Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Snow Leopards Spotted in Gangotri National Park
Why in News?
Recently, a Snow Leopard was spotted in Gangotri National Park in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
Key Points
- In the latest snow leopard census of India, released earlier in 2024, there are 718 snow leopards in India. Out of which, 124 are in Uttarakhand.
- The hill state has the second highest snow leopard population in India, after Ladakh (477). The Gangotri National Park boasts a population of 38–40 snow leopards.
- Listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, it is estimated that the global population of snow leopards is less than 10,000.
- In Uttarakhand, snow leopards are found in Uttarkashi, Tehri, Rudraprayag, Chamoli, Pithoragarh, and Bageshwar districts.
Gangotri National Park
- It was established in 1989 and is situated in Uttarkashi, Uttrakhand in the upper catchment of Bhagirathi River.
- Gaumukh at Gangotri glacier, the origin of river Ganga, is located inside the park.
- The park area forms a viable continuity between Govind National Park and Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Flora: The park is enveloped by dense coniferous forests that are mostly temperate. Chirpine, deodar, fir, spruce, oak and rhododendron are the common vegetation.
- Fauna: Various rare and endangered species like bharal or blue sheep, black bear, brown bear, himalayan monal, himalayan snowcock, himalayan tahr, musk deer and snow leopard are found in the park.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Chinese Heron Sighted in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
Recently, The Chinese Pond Heron, a bird usually found in the northeastern states, Rajasthan and Bhutan, has been seen for the first time in Uttarakhand.
Key Points
- According to experts, there was no record of the presence of the Chinese Pond Heron in Uttarakhand.
- For the first time, the bird has chosen the Kotdwar area of Lansdowne forest division for breeding.
- Many migratory birds are visible in the dense forests of Saneh area of Kotdwar and Lansdowne forest division during the summer.
- The arrival of birds from northeastern states here is an indication that the environment here is favourable for them.
Chinese Pond Heron
- The Chinese pond heron (Ardeola bacchus) is an East Asian freshwater bird of the heron family.
- It is one of six species of birds known as "pond herons" (genus Ardeola).
- It is typically 47 cm (19 in) long with white wings, a yellow bill with a black tip, yellow eyes and legs.
- Its overall colour is red, blue and white during breeding season, and greyish-brown and flecked with white at other times.
- It is found in shallow fresh and saltwater wetlands and ponds.
- It is fairly common and considered a Least concern (LC) species by the IUCN Red List.


Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Swami Vivekananda National Football Championship
Why in News?
Recently, the Swami Vivekananda U-20 Men’s National Football Championships quarter finals were held at the Ramakrishna Mission Ashrama Ground, Narainpur, Chhattisgarh.
Key Points
- Assam loses the quarter finals of the Football Championships to Mizoram. A total of 32 states participated in the championship.
- All India Football Federation (AIFF) announced the Swami Vivekananda U20 National Football Championship in April 2024.
- Apart from the newly introduced U20 championship, the AIFF also holds two other men’s age group competitions, the Junior NFC and the Sub-Junior NFC.
All India Football Federation (AIFF)
- The AIFF is the organization that manages the game of association football in India.
- It administers the running of the India national football team and also controls the I-League, India's premier domestic club competition, in addition to various other competitions and teams.
- The AIFF was founded in 1937, and gained FIFA affiliation in the year 1948, after India's independence in 1947.
- Currently, it has an office in Dwarka, New Delhi. India was one of the founding members of the Asian Football Confederation in 1954.


Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Naxalite killed in Encounter
Why in News?
Recently, a Naxalite was killed in an exchange of fire with security personnel in Chhattisgarh’s Sukma district.
Key Points
- The gunfight took place in the morning on a forested hill between Tolnai and Tetrai villages when a team of security personnel was out on an anti-Naxal operation.
- With this incident, 105 Naxalites have been killed so far in 2024 in separate encounters with security forces in Chhattisgarh.
Naxalism in India
- The term Naxalism derives its name from the village Naxalbari of West Bengal.
- It originated as rebellion against local landlords who bashed a peasant over a land dispute. The rebellion was initiated in 1967, with an objective of rightful redistribution of the land to working peasants under the leadership of Kanu Sanyal and Jagan Santhal.
- Started in West Bengal, the movement has spread across Eastern India; in less developed areas of states such as Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- It is considered that Naxals support Maoist political sentiments and ideology.
- Maoism is a form of communism developed by Mao Tse Tung. It is a doctrine to capture State power through a combination of armed insurgency, mass mobilization and strategic alliances.


Haryana Switch to Hindi
Report on Haryana Government Schools
Why in News?
A recent government report revealed that 19 schools in the state are without any students, 811 schools have just one teacher, and a total of 3,148 schools have less than half of their student capacity filled.
Key Points
- The report, which outlined key points from a meeting held by the Union education ministry’s project approval board in February 2024, pinpointed 14,562 government schools in the state.
- The report highlighted the insufficient number of teachers, particularly in elementary schools, and advised the government to promptly fill these vacancies.
- The shortage of teachers has impacted the central funding allocated for salary payments.
- In the primary sector, the financial assistance has decreased to Rs 14 lakh from Rs 19 lakh in the 2021-22 period.
- Similarly, in higher education, grants have dropped from Rs 20 lakh to Rs 14 lakh due to several unfilled positions.
- Apart from the shortage of teachers, the report also pointed to lack of basic infrastructure for students in these schools.
- While the schools are 18% short of their target for additional classrooms, toilets for boys and girls are 1% and 1.8% fewer than what they should be. Smart classrooms are also 1.4% behind the required number.
- The report emphasized that non-recurring approvals from the past, which have not been addressed by the state for years, will eventually become the state's sole responsibility after a period of 5 years according to the Samagra Shiksha framework.
- Schools that have not set up facilities must withdraw their initial proposals and think about submitting new ones.
- The state government has been directed to regularly update the progress of pending tasks on the Prabandh portal to avoid any errors in the data presented.
Samagra Shiksha Scheme
- It is an integrated scheme for school education covering the entire gamut from pre-school to class XII.
- It aims to deliver inclusive, equitable, and affordable school education.
- It subsumes the three Schemes of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA) and Teacher Education (TE).
- The scheme covers 1.16 million schools, over 156 million students and 5.7 million Teachers of Govt. and Aided schools (from pre-primary to senior secondary level).
- It is being implemented as a centrally sponsored scheme. It involves a 60:40 split in funding between the Centre and most States. It was launched by the Ministry of Education in 2018.
Samagra Shiksha Scheme 2.0
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT):
- In order to enhance the direct outreach of the scheme, all child-centric interventions will be provided directly to the students through DBT mode on an IT-based platform over a period of time.
- This DBT would include RTE (Right to Education) entitlements such as textbooks, uniforms and transport allowance.
- On NEP Recommendations:
- Encouraging Indian languages:
- It has a new component for appointment of language teachers, which includes salaries, and training costs as well as bilingual books and teaching learning material as recommended in NEP.
- Pre-primary Education:
- It will now include funding to support pre-primary sections at government schools, i.e. for teaching and learning materials, indigenous toys and games and play-based activities.
- Master trainers for pre-primary teachers and anganwadi workers will be supported under the scheme.
- NIPUN Bharat Initiative:
- Under this initiative, an annual provision of Rs. 500 per child for learning materials, Rs. 150 per teacher for manuals and resources and Rs. 10-20 lakh per district will be given for assessment for foundational literacy and numeracy.
- On Digital Initiatives:
- There is a provision for ICT labs and smart classrooms, including support for digital boards, virtual classrooms and DTH channels which have become more important in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- For out-of-school children:
- It includes a provision to support out of school children from age 16 to 19 with funding of Rs. 2000 per grade to complete their education via open schooling.
- There will also be a greater focus on skills and vocational education, both for students in school and dropouts.
- Encouraging Indian languages:


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Datia- Third Hottest Place in India
Why in News?
According to the India Meteorological Department, the temperature in Datia district of Madhya Pradesh reached 47.5 degrees Celsius, making it the third hottest place.
Key Points
- Najafgarh in Delhi recorded the highest temperature in the country at 47.8 degrees Celsius, with Agra closely behind at 47.7 degrees.
- According to the sources, Rain or thunderstorms may occur in certain areas of the eastern Madhya Pradesh districts.
- Heatwave conditions could be experienced in isolated regions in western and eastern Madhya Pradesh.
Heat Waves
- About:
- Heatwaves are prolonged periods of excessively hot weather that can cause adverse impacts on human health, the environment, and the economy.
- India, being a tropical country, is particularly vulnerable to heatwaves, which have become more frequent and intense in recent years.
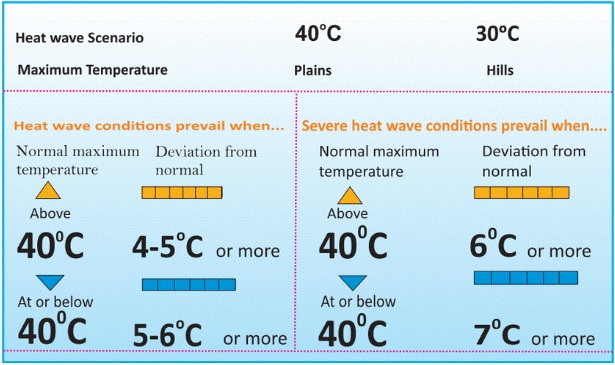
- IMD Criteria for Declaring Heat Wave in India:
- Heat waves need not be considered till the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C for Plains and at least 30°C for Hilly regions.
- If the normal maximum temperature of a station is less than or equal to 40°C, then an increase of 5°C to 6°C from the normal temperature is considered to be heat wave condition.
- Further, an increase of 7°C or more from the normal temperature is considered a severe heat wave condition.
- If the normal maximum temperature of a station is more than 40°C, then an increase of 4°C to 5°C from the normal temperature is considered to be heat wave condition. Further, an increase of 6°C or more is considered a severe heat wave condition.
- Additionally, if the actual maximum temperature remains 45°C or more irrespective of normal maximum temperature, a heat wave is declared.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan