordination can lead to potential collisions and accidents in space, posing risks to operational spacecraft and increasing space debris.
- Technological Challenges:
- Developing and deploying space missions requires cutting-edge technology, which can be expensive and prone to technical failures. Space agencies and private companies must address these challenges to ensure the success of their missions.
- Geopolitical Tensions:
- As more countries become spacefaring nations, there is potential for geopolitical tensions in outer space.
- Competing interests and territorial claims can create diplomatic challenges and hinder international cooperation.
What are the Initiatives to Deal with Space Debris?
- India:
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris.
- ISRO also carried out 21 collision avoidance manoeuvres of Indian operational space assets in 2022 to avoid collisions with other space objects.
- ISRO has also set up a Centre for Space Debris Research to monitor and mitigate the threat of space debris.
- ‘Project NETRA’ is also an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
- Global:
- The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC), an international governmental forum, was established in 1993 to coordinate efforts between spacefaring nations to address the issue of space debris.
- The United Nations has established the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) to develop guidelines for the long-term sustainability of outer space activities, including the mitigation of space debris.
- The European Space Agency (ESA) has launched the Clean Space initiative, aimed at reducing the amount of space debris and promoting sustainable space activities.
What are the UN’s Five Treaties to Deal with Space Activities?
- The Outer Space Treaty 1967:
- Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies.
- Rescue Agreement 1968:
- Agreement on the Rescue of Astronauts, the Return of Astronauts and the Return of Objects Launched into Outer Space.
- Liability Convention 1972:
- It deals mainly with damage caused by space objects to other space assets, but it also applies to damage caused by falling objects on earth.
- The Convention makes the launching country “absolutely liable” to pay compensation for any damage caused by its space object on the earth or to a flight in air. The country where the junk falls can stake a claim for compensation if it has been damaged by the falling object.
- The Registration Convention 1976:
- Convention on Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space.
- The Moon Agreement 1979:
- Agreement Governing the Activities of States on the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies.
- India is a signatory to all five of these treaties but has ratified only four. India did not ratify the Moon agreement.
Way Forward
- Improving the ability to track and monitor space debris can help mitigate the risks it poses to operational satellites and human space missions.
- Using reusable launch vehicles instead of single-use rockets can help reduce the number of new debris generated from launches.
- Using more durable materials and designing satellites for eventual de-orbiting can reduce the number of debris generated in the long term.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above their territory. What do you understand by ‘airspace’? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggest ways to contain the threat. (2014)
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Repealing Regulations, 2023
For Prelims: Telecom Regulatory Authority of India, OTT Communication service, Dial-up and Leased Line Internet Access.
For Mains: Developments in Telecom Sector in India, Issues Related to Telecom Sector in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) took a significant step in modernizing the regulatory landscape by issuing the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Repealing Regulations, 2023.
- This regulation aimed to repeal the outdated Regulation on quality of service of dial-up and leased line internet access service, 2001, which had been in effect since December 10, 2001.
What is Dial-up and Leased Line Internet Access?
- Dial-up internet access is a form of internet access that uses the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to establish a connection to an ISP via a telephone line.
- It is the least expensive way to access the Internet, but it is also the slowest connection.
- Leased line internet access is a dedicated point-to-point data circuit that provides guaranteed bandwidth and symmetric upload and download speeds.
- They are typically used by businesses or organizations that need high-performance and reliable internet connectivity for their operations.
How was Dial Up and Leased Line Internet Access Regulated, and Why is it Now Outdated?
- The Regulation on quality of service of dial-up and leased line internet access service, 2001, was initially introduced to govern the quality of internet services provided by Basic Service Operators and Internet Service Providers (ISPs) in India.
- The regulation applied to all providers, including the incumbent operators such as BSNL, MTNL, and VSNL.
- When the regulations were introduced, dial-up services were the predominant means of accessing low-speed internet. However, over time, the telecommunication networks have undergone significant transformations.
- The emergence of various technologies, including FTTH, LTE, and 5G, has made high-speed broadband services widely available to consumers.
- Moreover, leased line access services are now predominantly offered by Internet Gateway Service Providers (IGSPs) to enterprises, and these services are governed by Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
- SLAs inherently include provisions to safeguard concerns regarding service quality, making the 2001 regulation less relevant in the current context.
- With this regulatory burden lifted with Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Repealing Regulations, 2023, service providers can focus more on delivering cutting-edge services and improving customer experiences.
- Additionally, the telecommunications sector may experience increased competition and innovation, leading to enhanced service quality, expanded coverage, and potential cost efficiencies.
What are the Current Major Challenges Related to Telecom Sector?
- Financial Stress: The telecom sector in India has been grappling with intense competition, low tariffs, and high debt burdens.
- Several telecom companies were facing financial challenges, and some even declared bankruptcy or merged with other players to stay afloat.
- Rural-Urban Disparity: Although adequate tele-density has been achieved, there is a significant discrepancy in the share of telecom subscribers between urban (55.42%) and rural (44.58%) areas of India.
- Also, fixed broadband penetration in the country is among the lowest in the world at only 1.69 per 100 inhabitants.
- Issue with Over-the-Top Platforms (OTT): OTT Communication service platforms like WhatsApp and Telegram use the network infrastructure of telecom service providers to provide services such as voice calls and SMS services.
- Telecom Service Providers (TSPs) allege that these features result in a double whammy for them as they cut into their sources of revenue (voice calls, SMS).
- Mismanagement of E-waste: Telecom industry impacts the environment in multiple ways, including through the generation of e-waste. In India, more than 95% of e-waste is illegally recycled by informal waste pickers.
Way Forward
- AI-Enabled Network Management: Implement AI-driven network management systems that can optimize network performance, predict maintenance needs, and ensure seamless connectivity for users.
- Telecom Infrastructure on Wheels: Create mobile telecom infrastructure units that can be deployed to temporary or underserved locations, such as construction sites, festivals, or disaster areas, to provide reliable connectivity.
- Streamlined Regulatory Processes: Simplify and expedite regulatory approvals for telecom infrastructure deployment, reducing bureaucratic hurdles and promoting faster network expansion.
- Also, bringing OTT communication services under the ambient of regulation is the need of hour.
What is Telecom Regulatory Authority of India?
- About:
- The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) was established with effect from 20th February 1997 by Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997.
- Composition:
- TRAI consists of a chairperson and not more than two whole-time Members and not more than two part-time Members.
- Functions:
- To regulate telecom services, including fixation/revision of tariffs for telecom services which were earlier vested in the Central Government.
- Ensure quality of service and transparency in tariff
- Advise the government on policy matters and licensing issues
- The recommendations of the TRAI are not binding upon the Central Government.
- Appellate Authority:
- The TRAI Act was amended by an ordinance, effective from 24 January 2000, establishing a Telecommunications Dispute Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT) to take over the adjudicatory and disputes functions from TRAI.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is/are the aims/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Healthcare Bills to Reform Nursing, Midwifery, and Dentistry
For Prelims: National Nursing and Midwifery Commission bill (NNMC), National Dental Commission bill
For Mains: Significance of Health Sector in an Economy, Challenges in Nursing, Midwifery, and Dentistry, Government initiatives
Why in News?
Recently, the Lok Sabha passed National Nursing and Midwifery Commission Bill (NNMC), 2023, and the National Dental Commission bill, 2023.
- The Bills aim to repeal existing acts and bring about improvements in the quality of healthcare in different medical fields.
What is the National Nursing and Midwifery Commission (NNMC) Bill,2023?
- About:
- The NNMC Bill is a significant healthcare legislation aimed at reforming and enhancing nursing and midwifery professions in India.
- Establish the National Nursing and Midwifery Commission (NNMC) as a regulatory body for nursing and midwifery professionals.
- Repeal the existing Indian Nursing Council Act, of 1947. As the act is outdated and does not reflect the current needs and demands of the nursing and midwifery profession, which has evolved significantly over the years in terms of education, training, practice, and service standards.
- Key Features:
- National Nursing and Midwifery Commission:
- Composition:
- NNMC will consist of 29 members.
- Chairperson with a postgraduate degree in nursing and midwifery and 20 years of field experience.
- Ex-officio members from Department of Health and Family Welfare, National Medical Commission, Military Nursing Services, and Directorate General of Health Services.
- Other members from nursing and midwifery professionals and charitable institutions.
- Functions:
- Framing policies and regulating standards for nursing and midwifery education.
- Providing a uniform admission process for nursing and midwifery institutions.
- Regulating nursing and midwifery institutions.
- Establishing standards for faculty in teaching institutions.
- Composition:
- Autonomous Boards:
- Nursing and Midwifery Undergraduate and Postgraduate Education Board: Regulate education and examination at undergraduate and postgraduate levels.
- Nursing and Midwifery Assessment and Rating Board: Provide the framework for assessing and rating nursing and midwifery institutions.
- Nursing and Midwifery Ethics and Registration Board: Regulate professional conduct and promote ethics in the profession.
- State Nursing and Midwifery Commissions:
- To be constituted by state governments.
- Will consist of 10 members, including representatives from the health department and nursing/midwifery colleges.
- Functions include enforcing professional conduct, maintaining state registers, issuing certificates of specialization, and conducting skill-based examinations.
- Establishment of Institutions:
- Permission from Assessment and Rating Board required to establish new nursing and midwifery institutions or increase seats/postgraduate courses.
- Appeals process available to National Commission and Central Government in case of disapproval.
- Practicing as a Professional:
- Individuals must be enrolled in the National or State Register to practice nursing or midwifery.
- Non-compliance may result in imprisonment or a fine.
- Advisory Council:
- Provides advice and support to the National Commission on Nursing and Midwifery education, services, training, and research.
- Includes representatives from each State and Union Territory, Ministry of Ayush, University Grants Commission, National Assessment and Accreditation Council, Indian Council of Medical Research, and nursing/midwifery professionals.
- National Nursing and Midwifery Commission:
What is the National Dental Commission Bill, 2023?
- About:
- The National Dental Commission Bill focuses on the regulation and improvement of dentistry in India.
- Key Features:
- Establish the National Dental Commission (NDC) to regulate the profession of dentistry.
- Repeal the Dentists Act of 1948.
- Key Features:
- National Dental Commission:
- Composition:
- Constituted by the central government with 33 members and will be chaired by an eminent and experienced dentist.
- Chairperson appointed by the central government upon recommendation of a search-cum-selection committee which is chaired by Cabinet Secretary.
- Ex-officio members of the commission include Presidents of three autonomous Boards, Director General of Health Services, Chief of the Centre for Dental and Educational Research, AIIMS.
- Part-time members include faculties of dentistry from government institutes and representatives of states and union territories.
- Functions:
- Regulating dental education, institutions, research, and infrastructure, as well as ensuring admissions through National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (NEET).
- Composition:
- Autonomous Boards:
- Undergraduate and Postgraduate Dental Education Board: Responsible for determining education standards, developing curriculum, and granting recognition to dental qualifications.
- Dental Assessment and Rating Board: Responsible for determining compliance assessment procedure for dental institutions, granting permission to establish new institutions, and conducting inspections and ratings.
- Ethics and Dental Registration Board: Responsible for maintaining online national registers of dentists/dental auxiliaries, suspending/cancelling licenses, and regulating standards of conduct, ethics and the scope of the practice.
- State Dental Councils:
- To be established within a year, responsible for maintaining registers, handling grievances, and implementing provisions.
- Entrance Examinations:
- Admission to Bachelor of Dental Surgery through NEET, and National Exit Test (Dental) for licensing and postgraduate admissions.
- Clearing National (Exit) Test grants a license to practice dentistry, but registration in state/national register required before commencing practice.
- Dental Advisory Council:
- Advise the Commission on education, training, research, and equitable access to dental education.
- Ex-officio members of the Commission are ex-officio members of the Council.
- National Dental Commission:
Challenges Faced by Regional Connectivity Scheme
For Prelims: Challenges Faced by Regional Connectivity Scheme, UDAN Scheme, Regional Connectivity Scheme.
For Mains: Challenges Faced by Regional Connectivity Scheme.
Why in News?
UDAN, a Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) of the Ministry of Civil Aviation is facing challenges due to many airports built under the scheme not being able to be operationalized.
- Despite the claims of building 74 airports, only 11 greenfield airports have become operational since May 2014.
What is the Regional Connectivity Scheme?
- About:
- UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagarik) was launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation for regional airport development and regional connectivity enhancement.
- It is a part of the National Civil Aviation Policy 2016.
- The scheme is applicable for a period of 10 years.
- Objectives:
- Improve the air connectivity to remote and regional areas of India.
- Development of remote areas and enhancing trade and commerce and tourism expansion.
- Enable common people to access air travel with affordable rates.
- Employment creation in the aviation sector.
- Key Features:
- Under the scheme, airlines have to cap airfares for 50% of the total seats at Rs. 2,500 per hour of flight.
- This would be achieved through:
- A financial stimulus in the form of concessions from Central and State governments and airport operators and
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF) – A government grant provided to the airlines to bridge the gap between the cost of operations and expected revenue.
- Regional Connectivity Fund (RCF) was created to meet the viability gap funding requirements under the scheme.
- The partner State Governments (other than UTs and NER states where contribution will be 10%) would contribute a 20% share to this fund.
What are the Phases of UDAN Scheme?
- Phase 1 was launched in 2017, with the objective of connecting underserved and unserved airports in the country.
- Phase 2 was launched in 2018, with the aim of expanding air connectivity to more remote and inaccessible parts of the country.
- Phase 3 was launched in November 2018, with the focus on enhancing air connectivity to hilly and remote regions of the country.
- Phase 4 of the UDAN scheme was launched in December 2019, with a focus on connecting islands and other remote areas of the country.
- Phase 5 was launched in April 2023, with a focus on Category-2 (20-80 seats) and Category-3 (>80 seats) aircrafts with no restriction on the distance between the origin and the destination of the flight.
What are the Challenges to the RCS Scheme?
- Commercial Viability:
- Many of the routes identified under the scheme have been found to be commercially unviable for airlines. The low demand for air travel on certain routes makes it difficult for airlines to operate profitably, even with subsidies provided under UDAN.
- Airport development under RCS involved launching 479 routes to revive under-utilized airports. However, out of these, 225 routes have ceased operations.
- Infrastructural Constraints:
- The lack of adequate airport infrastructure in some of the remote regions poses challenges for airlines.
- Many airports require upgradation and improvements to meet safety standards and handle increased air traffic.
- Subsidization of Air Travel:
- The RCS aimed to make air travel affordable by providing subsidies and viability gap funding to airlines operating on selected routes. However, the scheme faced issues as some routes were found to be commercially unviable despite the subsidies.
- High Operating Costs:
- Airlines operating in remote areas often face higher operating costs, including increased fuel expenses, maintenance costs, and logistical challenges, which can affect their profitability.
- Airfare Caps:
- The cap on airfares for RCS flights can impact the revenue potential of airlines, especially when operational costs are high. It may discourage airlines from operating on certain routes.
- Passenger Awareness:
- Lack of awareness among potential passengers about the availability of air travel options under UDAN can limit demand and utilization of regional air services.
Way Forward
- The Regional Connectivity Scheme played a significant role in airport development, but challenges related to commercial viability and airlines' sustainability have hindered its overall success.
- As the aviation sector continues to evolve, addressing these issues will be crucial to achieving sustainable air connectivity for smaller cities and regions across the country.
- Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from the government, aviation industry stakeholders, and local authorities.
- Enhancing airport infrastructure, streamlining subsidy disbursal, addressing operational constraints, and promoting regional air travel awareness are key areas that need attention to ensure the success and sustainability of India's UDAN Regional Connectivity Scheme.
International Tiger Day 2023: Indian Tiger Conservation
For Prelims: International Tiger Day, Project Tiger 1973, National Tiger Conservation Authority, tiger reserves
For Mains: Significance of Tiger Conservation, Related initiatives
Why in News?
Recently, on International Tiger Day 2023, two significant reports have brought attention to the state of tiger conservation in India and the challenges it faces.
- The Management Effectiveness Evaluation (MEE) of tiger reserves in India, 2022 (Fifth Cycle) report for Indian tiger reserves prepared by the Wildlife Institute of India and the National Tiger Conservation Authority revealed a mixed picture of progress and challenges.
- On the other hand, a study by Panthera, the global wild cat conservation organization, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences highlights the alarming situation of tiger poaching and trafficking in Bangladesh.
- Concerns are emerging as India's wild tiger population has increased to a healthy 3,167 in 2022 from just 1,400 in 2006, prompting discussions about the nation's forest capacity to sustain these numbers.
What is International Tiger Day 2023?
- 29th July is observed as International Tiger Day (ITD) to promote the conservation of the striped cat as well as to advocate a global system for protecting its natural habitats.
- ITD was established in 2010 at St Petersburg Tiger Summit in Russia to raise awareness about the decline of wild tiger numbers, leaving them on the brink of extinction, and to encourage the work of Tiger Conservation.

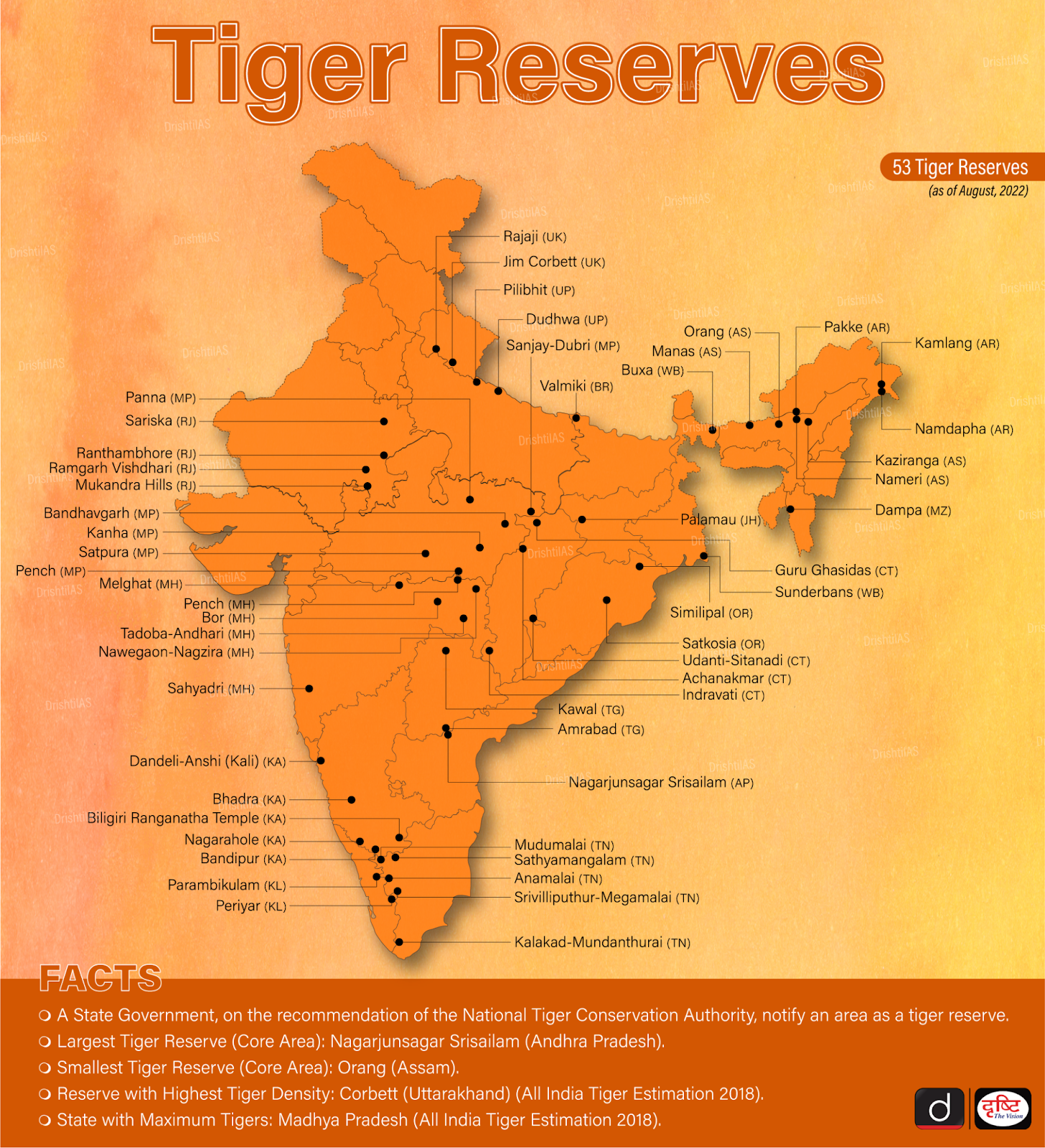
What are the Key Highlights of the MEE Report?
- Overall Management Performance Improvements:
- The report evaluated 51 tiger reserves using 33 parameters for the analysis.
- The results were divided into four groups based on the percentage of the maximum score. Among the Tiger Reserves, 12 achieved the 'Excellent' category (scoring >= 90%), 21 were classified as 'Very Good' (scoring 75-89%), 13 as 'Good' (scoring 60-74%), and 5 as 'Fair' (scoring 50-59%) categories.
- The mean score for management performance in tiger reserves indicates an overall mean score of 78.01% (ranging between 50% to 94%) for 51 Tiger Reserves.
- Climate Action Identified as Weakest Area:
- The report identifies climate change and carbon capture efforts as the weakest performing area for Indian tiger reserves, receiving the lowest score of 60% in the current cycle.
- Climate change poses a major concern for tiger reserves, particularly those affected by high-intensity climatic impacts like the Sundarbans.
- Fund Flow Hinders Conservation Efforts:
- Inadequate funds from the Union and state governments, as well as other donors, pose significant challenges for tiger reserve management.
- Three parameters related to fund flow rank among the five poorest performing areas in tiger reserves.
- Actual fund allocation for tiger conservation has decreased since 2018-19, with a surge in 2022-23 but limited actual fund release.
- Complex requisition and release processes have further slowed down the fund flow, causing delays in conservation efforts.
- Lack of funds affects infrastructure maintenance, village relocation, and human-wildlife conflict management.
- Resilience in Landscape Integration and Human-Wildlife Conflicts:
- Landscape integration and countering human-wildlife conflicts were found to be the better-performing indicators, scoring over 85% marks.
- Top-Performing and Poorly Performing Reserves:
- Periyar Tiger Reserve in Kerala stands out as the best performer with a MEE score of around 94% followed by Satpura in Madhya Pradesh and Bandipur in Karnataka.
- Sundarbans in West Bengal, the only tiger forest in the world with mangroves, continued to be in the ‘very good’ category and got a rank position of 32nd.
- Dampa in Mizoram is identified as the poorest performing tiger reserve with only 50% followed by Indravati in Chhattisgarh and Nameri in Assam.
- Overall, 29 tiger reserves have improved their status compared to the previous assessment, while two reserves deteriorated.
- Significance of MEE:
- The report has been prepared based on a detailed analysis involving top-notch Indian wildlife experts and follows a framework by the International Union for Conservation of Nature's World Commission on Protected Areas.
- It identifies gaps in conservation efforts and helps adopt more effective strategies for the long-term survival of tigers.
- The report has been prepared based on a detailed analysis involving top-notch Indian wildlife experts and follows a framework by the International Union for Conservation of Nature's World Commission on Protected Areas.
What are the Key Highlights of Research Conducted by Panthera?
- The study conducted by Panthera highlighted Bangladesh as a major hub for the illicit poaching and trafficking of endangered tigers.
- It identified a growing class of Bangladeshi elite both within the country and abroad, driving the demand for tiger parts for medicinal, spiritual, and ornamental purposes.
- The research revealed that tiger parts from Bangladesh were being supplied to 15 countries, including India, China, and Malaysia, as well as developed G20 nations like the United Kingdom, Germany, Australia, and Japan.
- The Sundarbans, a vital tiger habitat in Bangladesh, witnessed infiltration by pirate groups involved in tiger poaching, leading to a significant decline in the tiger population.
- The study identified four source sites for tiger poaching, including the Sundarbans in India and Bangladesh, Kaziranga-Garampani Parks in India, Myanmar's Northern Forest Complex, and Namdapha-Royal Manas Parks in India.
- Traders involved in tiger trafficking concealed illegally sourced tiger parts easily by owning logistics companies and holding licenses for legal wildlife trade.
- The research suggested a problem-oriented approach by the Bangladesh government, targeting specific players, trade routes, and poaching issues.
What are the Concerns about India's Forest Capacity Reaching its Limit to Support Tigers?
- Roaming Outside Protected Areas: Almost 30% of the tiger population roams outside protected areas and regularly enters human habitations, leading to human-tiger conflicts.
- With the increasing tiger population, questions arise about whether India's forests are nearing their carrying capacity to sustain these apex predators.
- Shrinking Tiger Corridors: The construction of linear infrastructure, such as railway lines, highways, and canals, has resulted in the shrinking of tiger corridors, essential patches that connect two large forest areas.
- Foraying into Human-Dominated Landscapes: Tigers are believed to leave forests in search of herbivores that increasingly venture into human-dominated landscapes. This behavior is driven by the takeover of natural flora by invasive species like lantana, which disrupts the natural ecosystem and forces herbivores to seek food in areas inhabited by humans.
- Inequitable Population Distribution: While India has 53 tiger reserves spread over 75,000 sq km, just 20 reserves cover one-third of the area for tiger conservation, leading to inequitable population distribution.
Way Forward
- Strengthen forest management practices for better conservation of tiger habitats.
- Protect and restore tiger corridors to enable unrestricted movement between forest areas.
- Implement evidence-based strategies for managing human-wildlife conflicts.
- Expedite voluntary village relocation within tiger reserves to reduce conflicts.
- Adopt an inclusive approach to conservation, considering human rights and other species' needs.
- Conduct research on tiger movements and social tolerance in human-dominated landscapes.
- Ensure sustainable infrastructure development to minimize habitat disturbances.
- Foster continued support from local communities for tiger conservation efforts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020)
(a) Corbett
(b) Ranthambore
(c) Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam
(d) Sundarbans
Ans: (c)
- Critical Tiger Habitats (CTH), also known as core areas of tiger reserves, are identified under the Wild Life Protection Act, 1972 based on scientific evidence that “such areas are required to be kept as inviolative for the purpose of tiger conservation, without affecting the rights of the Scheduled Tribes or such other forest dwellers”.
- The CTHs are notified by the state government in consultation with the expert committee constituted for the purpose.
- Area of the Core/Critical Tiger Habitat
- Corbett (Uttarakhand): 821.99 sq. Kms
- Ranthambore (Rajasthan): 1113.36 sq. Kms
- Sundarbans (West Bengal): 1699.62 sq. Kms
- Nagarjunsagar Srisailam (part of Andhra Pradesh): 2595.72 sq. Kms
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Akira Ransomware
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian government's Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) issued a warning about the Akira ransomware, which has emerged as a significant cybersecurity threat, targeting both Windows and Linux devices.
- Ransomware is a type of malware that hijacks computer data and then demands payment (usually in bitcoins) in order to restore it.
What is Akira Ransomware?
- About:
- It is malicious software that poses a significant threat to data security.
- It targets both Windows and Linux devices, encrypting data and demanding a ransom for decryption.
- Key Characteristics of Akira Ransomware:
- Designed to encrypt data and create a ransomware note with a unique ".akira" extension appended to encrypted filenames.
- Capable of deleting Windows Shadow Volume copies and shutting down Windows services to prevent interference during encryption.
- Exploits VPN services and malicious files to infect devices, making it challenging to detect and prevent.
- Mode of Operation:
- Akira ransomware spreads through various methods, including spear phishing emails with malicious attachments, drive-by downloads, and specially crafted web links in emails.
- Insecure Remote Desktop connections are another avenue for ransomware transmission.
- Implications of an Akira Attack:
- Once infected, Akira ransomware steals sensitive data and encrypts it, rendering it inaccessible to the victim.
- Attackers then demand a ransom for decryption and threaten to leak the stolen data on the dark web if their demands are not met.
- Protection Measures Against Akira Ransomware:
- Regularly maintain up-to-date offline backups to prevent data loss in case of an attack.
- Keep operating systems and networks updated, including virtual patching for legacy systems, to address potential vulnerabilities.
- Implement security protocols such as Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC), Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Sender Policy for email validation.
- Enforce strong password policies and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to enhance user authentication.
- Establish a strict policy for external device usage and ensure data-at-rest and data-in-transit encryption.
- Block attachment file types with suspicious extensions like .exe, .pif, and .url to avoid downloading malicious code.
- Educate users to be cautious about clicking on suspicious links to prevent malware downloads.
- Conduct regular security audits, especially for critical systems like database servers, to identify and address vulnerabilities.
What is CERT-IN?
- Computer Emergency Response Team - India is an organisation of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology with the objective of securing Indian cyberspace.
- It is a nodal agency which deals with cybersecurity threats like hacking and phishing.
- It collects, analyses and disseminates information on cyber incidents, and also issues alert on cybersecurity incidents.
- CERT-IN provides Incident Prevention and Response Services as well as Security Quality Management Services.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The terms ‘WannaCry, Petya and EternalBlue’ sometimes mentioned in the news recently are related to (2018)
(a) Exoplanets
(b) Cryptocurrency
(c) Cyber attacks
(d) Mini satellites
Ans: (c)
Q. In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
AMC Repo Clearing Limited
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Finance inaugurated the Limited Purpose Clearing Corporation (LPCC) called AMC Repo Clearing Limited (ARCL).
What is AMC Repo Clearing Limited (ARCL)?
- About:
- ARCL is a Limited Purpose Clearing Corporation that provides clearing and settlement services to all trades made in corporate debt securities on the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
- It received in-principle approval from the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) under the Stock Exchanges and Clearing Corporations (SECC) Regulations, 2018.
- Also, ARCL has been granted Certificate of Authorization by RBI under Payment and Settlement Systems (PSS) Act, 2007 to offer Central counterparty clearing house (CCP) services for repo transactions in corporate debt securities.
- Functions:
- ARCL offers triparty repo services and central counterparty services to facilitate repo transactions in corporate bonds, which are short-term borrowings backed by securities as collateral.
- ARCL will help to widen and deepen the corporate bond repo market, which is currently underdeveloped and illiquid compared to the government bond repo market.
- It allows holders of bonds to meet short-term liquidity needs without liquidating their assets, providing flexibility to market participants.
- ARCL will also reduce the counterparty risk, operational risk and settlement risk for the participants in the corporate bond repo market.
Note:
- Secondary Market: The secondary market, also known as the aftermarket, refers to the financial market where previously issued financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, derivatives, and other securities, are bought and sold among investors.
- Corporate Bond: Corporate bonds are debt securities issued by corporations to raise capital for various purposes, such as expanding operations, funding projects, or refinancing existing debt.
- Triparty Repo Services: Triparty repo services are financial transactions where a third party, often a custodian or clearing agent, acts as an intermediary between the two parties involved in a repurchase agreement (repo).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is issued by registered foreign portfolio investors to overseas investors who want to be part of the Indian stock market without registering themselves directly? (2019)
(a) Certificate of Deposit
(b) Commercial Paper
(c) Promissory Note
(d) Participatory Note
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following markets: (2023)
- Government Bond Market
- Call Money Market
- Treasury Bill Market
- Stock Market
How many of the above are included in capital markets?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
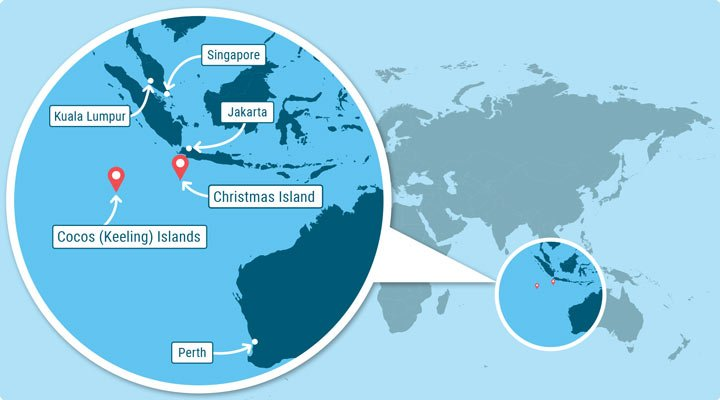
Australia's Strategic Cocos Islands
Indian Navy and Indian Air Force aircraft recently visited Australia's Cocos (Keeling) Islands (CKI) in the Southern Indian Ocean, strengthening strategic reach and interoperability between India and Australia's militaries in the Indian Ocean.
- The cooperation between India and Australia extends to support for India's Gaganyaan mission with a ground station at CKI and the planned upgrade of the CKI runway for use as a forward operating base.
- Both countries are also focused on enhancing maritime domain awareness and anti-submarine warfare, and they will participate in the upcoming Malabar multilateral naval exercise with Japan and the U.S. in Australia.
- The military-to-military engagements aim to bolster monitoring and response capabilities in the region, particularly in response to increased Chinese naval presence in the Indian Ocean.
Read more: Cocos Island
Seven Unique Indian Crafts Receive Geographical Indication Tags
The Geographical Indications Registry in Chennai has awarded Geographical Indication (GI) tags to seven products from different regions of India, showcasing the country's diverse craftsmanship. New GI Tags for Indian Crafts:
- 'Jalesar Dhatu Shilp' - a metal craft from Jalesar, Uttar Pradesh, known for decorative metal crafts and brassware.
- Goa's 'Mankurad Mango', also called 'Malcorada', represents a unique variety of mangoes.
- 'Goan Bebinca' - the traditional Indo-Portuguese pudding, known as the 'queen of Goan desserts'.
- Rajasthan's four GI tags:
- Udaipur Koftgari Metal Craft
- Bikaner Kashidakari Craft
- Jodhpur Bandhej Craft
- Bikaner Usta Kala Craft
Read more: Geographical Indication Tag
WHO Endorses Polypills for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention
The World Health Organization has included three fixed-dose combinations of cardiovascular medicines or polypills in its revised Model Lists of Essential Medicines (EML) 2023 for primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.
- Polypills are fixed-dose combination medications that contain multiple active ingredients in a single pill.
- Studies conducted by various researchers demonstrated that polypills reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes by about 40% to 50%.
- Polycap, a four-drug combination manufactured by Cadila in India, was included in the EML.
Read more: National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM)
Tasteless Boiled Water
- Naturally occurring water contains various dissolved substances, including gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, sulphates, carbonates of calcium and magnesium, and elements like iron, influenced by the soil's composition.
- These constituents contribute to both the taste and hardness of water, with hardness indicating a higher mineral content.
- Boiling water releases dissolved gases and reduces hardness. The process also forms carbonates and hydroxides, which are insoluble, and they are deposited on the surfaces and the bottom of the vessel holding the water as a scaly coating.
- The separation of these substances from the water deprives it of its familiar taste.
The Iberian Wolf
A recently released report for the year 2020 by the Program of Actions for the Conservation of the Iberian Wolf in Andalusia, conducted under the Government of Andalusia, stated that there was no indication of Iberian wolf presence in Andalusia (an autonomous territory of Spain).
- The Iberian wolf (Canis lupus signatus), the species of gray wolf native to the Iberian Peninsula comprising Spain and Portugal, has been extinct in the historic region of Andalusia, Spain since 2020.
- Grey Wolf Canis lupus is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
- Comprehensive report reveals the absence of wolf presence through "control" tours and camera trap data.