Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Focuses on Gems & Jewellery Growth
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government, is taking substantial steps to enhance the gems and jewellery sector, focusing on economic value addition and export growth.
Key Points
- Uttar Pradesh, with its rich cultural heritage and skilled craftsmanship, is a significant player in India’s gems and jewellery sector.
- The state’s annual trade in this industry is estimated at over Rs 1 trillion, involving more than one million traders, retailers, craftsmen, and designers.
- Major Hubs:
- The hubs for gems and jewellery trade in Uttar Pradesh include Meerut, Lucknow, NOIDA Export Processing Zone, Moradabad, Kanpur, and Agra.
- These centers are pivotal in both manufacturing and exports, contributing significantly to the state’s economy.
- The organized segment of the trade accounts for about 35% of the overall market, highlighting the importance of structured growth and development.
- Government Initiatives & Significance:
- The CM of Uttar Pradesh has drafted a comprehensive blueprint to develop Meerut as a major jewellery manufacturing and trading hub for North India.
- Meerut’s jewellery industry, with an annual turnover of over Rs 2,000 crore, employs approximately 40,000 goldsmiths, gemstone makers, and jewellery traders.
- The proposed hub, spanning 32,000 square meters, aims to position Meerut as a key center for gems, precious stones, and gold jewellery.
- To support this vision, the government plans to construct a modern multi-storey flatted factory complex to foster business growth and encourage startups in the sector.
- National and Global Significance:
- The gems and jewellery sector in Uttar Pradesh is not only vital for the state but also contributes 10-12% of India’s total merchandise exports.
- In 2023, the domestic market for gems and jewellery was valued at USD 92 billion, underscoring its importance in the national economy.
- Uttar Pradesh’s thriving wholesale jewellery market serves clients from other states, further solidifying its role as a key player in the industry.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Government Boosts Police & Forensic Capacity
Why in News?
On Constitution Day (26th November), Chief Minister of UP highlighted the state’s commitment to transparent police recruitment and establishing forensic labs at the zonal level during the National Conference on Forensic Science and Cybersecurity.
- These initiatives are part of broader efforts to enhance law and order, ensuring timely justice for victims and maintaining good governance.
Key Points
- Highlights of the Conference:
- New Criminal Laws:
- India has recently implemented three new criminal laws: Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023, Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023, and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam, 2023.
- These laws, effective from 1st July 2024, aim to protect citizens by ensuring that no one is declared guilty without proper evidence.
- Challenges and Reforms in Law and Order:
- Before 2017, Uttar Pradesh faced significant challenges in maintaining law and order, with a high prevalence of hooliganism (vandalism/violence).
- The Uttar Pradesh Government has observed that over half of the positions within the Uttar Pradesh Police were unfilled during previous government. Addressing this situation has become a key focus for the current government.
- Transparent Recruitment and Forensic Labs:
- The state government has recruited over 154,000 police personnel transparently and recently initiated the recruitment of an additional 7,200 policemen.
- Earlier, forensic labs were limited to four locations. Now, high-quality forensic labs have been established at the zonal level, with plans to expand them to the range level.
- These labs are crucial for gathering evidence in criminal cases and ensuring justice.
- Cybersecurity and Forensic Science Initiatives:
- Today, 1,775 police stations in Uttar Pradesh are equipped with cyber helplines, enhancing the state’s ability to tackle cybercrime.
- Additionally, the Uttar Pradesh State Institute of Forensic Sciences has been established to further support forensic investigations and improve the quality of evidence presented in court.
- New Criminal Laws:
Constitution Day
- The Constitution Day, also known as National Law Day or Samvidhan Diwas, is celebrated in India on 26th November every year to commemorate the adoption of the Constitution of India.
- On 29th August, 1947, the Constituent Assembly set up a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar to prepare a Draft Constitution for India.
- On 26th November 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India adopted the Constitution of India, which came into effect on 26th January 1950.
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment on 19th November, 2015, notified the decision of the Government of India to celebrate 26 November as 'Constitution Day'.
- The day is observed to spread the importance of the constitution and the thoughts and ideas of B. R. Ambedkar, the chief architect of the constitution.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
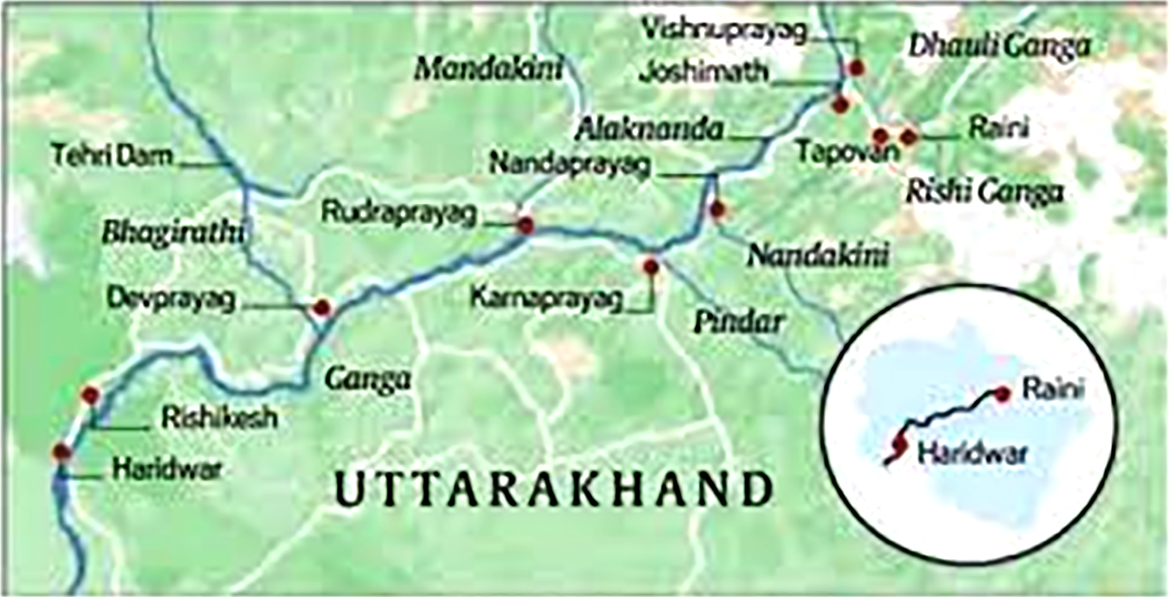
Environmental Crisis Over the Rivers in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
Uttarakhand, known for its pristine rivers and streams, is facing an unprecedented environmental crisis.
- Changing weather patterns, climate change, and increasing human activities are pushing the state’s 206 perennial rivers and streams toward the brink of drying up.
Key Points
- Current Situation:
- According to a report by the Spring and Rejuvenation Authority (SARA), a staggering 5,428 water sources in Uttarakhand are currently under threat.
- Climate change experts at SARA, highlighted that human intervention, rather than natural causes, is primarily responsible for the degradation of these water bodies.
- Establishment of SARA:
- In response to this crisis, the Uttarakhand government established SARA to investigate the state of its perennial rivers and streams.
- This initiative aims to understand the impacts of climate change on these vital water sources.
- SARA recommended all relevant state departments to collaborate and provide data on the condition of these water bodies. The findings have raised serious concerns within the government, prompting the need for urgent interventions.
- In response to this crisis, the Uttarakhand government established SARA to investigate the state of its perennial rivers and streams.
- Pilot Projects for River Rejuvenation:
- SARA has prepared a pilot project to revive five key rivers:
- The Song River in Dehradun, the Western Nayar and Eastern Nayar in Pauri, the Shipra River in Nainital, and the Gaudi River in Champawat.
- The National Institute of Hydrology (NIH) and IIT Roorkee have been assigned to study these rivers, with plans to extend the project to other rivers based on the findings.
- SARA has prepared a pilot project to revive five key rivers:
- Impact of Climate Change:
- The rise in temperature due to climate change has been more pronounced in Tibet and the Himalayas than in the rest of the world over the past 150 years.
- This alarming trend is leading to significant environmental consequences, including the drying up of water sources.
- Data from the Water Resources Department reveals that 288 water sources in the state have less than 50% of their original water levels remaining, with nearly 50 sources having less than 75% of their water left.
- Related Observations & Impact:
- Environmentalists and local officials have observed drastic changes in water levels and river courses.
- In Bhimtal, the lake has started to resemble a plain, and similar crises are emerging across other rivers and water sources.
- Climate scientists warn that climate change is causing mountains to crumble and rivers to either change their courses or wreak havoc during floods.
- In Haldwani, the water levels of the Gaula and Kosi rivers have dropped, creating a crisis for drinking water and irrigation.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand's Grassland Conservation SOP
Why in News?
The forest department of Uttarakhand government will prepare a standard operating procedure (SOP) to conserve grasslands in the Upper Himalayan Region of the state.
- This initiative aims to address the increasing frequency of landslides and land subsidence caused by both natural and human activities.
Key Points
- Grassland Conservation Initiatives:
- Dayara Bugyal, a sensitive ecological area, has shown positive results from previous ecological restoration efforts. To extend these benefits to other grasslands, the forest department plans to develop a SOP for conservation.
- This SOP will focus on reducing biological pressure and preventing further degradation.
- So far, conservation work has been carried out on approximately 83 hectares of land across 22 grasslands under the Bugyal Conservation Scheme.
- Dayara Bugyal, a sensitive ecological area, has shown positive results from previous ecological restoration efforts. To extend these benefits to other grasslands, the forest department plans to develop a SOP for conservation.
- Snow Leopard Conservation Center:
- During their visit, the officials also inspected a snow leopard conservation center under construction at Lanka near Gangotri.
- The center is expected to be ready within a year, offering tourists an opportunity to experience the natural environment and observe snow leopards in their habitat.
- Gangotri National Park has emerged as a significant trans-Himalayan national park over the past decade.
- The Wildlife Institute of India has recorded a substantial presence of snow leopards in the park, which was relatively unknown until recently.
- During their visit, the officials also inspected a snow leopard conservation center under construction at Lanka near Gangotri.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana Farmers Face Fertilizer Shortfall
Why in News?
Haryana, a state pivotal to India's agricultural economy, is facing an escalating crisis of fertilizer shortage and penalty for stubble burning.
- It highlights the challenges of governance, rural distress, and the delicate balance between policy implementation and farmers' welfare.
Key Points
- Fertilizer Shortages:
- Despite government denials at both the state and central levels, Haryana has witnessed acute shortages of diammonium phosphate (DAP), a crucial fertilizer for the Rabi season.
- Shortfall in Supply:
- A 38% gap between assessed requirements and availability in October 2024, exacerbated by reduced imports despite stable global DAP prices.
- Dependence on Imports:
- India’s heavy reliance on imported fertilizers and raw materials like phosphoric acid has made the sector vulnerable to global price volatility and monopolies.
- Policy Gaps:
- The introduction of Point of Sale machines to regulate fertilizer distribution has inadvertently restricted access, forcing many farmers to resort to black markets.
- Stubble Burning:
- Stubble burning, a seasonal practice by farmers to clear fields for Rabi sowing, has drawn severe criticism for its contribution to air pollution, particularly in the National Capital Region (NCR).
- The Haryana government, following central directives, has imposed hefty fines and introduced "red entries" in farm records to penalize offenders.
- Stubble burning, a seasonal practice by farmers to clear fields for Rabi sowing, has drawn severe criticism for its contribution to air pollution, particularly in the National Capital Region (NCR).
- Related Challenges:
- Farmer Resistance: Farmers argue that stubble burning is a necessity in the absence of viable alternatives.
- Penalties, FIRs, and blacklisting of crops for procurement have fueled resentment.
- Disproportionate Blame: While stubble burning is a contributor to air pollution, farmers feel unfairly targeted compared to other sources like construction and industrial emissions.
- Policy Contradictions: Despite previous assurances of no criminal liability, the government has intensified punitive measures, creating distrust among the farming community.
- Broader Agrarian Distress: The twin crises of fertilizer shortages and stubble burning penalties reflect deeper systemic issues in Haryana’s agricultural governance.
- Farmers also face challenges such as black-marketing of fertilizers, irregularities in mandi procurement processes, and inadequate support for tenant farmers.
- Farmer Resistance: Farmers argue that stubble burning is a necessity in the absence of viable alternatives.
- Way Forward
- The issue calls for comprehensive strategies such as promoting stubble management technologies and incentivizing alternatives rather than punitive measures alone.
- There is a need for better coordination between environmental objectives and agricultural realities.
- Ensuring timely availability of essential inputs like fertilizers through robust procurement, storage, and distribution mechanisms.
- Developing farmer-friendly alternatives to stubble burning and providing adequate subsidies for technological interventions.
- Reducing dependency on imports through investments in domestic production of fertilizers and raw materials.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan