Haryana Switch to Hindi
Waste Crisis in Gurugram
Why in News?
A 2024 survey by the Municipal Corporation of Gurugram (MCG) identified around 100 illegal dumping spots in the city, with the Aravallis along the Gurugram-Faridabad Road among the worst affected.
- Despite declaring a waste crisis in 2024, authorities have failed to appoint a dedicated waste collection agency since 2021.
Key Points
- About the Issue:
- Despite being discussed during Lok Sabha and Vidhan Sabha elections, the issue of illegal dumping failed to gain significant attention.
- With conditions worsening, residents are now demanding clear solutions from leaders.
- Environmentalists criticized the lack of action, stating that Gurugram has turned into a massive concrete dumpyard.
- Unchecked debris dumping is clogging green belts, empty spaces, and roads, leading to severe waterlogging.
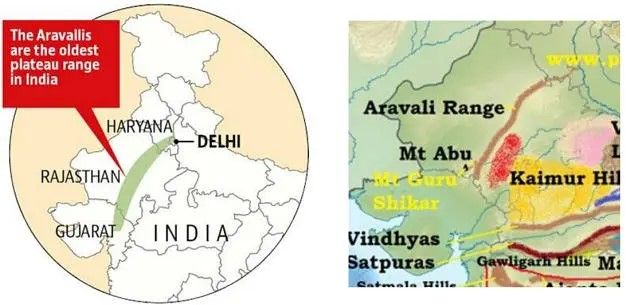
Aravali Mountain Range
- The Aravallis, is the oldest fold mountains on Earth. Geological studies indicate that it is three billion years old.
- It spans over 800 km from Gujarat to Delhi (through Rajasthan and Haryana).
- The highest peak in the Aravalli Range is Guru Peak on Mount Abu.
- Influences Climate:
- The Aravallis have an impact upon the climate of northwest India and beyond.
- During monsoons, the mountain range gently guides the monsoon clouds eastwards towards Shimla and Nainital, thus helping nurture the sub-Himalayan rivers and feeding the north Indian plains.
- During the winter months, it shields the fertile alluvial river valleys of the Indus and Ganga from the harsh cold westerly winds blowing in from Central Asia.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan