Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
High Court Ruled Garlic a Vegetable
Why in News?
Recently, the Indore bench of the Madhya Pradesh High Court has officially declared garlic as a vegetable.
Key Points
- This ruling is expected to benefit farmers by enabling them to sell garlic directly in the market without paying commissions to agents.
- In 2015, a farmers' organisation in Madhya Pradesh urged the Mandi Board to classify garlic as a vegetable.
- However, the Agriculture Department soon reversed this decision, reclassifying garlic as a spice under the Agricultural Produce Market Committee Act, 1972.
- This led to a legal challenge by the Potato, Onion, and Garlic Commission Agent Association in 2016.
- In 2017, a single judge ruled in favour of the association, allowing garlic to be sold as a vegetable.
Garlic
- Botanically, garlic (Allium sativum) is considered a vegetable, as it has a bulb, tall stem, and long leaves.
- The distinctive smell of garlic and onion is due to the presence of sulphur-containing chemicals.
- Garlic grows best in well-drained, fertile loamy soil with a pH range of 6-8. Soils rich in organic matter are preferred for their moisture and nutrient retention and reduced risk of crusting and compaction. Heavy soils may cause deformed bulbs, while poorly drained soils can lead to discoloured bulbs.
- Garlic thrives at 1200–2000 meters above sea level. Requires cool, moist climate during growth and warm, dry weather during maturity.
- Production: India is the world's second-largest garlic exporter, with record-high exports in 2023 due to supply chain issues in China.
- Indian garlic flakes have become more popular in West Asian countries, with the United States, Malaysia, Brazil, Germany, and the United Kingdom being India's main garlic export markets.
- Geographical Indication Tag:
- Riyawan Garlic, a GI-tagged garlic from Madhya Pradesh, is renowned for its high yield, pungent and robust flavour, and higher oil content compared to other varieties.
- Kodaikanal Malai poondu (Hill Garlic) a GI-tagged garlic from Tamil Nadu, is known for its medicinal and preservative properties due to its antioxidant and antimicrobial potential, which are attributed to the presence of the higher amount of organosulfur compounds, phenols and flavonoids compared to the garlic varieties.
- Kanthalloor Vattavada Veluthuli, a GI-tagged garlic from Kerala, is renowned for its strong aroma and flavour. Grown in the high-altitude areas of Kanthalloor and Vattavada, this small-sized garlic is prized for its medicinal properties and culinary use.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Chhattisgarh CM Announces New Security Camps
Why in News?
Recently, Chhattisgarh chief minister announced that the state government is working to open new security camps in the remote areas of Bastar to bring an end to the Leftwing extremism in the region.
Key Points
- 32 new security camps were opened in Bastar's Maoist-infested areas in the last eight months, and 29 more such facilities would be established soon.
- The state government has constituted the State Investigation Agency (SIA) in the line of National Investigation Agency (NIA) for effective and speedy investigation and prosecution action in the Naxal-related incidents.
- The state government has also launched a new scheme ‘Niyad Nellanar’ (your good village) to combat Maoism in the state.
Niyad Nellanar Scheme
- Niyad Nellanar, meaning “aapka achcha gaon” or “your good village” is the local Dandami dialect (spoken in south Bastar).
- Under this scheme, amenities and benefits will be provided in villages located within 5 kilometers of security camps in Bastar region.
- 14 new security camps have been set up in Bastar. These camps will also help to facilitate the implementation of the new scheme. Around 25 basic amenities will be provided in such villages under Niyad Nellanar.
- Families in these villages will receive free gas cylinders under the Ujjwala scheme, four free rice, gram-salt, jaggery, and sugar, ration cards, irrigation pumps, free electricity, community halls, Anganwadi, and certificates of forest rights.
- In addition to all-weather roads, a sub health center, elementary school, sports field, bank, ATM, mobile tower, helipad, etc., will be constructed.
National Investigation Agency (NIA)
- The NIA is a federal agency of the Indian government responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes related to Terrorism, Insurgency, and other national security matters.
- Federal agencies in a country typically have jurisdiction over matters that affect the country as a whole, rather than just individual states or provinces.
- It was established in 2009 following the Mumbai terrorist attacks in 2008, under the National Investigation Agency (NIA) Act, 2008, operates under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The National Investigation Agency (Amendment) Act, 2019 was passed in July 2019, amending the NIA Act, 2008.
- The NIA has the power to take over investigations of terrorism-related cases from state police forces and other agencies. It also has the authority to investigate cases across state boundaries without obtaining prior permission from state governments.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Jharkhand Personnel to Receive Gallantry, Service Medals
Why in News?
According to the sources, as part of the 78th Independence Day celebrations, 19 employees and officials from Jharkhand were honored for their exemplary service and bravery in a special ceremony in Delhi.
Key Points
- Garhwa Superintendent of Police (SP) Deepak Kumar Pandey to be awarded gallantry medal for eliminating rewarded Naxalite.
- The other recipients of the gallantry medal includes Sub Inspector Vishwajeet Kumar Singh, Havildar Umesh Singh, Constable Subhash Das, Constable Gopal Ganjhu, Constable Ravindra Toppo, and Assistant Sub Inspector (ASI) Sachchidanand Singh.
- 11 police personnel from Jharkhand will receive the commendable service medal.
- The recipients include Head Constable Salomi Minj, Constable Vimal Kumar Chhetri, Constable Randhir Kumar Singh, Constable Sanjeev Kumar Gupta, Constable Hema Rani Kullu, Head Constable Sanjay Oraon, Head Constable Arun Oraon, Constable Rekha Kumari, Head Constable Rituraj, Head Constable Rajendra Ram, and Head Constable Sanjay Kumar.
Gallantry Awards
- Gallantry Awards have been instituted by the Government of India to honour the acts of bravery and sacrifice of the officers/personnel of the Armed Forces, other lawfully constituted Forces and civilians.
- Post-independence, the first three gallantry awards namely Param Vir Chakra, Maha Vir Chakra and Vir Chakra were instituted by the Government of India on 26th January 1950 and were deemed to have effect from the 15th August 1947.
- After that, other three gallantry awards i.e. Ashoka Chakra Class-I, Ashoka Chakra Class-II and Ashoka Chakra Class-III were instituted by the Government of India on 4th January, 1952, which were deemed to have effect from the 15th August, 1947.
- These awards were renamed as Ashoka Chakra, Kirti Chakra and Shaurya Chakra respectively in January, 1967.
- After that, other three gallantry awards i.e. Ashoka Chakra Class-I, Ashoka Chakra Class-II and Ashoka Chakra Class-III were instituted by the Government of India on 4th January, 1952, which were deemed to have effect from the 15th August, 1947.
- These gallantry awards are announced twice in a year, first on the occasion of the Republic Day and then on the occasion of the Independence Day.
- Gallantry awards are categorized into two types:
- Wartime Gallantry Awards
- These awards are given for bravery in the face of the enemy.
- Peacetime Gallantry Awards
- These awards are given for bravery other than in the face of the enemy.
- Wartime Gallantry Awards
- Order of precedence of these awards is the Param Vir Chakra, the Ashoka Chakra, the Mahavir Chakra, the Kirti Chakra, the Vir Chakra and the Shaurya Chakra.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Scheme to Promote Entrepreneurship Among Youth
Why in News?
Recently, Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister announced the launch of a new initiative, the Mukhyamantri Yuva Udyam Vikas Abhiyan Yojana, aimed at empowering youth.
Key Points
- Under the scheme, financial support will be provided to young individuals interested in entrepreneurship, with a target of establishing one million micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSME) units across the state.
- Over 16.2 million young people have secured employment through investments made in the State.
- 62 lakh youth have been connected with self-employment opportunities by leveraging both Central and State Government schemes.
- To further boost entrepreneurship, a dedicated start-up fund has been established to finance new ventures.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Aravalis of Haryana Get Protected Forest Tag
Why in News?
Recently, Haryana has designated 24,353 hectares of Aravali land in five of its districts as protected forest, under the compensatory afforestation swap intended to offset the destruction of tropical rainforests in Great Nicobar.
Key Points
- Though the goal was 26,000 hectares, Haryana was able to secure 24,353 hectares. For the remaining 1,647 hectares, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) is in discussions with the government of Madhya Pradesh.
- In November 2022, MoEFCC gave its approval, paving the way for a colossal project in Great Nicobar.
- This project involves constructing an international airport, a shipping port, a power plant, and a township, spanning an area of 160 square kilometers.
- More than 80% of this land is part of a pristine tropical forest, resulting in the loss of almost a million trees.
- In February 2023, it was decided that the compensatory afforestation for this forest destruction in an island off India's mainland will be carried out in the Aravalis of Haryana.
- The government of Haryana, which submitted its plan for compensatory afforestation will receive Rs 3,000 crore to revive the Aravalis in five of its districts.
- The five districts are - Gurgaon, Nuh, Rewari, Mahendergarh and Charkhi Dadri.
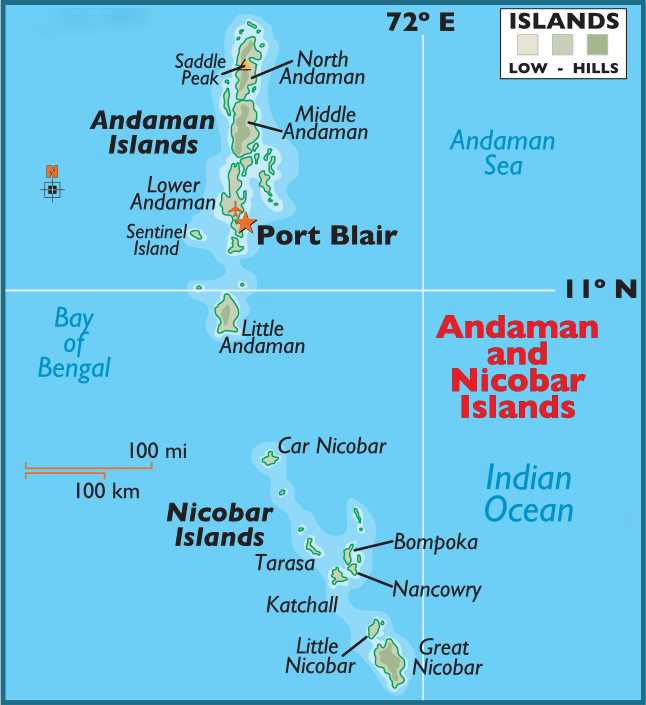
Great Nicobar Island
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands, a sparsely inhabited 910-sq-km patch of mainly tropical rainforest in southeastern Bay of Bengal.
- Indira Point on the island, India’s southernmost point, is located 90 nautical miles (<170 km) from Sabang at the northern tip of Sumatra, the largest island of the Indonesian archipelago.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands consist of 836 islands, divided into two groups known as the Andaman Islands located in the north and the Nicobar Islands situated in the south, separated by the 10° Channel which is 150 kilometres wide.
- Great Nicobar has two national parks, a biosphere reserve, small populations of the Shompen, Onge, Andamanese and Nicobarese tribal peoples, and a few thousand non-tribal settlers.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)



.jpg)






.png)
.png)



 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan