Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand First in the Country in SDG 2023-24
Why in News?
Uttarakhand secured the top position in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG INDEX) 2023-2024 report released by NITI Aayog.
Key Points
- According to the Chief Minister of Uttarakhand , the state government is committed to advancing towards a 'Developed Uttarakhand' by balancing ecology and economy.
- The SDG India Index is a tool developed by NITI Aayog to measure and track India’s progress towards the SDGs set by the United Nations.
- The Index supports the localization of SDGs, encouraging states to integrate these goals into their development plans.
- It serves as a benchmark for policymakers to identify gaps and prioritise actions towards achieving sustainable development by 2030.
- India's overall SDG score improved to 71 in 2023-24 from 66 in 2020-21 and 57 in 2018. All states have shown improvement in overall scores.
- Progress has been largely driven by targeted government interventions in poverty reduction, economic growth, and climate action.
- Top Performers: Kerala and Uttarakhand emerged as the best-performing states, each scoring 79 points.
- Lowest Performer: Bihar lagged behind with a score of 57 points, followed by Jharkhand at 62 points.
- Front-Runner States: 32 states and union territories (UTs) are in the front-runner category, with 10 new entrants including Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Chhattisgarh, and Uttar Pradesh.
NITI Aayog
- The Planning Commission in India was replaced by NITI Aayog in 2015, with a shift towards a 'Bottom-Up' approach and emphasis on cooperative federalism.
- The composition of NITI Aayog includes the Prime Minister as Chairperson, Chief Ministers of all states and Lt. Governors of Union Territories in the Governing Council, and experts nominated by the Prime Minister as Special Invitees.
- Chief Executive Officer appointed by the Prime Minister for a specific term, holding the rank of Secretary to the Government of India.
- The key objectives are to promote cooperative federalism with states, develop plans at the village level, incorporate national security into economic strategy, focus on marginalised sections of society, encourage partnerships with stakeholders and think tanks, create a support system for knowledge and innovation, resolve inter-sectoral issues, and maintain a resource centre for good governance and sustainable development practices.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand New Hydel Power Projects
Why in News?
Recently, Uttarakhand Chief Minister Pushkar Singh Dhami sought the clearance of 21 new hydel power projects with a capacity of 2123 MW for the state from the Centre.
Key Points
- The Union Minister of Power Manohar Lal Khattar is on a visit to the state to review the progress of Tehri Hydro Power Complex and various urban development projects in the state.
- According to the CM, only 40% of Uttarakhand's total capacity for hydro electricity generation is being utilised at present.
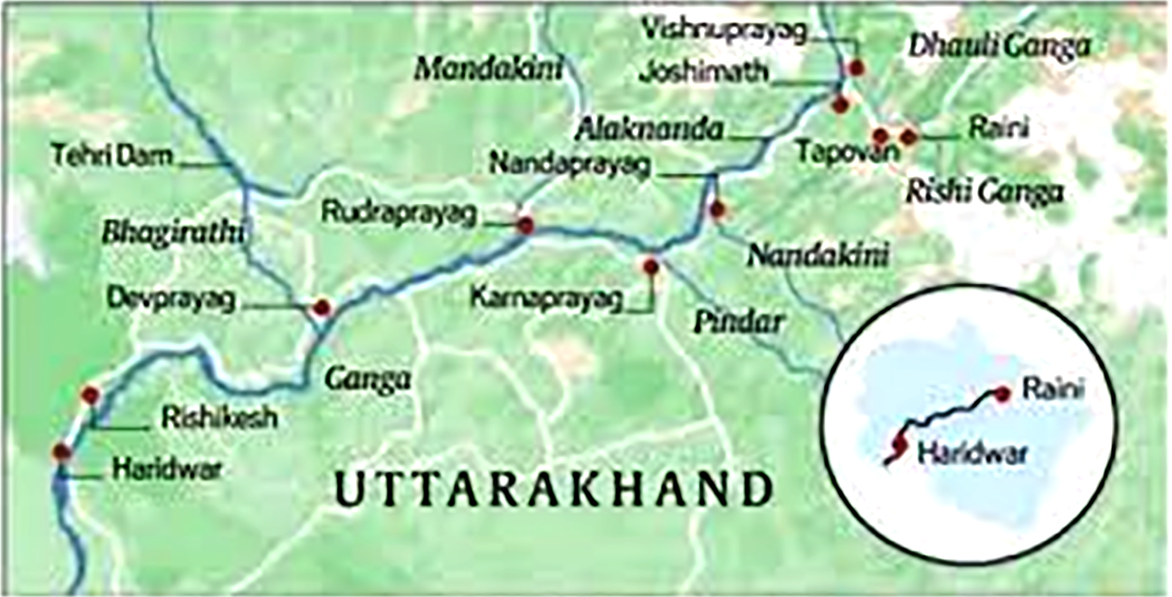
- Expert committees have recommended the implementation projects on the Alaknanda and Bhagirathi rivers and their tributaries.
Alaknanda River
- It is one of the headstreams of the Ganga.
- It rises at the confluence and feet of the Satopanth and Bhagirath glaciers in Uttarakhand.
- It meets the Bhagirathi River at Devprayag after which it is called the Ganga.
- Its main tributaries are the Mandakini, Nandakini, and Pindar rivers.
- The Alaknanda system drains parts of Chamoli, Tehri, and Pauri districts
- The Hindu pilgrimage center of Badrinath and the natural spring Tapt Kund lie along the banks of the Alaknanda River.
Bhagirathi River
- It is a turbulent Himalayan river of Uttarakhand, and one of the two headstreams of the Ganges.
- The Bhagirathi rises at the foot of Gangotri Glacier, at Gaumukh, at an elevation of 3892m and fanning out into the 350 km wide Ganga delta, it finally empties into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Bhagirathi and Alaknanda join at Devprayag in Garhwal andare thereafter known as the Ganges.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand’s First Bird Gallery
Why in News?
Recently, The Uttarakhand Forest Department established the state's first bird gallery at the Nature Education Centre, in Dehradun.
Key Points
- This gallery displays high-resolution images of birds in Uttarakhand, providing visitors with a stunning showcase of the state's avian residents.
- It is an attempt to highlight Uttarakhand's avian diversity and promote a greater appreciation for these unique species.
- By educating visitors about the numerous bird species and their functions in the ecosystem, the gallery would facilitate conservation and create awareness about these avian species
- Uttarakhand has over 710 bird species, which is more than 50% of India's bird species.


Haryana Switch to Hindi
IT Saksham Yuva Scheme
Why in News?
Recently, The Haryana government has introduced the IT Saksham Yuva Scheme 2024 to boost youth empowerment and employment. The scheme aims to provide jobs to 5,000 youth in its first phase.
Key Points
- The scheme is part of the broader 'Mission 60,000'. It was announced during the 2024-25 budget speech and aims to employ at least 60,000 young individuals from poor families.
- Under this scheme, graduate and postgraduate applicants with IT backgrounds will undertake the Haryana IT Programme, a specially designed short-term course lasting a minimum of three months.
- Participants in the IT Saksham Yuva Scheme will receive a monthly remuneration of Rs 20,000 for the first six months, which will then increase to Rs 25,000 from the seventh month onwards, provided by the employing entities.
- If an 'IT Saksham Yuva' is unable to secure deployment, the government will provide an unemployment allowance of Rs 10,000 per month.
- The primary training agencies for this scheme are the Haryana State Electronics Development Corporation Ltd (HARTRON), Haryana Knowledge Corporation Ltd (HKCL), and Shri Vishwakarma Skill University (SVSU).
- As the state university, SVSU will issue completion certificates to candidates according to the norms established by the Haryana Skill Development Mission (HSDM).
Haryana Skill Development Mission (HSDM)
- It was established in May 2015 by the State Government.
- Its aim is to empower youth to take part in the economic and all around growth of Haryana and India.
- It is a single point of contact within the Government to formulate and steer skill development schemes across the Department.
- HSDM acts as an integrated mission which combines the efforts of various State Departments in achieving the skill development target of the State.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
ASI Submits Bhojshala Survey Report
Why in News?
Recently, The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) submitted its scientific survey report of the disputed Bhojshala-Kamal-Maula mosque complex to the Indore bench of the Madhya Pradesh High Court.
Key Points
- As per the sources, the report contains traces of medieval- era structure dating to the Paramara dynasty/ period (between 9th and 11th century). The site was built and developed by Raja Bhoj in Dhar district.
- The survey, which spanned nearly 98 days, uncovered approximately 1700 relics and other evidence.
- The carvings discovered encompassed a diverse array of images, including desecrated idols of deities, artifacts, and other remnants (human and animal figures).
- The report implies that the existing structure at Bhojshala was originally a temple and also served as a hub of literary and educational activities.
- The Hindu community regards Bhojshala as a temple dedicated to Vagdevi (Goddess Saraswati), whereas the Muslim community refers to it as Kamal Maula Mosque.
Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)
- ASI, under the Ministry of Culture, is the premier organization for the archaeological research and protection of the cultural heritage of the nation.
- It administers more than 3650 ancient monuments, archaeological sites, and remains of national importance.
- Its activities include carrying out surveys of antiquarian remains, exploration and excavation of archaeological sites, conservation and maintenance of protected monuments, etc.
- It was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, the first Director-General of ASI. Alexander Cunningham is also known as the “Father of Indian Archaeology”.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Encroachment at Karbatal Wetland
Why in News?
Recently, The Eastern Zone Circuit Bench of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) has set up a four member committee to look into allegations made in encroachment of Karbatal wetland at Begusarai district in Bihar.
Key Points
- The allegations of encroachment and degradation of the Ramsar Site were made by an environmental activist who approached the NGT.
- The site of Karbatal wetlands was designated as Bird Sanctuary by the Government of Bihar in 1989.
- It was designated as a Ramsar site in 2020 and is recognized as Asia's largest freshwater oxbow lake.
- The wetland, comprising a cluster of 16-17 waterbodies and serving as a catchment area for rainwater, has faced encroachment over time, leading to allegations that the area has been permitted to diminish.
- According to the 2019 post-monsoon report, approximately 82% of the site was marshland (with 25% of it being cultivated), 16% was open water, and the remainder consisted of plantations or borrow land.
- Environmental experts have raised concerns that encroachment and the drying of the lake have severely impacted birds by depriving them of their habitat.
Oxbow Lake
- An oxbow lake is a curved lake formed alongside a winding river as a result of erosion and sediment deposition over time.
- Oxbow lakes are typically crescent-shaped and are common features in floodplains and low-lying areas near rivers.
Ramsar Site
- Ramsar Convention on Wetlands is an intergovernmental treaty adopted in 1971 in the Iranian city of Ramsar, on the southern shore of the Caspian Sea.
- It came into force for India on 1st February, 1982. Those wetlands which are of international importance are declared as Ramsar sites.
- The Convention’s mission is “the conservation and wise use of all wetlands through local and national actions and international cooperation, as a contribution towards achieving sustainable development throughout the world”.
- The Montreux Record is a register of wetland sites on the List of Wetlands of International Importance where changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological developments, pollution or other human interference.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan