Indian History
Kargil Vijay Diwas
- 26 Jul 2024
- 12 min read
For Prelims: Kargil Vijay Diwas, Kargil War, Nuclear States, Siachen Glacier, Lahore Declaration, Kashmir Conflict, Line of Control (LOC), Operation Vijay, Operation Safed Sagar, Operation Talwar, Kargil Review Committee (KRC), Cold Start Doctrine.
For Mains: Significance of Post-Independence Developments in India’s Neighbourhood and their Impacts.
Why in News?
Kargil Vijay Diwas is celebrated every year on July 26 to pay tribute to the bravery of Indian soldiers who made the ultimate sacrifice for the country during the Kargil War (1999).
- This event marks the conclusion of the Kargil War between India and Pakistan that started in May 1999.
What is Kargil Vijay Diwas?
- About: Kargil Vijay Diwas, or Kargil Victory Day, is a significant day observed annually on July 26 in India.
- The day commemorates India's triumph in the 1999 conflict with Pakistan and honours the bravery and sacrifices of Indian soldiers during the war.
- The Kargil war of 1999 was the first military confrontation in a nuclearized SouthAsia, and arguably the first real war between two Nuclear States.
- Background:
- India and Pakistan have a history of conflicts, including a significant one in 1971 that led to the creation of Bangladesh.
- Post-1971, both nations faced ongoing tensions, particularly vying for control over the Siachen Glacier through military outposts on nearby mountain ridges.
- In 1998, both countries conducted nuclear tests, escalating tensions. The Lahore Declaration in February 1999 aimed to resolve the Kashmir conflict peacefully and bilaterally.
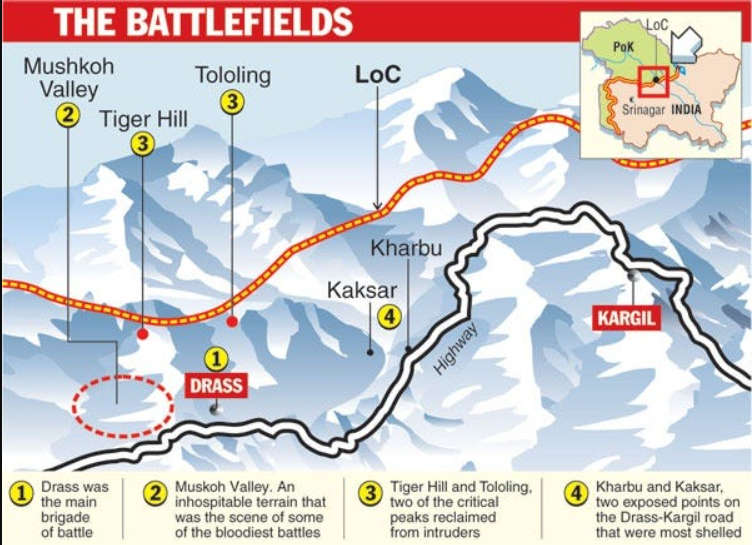
- During the winter of 1998-1999, Pakistani armed forces covertly trained and deployed troops across the Line of Control (LOC) to seize fortified positions overlooking NH 1A in the Drass and Batalik Sectors of Kargil, Ladakh.
- Indian troops initially mistook the infiltrators for terrorists or 'jihadis,' but it soon became clear that the attack was a well-organised military operation.
- It was fought in the summer of 1999 along a 170km mountain frontier, stretching from Mashkoh Valley to Turtuk in the Kargil sector,
- In response, India launched Operation Vijay, deploying over 200,000 troops to the region to counter the incursion.
- Significance of Kargil War Diwas:
- Since 1999, July 26 has been observed as Kargil Vijay Diwas to remember and honour the supreme sacrifices made by Indian soldiers during the war.
- The Kargil War memorial in Dras was built in 2000 by the Indian Army to commemorate the success of Operation Vijay in 1999.
- It was later renovated in 2014. It is also known as the "Dras War Memorial" due to its location in the town of Dras in the Kargil district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- The National War Memorial, inaugurated in 2019. It is dedicated to soldiers who sacrificed their lives in various conflicts and missions, including the Sino-Indian war in 1962, Indo-Pak wars in 1947, 1965, and 1971, Indian Peace Keeping Force Operations in Sri Lanka 1987-90, and the Kargil Conflict in 1999.
- Impact of Kargil War:
-
Global Recognition of the Line of Control (LoC): The international community largely recognized the LoC as the de facto border between India and Pakistan, reinforcing India's stance on the territorial integrity of Jammu and Kashmir.
-
Strengthened Strategic Partnerships: Kargil also marked the turning point in Indo- US relations. India was regarded as a responsible nuclear actor in the international arena leading to the next step in Strategic Partnership, culminating in the Indo-US Nuclear Deal.
-
Diplomatic Gains: The war placed significant diplomatic pressure on Pakistan, culminating in a high-profile visit by Pakistan’s Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif to the U.S. on July 4, 1999, where he faced strong criticism from the US President. This international condemnation of Pakistan’s actions helped isolate it diplomatically.
- Highlighting Nuclear Diplomacy: The conflict brought global attention to the volatile relationship between India and Pakistan, especially concerning nuclear risks. The war underscored the potential for conflict escalation in a nuclear-armed region.
- Impact on Global Perception: The war highlighted India’s military capabilities and its ability to effectively manage and respond to regional conflicts, enhancing its global stature as a rising power with robust defence capabilities.
-
Operations Associated with the Kargil War
- Operation Vijay: Operation Vijay was the code name for India's military response to the Pakistani incursion in the Kargil region.
- The operation aimed to clear the infiltrators from the Indian side of the Line of Control (LOC) and restore the status quo.
- Operation Safed Sagar: The Indian Air Force conducted "Operation Safed Sagar" to support ground operations. High-altitude operations involved aircraft like MiG-21s, MiG-23s, MiG-27s, Mirage 2000, and Jaguars.
- Operation Talwar: The Indian Navy’s "Operation Talwar" ensured maritime security and deterrence. The Navy's readiness sent a strong message to Pakistan about potential responses to further aggression.
What Reforms were Undertaken After the Kargil War?
- Security Sector Reforms: The Kargil War prompted a review of India’s National Security Structure, leading to increased transparency and the establishment of the Kargil Review Committee (KRC) led by K Subrahmanyam. The KRC report highlighted deficiencies in intelligence, border, and defence management, leading to significant security sector reforms and institutional changes.
- Creation of the Chief of Defence Staff (CDS): It was created to promote "jointness" among the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- The CDS acts as the single-point military advisor to the government and oversees the integration of the three services.
- Establishment of Tri-Service Commands: Andaman and Nicobar Command was created as a test-bed for future theatre commands, integrating resources from the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- Intelligence Reforms: National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO) was established to enhance technical intelligence capabilities.
- Defence Intelligence Agency (DIA) was formed to coordinate intelligence across all three services.
- Technical Coordination Group was created to oversee high-tech intelligence acquisitions.
- National Security Advisor (NSA) was designated as the coordinator of all intelligence agencies, supervising the NTRO and ensuring better intelligence integration.
- Border Management Enhancements: Improved surveillance and patrolling along the borders to prevent incursions. Deployment of better technology for border security. E.g., installation of thermal imaging cameras, motion sensors and radar systems.
- Operational Reforms: Weapon systems, artillery, and communication equipment were modernised. Increased focus on specialised training for high-altitude warfare and joint operations. E.g., Dhanush Artillery Gun, Akash surface-to-air missile etc.
-
Improved Coordination and Communication: Emphasis was put on joint exercises and operations among the Army, Navy, and Air Force to ensure better coordination. Enhanced mechanisms were established for real-time sharing of intelligence between different agencies and military branches.
-
Counter-Terrorism Measures: Intelligence Bureau (IB) became the principal counter-terrorism agency. Cunter-terrorism capabilities and coordination among various security agencies were strengthened.
- Indigenous Satellite Navigation System: The space-based navigation system maintained by the US government would have provided vital information, but the US denied it to India. A need for an indigenous satellite navigation system was felt earlier, but the Kargil experience made the nation realise its inevitability. E.g., Development of Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
- Doctrinal Changes: The war led to the evolution of Indian military doctrines, including the Cold Start Doctrine. Kargil highlighted the need for a holistic doctrine to address multi-dimensional proxy wars and shaped future military strategies.
Conclusion
The Kargil War of 1999 was a pivotal event for India, significantly impacting its military strategy and national security policies. Operation Vijay's success restored control over strategic areas and strengthened India's defence capabilities. The war highlighted the need for robust security measures and prompted major reforms in national security infrastructure. It reaffirmed the Line of Control (LoC) as an effective international border and accelerated the development of new military doctrines, such as the Cold Start Doctrine. The conflict’s legacy continues to shape India's defence strategies and diplomatic relations.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. The Kargil War of 1999 made a significant impact on the regional dynamics of the South Asian region. Discuss. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q.“Increasing cross-border terrorist attacks in India and growing interference in the internal affairs of several member-states by Pakistan are not conducive for the future of SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation).” Explain with suitable examples. (2016)
Q.The terms ‘Hot Pursuit’ and ‘Surgical Strikes’ are often used in connection with armed action against terrorist attacks. Discuss the strategic impact of such actions. (2016)
Q.Terrorist activities and mutual distrust have clouded India-Pakistan relations. To what extent the use of soft power like sports and cultural exchange could help generate goodwill between the two countries. Discuss with suitable examples. (2015)