Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
WAVES 2025
Why in News?
The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India, is organizing the WAVE (World Audio Visual & Entertainment) Summit in Mumbai from 1-4 May 2025.
Key Points
- About WAVES Summit 2025:
- WAVES is India's first global-scale platform focused on the Media and Entertainment (M&E) sector.
- The summit will bring together industry leaders, innovators, investors, and policymakers to foster collaboration and shape the future of M&E.
- Key sectors in focus include broadcasting, films, gaming, animation, visual effects, music, advertising, digital and social media, generative AI, AR/VR/XR, among others.
- WAVES aims to position India as a global hub for creative content, IP generation, and M&E innovation.
- Anti-Piracy Challenge:
- The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting also has announced the finalists of the Anti-Piracy Challenge, a flagship initiative under the Create in India Challenge Season 1 of the WAVES Summit 2025.
- Objective:
- The challenge was launched on 12 September 2024, with the goal of promoting Make in India technologies to combat digital piracy.
- It focused on cutting-edge anti-piracy technologies like fingerprinting, watermarking, blockchain, and steganography.
- The initiative aims to strengthen India’s digital ecosystem by encouraging homegrown innovation in content protection.
- The top 7 teams will present their solutions during the WAVES 2025 Summit in front of a live audience and a final jury panel.
- Winners will be honored at the Grand Finale, with opportunities for national recognition, mentorship, and industry partnerships.
- Anti-Piracy Innovation Importance:
- According to Media Partners Asia, 90 million users in India engaged in video piracy in 2024, causing losses of USD 1.2 billion. This number could surge to 158 million by 2029 without strong intervention.
- Digital content faces increasing threats from piracy, illegal distribution, and manipulation, which affects content creators, broadcasters, and IP rights holders.
- Criminal networks continue to evolve, making enforcement and detection more complex—hence the urgency for technological solutions.
- Strategic Support and Industry Involvement:
- The challenge was conducted by Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) with support from IPHouse, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), and Hack2Skill.
- These organizations played a key role in evaluation and industry engagement.
Confederation of Indian Industries
- CII is a non-government, not-for-profit, industry-led and industry-managed organization.
- It works to create and sustain an environment conducive to the development of India, partnering industry, Government and civil society, through advisory and consultative processes.
- Founded in 1895, it is headquartered in New Delhi.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
SC Upholds Use of Urdu Signboards in Maharashtra
Why in News?
On 17 April 2025, the Supreme Court upheld the use of Urdu on the signboard of a municipal council building in Maharashtra’s Akola district, stating that a language belongs to a community, a region, and its people—not to any religion.
Key Points
- About the Petition:
- The petition was filed by a former municipal councillor, who argued that only Marathi should be used under the Maharashtra Local Authorities (Official Languages) Act, 2022.
- Equal Constitutional Status:
- The court ruled that both Urdu and Marathi enjoy equal constitutional recognition.
- It noted that the use of Urdu does not violate any legal provision and that the Municipal Council had been using it since 1956 due to its wide acceptance among the local population.
- The court denounced the colonial legacy of associating Hindi with Hindus and Urdu with Muslims.
- The court also observed that the Municipal Council used Urdu for effective communication with the local population, aligning with the Bombay High Court’s earlier reasoning.
Urdu
- Historical Background
- Urdu had developed and flourished in Delhi during the period of ‘Delhi Sultanate’ from 12th to 16th century and then during the period of ‘Mughal Empire’ in Delhi from 16th century to 19th century when several court poets used this language in their great poetry and writings.
- Its first major folk poet Amir Khusrau (1253-1325), composed dohas (couplets) and riddles in the newly-formed speech, then called Hindavi.
- The divide between Urdu and Hindi occurred under the colonial impact.
- Hindi and Urdu got split along religious lines with Hindi in Nagari script becoming identified with Hindus, and Urdu in Persian script identifying with Muslims.
- Contemporary Context: Urdu is a major language of South Asia.
- It is spoken in countries including India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Nepal.
- It has become the culture language and lingua franca of the South Asian Muslim diaspora outside the sub-continent, especially in the Gulf and the Middle East, Western Europe, Scandinavia, USA and Canada.
- Urdu had developed and flourished in Delhi during the period of ‘Delhi Sultanate’ from 12th to 16th century and then during the period of ‘Mughal Empire’ in Delhi from 16th century to 19th century when several court poets used this language in their great poetry and writings.
- Status in India:
- Scheduled Language: Urdu is one of the languages mentioned in the 8th Schedule to the Constitution.
- The Constitutional provisions relating to the 8th Schedule are articles 344(1) and 351.
- Presently, 8th Schedule consists of the 22 languages namely (1) Assamese, (2) Bengali, (3) Gujarati, (4) Hindi, (5) Kannada, (6) Kashmiri, (7) Konkani, (8) Malayalam, (9) Manipuri, (10) Marathi, (11) Nepali, (12) Oriya, (13) Punjabi, (14) Sanskrit, (15) Sindhi, (16) Tamil, (17) Telugu, (18) Urdu (19) Bodo, (20) Santhali, (21) Maithili and (22) Dogri.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Hindi as Compulsory 3rd language in Maharashtra
Why in News?
The Maharashtra government has made Hindi a compulsory third language for Classes I to V in Marathi and English medium schools, aligning with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Key Points
- National Education Policy 2020:
- About:
- The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 aims to address India's evolving development needs by overhauling the education system to meet 21st century goals and Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG4), while preserving India's cultural heritage.
- It replaced the National Policy on Education, 1986, which was modified in 1992.
- Salient Features:
- Universal Access: Focuses on providing access to education from preschool through secondary levels.
- Early Childhood Education: Transitions from the 10+2 to a 5+3+3+4 system, including children aged 3-6 in the school curriculum with an emphasis on Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE).
- Multilingualism: Promotes using mother tongues or regional languages as the medium of instruction up to Grade 5, with options for Sanskrit and other languages. Indian Sign Language (ISL) will be standardised.
- Inclusive Education: Emphasises support for Socially and Economically Disadvantaged Groups (SEDGs), children with disabilities, and the establishment of "Bal Bhavans."
- Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) Enhancement: Aim to raise the Gross Enrolment Ratio from 26.3% to 50% by 2035, adding 3.5 crore new seats.
- About:
Hindi Language
- Articles Related to Hindi: Article 210 states that the language to be used in the legislature can be the official language of the state, Hindi, or English.
- Article 351 states that it shall be the duty of the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language, to develop it so that it may serve as a medium of expression for all the elements of the composite culture of India.
- Hindi is one of the 22 languages listed in the eighth schedule of the Constitution of India and It is not a classical language.
- The language is named after the Persian word 'Hind' meaning 'land of the Indus River' and is a descendant of Sanskrit.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
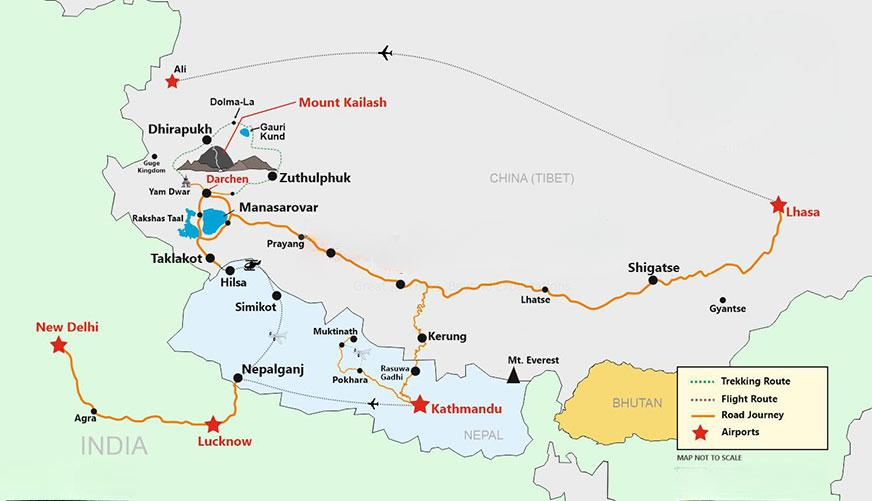
Kailash Mansarovar Yatra
Why in News?
Indian and Chinese officials are stepping up efforts to finalise an agreement to resume the Kailash Mansarovar annual pilgrimage, which has been suspended since 2019.
Key Points
- About the Developments:
- The pilgrimage, suspended since 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic and border tensions, is set to recommence.
- Both nations have agreed in principle to resume direct air services, aiming to facilitate travel for pilgrims and strengthen people-to-people connections.
- Discussions are underway to resume the exchange of hydrological data and cooperation on trans-border rivers, enhancing mutual trust and collaboration.
- The year 2025 marks the 75th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and China, providing an opportune moment to rebuild ties through initiatives like the Yatra.
Mount Kailash
- It is a diamond-shaped peak made of black rock, located in Tibet.
- India organizes the annually between June and September through the Lipulekh Pass (since 1981) in Uttarakhand and the Nathu La Pass (since 2015) in Sikkim.
- Mount Kailash stands at 6,638 meters and is considered a sacred peak by Hindus, Buddhists, Jains, and Bons (indigenous religion of Tibet).
- For Tibetans Buddhists, Kailash is the cosmic axis, or Mount Meru, connecting heaven and earth.
- In Hinduism, it is the abode of Lord Shiva and Goddess Parvati.
- In Jainism, Kailash is Ashtapada, where Rishabhanatha attained enlightenment.
- Mount Kailash is considered the spiritual center of the Earth, with the Sutlej, Brahmaputra, Kamali, and Indus rivers originating from it.
- Lake Mansarovar is located at the base of the mountain.
- Mount Kailash, though lower in height than Mount Everest (8,849 meters), remains unclimbed as its ascent is prohibited due to its sacred significance.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Chief Minister's Ladli Behna Scheme
Why in News?
The Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister announced that funds under the Ladli Behna Yojana will be transferred from Mandla district and disbursed regularly around the 15th of each month.
Key Points
- About the Scheme:
- Objective: The main objective of Ladli Behna Yojana is to economically empower the women of Madhya Pradesh .
- Under the Ladli Behna Yojana, so far Rs. 1553 crore has been transferred to the accounts of 1.27 crore women beneficiaries.
- With the state government increasing the amount to Rs. 3000 per month, more women will now be able to take advantage of this and improve their economic condition.
- Beginning: This scheme was launched by the state government in May 2023 and under this, married women between 21 and 60 years of age were initially given assistance of Rs 1000. Which was later increased to Rs 1250 per month.
- Ladli Behna Yojana is included among the biggest DBT schemes of the state.
- Eligibility and Rules:
- The annual income of the woman's family should be less than Rs 2.5 lakh.
- No member of the family holds a government job .
- Apart from this, the family should not have more than 5 acres of land or tractor or four-wheeler.
- Objective: The main objective of Ladli Behna Yojana is to economically empower the women of Madhya Pradesh .
Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Scheme
- Objective : The scheme is designed to aid faster flow of information and funds to the beneficiaries and to reduce fraud in the distribution system.
- Implementation : It was launched by the Government of India on January 1, 2013 as a mission to reform the government delivery system.
- The old version of the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) of the Accountant General's Office i.e. 'Central Plan Scheme Monitoring System' was chosen as a platform for direct benefit transfer.
- Components of DBT: The primary components for implementation of Direct Benefit Scheme include beneficiary account verification system; integrated, stable payment and settlement platform with RBI , NPCI , public and private sector banks, Regional Rural Banks and Co-operative Banks (viz. Core Banking Solution of banks, settlement systems of RBI and Aadhaar Payment System of NPCI etc.).
- Aadhaar not mandatory: Aadhaar is not mandatory in DBT schemes . Since Aadhaar provides unique identification and is useful in targeting the intended beneficiaries, Aadhaar is preferred and beneficiaries are encouraged to have Aadhaar.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Parth Scheme
Why in News?
Parth Scheme (Parth - Police Army Recruitment Training & Skills) will be implemented by the Sports and Youth Welfare Department as a pilot project in 9 major cities of Madhya Pradesh from May 1 2025 .
Key Points
- About the Scheme:
- The initial launch of this scheme was done in January 2025.
- This scheme will be implemented as a pilot project in Bhopal, Jabalpur, Gwalior, Rewa, Morena, Shahdol, Sagar, Indore and Ujjain .
- 50 youth will be selected from each city , thus a total of 450 youth will be benefited.
- Training:
- This scheme will provide complete training to the youth for recruitment in army, police and paramilitary forces. The training will include:
- Physical fitness studies
- Written Exam Coaching (General Knowledge, Maths, English etc.)
- personality development
- This scheme will provide complete training to the youth for recruitment in army, police and paramilitary forces. The training will include:
- Structure:
- Division level training centers will be established, which will be run by the District Sports and Youth Welfare Officer.
- Rural youth coordinators and departmental staff will assist in the training program.
- This scheme is completely self-reliant , the government has not allocated a separate budget for it.
- The scheme will be operated through fixed fees to be charged from the participants
- Objective:
- To physically prepare the youth of the state for police and army recruitment .
- To provide them discipline, self-confidence and leadership skills through sports training.
- Increasing employment opportunities by providing skill-based training .
- To promote sports culture in the state and institutionalize sports activities at the school level


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Data Center Policy 2025
Why in News?
Keeping in view the increasing importance of data centers, the Rajasthan Government has implemented the "Rajasthan Data Center Policy-2025".
Key Points
- About the Policy:
- The objective of this policy is to make Rajasthan a major hub for data centers , attract investments and generate employment opportunities in the IT sector.
- Under this policy, comprehensive concessions, environment-friendly incentives and modern infrastructure will be provided to the investors.
- There is a plan to attract investment of Rs 20,000 crore in the next five years .
- Key provisions:
- Many attractive provisions have been made to promote the data centre sector , which includes an annual asset creation incentive of Rs 10 to 20 crore for 10 years .
- Private companies investing more than Rs 100 crore in the state will be given an additional 25 per cent sunrise incentive .
- Under the policy, 5% interest subsidy will be provided for 5 years, which will reduce the cost of setting up data centres.
- Data centres will be given 100% waiver in banking, transmission and wheeling charges .
- Flexible payment arrangements have been introduced to bring flexibility in land related processes , along with exemption in stamp duty, land conversion fee and electricity charges .
- Additionally, data centres will be exempted from external development charges up to Rs 10 crore .
- Environmental protection has also been given priority in this policy , under which 50% of the expenditure incurred on green solutions will be reimbursed , up to a maximum of Rs 12.5 crore .
- To enhance the efficiency of employees, 50% of the cost incurred on their training or efficiency improvement will be reimbursed.
- The state government has also made provision to provide assistance on intellectual property rights such as GI tag, patent, copyright and trademark registration , which can be up to 50 per cent up to a maximum of Rs 1 crore .
- The policy also includes provisions for relaxation in building bylaws and ensuring uninterrupted power supply to ensure the operational efficiency and safety of data centres.
Intellectual Property Rights
- The rights given to individuals in the context of their intellectual creation are called Intellectual Property Rights. In fact, it is believed that if a person creates any kind of intellectual creation (such as writing a literary work , research , invention , etc.), then first of all, that person should have exclusive rights over it.
- The basic purpose of granting intellectual property rights is to encourage human intellectual creativity . Since the scope of intellectual property rights is wide, it was considered necessary that relevant rights and related rules etc. should be arranged for a particular area


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
'One KGBV, One Game' Scheme
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government has launched the 'One KGBV, One Sport' scheme to enhance the sporting talent of girls studying in Kasturba Gandhi Residential Girls Schools (KGBVs).
Key Points
- About the Scheme:
- This scheme is an effort to give special training to girls in the field of sports as well as encourage them towards physical, mental and social development.
- The aim of the government is to enable girls from backward and underprivileged communities to specialise in sports and prepare them to compete at the national level.
- Two KGBV schools from each of the 73 districts (except Kanpur Dehat, which has only one) will be included in the pilot project.
- Sports selection process : A sports committee will be formed in every school, which will select the sport based on the interest and resources of the students.
- Training : With the help of sports experts, special sports training will be given to the girl students. Along with this, health check-up, nutrition and health awareness programmes will also be organised.
- Social and departmental support : Former national and international level players will be invited to motivate the students and awards will also be given to the girls who perform exceptionally well.
- Sports Associations and Corporate Support : Support would be sought from state and national level sports associations as well as corporate groups to provide necessary sports equipment and other facilities.
Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya (KGBV) Scheme
- The KGBV scheme was launched by the Government of India in August 2004. The scheme aims to provide quality education through residential schools at the upper primary level to girls belonging to Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), Other Backward Classes (OBC) and minority communities in remote and educationally backward areas .
- The KGBV scheme is implemented in educationally backward blocks (EBB) where the rural female literacy rate is lower than the national average and the gender literacy gap is higher than the national average.
- Out of the total seats under the scheme, 75% of the seats are reserved for girls from SC, ST, OBC and minority communities while the remaining 25% seats are given to girls living below the poverty line (BPL) .
- Under the scheme, girls in the age group of 10 to 18 years , especially those who are from disadvantaged backgrounds or reside in areas with low female literacy , are eligible for enrolment.
- Additionally, girls who have not completed primary education , or are living in difficult circumstances , may also be granted exceptional enrolment.
- The scope of the KGBV scheme is limited to areas where –
- There is concentration of tribal, SC, OBC and minority population ,
- low female literacy rate or a high number of girls out of school ,
- There may be small and scattered settlements which may not be suitable for schools.
- At present, under the KGBV Scheme, at least one school is established in each EBB, providing education with residential facilities to girls from class VI to XII .












%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)





















 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan