Governance
National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM)
- 14 Sep 2022
- 6 min read
For Prelims: National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM), World Health Organisation (WHO), World Health Assembly (WHA), National Pharmaceuticals Pricing Authority (NPPA).
For Mains: Significance of National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM).
Why in News?
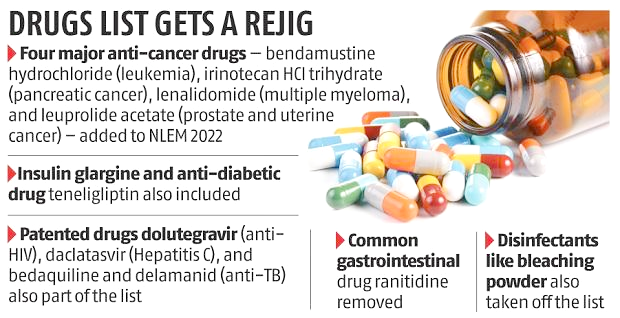
Recently, The Union Health Ministry launched the new National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM), where 384 drugs have been included in this list with addition of 34 drugs, while 26 from the previous list have been dropped.
- As per the World Health Organisation (WHO), Essential Medicines are those that satisfy the priority health care needs of the population.
What is the National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM)?
- About:
- The National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) is a list released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The medicines listed in the NLEM are sold below a price ceiling fixed by the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA).
- In India, it was framed on the lines of the Essential Medicines List (EML) released by the WHO.
- The National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) is a list released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- History:
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare prepared and released the first National List of Essential Medicines of India in 1996 consisting of 279 medicines. This list was subsequently revised in 2003, 2011, 2015 and 2022.
- Purpose:
- Guide safe and effective treatment of priority disease conditions of a population.
- Promote the rational use of medicines.
- Optimize the available health resources of a country. It can also be a guiding document for:
- State governments to prepare their list of essential medicines
- Procurement and supply of medicines in the public sector.
What are the Criteria for a Medicine to be Included in NLEM?
- Several factors are looked at before including a drug in the NLEM. These are:
- Essentiality: A medicine may be essential considering the population at large and should fit into the definition mentioned earlier.
- Changing disease burden: With time, the disease burden keeps changing in the country. At one point, TB might be more important to tackle. At the next moment, another disease like Covid-19 may become more important. So, the prevalent disease is considered while preparing the list.
- Efficacy and Safety: The medicine must have "unequivocal" evidence of efficacy and wider acceptance based on its safety to be included in the list.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The total price of the treatment must be considered while including the drug in NLEM. Only unit price may not be the best benchmark for this.
- Fixed Dose Combinations (FDCs): The single-dose medicines are considered for inclusion in NLEM. FDCs are only included if they have a proven advantage concerning the therapeutic effect.
- Turnover: High sales turnover alone is not considered a good benchmark for inclusion in the NLEM. Other factors are also required to be essentially considered for it.
When is a Medicine Deleted from NLEM?
- A drug is deleted from the list if it gets banned in India. Also, it is removed if reports of concerns about drug safety emerge.
- If medicine with better efficacy or favourable safety profile and better cost-effectiveness is now available, then it is removed from NLEM.
What is an Essential Medicine List (EML)?
- About:
- The list is made with consideration of disease prevalence, efficacy, safety and comparative cost-effectiveness of the medicines.
- Such medicines should be available in such a way that an individual or community can afford them.
- The WHO EML is updated every two years by the Expert Committee on Selection and Use of Essential Medicines.
- History:
- The first country in the world to compose its EML was Tanzania in 1970. Then in 1975, the World Health Assembly (WHA) requested WHO to assist member states in selecting and procuring essential medicines, assuring good quality at a reasonable cost.
- Subsequently, the first WHO model list of essential medicines was published in the year 1977 which contained 186 medicines.
- It stated that essential medicines were “of utmost importance, basic, indispensable and necessary for the health and needs of the population” and the criteria for selection were based on efficacy, safety, quality and total cost.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What do you understand by Fixed Dose Drug Combinations (FDCs)? Discuss their merits and demerits. (2013)