Biodiversity & Environment
UN Sustainable Development Report 2024
- 20 Jun 2024
- 10 min read
For Prelims: United Nations, Sustainable Development Goals, Least developed countries, OECD, Climate Finance
For Mains: Progress of India in Achieving SDGs, Measures to Boost SDG Financing.
Why in News?
Recently, the 9th edition of the Sustainable Development Report released by UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN) has highlighted that the world is significantly behind schedule in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations in 2015.
UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN)
- It is a global network established in 2012 by the United Nations (UN).
- It aims to promote practical solutions for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) at national and international levels.
- It focuses on mobilising expertise by connecting universities, research institutions, and national laboratories to identify and develop solutions for tackling critical sustainability challenges.
- The Secretariat of the SDSN is located in Paris, France; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia and New York, US.
What are the Key Findings of the Sustainable Development Report 2024?
- Global SDG Progress:
- Only 16% of SDG targets are on track to be achieved by 2030, with 84% showing limited or reversed progress.
- Since 2020, global SDG progress has stagnated, particularly for SDGs 2 (Zero Hunger), 11 (Sustainable Cities), 14 (Life Below Water), 15 (Life on Land), and 16 (Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions).
- Significant reversals in progress is observed in obesity rates (SDG 2), press freedom (SDG 16), red list index (SDG 15), sustainable nitrogen management (SDG 2), and life expectancy at birth (SDG 3), influenced by Covid-19 and other factors.
- Progress towards SDG9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure), is showing slightly positive trends.
- Food and Land Systems:
- SDG targets related to food and land systems are off-track.
- It reported that globally 600 million people will still suffer from hunger by 2030 combined with increasing obesity globally.
- Greenhouse gas emissions from Agriculture, Forestry, and Other Land Use (AFOLU) represent almost a quarter of annual global GHG emissions.
- Regional and Country Group Variations:
- Nordic countries lead in SDG achievement, with Finland (score 86.4) ranked first, followed by Sweden (85.7), Denmark (85.0), Germany (83.4), and France.
- BRICS and BRICS+ countries (Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE) have shown faster-than-average SDG progress since 2015.
- Bottom 3 Countries: South Sudan, Central African Republic and Chad.
- East and South Asia are the regions with the most SDG progress since 2015.
- Investment Challenges:
- According to the World Bank, about 10% of the world's population lives in extreme poverty, surviving on less than USD 1.90 a day.
- It also reports that only 43% of adults in low-income countries (LICs) have access to formal financial services, limiting their ability to invest and save for the future.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimates that LICs face an annual gap of USD 290 billion in funding for their SDGs.
- The Global Education Monitoring Report by UNESCO states that around 262 million children and youth are out of school, with more than half of them in sub-Saharan Africa and Southern Asia.
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) highlights that around 152 million children are involved in child labour, depriving them of education and proper development opportunities.
- According to the World Bank, about 10% of the world's population lives in extreme poverty, surviving on less than USD 1.90 a day.
- Global Cooperation:
- The report has introduced a new Index on countries' support to UN-based multilateralism (UN-Mi) ranks countries based on their engagement with the UN system.
- Barbados has topped the Un-Mi index followed by Antigua and Barbuda, Uruguay, Mauritius, and the Maldives.
- Bottom 5 countries include the United States, Somalia, South Sudan, Israel, and the Democratic Republic of Korea..
- This index takes into account factors such as treaty ratification, votes at the UNGA, membership in UN organizations, participation in conflicts and militarisation, use of unilateral sanctions, and financial contributions to the UN.
What is the Performance of India in SDG Index?
- Ranking: India secured 109th rank with the overall score of 64.0.
- Status of SDG Targets: Only around 30% of SDG targets are on track or have been achieved.
- There is limited progress in the other 40% of the targets and in around 30% of targets the situation is worsening.
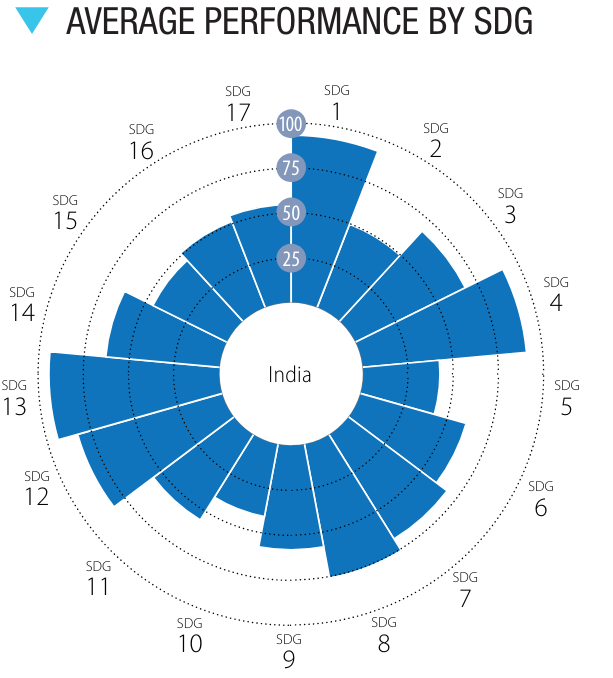
- Average Performance of SDGs: Highest performance is observed in achieving SDG 1, SDG 4, SDG 12 and SDG 13.
- SDG Dashboard and Trends:
- International Spillover Index: This index is a metric used to assess how a country's actions impact the ability of other countries to achieve the SDGs.
- It measures the international ripple effects of a country's policies and practices.
- It considers three main dimensions of these effects.
- Environmental & social impacts embodied in trade (e.g., pollution caused by production for export).
- Economic & financial spillovers (e.g., financial crises spreading across borders).
- Security spillovers (e.g., instability in one country impacting the safety of others).
- Statistical Performance Index: India scored 74.5 in this index.
- It measures the strength of a country's national statistical system. A higher score indicates a country has a more reliable and comprehensive statistical system, which is crucial for effectively tracking progress towards the SDGs.
What are the Key Recommendations of the Report?
- Strengthen Global Cooperation and Multilateralism: The report recommends nations to collaborate by sharing resources, preventing duplication of efforts, and developing fair solutions for global issues.
- Revitalised international institutions, clear goals, tracking systems, and engagement from all stakeholders are crucial.
- Examples such as the Paris Agreement and the Montreal Protocol illustrate the power of collaboration.
- Addressing Financing Gaps for Sustainable Development: The report recommends setting up new institutional frameworks to facilitate and channel financing towards sustainable development initiatives.
- It proposes the implementation of innovative global taxation mechanisms to generate additional resources for sustainable development.
- The report calls for a shift in investment priorities towards funding public goods, such as quality education (SDG 4), as a crucial component of sustainable development.
- It emphasises the need to improve the availability and accessibility of affordable long-term capital, particularly for low and middle-income countries.
- "FABLE" Pathways: Innovative solutions, such as the "FABLE" (Food, Agriculture, Biodiversity, Land-Use, and Energy) pathways should be implemented to address the challenges in the food and land systems.
- Reducing overconsumption and limiting the intake of animal-based protein emphasising the need to respect cultural preferences and dietary habits.
- Targeted investments to enhance agricultural productivity, particularly in high-demand areas.
- Establishment of inclusive and transparent monitoring systems involving various stakeholders and local communities to curb deforestation.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss India's progress towards achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and analyse the key challenges hindering its path. How can India further accelerate its efforts to meet the SDGs by 2030? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Sustainable Development Goals were first proposed in 1972 by a global think tank called the ‘Club of Rome’.
- The Sustainable Development Goals have to be achieved by 2030.
- Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. Sustainable development is described as the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In this perspective, inherently the concept of sustainable development is intertwined with which of the following concepts? (2010)
(a) Social justice and empowerment
(b) Inclusive Growth
(c) Globalization
(d) Carrying capacity
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).” Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)
Q. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient the education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)