Internal Security
India's Border and It’s Management
- 21 Jun 2024
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Indian Borders, Tropical Evergreen Forests, Territorial Water, Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), Minerals, Line of Control (LoC), Line of Actual Control (LAC), Thar Desert, Golden Triangle, Army, Navy, Air Force, Border Security Force (BSF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), Assam Rifles (AR), Indian Coast Guard, Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB), Ordinance Supply Chain, Long-range reconnaissance and observation systems (LORROSs), Wireless Message Transfer Unit (WMTU), Group of Ministers (GoM), Department of Border Management, Integrated Check Posts (ICPs), Night Vision Devices, Radars, Border Area Development Program (BADP), Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP), Radiological Material, Public Private Partnership (PPP), Community Police Forces.
For Mains: Role of armed forces in securing Indian frontiers and safeguarding the nation.
What is Border Management?
- Border management is a security function that aims to secure our frontiers and safeguard our nation from the risks involved in the movement of goods and people from India to other countries and vice versa.
- It includes regulation of legal and illegal immigration, ensuring safe and secure movement of authorized people and goods, and prevention of smuggling, human trafficking and infiltration.
- The principle of “One Border, One Border Guarding Force” is followed by the Government of India to secure the border. In line with this philosophy
- The Bangladesh and Pakistan border is looked after by Border Security Force (BSF)
- The China border is looked after by Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP)
- The Nepal and Bhutan border is looked after by Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB)
- The Myanmar border is looked after by Assam Rifles (AR).
- The Line of Control (LoC) on the Indo-Pakistan border and the Line of Actual Control (LAC) on the Indo-China border are protected by the Indian Army.
- Security of the coastal borders lies with the Indian Navy and Indian Coast Guard, with the State (Marine) Police acting as the second line of defense
How Many Countries are Sharing Border with India?
- India shares borders with seven different countries namely Bangladesh, China, Pakistan, Nepal, Myanmar, Bhutan and Afghanistan.
- The border passes through all varied terrains namely deserts, fertile lands, swampy marshes, snow-covered peaks and tropical evergreen forests.
- This kind of vast terrain makes us vulnerable to insurgency, illegal migration and smuggling.
How does India's Maritime Boundries Differentiated?
- Territorial Water:
- It extends upto 12 nautical miles.
- This zone is our sovereign territory and other countries have to take permission from India to enter this area.
- Contiguous Zone:
- It extends up to 24 nautical miles and is a zone of hot pursuit i.e., in this zone, a state can chase and apprehend vessels violating its laws or regulations
- Any infringement of customs, sanitary, immigration and fiscal regulations in the contiguous zone can also attract punishment from coastal states.
- Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ):
- It extends from the outer limit of the territorial sea up to 200 nautical miles.
- This is the zone where coastal states hold the right to natural and economic resources such as minerals, oil exploration and fishing.
- Ships of other countries can pass through this zone as long as they do not pose any threat to the coastal states.
What is the Role of the Department of Border Management?
- The Department of Border Management was formed under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) in January 2004, following recommendations from the Group of Ministers (GoM) on border security.
- This department has been entrusted with the responsibility of all matters associated with land borders and coastal borders, with the exception of LoC in the Jammu and Kashmir sector.
- The roles and responsibilities of the Department of Border Management include fencing and floodlighting, surveillance and patrolling, security infrastructure development, intelligence report analysis, and development of Integrated check posts (ICPs).
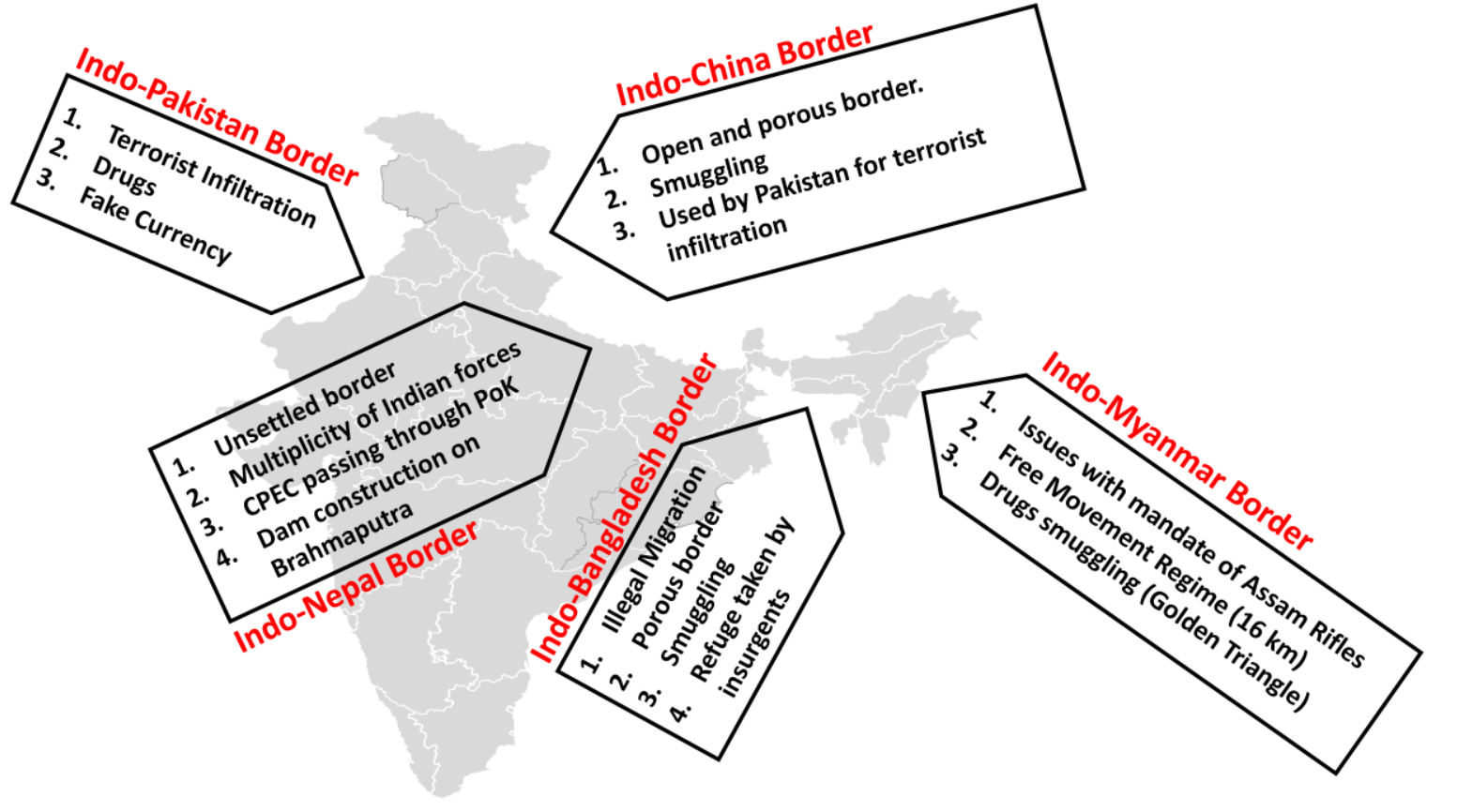
What are the Challenges in Managing Indian Borders?
- Indo-Pak Border Challenges:
- Varied Climatic Conditions: India-Pakistan border runs from the hot Thar desert in Rajasthan to the cold Himalayas in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Infiltration: Political instability and crisis in Pakistan also lead to an upsurge in cross-border infiltration and threats due to terrorism.
- Cross-Border Terrorism: It stands out as one of the major reasons for disaccord between India and Pakistan.
- Indo-China Border Challenges:
- It remains disputed along its entire length and is one of the key points of friction between the two countries over the past years.
- Chinese intrusions and face-off have become more frequent and threaten to lead to all-out conflict between the two Asian giants.
- Indo-Bangladesh Border Challenges:
- Illegal immigration: Due to the porosity of the border, the primary challenge has been the influx of illegal immigrants in India.
- Smuggling: A Major challenge with this part of the Indian border is the smuggling of arms, ammunition and drugs.
- Indo-Nepal Border Challenges:
- Smuggling: Open borders lead to illegal activities such as smuggling of drugs, stolen vehicles and arms and ammunition into India.
- Terrorism: Lately, anti-social elements and terrorist organizations are also using this open border for a least resistance passage into India.
- Indo-Myanmar Border Challenges:
- Drug Trafficking: Insurgents are extensively involved in drug trafficking, especially in areas such as Moreh in Manipur and Golden Triangle covering Northern Thailand, Laos and Myanmar.
- Insurgency: The open border and cross-ethnic ties among the tribal community help insurgents escape from the hands of the border security forces.
- Indo-Bhutan Border Challenges:
- Smuggling: It is one of the major concerns along this border.
Way Forward
- Smart Identity Management: The use of biometrics (photographs, fingerprints, face, iris, etc.) for identification is one of the smart ways of identity management.
- Smart Inspection System: Non-invasive inspection techniques such as explosive vapor detectors, full-body scanners, metal detectors and handheld substance detectors can be used for the detection of concealed weapons, drugs, illicit radiological material, etc.
- Security and Surveillance System: Intrusion detection systems, watchtowers, surveillance cameras and laser curtains need to be deployed at border areas along the border fence.
- Cross-Border Cooperation (CBC): It includes information sharing and collaborative approach between neighboring countries for border security for issues such as human trafficking, arms or drugs smuggling, terrorist threats, etc.
- Development of Border Areas: The government initiated the Border Area Development Program (BADP) in 1987 to facilitate the provision of the required socio-economic infrastructure and adequate security. Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP) was launched for comprehensive development of the select villages in 19 districts of abutting the northern border in the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand and UT of Ladakh.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q.The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) by our adversaries across the borders. to ferry arms / ammunition, drugs, etc., is a serious threat to the internal security. Comment on the measures being taken to tackle this threat. (2023)
Q.What are the maritime security challenges in India? Discuss the organizational, technical and procedural initiatives taken to improve the maritime security. (2022)
Q.For effective border area management, discuss the steps required to be taken to deny local support to militants and also suggest ways to manage favourable perception among locals. (2020)
Q.Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. (2016)
Q.How illegal transborder migration does pose a threat to India’s security? Discuss the strategies to curb this, bring out the factors which give impetus to such migration. (2014)
Q.How far are India’s internal security challenges linked with border management, particularly in view of the long porous borders with most countries of South Asia and Myanmar? (2013)