Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan: First State to Adopt Road Safety Action Plan
Why in News?
Rajasthan is going to become the first State in the country to adopt an action plan for road safety for the next 10 years. The action plan will be aimed at reducing road accidents in the State by 50% till 2030.
Key Points
- The policy would generate awareness among the public at large about road safety provisions and bring about behavioural changes for complying with road safety rules.
- According to the sources, the World Bank would render assistance to the State government in the preparation of an action plan and road safety policy by incorporating the best practices adopted in different countries.
- The action plan will be implemented in three stages. The first stage from 2025 to 2027, second from 2027 to 2030 and the third from 2030 to 2033.
- It will lay emphasis on different aspects of speed limit, safe distance, traffic signals, use of road barriers, pedestrian safety, use of seatbelts, helmets, and vehicle insurance.
Initiatives Related to Road Safety
- Global:
-
Brasilia Declaration on Road Safety (2015):
- The declaration was signed at the second Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety held in Brazil. India is a signatory to the Declaration.
- The countries plan to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 3.6 i.e., to halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents by 2030.
- Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030:
- The UN General Assembly adopted resolution "Improving global road safety " with the ambitious target of preventing at least 50% of road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030.
- The Global Plan aligns with the Stockholm Declaration, by emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to road safety.
- The International Road Assessment Programme (iRAP) :
- It is a registered charity dedicated to saving lives through safer roads.
-
- India:
-
Motor Vehicles Amendment Act, 2019:
- The Act hikes the penalties for traffic violations, defective vehicles, juvenile driving, etc.
- It provides for a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund, which would provide compulsory insurance cover to all road users in India for certain types of accidents.
- It also provides for a National Road Safety Board, to be created by the Central Government.
- The Carriage by Road Act, 2007:
- The Act provides for the regulation of common carriers, limiting their liability and declaration of the value of goods delivered to them to determine their liability for loss of, or damage to, such goods occasioned by the negligence or criminal acts of themselves, their servants or agents and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The Control of National Highways (Land and Traffic) Act, 2000:
- The Act provides for the control of land within the National Highways, right of way and traffic moving on the National Highways and also for removal of unauthorized occupation thereon.
- National Highways Authority of India Act, 1998:
- The Act provides for the constitution of an authority for the development, maintenance and management of NHs and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
-


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh to Become Self-Sufficient in Pulse Production
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh aims to be self-sufficient in pulse production in 3-4 years, with a 36% increase since 2016. The Government focuses on Arhar, Urad, and Moong cultivation.
Key Points
- During 2016-217 to 2023-2024, the production of pulses increased from 2.394 million metric tons to 3.255 million metric tons.
- To increase pulse production 27,200 hectares of crop demonstrations will be organised under the National Food Security Mission scheme.
- The target is set for the distribution of 31,553 quintals of seeds and the production of 27,356 quintals of certified seeds.
- To ensure fair prices for the produce of pulse crops in the market, the government is also ensuring the procurement of all these crops at Minimum Support Price (MSP).
- According to the sources, model pulse villages will be developed in the leading pulse production districts of Bundelkhand - Banda, Mahoba, Jalaun, Chitrakoot, and Lalitpur.
National Food Security Mission (NFSM)
- NFSM is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme launched in 2007 based on the recommendations of the agriculture sub- committee of National Development Council (NDC).
- The committee pointed out the need for improved agricultural extension services, technology transfer and decentralized planning as a result of which NFSM was conceptualized as a mission mode program.
Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- MSP is the guaranteed amount paid to farmers when the government buys their produce.
- MSP is based on the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), which considers various factors such as cost of production, demand and supply, market price trends, inter-crop price parity, etc.
- CACP is an attached office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare. It came into existence in January 1965.
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) chaired by the Prime Minister of India takes the final decision (approve) on the level of MSPs.
- The MSP is aimed at ensuring remunerative prices to growers for their produce and encouraging Crop Diversification.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Devotees Take Out Lord Jagannath Rath Yatra
Why in News?
Recently, The grand Rath Yatra of Lord Jagannath Swami Ji was organized in Allahabad under the auspices of the Shri Jagannath Swami Rath Yatra Committee Kydganj.
Key Points
- The Rath Yatra commenced from the Shri Jagannath Temple situated on Triveni Marg in Kydganj.
- In addition to the NandiGhosh Rath of Lord Jagannath, the chariots of Garuda Dev, Badri Vishal, Lord Ram, and Lord Dwarkadhish were also part of the procession.
- Tableaus depicting Radha Krishna, Narsingh Avatar, and Damodar Leela were also included in the Rath Yatra.
- Jagannath Rath Yatra is an annual Hindu festival that celebrates the journey of Lord Jagannath, his elder brother Lord Balabhadra, and his younger sister Goddess Subhadra from their home temple in Puri, Odisha to their aunt’s temple in Gundicha, about three kilometres away.
- The legend behind the festival is that once, Goddess Subhadra expressed her desire to visit her aunt’s place in Gundicha.
- To fulfill her wish, Lord Jagannath and Lord Balabhadra decided to accompany her on a chariot ride. This event is commemorated every year by taking the deities on a similar journey.
- The festival dates back to at least the 12th century CE, when the Jagannath temple was built by King Anantavarman Chodaganga Deva. However, some sources suggest that the festival was already in practice since ancient times.
- The festival is also known as Festival of Chariots, as the deities are carried on three massive wooden chariots that are pulled by devotees with ropes.
- It begins on the second day of the bright fortnight of the month of Ashadha (June-July) and lasts for nine days.
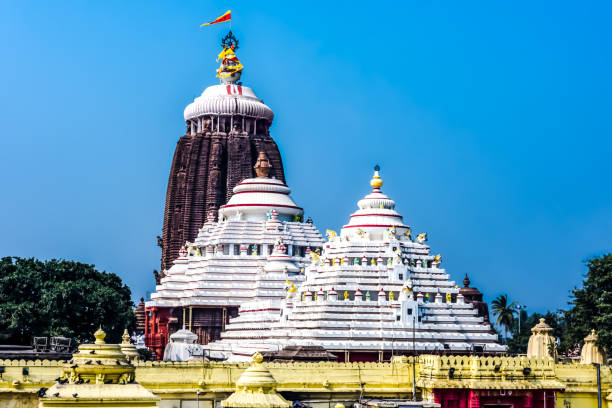
Jagannath Puri Temple
- It is one of the most impressive monuments of the Indian State Odisha.
- This temple is known as the “White Pagoda” and is a part of Char Dham pilgrimages (Badrinath, Dwaraka, Puri, Rameswaram).
- It is a splendid example of Kalinga architecture, which is characterised by curvilinear towers, intricate carvings and ornate sculptures.
- The temple complex is surrounded by a high wall with four gates facing the four cardinal directions.
- The main temple consists of four structures: the vimana (sanctum), the jagamohana (assembly hall), the nata-mandira (festival hall) and the bhoga-mandapa (offering hall).
- Jagannath Puri temple is called ‘Yamanika Tirtha’ where, according to the Hindu beliefs, the power of ‘Yama’, the god of death has been nullified in Puri due to the presence of Lord Jagannath.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
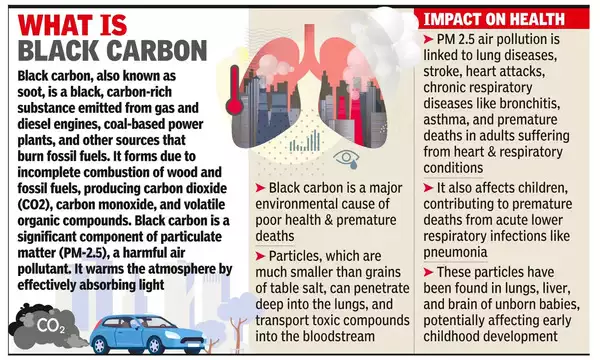
Decline in Black Carbon Level in Varanasi
Why in News?
According to a study at Banaras Hindu University (BHU), an annual average decline of 0.47 micrograms per cubic metre in carbon level has been observed in Varanasi and the central Indo-Gangetic plains.
Key Points
- The study utilized black carbon data generated under the Aerosol Radiative Forcing over India (ARFI) program of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- An analysis of a decade-long measurement of black carbon mass concentration was conducted at a representative location in the central Indo-Gangetic plain, Varanasi, from 2009 to 2021.
- The purpose of this analysis was to understand the physical, optical, and radiative impact of black carbon in this region.
- The study recorded an average annual decrease of 0.47 micrograms per cubic metre in black carbon levels.
- Black carbon levels also showed a consistent seasonal decline, with a post-monsoon average decrease of 1.86 micrograms per cubic metre and a pre-monsoon average decrease of 0.31 micrograms per cubic metre.
- The study found that the black carbon in Varanasi and central Indo-Gangetic plains mostly originates from distant sources, rather than local factors.
- These particles are transported over long distances from the lower and upper Indo-Gangetic plains, Pakistan, the Middle East, and southern peninsular regions.
Black Carbon
- Black Carbon (BC) is a short-lived pollutant that is the second-largest contributor to warming the planet behind carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Unlike other greenhouse gas emissions, BC is quickly washed out and can be eliminated from the atmosphere if emissions stop.
- Unlike historical carbon emissions it is also a localised source with greater local impact.
- Black carbon is a kind of an aerosol.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar Bridge Collapse Over Gandaki River
Why in News?
Recently, a 15-year-old bridge over the Gandaki River collapsed in Bihar's Saran district marking the third bridge collapse incident in the district within 24 hours.
Key Points
- According to the sources, at least 12 bridges have collapsed across Bihar in the past 17 days. No casualties have been reported yet.
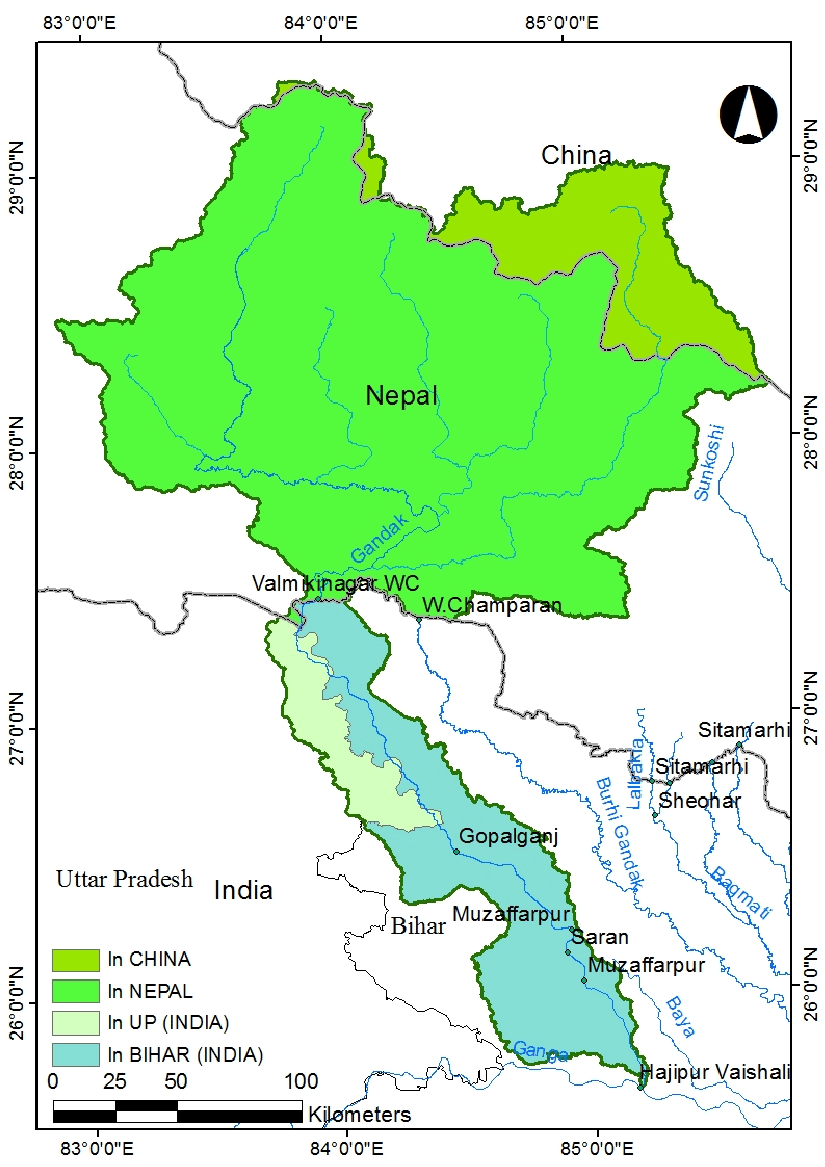
River Gandak
- About:
- The river Gandak, is also known as the Gandaki and Narayani River in Nepal. It is a significant river that flows through the northern part of India and Nepal.
- Valmiki National Park and Tiger Reserve in Bihar is located on the banks of this river.
- Source:
- The river Gandak originates at an altitude of 7620 m above main sea level in the north of Dhaulagiri in Tibet near Nepal border. Originating from the Himalayas, the river stretches over a length of 630 kilometers, with 445 kilometers running through India and 185 kilometers in Nepal.
- Drainage Basin:
- The Gandak River has a total drainage basin area of 29,705 square kilometers.
- The river flows through the Indian states of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, and joins the Ganges near Patna just downstream of Hajipur.
- Tributaries:
- The major tributaries of the Gandak River include the Mayangadi, Bari, Trisuli, Panchand, Sarhad, Budhi Gandak.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Hectares of Jungle Freed From Encroachers
Why in News?
Recently, The Khandwa forest department stated that they had reclaimed approximately 100 hectares of jungle that had been encroached upon by individuals for agricultural purposes.
- To reclaim the forest, the department destroyed the crops cultivated by the encroachers by felling a significant number of trees.
Key Points
- Earthmoving machines and tractors were used to destroy the illegal crops and level the fields.
- The official stated that the remaining areas are anticipated to be cleared in the upcoming days, which will then be followed by initiatives to revive the forest through the planting of seed balls and the installation of wire fencing.
- These encroached forests were utilized for the cultivation of soybean and corn crops, which has resulted in substantial harm to the forest ecosystem.
Encroachment
- It is the unauthorised use or occupation of someone else’s property. This can occur on abandoned or unused spaces if the legal owner is not actively involved in its upkeep. It is important for property owners to be aware of the legal steps to take and their rights in such cases.
- Urban encroachment refers to the unauthorised occupation or use of land or property within urban areas.
- This could include illegal construction, squatting, or any other form of occupation without proper permission or legal rights.
Soybean Crop
- Soybean is a Kharif crop in India.
- Soybean (Glycine max) is the world’s most important seed legumes which contributes 25% to the global edible oil, about two third of the world protein concentrate for livestock feeding and is a valuable ingredient in formulated feeds for poultry and fish.
- It is predominantly grown as a rainfed crop in Vertisols and associated soils with an average crop season rainfall of 900 mm.
- Major Producing States in India: Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.












%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)



.jpg)






.png)
.png)



 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan