West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Surface Ozone Pollution
Why in News?
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur study reveals that surface ozone pollution is severely affecting India's major food crops, especially in the Indo-Gangetic Plain and central India.
Key Points
- About Surface Ozone Pollution:
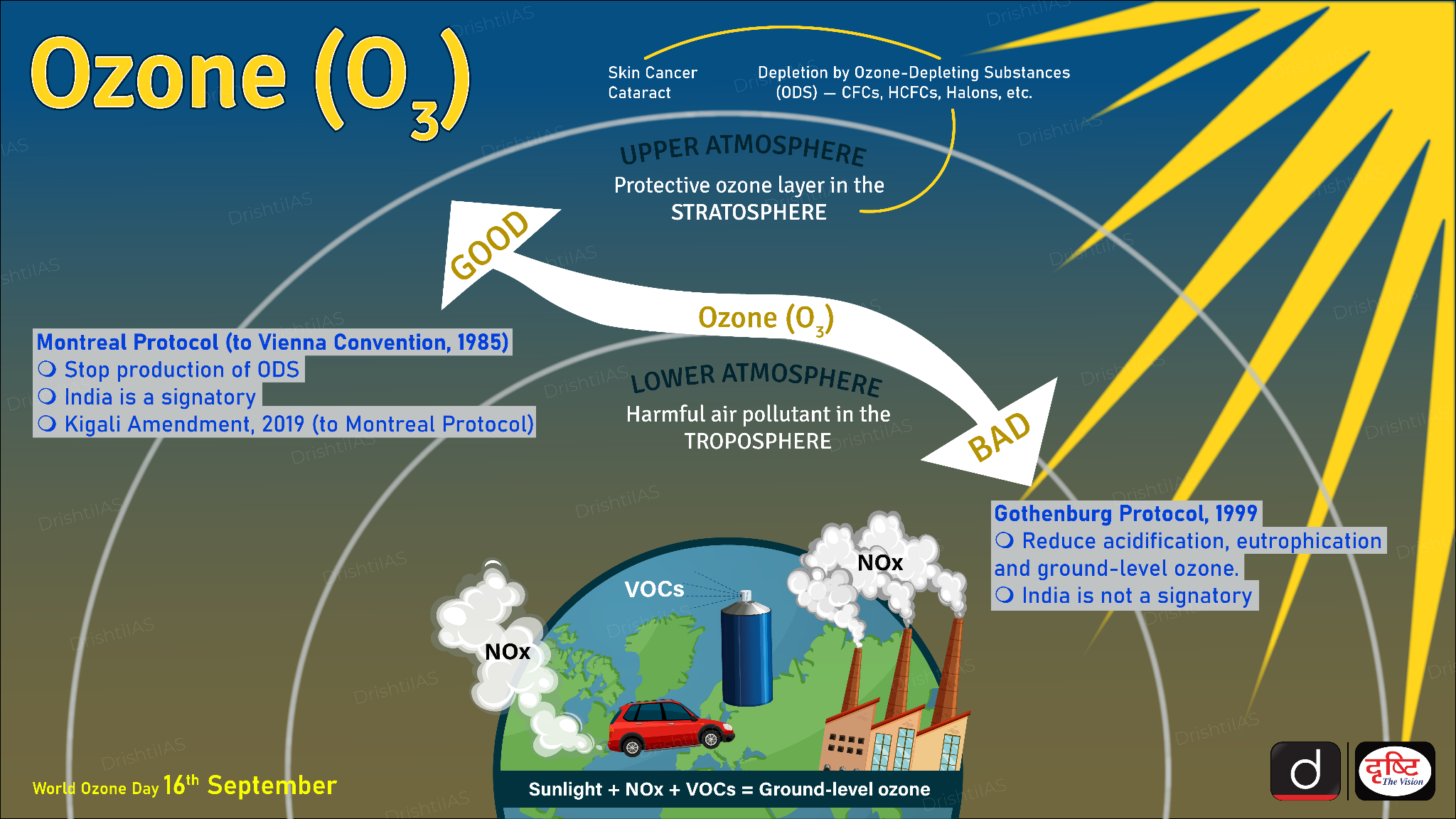
- Surface ozone (O₃) pollution refers to the excess presence of ozone at the Earth’s surface, which is formed through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
- Unlike the ozone layer in the stratosphere, which protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation, Surface ozone is a harmful pollutant that poses significant health risks and environmental damage.
- Surface ozone (O₃) pollution refers to the excess presence of ozone at the Earth’s surface, which is formed through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
- About the study:
- Surface ozone pollution is damaging major food crops such as wheat, rice, and maize.
- The study argues that rising ozone pollution jeopardizes India's progress toward Sustainable Development Goal 1 (No Poverty) and Goal 2 (Zero Hunger) by 2030.
- Declining crop yields could directly affect livelihoods and food access, especially for vulnerable populations.
- Key Findings of the Study:
- The research at the Centre for Oceans, River, Atmosphere and Land Sciences (CORAL), highlights the “lesser-known but potent” threat posed by surface ozone.
- Ozone acts as a strong oxidant that damages plant tissues, causes foliar injuries, and leads to significant drops in crop productivity.
- Using data from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase-6 (CMIP6), the study assessed both historical and future trends of ozone-induced damage.
- Without adequate mitigation, wheat yields may decline by up to 20%, while rice and maize could see losses of around 7%.
- In the worst-case scenarios, ozone exposure in key agricultural zones could exceed safe limits by six times.
- The research warns that ozone-related yield losses could undermine India’s ability to ensure food security at home and impact food grain exports to Asian and African nations.
- The research at the Centre for Oceans, River, Atmosphere and Land Sciences (CORAL), highlights the “lesser-known but potent” threat posed by surface ozone.
- Gaps in Current Air Quality Initiatives:
- The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) largely focuses on urban air pollution, leaving agricultural regions underserved.
- The study highlights the need for targeted interventions to monitor and curb surface ozone pollution in farmlands.
- Call for Policy Action:
- The researchers advocate for urgent policy measures to reduce ozone emissions and protect crop health.
- Effective pollution control strategies in agricultural areas could boost food production and help meet both national and global food security goals.
Formation of Surface Level Ozone
- Surface-level ozone is a secondary pollutant, meaning it is not directly emitted but formed through chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- NOx (emitted by vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes) and VOCs (emitted from vehicles, petrol pumps, solvents, and waste burning).
- These reactions occur in the presence of sunlight, making ozone formation more significant during sunny days and warmer seasons.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- About:
- The NCAP aims to systematically address air pollution by involving all stakeholders and ensuring necessary action.
- Under NCAP, 131 cities have been identified for implementation of city specific action plans.
- Objective:
- This is the first attempt in the country to develop a national framework for air quality management with the goal of time-bound reduction .
- It aims to reduce the concentration of coarse (PM10) and fine particles (PM2.5) by at least 20% over the next five years (base year for comparison – 2017).






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan