Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
PM Virtually Lays Foundation of Health Projects in Jharkhand
Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually laid the foundation of various health projects worth around Rs 177 crore in Jharkhand.
Key Points
- Under PM-ABHIM (Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission), the projects include two Nursing Colleges, four Critical Care Blocks (CCBs) and three Block Public Health Units (BPHU).
- The nursing colleges will be constructed at Koderma Medical College and Phulo Jhano Medical College at Dumka.
- The four CCBs will be set up in four different districts, including one at Rajendra Institute of Medical College (RIMS), Ranchi.
- The three BPHU will be set up in Deoghar district.
PM-ABHIM (Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission)
- Launched in 2021, it is one of the largest pan-India schemes for strengthening healthcare infrastructure across the country.
- Its objective includes:
- To ensure a robust public health infrastructure in both urban and rural areas, capable of responding to public health emergencies or disease outbreaks.
- To establish an IT-enabled disease surveillance system through a network of surveillance laboratories at block, district, regional and national levels.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
India-Japan: Dharma Guardian
Why in News?
Recently, the fifth edition of joint military exercise ‘Dharma Guardian’ between Indian and Japanese land forces commenced at the Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan.
Key Points
- The two-week drill is an annual exercise conducted alternatively in India and Japan.
- The Japanese contingent is being represented by troops from the 34th Infantry Regiment and the Indian Army is being represented by a battalion from the Rajputana Rifles.
- The aim of the exercise is to foster military cooperation and enhance combined capabilities to execute joint operations in semi-urban environments under the United Nations Charter.
- The event would focus on a high degree of physical fitness, joint planning, joint tactical drills and basics of special arms skills.
The Rajputana Rifles
- It is the oldest rifle regiment of the Indian Army.
- It was originally a part of the British Indian Army, when six previously existing regiments were amalgamated to form six battalions of the 6th Rajputana Rifles.
- In 1945, the numeral designation was dropped from the title and in 1947 the regiment was transferred to the newly independent Indian Army.
- Since independence, the regiment has been involved in a number of conflicts against Pakistan, as well as contributing to the Custodian Force (India) in Korea under the aegis of the United Nations in 1953–54 and to the UN Mission to the Congo in 1962.
Charter of the United Nations
- The Charter of the UN is the founding document of the UN. It was signed on 26th June 1945, in San Francisco and came into force on 24th October 1945.
- The UN can take action on a wide variety of issues due to its unique international character and the powers vested in its Charter, which is considered an international treaty.
- As such, the UN Charter is an instrument of international law, and UN Member States are bound by it.
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ), the primary judicial body of the United Nations (UN), operates by its Statute, annexed to the UN Charter as an integral part.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand Public and Private Property Damage Recovery Bill
Why in News?
Uttarakhand is set to bring a Bill on the lines of recovery of damages to property bills brought by Uttar Pradesh and Haryana.
Key Points
- Under this legislation, losses to public and government properties incurred during protests and strikes will be recovered from the accused involved in the disturbance.
- A tribunal, headed by a retired judge, would investigate the charges against the identified accused, after the State’s complaint.
- The assessment and orders for damage recovery would be issued by the tribunal after detailed discussions with the affected parties, both government and otherwise.
- The decision to have a Bill to recover damages to public property came after the violence in Haldwani in Uttarakhand.
- Violence ensued after the district administration and civic body demolished a mosque and madrasa built on nazool (government) land in an anti-encroachment drive.
Encroachment
- It is the unauthorised use or occupation of someone else’s property.
- This can occur on abandoned or unused spaces if the legal owner is not actively involved in its upkeep.
- It is important for property owners to be aware of the legal steps to take and their rights in such cases.
- This could include illegal construction, squatting, or any other form of occupation without proper permission or legal rights.
- Land encroachment, as defined by Section 441 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), 1860, is the act of unlawfully entering someone else’s property without permission to commit an offence, threaten possession of the property, or stay on the land uninvited.
Nazool land
- It is owned by the government but most often not directly administered as state property.
- The state generally allots such land to any entity on lease for a fixed period, generally between 15 and 99 years.
- In case the lease term is expiring, one can approach the authority to renew the lease by submitting a written application to the Revenue Department of the local development authority.
- The government is free to either renew the lease or cancel it — taking back Nazool land.
- The government generally uses Nazool land for public purposes like building schools, hospitals, Gram Panchayat buildings, etc.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
The Savera Programme
Why in News?
Recently, Haryana Chief Minister inaugurated the Savera programme, aimed at early detection and prevention of Breast Cancer. It was initiated by the Medanta Foundation in collaboration with the Health Department in Gurgaon.
Key Points
- Under the scheme, visually impaired people will conduct screening for breast cancer as they have natural tactile sensitivity.
- The importance of this ability has been understood, tested, and used by people associated with the medical world. Visually impaired people can detect breast cancer up to half a centimeter, whereas a normal doctor can detect it up to one centimeter, after examination.
- In its initial phase, the programme will be launched at Civil Hospital in Sector 10, the polyclinic in Sector 31, and PHC in Wazirabad.
- According to the CM, about 90,000 women across the country lose their lives due to breast cancer, on a daily basis.
- He also mentioned the establishment of the National Cancer Institute at AIIMS in Jhajjar district, which has been equipped with 1,000 beds.
Cancer
- About:
- It is a complex and broad term used to describe a group of diseases characterised by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
- These abnormal cells, known as cancer cells, have the ability to invade and destroy healthy tissues and organs.
- In a healthy body, cells grow, divide, and die in a regulated manner, allowing for the normal functioning of tissues and organs.
- However, in the case of cancer, certain genetic mutations or abnormalities disrupt this normal cell cycle, causing cells to divide and grow uncontrollably.
- Breast Cancer
- It is a disease in which abnormal breast cells grow out of control and form tumours. If left unchecked, the tumours can spread throughout the body and become fatal.
- Breast cancer cells begin inside the milk ducts and/or the milk-producing lobules of the breast.
- The earliest form (in situ) is not life-threatening. Cancer cells can spread into nearby breast tissue (invasion). This creates tumours that cause lumps or thickening.
- Invasive cancers can spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs (metastasize). Metastasis can be fatal.
- Treatment is based on the person, the type of cancer and its spread. Treatment combines surgery, radiation therapy and medications.
- It is a disease in which abnormal breast cells grow out of control and form tumours. If left unchecked, the tumours can spread throughout the body and become fatal.
- Cervical Cancer:
- Cervical cancer develops in a woman's cervix (the entrance to the uterus from the vagina).
- Almost all cervical cancer cases (99%) are linked to infection with high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV), an extremely common virus transmitted through sexual contact.
- Two HPV types (16 and 18) are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers.
- Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women globally. About 90% of the new cases and deaths worldwide in 2020 occurred in low- and middle-income countries.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Khelo India Youth Games 2024 Medal Tally
Why in News?
Recently, Haryana emerged among the top three states in Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG) 2024, the sixth edition of the flagship event under the Indian government’s Khelo India initiative.
Key Points
- Over 5,600 athletes from all over the country competed at the Khelo India Youth Games 2024, which ran from 19th to 31st January, 2024. Tamil Nadu hosted the KIYG 2024 in four cities - Chennai, Madurai, Trichy and Coimbatore.
- Maharashtra defended their Khelo India Youth Games title after topping the medals tally with 57 gold medals, 48 silver and 53 bronze. It was their fourth KIYG title.
- Host state Tamil Nadu finished second with 38 gold, 21 silver and 39 bronze for their best-ever finish.
- Haryana, who have won two KIYG titles, came third with 35 gold, 22 silver and 46 bronze medals.
- A total of 926 medals - 278 gold, 278 silver and 370 bronze - were on offer across 26 sports at KIYG 2024 Tamil Nadu.
- Squash made its KIYG debut this year while Silambam, a form of indigenous martial arts, featured as a demonstration sport.
Silambam
- It is an ancient weapon-based martial art that emerged in Tamilakam, which is now the Tamil Nadu region of India. It is one of the oldest martial arts in the world.
- The term Silambam contains a meaning which itself reveals about the sport, silam stands for a ‘mountain’ and bam stands for bamboo which is the main weapon used in this form of martial arts.
- It is closely linked to the Kerala martial art kalaripayattu.

Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana Budget 2024-25
Why in News?
Recently, Chief Minister of Haryana Manohar Lal Khattar unveiled the budget for the financial year 2024-25, setting aside Rs 1.89 lakh crore, an increase of over 11% from 2023-24.
Key Points
- Key highlights of the budget 2024-25:
- The budget of Rs. 1,89,876.61 crore is presented for the year 2024-25, with no new taxes proposed.
- This includes Rs. 1,34,456.36 crore as revenue expenditure and Rs. 55,420.25 crore as capital expenditure, accounting for 70.81% and 29.19% of the total budget respectively.
- During the period 2014-15 to 2023-24, Haryana's Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP), at constant prices (2011-12 prices ), has recorded a compound annual growth rate of 6.1% from Rs. 3,70,535 crore in 2014-15 to Rs. 6,34,027 crore in 2023-24.
- In 2023-24, the share of the tertiary sector in Gross State Value Added (GSVA) is estimated at 52.6% and 18.1% in the primary sector. The primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors have recorded growth of 8.6 percent, 6.3%, and 13.8% in 2023-24.
- The share of the secondary sector has been estimated at 29.3%.
- The turnover of State Public Enterprises (PSE) in 2022-23 was estimated at Rs. 79,907 crore, indicating an increase of 11.94%.
- The CM also announced that the interest and penalty will be waived on crop loans taken by farmers from Primary Agriculture Credit Societies (PACS).
Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP)
- It is a measure in monetary terms, the sum total volume of all finished goods and services produced during a given period of time, usually a year, within the geographical boundaries of the State, accounted without duplication.
- These estimates of the economy, over a period of time, reveal the extent and direction of the changes in the levels of economic development.
- It is classified under three broad sectors such as Primary sector, Secondary sector and Tertiary sector and is compiled economic activity wise as per the methodology prescribed by the National Accounts Division, National Statistical Office, Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation.
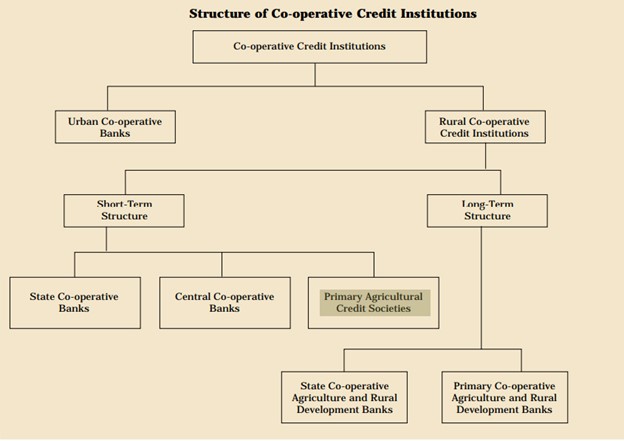
Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)
- PACS are village level cooperative credit societies that serve as the last link in a three-tier cooperative credit structure headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Credit from the SCBs is transferred to the District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs), which operate at the district level. The DCCBs work with PACS, which deal directly with farmers.
- PACSs provide short-term, and medium-term agricultural loans to the farmers for the various agricultural and farming activities.
- The first PACS was formed in 1904.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan