Indian Heritage & Culture
Pilgrim Safety Challenges in Char Dham Yatra
- 29 Jun 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Char Dam Project, Char Dham yatra, Flash floods, Landslides
For Mains: Disaster management challenges
Why in News?
The Char Dham yatra, a pilgrimage to four sacred Hindu shrines in the Himalayas, has witnessed a high number of deaths among the devotees this year.
- According to official data, 149 pilgrims have died since the commencement of the yatra in April 2023, mostly due to cardiac arrest and other health ailments. The yatra, which attracts millions of pilgrims every year, has also been marred by road accidents and landslides.
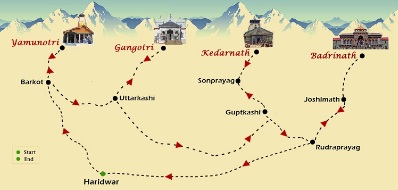
What is Char Dham Yatra?
- About:
- Char Dham Yatra is a pilgrimage circuit in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
- It involves visiting four sacred Hindu shrines located in the Himalayas.
- The four shrines included in the yatra are Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri.
- It is believed that one should complete the Char Dham Yatra in a clockwise direction: Yamunotri, Gangotri, Kedarnath, and Badrinath.
- Religious Significance:
- Each of these shrines holds significant religious and mythological importance in Hinduism.
- It is believed that undertaking the Char Dham Yatra can cleanse one's sins and lead to spiritual salvation.
- Pilgrimage Season:
- Usually starts in April or May and continues until November, depending on weather conditions.
- The yatra involves trekking through challenging terrains, including high altitudes and mountainous regions.
- Economic Importance:
- The yatra is not only a religious journey but also a significant cultural and tourism event for Uttarakhand, attracting visitors from across India and around the world.
- It holds great economic importance for the local communities, providing employment opportunities and boosting the tourism industry in the region.
- Note:
- Yamunotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Yamuna.
- River Yamuna is the second-most sacred river in India after River Ganga.
- Gangotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Ganga.
- Considered the most sacred of all Indian rivers.
- Kedarnath Dham:
- Location: Rudraprayag district.
- Dedicated to: Lord Shiva.
- Situated on the bank of the Mandakini River.
- One of the 12 Jyotirlingas (divine representations of Lord Shiva) in India.
- Badrinath Dham:
- Location: Chamoli district.
- Home to the sacred Badrinarayan Temple.
- Dedicated to: Lord Vishnu.
- One of the holy shrines for Vaishnavites .
- Yamunotri Dham:
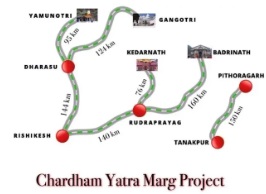
What is the Char Dam Project?
- Char Dam Project is a major infrastructure initiative in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
- It aims to improve connectivity and pilgrimage tourism to the four holy Hindu sites, known as Char Dham.
- Expected to boost tourism, trade, transport, and employment opportunities in Uttarakhand.
- Enhances safety and security for pilgrims and strengthens military operations in border areas.
- Facilitates disaster management and relief operations in emergencies.
What are the Disaster Management Challenges of Char Dham Yatra?
- Disaster Management Challenges:
- Harsh Weather Conditions:
- Extreme Temperatures: Exposure to cold temperatures can lead to hypothermia and other health complications.
- Snowfall: Makes the pilgrimage route slippery and difficult to navigate.
- Vulnerable Terrain:
- Mountainous Region: Steep slopes and rugged terrain pose challenges for infrastructure development and maintenance.
- Remote Locations: Limited access to medical facilities, emergency services, and communication networks.
- Limited Evacuation Routes: In the event of a disaster or medical emergency, evacuating pilgrims from remote areas becomes challenging.
- Health Hazards:
- High Altitudes: Pilgrims experience altitude sickness, which can lead to dizziness, nausea, and shortness of breath.
- Strenuous Treks: Long and arduous walks, especially at higher altitudes, can cause physical exhaustion and injuries.
- Lack of Acclimatization: Insufficient time for pilgrims to adjust to the high altitudes and harsh weather conditions.
- Natural Disasters:
- Landslides: Unstable slopes and heavy rainfall increase the risk of landslides, obstructing the pilgrimage route.
- Flash floods: Sudden and intense rainfall can result in flash floods, posing dangers to pilgrims near rivers and streams.
- In June 2013 flash floods of Kedarnath killed thousands of pilgrims and left many stranded.
- Earthquakes: Uttarakhand falls under a seismic zone, making it susceptible to earthquakes, which can trigger landslides and infrastructure damage.
- Harsh Weather Conditions:
- Precautionary Measures and Mitigation Strategies:
- Weather Monitoring and Early Warning Systems:
- Install weather monitoring stations along the pilgrimage route to track weather changes and implement an early warning system for severe weather events.
- Infrastructure Development and Maintenance:
- Improve road infrastructure, including widening and strengthening roads, constructing protective barriers in landslide-prone areas, and encouraging public-private partnerships for easy and safe travel.
- Preventing Soil Erosion and Landslides:
- Implement slope stabilization techniques and afforestation programs to prevent soil erosion and landslides.
- Emergency Services and Medical Facilities:
- Establish medical facilities and emergency response centers along the route, improve communication networks, and provide training for medical staff and emergency responders.
- Pilgrim Safety and Awareness:
- Conduct pre-yatra orientation programs, provide detailed route information, and encourage medical check-ups for pilgrims.
- Disaster Response and Evacuation Plans:
- Develop comprehensive disaster response plans, designate safe assembly points and temporary shelters, and conduct regular mock drills to ensure preparedness.





-min.jpg)