Biodiversity & Environment
Heatwave Conditions
- 14 Jun 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Criteria for Heat Waves, El Nino, Indian Meteorological Department,National Action Plan for Climate Change (NAPCC)
For Mains: Causes,Impact,Mitigation strategies of Heat Waves, Urban Heat Island,Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
Why in News?
Odisha is currently facing an intense heatwave since April 2023, with temperatures exceeding 40°C in most monitoring centers across the state.
- Delayed monsoon could be a contributing factor for this heat wave. In 2023, the monsoon arrived over the Kerala coast on June 8, which is a delay compared to its normal onset date of June 1.
What are Heat Waves?
- About:
- Heatwaves are prolonged periods of excessively hot weather that can cause adverse impacts on human health, the environment, and the economy.
- India, being a tropical country, is particularly vulnerable to heatwaves, which have become more frequent and intense in recent years.
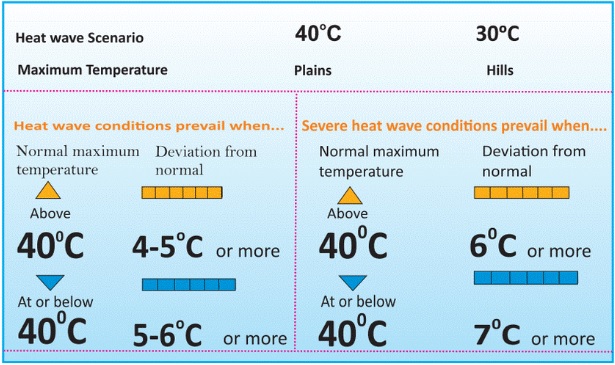
- IMD Criteria for Declaring Heat Wave in India:
- Heat Wave need not be considered till maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C for Plains and at least 30°C for Hilly regions.
- If the normal maximum temperature of a station is less than or equal to 40°C, then an increase of 5°C to 6°C from the normal temperature is considered to be heat wave condition.
- Further, an increase of 7°C or more from the normal temperature is considered a severe heat wave condition.
- If the normal maximum temperature of a station is more than 40°C, then an increase of 4°C to 5°C from the normal temperature is considered to be heat wave condition. Further, an increase of 6°C or more is considered a severe heat wave condition.
- Additionally, if the actual maximum temperature remains 45°C or more irrespective of normal maximum temperature, a heat wave is declared.
What are the Causes of Heat Waves?
- Global Warming:
- One of the primary causes of heatwaves in India is global warming, which refers to the long-term increase in Earth's average temperature due to human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial activities.
- Global warming can result in higher temperatures and changes in weather patterns, leading to heatwaves.
- Urbanisation:
- Rapid urbanisation and the growth of concrete jungles in cities can lead to the phenomenon known as the "urban heat island effect."
- Urban areas with high population density, buildings, and concrete surfaces absorb and retain more heat, leading to higher temperatures, particularly during heatwaves.
- Sparse Pre-Monsoon Season Showers:
- Less moisture in many areas, leaving large parts of India arid and dry.
- The sudden end of pre-monsoon rain showers, an uncommon trend in India, has contributed to the heat waves.
- El Nino Effect:
- El Nino often increases temperatures in Asia, combined with the weather pattern to create record high temperatures.
- Trade winds coming from South America normally blow westward towards Asia during the Southwest Monsoon and warming of the Pacific Ocean results in weakening of these winds.
- Therefore, moisture and heat content get limited and results in reduction and uneven distribution of rainfall across the Indian sub-continent.
What are Its Impacts?
- Impact on Health:
- Rapid rises in heat gain can compromise the body’s ability to regulate temperature and can result in a cascade of illnesses, including heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and hyperthermia.
- Deaths and hospitalizations from heat can occur extremely rapidly or have a lagged effect.
- Impact on Water Resources:
- Heatwaves can exacerbate water scarcity issues in India; drying up of water bodies, reduced water availability for agriculture and domestic use, and increased competition for water resources.
- This can lead to conflicts over water, affect irrigation practices, and impact water-dependent industries.
- Heatwaves can exacerbate water scarcity issues in India; drying up of water bodies, reduced water availability for agriculture and domestic use, and increased competition for water resources.
- Impact on Energy:
- Heatwaves can increase electricity demand for cooling purposes, leading to strain on power grids and potential blackouts.
- This can disrupt economic activities, affect productivity, and impact vulnerable populations who may not have access to reliable electricity for cooling during heatwaves.
Way Forward
- A Heat Waves Action Plan:
- As deaths due to heatwaves are preventable, the government must prioritise preparing a long-term action plan to safeguard human lives, livestock, and wildlife.
- Effective implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-30 with the State playing a leading role and sharing responsibility with other stakeholders is now the need of the hour.
- Implementing Climate Action Plans:
- National Action Plan for Climate Change (NAPCC) should be implemented in true spirit for inclusive growth and ecological sustainability.
- Nature-based solutions should be taken into account, not just for tackling climate change induced heat waves but also doing it in a way that is ethical and promoting intergenerational justice.
- Sustainable Cooling:
- Passive cooling technology, a widely-used strategy to create naturally ventilated buildings, can be a vital alternative to address the urban heat island for residential and commercial buildings.
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in the third part of its AR6 stated that ancient Indian building designs that have used this technology, can be adapted to modern facilities in the context of global warming.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What are the possible limitations of India in mitigating global warming at present and in the immediate future? (2010)
- Appropriate alternate technologies are not sufficiently available.
- India cannot invest huge funds in research and development.
- Many developed countries have already set up their polluting industries in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world. (2013)