Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Spreading Awareness on Cleanliness
Why in News?
Women from a self-help group in Burhanpur, Madhya Pradesh, are going door-to-door to raise awareness about cleanliness among the locals.
Key Points
- The municipal corporation has offered a special job to women in self-help groups to promote cleanliness in households in the region, paying them ₹100 for the task.
- Under this initiative, women associated with the Vaibhav Lakshmi Self-Help Group are going door-to-door in areas like Mahajanapeth and Shikarpura and spreading information related to cleanliness to the locals.
Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
- These are informal associations of people who choose to come together to find ways to improve their living conditions.
- It can be defined as a self governed, peer controlled information group of people with similar socio-economic background and having a desire to collectively perform common purpose.
- Villages face numerous problems related to poverty, illiteracy, lack of skills, lack of formal credit etc. These problems cannot be tackled at an individual level and need collective efforts.
- Thus SHG can become a vehicle of change for the poor and marginalized. SHG relies on the notion of “Self Help” to encourage self-employment and poverty alleviation.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Meteorological Department Issues Warning in Madhya Pradesh
Why in News?
The Meteorological Department in Madhya Pradesh has issued a warning for 15 districts. Over the past few days, the state has experienced storms, rain, and hailstorms in various areas.
Key Points
- Due to western disturbance, cyclonic circulation and trough line, a strong system is active in the state. There may be more activity of two western disturbances in the coming days. Due to this, rain and hail are expected.
- The Meteorological Department has also issued advisory for the people.
Western Disturbances
- These are a series of cyclonic storms that originate in the Mediterranean region, travel over 9,000 km to bring winter rains to northwest India.
- A Western Disturbance collects moisture from the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, and Caspian Sea and traverses over Iran and Afghanistan before hitting the western Himalayas.
- Western Disturbances are the primary source of snowfall that replenishes the Himalayan glaciers during winter.
- These glaciers feed major Himalayan rivers like the Ganga, Indus and Yamuna as well as myriad mountain springs and rivulets.
Monsoon Trough
- A trough is a belt of low pressure extending to a large area. This trough is seen during monsoon period, hence known as Monsoon trough.
- Monsoon trough is a part of the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) where the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere winds meet.
- This is normally shown as a line connecting the location of monsoon low pressure areas. These troughs run across continents during peak monsoon periods.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
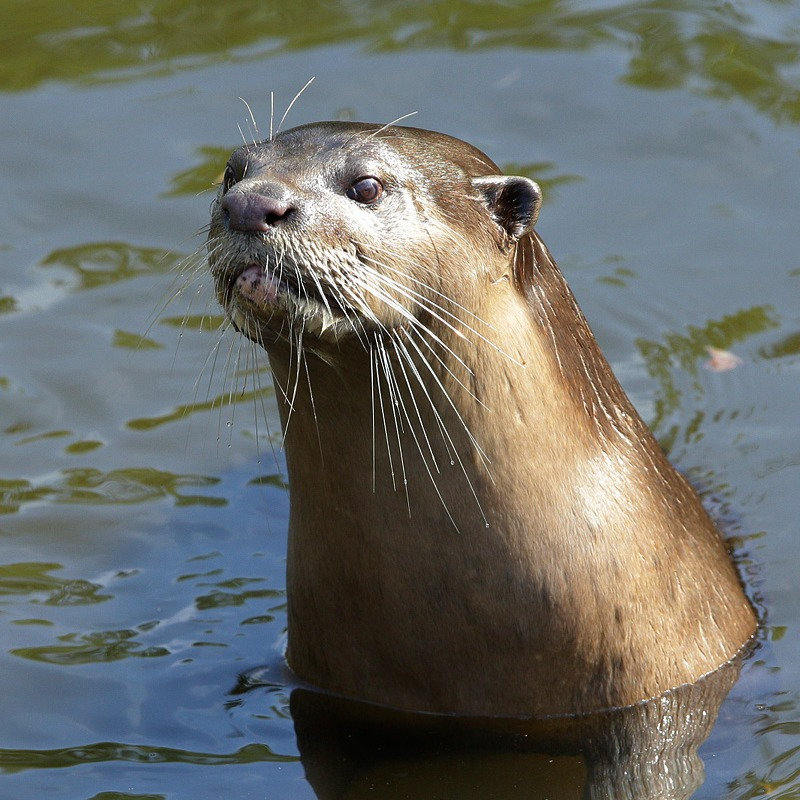
Eurasian Otter Radio-Tagged in Satpura Tiger Reserve
Why in News?
For the first time in India, a Eurasian otter was radio-tagged in the Satpura Tiger Reserve (STR) in Narmadapuram district in Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- There are three species of otters commonly found in India — smooth-coated otter, Asian small-clawed otter, and Eurasian otter.
- Apart from the smooth-coated otter, there had been no proof of the presence of the remaining two otter species in Central India until 2016 when the Eurasian otter was first captured on camera in STR, marking the expansion of the species' habitat to Central India.
- To fill this deficiency, a project was launched in Satpura in 2019 by the Madhya Pradesh forest department in partnership with Wildlife Conservation Trust (WCT).
- The aim is to investigate the ecology of Eurasian otters and explore forest riverine ecosystems, with backing from the Astral Foundation and the Alkyl Amines Foundation.
- Wildlife Conservation Trust is an Indian not-for-profit organisation based in Mumbai which was registered in 2002.
Smooth-Coated Otter
- It is a species of otter.Its scientific name is Lutrogale perspicillata.
- Distribution:
- They are found throughout much of southern Asia, from India eastward.
- There is also an isolated population found in the marshes of Iraq.
- Habitat:
- They are mostly found in lowlands, coastal mangrove forests, peat swamp forests, freshwater wetlands, large forested rivers, lakes, and rice paddies.
- Some build permanent burrows near water with an underwater entrance and a tunnel that leads to a chamber above the high-water line.
- Although adapted for water, smooth-coated otters are equally comfortable on land and can travel long distances overland in search of suitable habitat.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
Small-Clawed Otter
- Its scientific name is Aonyx cinereus.
- Distribution:
- It has a wide distribution range, extending through India in South Asia to eastwards in Southeast Asia and Southern China.
- In India it is found mostly in the protected areas of West Bengal, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh and in Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and some parts of Kerala in the Western Ghats region.
- They are primarily found in freshwater habitats such as rivers, streams, and wetlands.
- They feed on fish, crustaceans, and mollusks.
- Conservation Status:
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule I
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
Eurasian Otter
- About:
- It is a semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal.
- Its scientific name is Lutra lutra.
- Distribution:
- It has one of the widest distributions of all Palaearctic mammals.
- Its range covers parts of three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- In India, it occurs in northern, northeast, and southern India.
- Habitat:
- It lives in a wide variety of aquatic habitats, including highland and lowland lakes, rivers, streams, marshes, swamp forests, and coastal areas.
- In the Indian subcontinent, Eurasian otters occur in cold hills and mountain streams.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Near threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II
- CITES: Appendix I
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
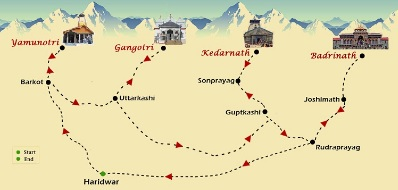
Char Dham Yatra
Why in News?
According to the Uttarakhand tourism department, the online registration for the 'Char Dham Yatra' has started on the tourism department's portal.
Key Points
- The Char-Dham yatra in Uttarakhand consists of visiting four temples, Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri.
- The Char Dham Yatra holds profound spiritual significance in Hinduism. This journey typically occurs from April/May to October/November.
Char Dham Yatra
- Yamunotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Yamuna.
- River Yamuna is the second-most sacred river in India after River Ganga.
- Gangotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Ganga.
- Considered the most sacred of all Indian rivers.
- Kedarnath Dham:
- Location: Rudraprayag district.
- Dedicated to: Lord Shiva.
- Situated on the bank of the Mandakini River.
- One of the 12 Jyotirlingas (divine representations of Lord Shiva) in India.
- Badrinath Dham:
- Location: Chamoli district.
- Home to the sacred Badrinarayan Temple.
- Dedicated to: Lord Vishnu.
- One of the holy shrines for Vaishnavites.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan's Mines Department Plans to Increase Revenue in FY25
Why in News?
The Rajasthan Department of Mines & Geology has developed a strategy to increase revenue during the current financial year (FY25).
Key Points
- Rajasthan is one of the richest states in terms of availability and variety of minerals, producing over 57 types of minerals.
- The mines department earned a revenue of over Rs 7,490 crore during FY2024.
- A plan has been made to ensure daily monitoring by preparing a road map for exploration, drilling, preparing blocks and plots for auction, creating an auction calendar, and revenue collection.
- According to the plan, better coordination with the concerned departments including forest, district administration, and police administration would be strengthened to stop illegal mining activities.
- There should be a regular system for collecting the revenue due to the government so that there is no need to make much effort for recovery at the last moment.
Illegal Mining
- Illegal mining is the extraction of minerals, ores, or other valuable resources from land or water bodies without the necessary permits, licenses, or regulatory approvals from government authorities.
- It can also involve the violation of environmental, labor, and safety standards.
- Government Initiatives Related to Mining
- National Mineral Policy 2019: It aims to increase mineral exploration and production, promote sustainable mining practices, and streamline regulatory processes.
- Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY): It is a welfare scheme for mining-affected areas, and the Sagarmala project, which aims to develop port infrastructure to support the growth of the mining sector.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Pahariya Tribe
Why in News?
Jharkhand’s Pahariya tribe aims to achieve seed independence by depositing native varieties in community-led banks.
Key Points
- In 2019, four community-led seed banks were set up in the hilly districts of Pakur and Godda. The banks cater to more than 1,350 households in 90 villages.
- They are operated under four panchayats: Bara Paktari, Bara Sindari, Kunjbona and Karma Tarn, and are managed by women-led committees.
- To register with the seed banks, members must deposit 2.5 kg of indigenous seeds. Seeds are also provided through state government programmes.
- During sowing season, the committees decide distribution on a case-by-case basis. So far, they have distributed 3,679 kg of seeds.
- Members currently provide 0.5 kg of seeds after every harvest to replenish the stocks.
- With immediate demands fulfilled, the residents are now focusing on improving crop yield and becoming self-sufficient in food.
Pahariya Tribe
- They live mainly in the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal. They are the original inhabitants of the Rajmahal Hills, known today as the Santal Parganas division of Jharkhand.
- They are listed as a Scheduled Tribe by the governments of West Bengal, Bihar and Jharkhand.
- They speak Malto, a Dravidian language.
- They practice jhum or shifting cultivation which involves clearing land by burning vegetation for farming for a few years.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan