Bihar Switch to Hindi
PM Inaugurates Various Projects in Bihar
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister laid the foundation for the All India Institute of Medical Science (AIIMS) hospital and other projects worth Rs 12,100 crore in Darbhanga, Bihar.
- 25 additional projects in rail, road, health, and energy sectors were also inaugurated across the region.
Key Points
- About the Projects:
- AIIMS, Darbhanga Project:
- The AIIMS project in Darbhanga, costing Rs 1264 crore and covering 187 acres in the Sobhan area, is expected to be completed within three years.
- This will be the second AIIMS in Bihar, aimed at expanding healthcare infrastructure in the state.
- The project will feature a super-speciality hospital, an AYUSH block, a medical college, a nursing college, along with a night shelter and residential facilities for staff.
- It will provide advanced tertiary healthcare services for people in Bihar and nearby regions.
- Jan Aushadhi Kendras:
- The PM will dedicate 18Jan Aushadhi Kendras at railway stations nationwide to increase the availability of affordable medicines.
- These centers aim to promote the use of generic medicines, helping to lower healthcare costs for passengers.
- It was launched to provide affordable and quality medicines, particularly for the poor and disadvantaged, and was revamped as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Yojana (PMJAY) in September 2015.
- National Highway Development:
- The PM will inaugurate and lay the foundation stones of several highway projects worth Rs 5,070 crore.
- This includes the new four-lane Galgalia-Araria section on NH-327E, providing an alternative route from Araria to West Bengal.
- Railway Infrastructure Projects:
- Railway projects worth over Rs 1,740 crore will be inaugurated, including gauge conversions and a bypass line to ease traffic congestion.
- New Mainline Electric Multiple Unit (MEMU) train services in the Jhanjharpur-Laukaha Bazar section will improve access to jobs and education for nearby communities.
- A MEMU is an Electric Multiple Unit (EMU) train that serves short and medium-distance routes.
- Petroleum and Natural Gas Sector Initiatives:
- The PM will initiate projects worth more than Rs 4,020 crore in the petroleum and natural gas sector.
- These include a City Gas Distribution network in five districts of Bihar – Darbhanga, Madhubani, Supaul, Sitamarhi and Sheohar – by the Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited.
- The PM also laid the foundation stone for a new bitumen-manufacturing unit at the Barauni refinery to reduce dependency on imports.
- AIIMS, Darbhanga Project:
AYUSH
- AYUSH is the acronym of the medical systems that are being practised in India such as:
- Ayurveda: Ancient system emphasising holistic well-being.
- Yoga: Union of body, mind, and spirit through physical postures and meditation.
- Naturopathy: Natural healing using elements like water, air, and diet.
- Unani: Balance restoration through herbal medicines and humoral theory.
- Siddha: Traditional Tamil medicine with roots in five elements and humours.
- Homeopathy: Highly diluted remedies stimulating self-healing responses.
- These systems are based on definite medical philosophies and represent a way of healthy living with established concepts on prevention of diseases and promotion of health.
- The Ministry of AYUSH, is responsible for developing education, research and propagation of AYUSH in India.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
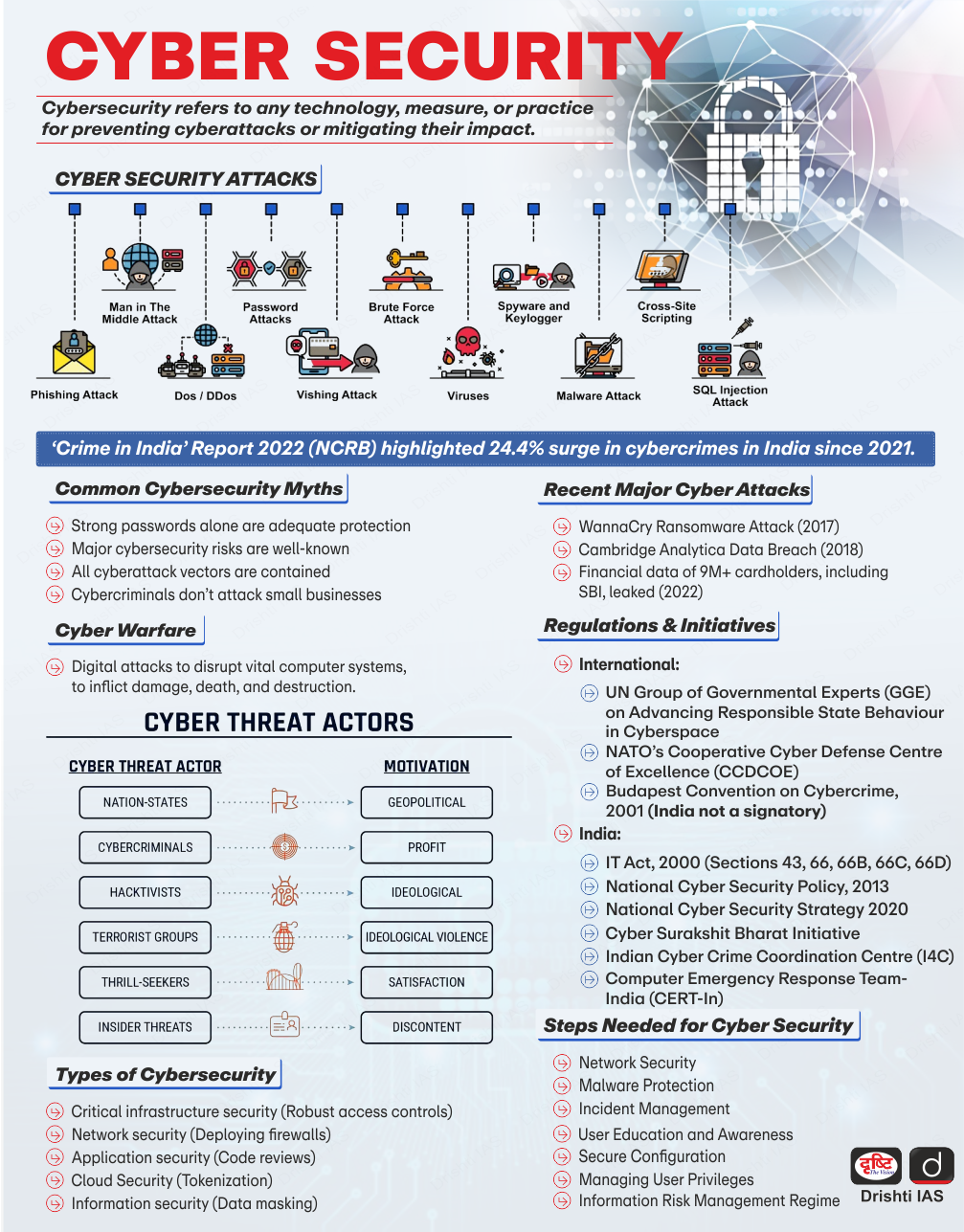
Cybersecurity Workshop in Uttar Pradesh
Why in News?
Recently, the National e-Governance Division (NeGD) of Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) in collaboration with the Government of Uttar Pradesh, organised a two-day Cybersecurity Workshop in Lucknow.
Key Points
- Cybersecurity Training Program by NeGD:
- NeGD’s Cybersecurity Training Program, part of the State Capacity Building Scheme, is designed to strengthen cybersecurity resilience among state government officials.
- The program equips Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and Deputy CISOs with critical skills to handle and mitigate cyber risks effectively.
- The NeGD was established in 2009 by the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology as an Independent Business Division under the Digital India Corporation.
- Its aim was to facilitate and catalyze the implementation of the Digital India Program across Ministries and State Governments.
- Objective:
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Increase understanding of cybersecurity issues, cyber threats, and e-governance frameworks.
- Cyber Resilience and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enhance participants’ knowledge of the Cyber Resilience Ecosystem and the role of AI in cybersecurity.
- Cyber Suraksha Kendra: Educate on the importance of Cyber Suraksha Kendra for protecting state-level e-governance systems.
- Data and Application Security: Provide insights into data protection (Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023) application security, and endpoint security.
- Crisis Management: Train participants in developing Cyber Crisis Management Plans (CCMP) for effective incident response.
- Identity and Access Management: Address challenges in identity and access management to secure government digital systems.
- State Capacity-Building Scheme:
- NeGD, under MeitY, has launched a series of capacity-building workshops for state leaders, CISOs, and officials across the nation.
- These workshops provide practical training and best practices for managing cyber threats, adopting secure IT frameworks, and strengthening digital governance.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- It aims to protect the digital personal data of individuals in India and regulate the collection, storage, processing, and sharing of such data.
- Key features:
- Establishes a Data Protection Board of India to enforce compliance.
- Requires explicit consent for data collection and processing.
- Mandates data fiduciaries to implement reasonable security safeguards.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Impact of PMUY in Jammu and Kashmir
Why in News?
A study was conducted to assess the impact of Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Under the scheme the government has distributed 10.3 crore Liquified Petroleum Gas connections.
Key Points
- Methodology and Aim of the Study:
- The study collected primary data from 820 households across 48 villages in Kulgam and Rajouri, two relatively disadvantaged districts in J&K.
- This study investigates the PMUY's impact on clean cooking fuel adoption in the districts, focusing on socio-economic and health outcomes, barriers to exclusive LPG use, and the role of awareness.
- The sample includes representation from various economic groups:
- The study collected primary data from 820 households across 48 villages in Kulgam and Rajouri, two relatively disadvantaged districts in J&K.
- Findings of the Study:
- LPG Connection Adoption:
- In rural J&K, 85.07% of households have official LPG connections, with 68% of these obtained through the PMUY.
- Only 4.41% of rural households, primarily in hilly areas like Rajouri, lack access to LPG, while 10.53% rely on unofficial connections.
- Despite increased LPG availability, traditional cooking methods remain common:
- 92% of households still use traditional chulhas, and 85% engage in fuel stacking by using both solid fuels and LPG.
- Health Benefits for PMUY Beneficiaries:
- PMUY adoption has led to significant health improvements for women, by reducing exposure to smoke from traditional fuels.
- Among BPL households, respiratory issues were reduced.
- AAY households also saw reduced health issues from 13% among non-beneficiaries to 10% for beneficiaries.
- Barriers to Exclusive LPG Usage:
- Lack of awareness remains a barrier, with 47% of households unaware of solid fuel health risks.
- The cost of LPG refills is prohibitive for many, leading to fuel stacking with cheaper solid fuels.
- Fuel stacking remains common in 85% of households, highlighting the need for additional financial support.
- Recommendations:
- Expanding the LPG distribution network in rural areas and providing additional financial support for refills can further promote clean fuel adoption and reduce reliance on solid fuels.
- LPG Connection Adoption:
Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- About:
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, introduced the ‘Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana’ (PMUY) as a flagship scheme with the objective of making clean cooking fuel such as LPG available to the rural and deprived households which were otherwise using traditional cooking fuels such as firewood, coal, cow-dung cakes etc.
- Usage of traditional cooking fuels had detrimental impacts on the health of rural women as well as on the environment.
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, introduced the ‘Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana’ (PMUY) as a flagship scheme with the objective of making clean cooking fuel such as LPG available to the rural and deprived households which were otherwise using traditional cooking fuels such as firewood, coal, cow-dung cakes etc.
- Objectives:
- Empowering women and protecting their health.
- Reducing the number of deaths in India due to unclean cooking fuel.
- Preventing young children from a significant number of acute respiratory illnesses caused due to indoor air pollution by burning fossil fuel.
- Features:
- The scheme provides a financial support of Rs 1600 for each LPG connection to the BPL households.
- Along with a deposit-free LPG connection, Ujjwala 2.0 will provide the first refill and a Stove, free of cost to the beneficiaries.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
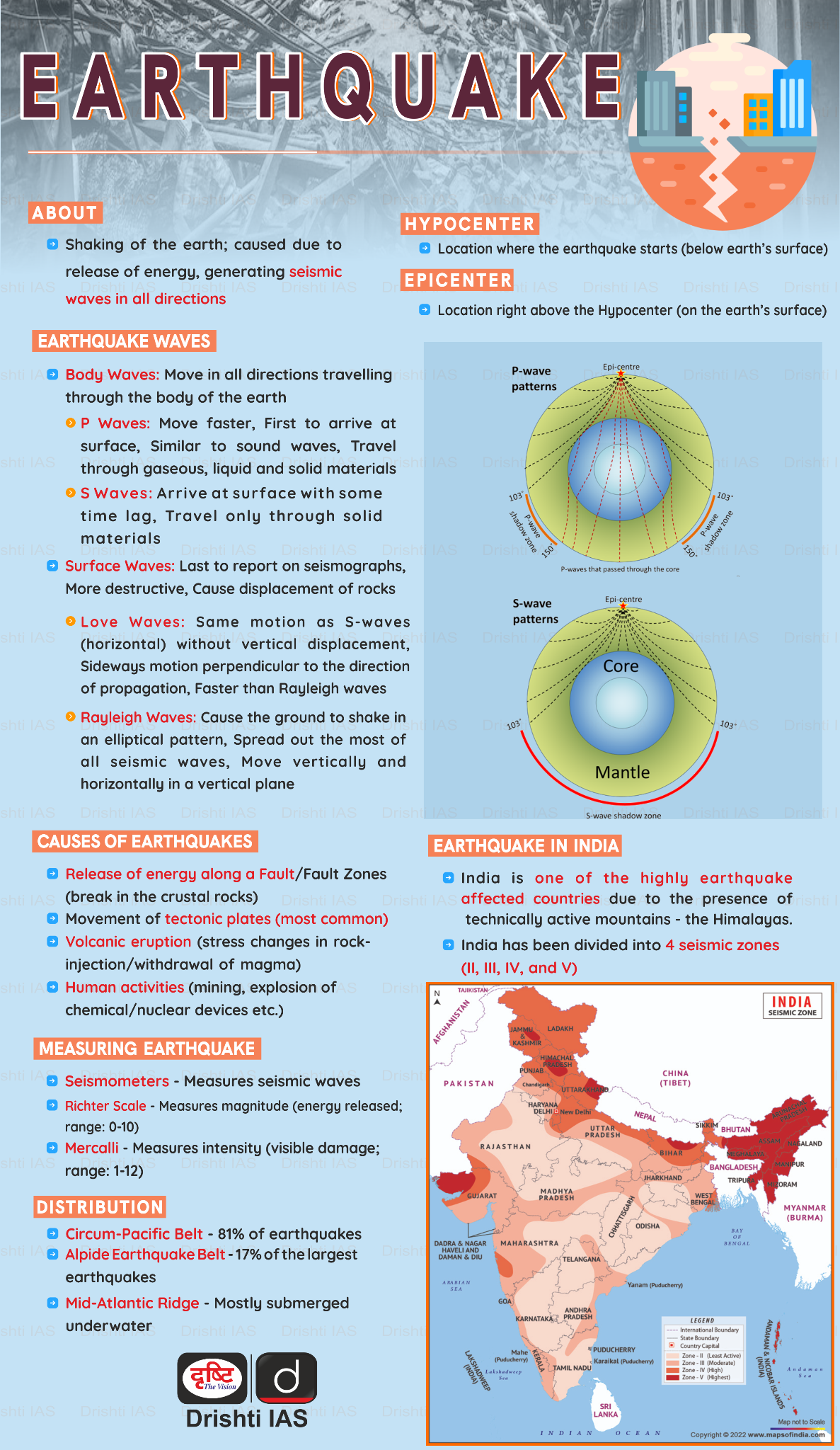
Earthquake in Jammu and Kashmir
Why in News?
Recently, an earthquake with a magnitude of 5.2 struck Jammu and Kashmir, but no loss of life or damage to property was reported.
- The earthquake originated in the Afghanistan region, with its tremors reaching the Kashmir Valley.
Key Points
- An earthquake is a natural phenomenon characterised by a sudden shaking of the ground caused by the passage of seismic waves through Earth's rocks.
- The vibrations called seismic waves are generated from earthquakes that travel through the Earth and are recorded on instruments called seismographs.
- The location below the earth’s surface where the earthquake starts is called the hypocenter, and the location directly above it on the surface of the earth is called the epicenter.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Leopard Died in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve
Why in News?
Recently, a leopard died at Madhya Pradesh’s Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (BTR).
- Earlier a group of elephants had also died in the BTR due to toxicity from over consumption of fungal-infected kodo millet plants.
Key Points
- About Leopard:
- The leopard (Panthera pardus) is the smallest of the Big Cat family (of genus Panthera namely the Tiger, Lion ,Jaguar, Leopard, and Snow Leopard), and is known for its ability to adapt in a variety of habitats.
- A nocturnal animal, feeds on smaller species of herbivores found in its range, such as the chital, hog deer and wild boar.
- Melanism in Leopards:
- Melanism is a common occurrence in leopards, wherein the entire skin of the animal is black in colour, including its spots.
- A melanistic leopard is often called a black panther and is mistakenly thought to be a different species.
- Melanism is a common occurrence in leopards, wherein the entire skin of the animal is black in colour, including its spots.
- Geographical Extent:
- Members of the cat family, leopards live in Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Russia, and the Indian subcontinent.
- The Indian leopard (Panthera pardus fusca) is found extensively across the Indian subcontinent.
- Members of the cat family, leopards live in Asia, sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Russia, and the Indian subcontinent.
- Population in India:
- As per the ‘Status of Leopards in India, 2022’, India's leopard population rose by 8% from 12,852 in 2018 to 13,874 in 2022.
- About 65% of the leopard population is present outside protected areas in the Shivalik landscape. Only about a third of the leopards are within protected areas.
- Madhya Pradesh has the highest number of leopards (3,907), followed by Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- As per the ‘Status of Leopards in India, 2022’, India's leopard population rose by 8% from 12,852 in 2018 to 13,874 in 2022.
- Threat:
- Habitat loss
- Poaching
- Human-wildlife conflict
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule I
Haryana Switch to Hindi
New SC Reservation Categories in Haryana
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Haryana implemented sub-classification within the Scheduled Castes (SC) for reservation in government jobs.
Key Points
- Supreme Court Ruling on SC Sub-Classification:
- On 1st August 2024, the Supreme Court ruled that states have the constitutional authority to create sub-classifications within the Scheduled Castes (SC) category, acknowledging its social diversity.
- Following the ruling, the Haryana government approved the SC sub-classification in its first cabinet meeting.
- Sub-Divisions in Haryana:
- The Haryana State Commission for Scheduled Castes recommended dividing SC reservations into two categories:
- Deprived Scheduled Castes (DSC): It includes 36 castes, such as Dhanaks, Balmikis, Mazhabi Sikhs, and Khatiks, which would receive 50% of the SC reservation quota in jobs due to inadequate representation.
- Other Scheduled Castes (OSC): It includes castes like Chamar, Jatia Chamar, Rehgar, Raigar, Ramdasi, Ravidasi, Jatav, Mochi, and Ramdasia.
- The Haryana State Commission for Scheduled Castes recommended dividing SC reservations into two categories:
- Educational Quota for DSC in Haryana:
- In 2020, Haryana enacted the Scheduled Castes (Reservation in Admission in Educational Institutions) Act, reserving 50% of SC seats in higher education institutions for the DSC category.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan