Science & Technology
Space Debris
- 03 Feb 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Space debris, Kessler Syndrome, Project NETRA, European Space Agency (ESA), Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC), Peaceful Uses of Outer Space.
For Mains: Potential Hazard related to Space Debris, Initiatives to Curb Space Debris.
Why in News?
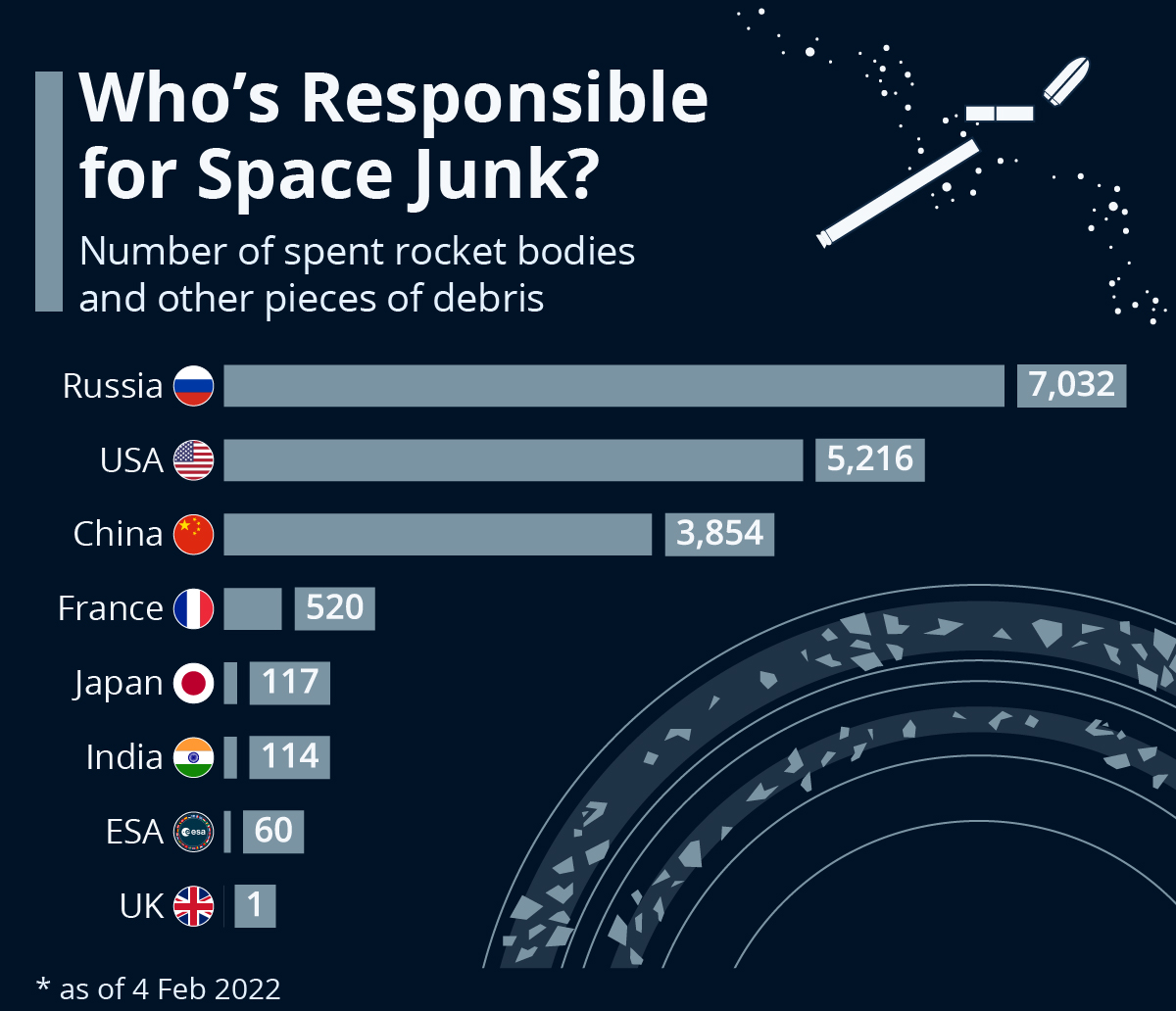
Recently, the Government of India has announced that 111 payloads and 105 space debris have been identified as Indian objects orbiting Earth.
- All orbiting debris will affect the future of outer space and future missions. Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has also been carrying out several studies on the impact of growing space debris on the space environment.
What is Space Debris?
- About:
- Space debris refers to man-made objects in Earth's orbit that no longer serve a useful purpose.
- This includes defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments of debris from collisions or other events.
- Space debris refers to man-made objects in Earth's orbit that no longer serve a useful purpose.
- Potential Hazard:
- Threat for Operational Satellites:
- The floating space debris is a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- This overpopulation of space with objects and debris is referred to as Kessler Syndrome.
- The floating space debris is a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- Reduction of Orbital Slots:
- The accumulation of space debris in specific orbital regions can limit the availability of desirable orbital slots for future missions.
- Space Situational Awareness:
- The increasing amount of space debris makes it more challenging for satellite operators and space agencies to accurately track and predict the orbits of objects in space.
- Threat for Operational Satellites:
- Initiatives to Curb Space Debris:
- India:
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris.
- ISRO also carried out 21 collision avoidance manoeuvres of Indian operational space assets in 2022 to avoid collisions with other space objects.
- ISRO has also set up a Centre for Space Debris Research to monitor and mitigate the threat of space debris.
- ‘Project NETRA’ is also an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris.
- Global:
- The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC), an international governmental forum, was established in 1993 to coordinate efforts between spacefaring nations to address the issue of space debris.
- The United Nations has established the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) to develop guidelines for the long-term sustainability of outer space activities, including the mitigation of space debris.
- The European Space Agency (ESA) has launched the Clean Space initiative, aimed at reducing the amount of space debris and promoting sustainable space activities.
- India:
Way Forward
- Improved Tracking and Monitoring: Improving the ability to track and monitor space debris can help mitigate the risks it poses to operational satellites and human space missions.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles: Using reusable launch vehicles instead of single-use rockets can help reduce the number of new debris generated from launches.
- Materials and Design improvements: Using more durable materials and designing satellites for eventual de-orbiting can reduce the number of debris generated in the long term.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q.2 Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)