Haryana Switch to Hindi
Outrage over Approval of New Slaughterhouses in Nuh District
Why in News?
Recently, the Haryana government's decision to approve 21 additional slaughterhouses in Nuh district has triggered protests from local residents, leading them to approach the National Green Tribunal (NGT) over environmental and health concerns.
Key Points
- Environmental Concerns:
- The NGT has issued notices to the Haryana State Pollution Control Board and Central Ground Water Authority to respond to allegations of contamination in air, water, and soil.
- Residents claim existing slaughterhouses violate pollution norms, leading to degradation of the local environment.
- Health Hazards:
- Local activists report that the villages around these slaughterhouses are experiencing severe health impacts, with children falling ill and blood from slaughterhouses contaminating fields.
- Waste is allegedly being dumped into the soil and water streams, creating an unbearable stench and causing health problems.
- Residents point out the contradiction in policies, with Uttar Pradesh shutting down slaughterhouses, while Haryana is expanding them in Nuh.
National Green Tribunal (NGT)
- It is a specialised body set up under the National Green Tribunal Act (2010) for effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and conservation of forests and other natural resources.
- With the establishment of the NGT, India became the 3rd country in the world to set up a specialised environmental tribunal, only after Australia and New Zealand, and the first developing country to do so.
- NGT is mandated to make disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of filing of the same.
- The NGT has five places of sittings, New Delhi is the Principal place of sitting and Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata and Chennai are the other four.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Army Opens Himalayan Battlefields to Boost Tourism
Why in News?
Recently, in a move to enhance border tourism and match China’s infrastructure efforts along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), the Indian Army has opened up historic battlefield locations in the Himalayas for tourists.
Key Points
- Tourism Infrastructure Development:
- India has identified 100 additional villages along the LAC to create infrastructure for tourism as part of a multi-pronged approach to counter China's efforts in the region.
- The Army is opening up Himalayan locations where key battles, such as the Kargil conflict,1999 took place.
- Tourists are now allowed to visit Tiger Hill, a critical site during the Kargil war.
- Border Security and Deterrence:
- According to the Army, opening these inaccessible areas and developing infrastructure in border regions will act as a deterrent to claims on undemarcated borders with China.
- A pilot project for tourism is being set up in Zemithang, the last Indian village near the LAC in Arunachal Pradesh. This is the route through which the 14th Dalai Lama entered India in 1959.
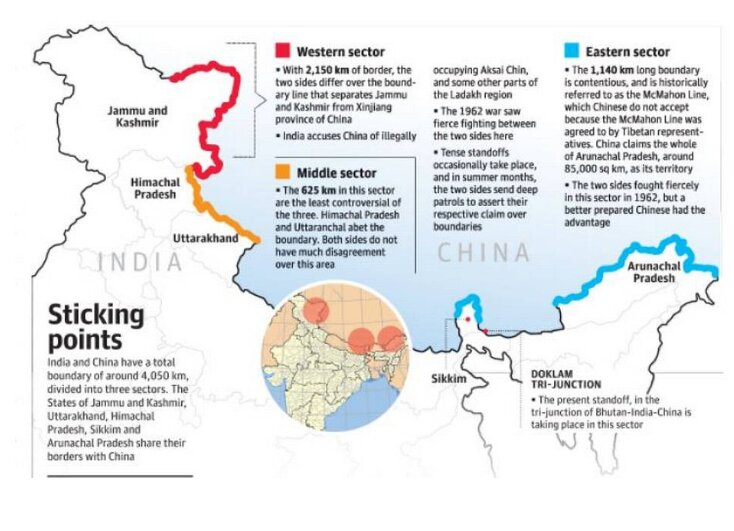
- Line of Actual Control: It is divided into three sectors.
- The eastern sector which spans Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim (1346 km).
- The middle sector in Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh (545 km).
- The western sector in Ladakh (1597 km).
- The alignment of the LAC in the eastern sector is along the McMahon Line of 1914.
- Case of Arunachal Pradesh: India's claim line is different from that of the LAC. It is the line seen in the official boundary marked on the maps as released by the Survey of India, including Aksai Chin (occupied by China). The state of Arunachal Pradesh is an ‘integral and inalienable’ part of India.
- In China’s case, LAC corresponds mostly to its claim line, but in the eastern sector, it claims the entire Arunachal Pradesh as South Tibet.
- China’s Intention: There have been reports of Chinese construction of villages in Arunachal Pradesh, 5 kilometres from the Bum La pass.
- The construction of the village has been seen by analysts as a move to bolster China’s claim to the area, and part of a broader recent push by China to build civilian settlements in disputed frontier areas, which it has also done with Bhutan.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Purple Revolution
Why in News?
The Lavender cultivation success in Jammu and Kashmir exemplifies the powerful collaboration between research institutions, industry, and youth entrepreneurship, offering a path to boost farmers' income and enhance the rural economy.
Key Points
- Aroma Mission and Lavender Cultivation:
- Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) launched the Jammu and Kashmir Aroma Arogya Gram (JAAG) project to promote alternative crops like medicinal and aromatic plants (MAPs).
- The Aroma Mission introduced lavender cultivation to boost farmers’ income and create employment.
- Farmers received free planting material, training, and support in cultivation, processing, and marketing.
- Originating in Bhaderwah, Doda, lavender cultivation has spread to other J&K districts and states like Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland.
- Economic Impact:
- Over 1,300 hectares in J&K are under lavender cultivation, with significant progress in districts like Udhampur, Poonch, and Rajouri.
- Lavender farms have gained national recognition and boosted tourism, as seen in the Republic Day tableau at Kartavya Path.
- In 2024, Doda district extracted 100 kg of lavender oil and harvested 10 quintals of dry flowers, generating significant revenue for farmers.
- Agricultural Challenges in J&K:
- Agriculture employs 65% of the population and contributes 27% to J&K’s economy.
- The region faced challenges like difficult terrain, monkey menace, and poor accessibility, limiting land utilization for traditional crops (rice, maize, wheat, pulses).
- Future Prospects:
- Lavender farming opens opportunities in value-added medicinal and cosmetic products.
- The initiative is a model for rural entrepreneurship, fostering growth in India's path to becoming a developed nation.
Purple Revolution
- Purple revolution is also known as Lavender Revolution and aims to promote the indigenous aromatic crop-based agro-economy by shifting from foreign aromatics to homegrown kinds.
- First-time producers were offered free lavender seedlings as part of the goal, and those who had previously produced lavender were paid Rs. 5-6 per plant.
- The CSIR-Aroma Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM)’s Initiative has begun lavender cultivation in the Ramban district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Lavender farming is done in nearly all of Jammu and Kashmir’s 20 districts.
- Particularly, the districts of Kathua, Udhampur, Doda, Kishtwar, Rajouri, Srinagar, Bandipora, Budgam, Ganderbal, Anantnag, Kulgam, Baramulla etc. have made huge progress in this direction.
- Lavender Cultivation:
- Native to Europe, lavender was introduced in the temperate regions of Jammu & Kashmir by the CSIR Aroma Mission.
- It is a small, perennial aromatic herb shrub used in fragrance, specialty food, and alternative medicine industries.
- Propagation Methods:
- Seeds
- Rooted cuttings
- Tissue culture
- Layering
- Soil:
- Grows well in light, well-aerated soil rich in organic matter.
- Thrives in neutral to alkaline soil that is free-draining.
- Sensitive to waterlogging but can grow in poor or eroded soil.
- Rainfall:
- Performs well with an annual rainfall range between 300 to 1400 mm.
- Climate:
- A hardy temperate plant, tolerant to drought and frost.
- Prefers cool winters and cool summers with ample sunlight.
- Can be cultivated in areas with snowfall and hilly terrain.
- Applications:
- Food and flavouring
- Pharmaceutical and therapeutic uses
- Cosmetic products
- Industrial purposes
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
NIA Court Awards Life Imprisonment in Conversion Case
Why in News?
Recently, a special National Investigation Agency (NIA) court in Lucknow sentenced Islamic scholar and 11 others to life imprisonment in an illegal religious conversion case.
Key Points
- Charges and Convictions:
- The convicts were charged under Section 121A (conspiring to commit certain offences against the state), Section 123 (concealing with intent to facilitate a design to wage war), Section 153A (promoting enmity between different groups based on religion), of the Uttar Pradesh Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion of Religion Act, 2021.
- Arrest and Allegations:
- Islamic Scholar was arrested in 2021 by the Uttar Pradesh Anti-Terrorism Squad from Meerut for allegedly running a nationwide syndicate for illegal religious conversion.
- He was accused of promoting enmity, disturbing India’s sovereignty and integrity, and receiving funds from international organisations to facilitate conversions.
- Islamic Scholar was arrested in 2021 by the Uttar Pradesh Anti-Terrorism Squad from Meerut for allegedly running a nationwide syndicate for illegal religious conversion.
National Investigation Agency (NIA)
- The NIA is the Central Counter-Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency of India mandated to investigate all the offences affecting the sovereignty, security and integrity of India. It includes:
- Friendly relations with foreign states.
- Against atomic and nuclear facilities.
- Smuggling of arms, drugs and fake Indian currency and infiltration from across the borders.
- The offences under the statutory laws enacted to implement international treaties, agreements, conventions and resolutions of the United Nations, its agencies and other international organisations.
- It was constituted under the National Investigation Agency (NIA) Act, 2008.
- The agency is empowered to deal with the investigation of terror related crimes across states without special permission from the states under written proclamation from the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
Uttar Pradesh Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion of Religion Act, 2021
- The law contains stringent provisions with regard to fraudulent or forced conversions.
- It provides for 20 years’ imprisonment or life sentence if it was found that conversion had taken place under threat, promise of marriage or conspiracy. It was placed in the category of most serious crime under the Bill.
- The bill allows any person to register an First Information Report (FIR) in cases related to religious conversion, not only parents, victims, or siblings.
- These cases would not be heard by any court below the sessions court. Bill has also made the crime non-bailable.
- Anyone wishing to convert of their own volition for the purpose of marriage must submit an application to the concerned district magistrate two months in advance.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan