Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Kashmir’s Spring Blooms
Why in News?
Kashmir’s unique agroclimatic conditions nurture a wide variety of endemic plants, especially spring blooms, which are crucial for the valley’s biodiversity and cultural heritage.
Key Points
- Notable Spring Blossoms:
- Colchicum luteum (Veer Kaum): This delicate yet radiant bloom often carpets hillocks and forest grooves.
- Sternbergia vernalis (Goul Tour): A golden-yellow flower that heralds the arrival of spring.
- Salix (Braed Mushuk): A culturally and ecologically important plant with multiple uses.
- Viburnum grandiflorum (Kulmansh): A shrub bearing large, soft pink flowers.
- Daffodils: Their bright yellow and white petals symbolise renewal and hold a special place in Kashmiri folklore.
- Cultural and Ecological Significance:
- These spring blooms provide vital ecosystem services by supporting pollinators essential for fruit tree pollination.
- For generations, local ethnic communities have relied on these blooms for medicinal and cultural practices.
- Mounting Threats to Spring Flora:
- Unsustainable development, deforestation, and human encroachment threaten these spring blooms.
- Climate change is altering blooming patterns, causing premature flowering, disrupting natural seasonal cycles.
- Despite their importance, there are no dedicated conservation programs for spring blooms.
- Current protection comes from national parks like Salim Ali and wildlife sanctuaries like Gulmarg Wildlife Sanctuary.
Gulmarg Wildlife Sanctuary
- About:
- Authorities officially notified the Gulmarg Wildlife Sanctuary as a protected area in 1987.
- They proposed it as a biosphere reserve in 1981 before granting it sanctuary status.
- It lies approximately 26 km southwest of Baramulla district headquarters.
- Altitude:
- The sanctuary spans altitudes ranging from 2,400 to 4,300 meters above sea level, supporting diverse ecological zones.
- Flora:
- The vegetation varies based on altitude, slope orientation, habitat conditions, and human interference.
- Coniferous forests dominate the landscape, covering nearly 85% to 90% of the total forested area, especially across the spurs and grooves.
- Fauna:
- The sanctuary provides critical habitat for several important wildlife species.
- Key species include the endangered Kashmir stag (Hangul), the Himalayan black bear, and the elusive musk deer.
Salim Ali National Park
- About:
- Salim Ali National Park lies amidst the scenic landscapes of Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir.
- The national park covers an area of 9.07 square kilometres, making it a compact yet ecologically significant habitat.
- Authorities established the park in 1986 as a protected area to conserve its unique flora and fauna.
- Initially known as the City Forest National Park, it was later renamed to honour Dr. Salim Ali.
- The renaming paid tribute to Dr. Ali’s pioneering work in Indian ornithology and his lifelong commitment to bird conservation.
- Ecological Significance:
- The park stands out for its ecological richness, particularly as a haven for bird species.
- It continues to serve as a vital green space within an urban setting, contributing to environmental stability and biodiversity conservation in Srinagar.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Himalayan Climate Research Centre in J&K
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Earth Sciences inaugurated the first-ever “Himalayan High Altitude Atmospheric & Climate Research Centre” in the elevated region of Nathatop, located in Udhampur district of Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Points
- Collaborative Efforts:
- The centre is the result of a multi-tier collaboration of the Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of J&K and Swiss National Science Foundation.
- A Strategic Location for Critical Research:
- The Nathatop site was chosen for its clean air and low pollution levels—ideal conditions to study cloud formation, aerosol interactions, and weather patterns.
- Researchers will be able to observe atmospheric processes in free tropospheric conditions, a rarity in most parts of India.
- Launch of ICE-CRUNCH:
- During the ceremony, the union minister also flagged off ICE-CRUNCH—a joint Indo-Swiss research project involving Indian scientists and researchers from university in Zurich.
- The study will explore ice-nucleating particles and cloud condensation nuclei in the north-western Himalayas both critical for understanding precipitation and climate behaviour.
- Tapping Himalayan Potential:
- The minister also cited national initiatives like the Aroma Mission and Floriculture Mission, which are helping unlock the Himalayas' economic and ecological potential.
- These missions aim to boost local livelihoods while contributing to India’s broader climate goals.
Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF)
- The SNSF, established in 1952, is a public funding organization that evaluates research proposals and allocates public research money based on a competitive principle, ensuring high-quality research in Switzerland.
Aroma Mission
- Objectives:
- To promote the cultivation of aromatic crops for essential oils that are in great demand by the aroma industry.
- To enable Indian farmers and the aroma industry to become global leaders in the production and export of some other essential oils on the pattern of menthol mint.
- To provide substantial benefits to the farmers in achieving higher profits, utilization of waste lands and protection of their crops from wild and grazing animals.
- Nodal Agencies:
- The nodal laboratory is CSIR-Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CSIR-CIMAP), Lucknow.
- The participating laboratories are CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology (CSIR-IHBT), Palampur; CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (CSIR-IIIM), Jammu etc.
Floriculture Mission
- Floriculture:
- It is a branch of horticulture that deals with the cultivation, processing and marketing of ornamental plants vis-à-vis landscaping of small or large areas, and maintenance of gardens so that the surroundings may appear aesthetically pleasant.
- Objectives:
- To focus on commercial floral crops, seasonal/annual crops, wild ornaments and cultivation of flower crops for honey bee rearing.
- Some of the popular crops include Gladiolus, Canna, Carnation, Chrysanthemum, Gerbera, Lilium, Marigold, Rose, Tuberose etc.
- Implementing Agencies:
- Along with Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), other implementing agencies involved are:
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
- Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC)
- APEDA and TRIFED
- Fragrance and Flavour Development Centre (FFDC), Kannauj, and
- Ministry of Commerce and Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME).
- Along with Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), other implementing agencies involved are:


Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Dokra Art of Chhattisgarh
Why in News?
During his visit to Bangkok, the Prime Minister of India presented traditional Indian handicrafts to Thai Prime Minister Srettha Thavisin and his spouse.
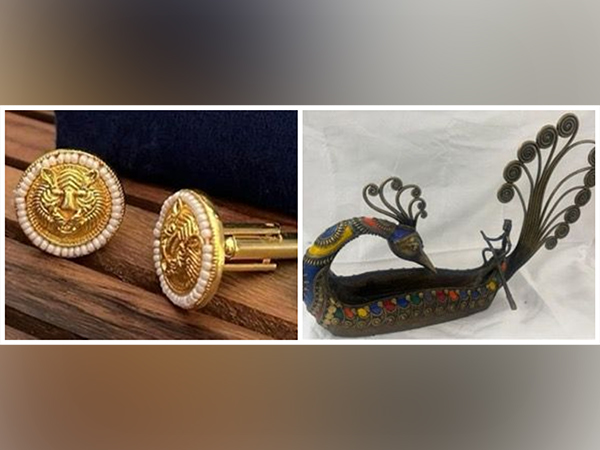
- Among the gifts was a Dokra Brass Peacock Boat with a Tribal Rider—a fine example of tribal metal artistry from Chhattisgarh, reflecting India’s rich cultural heritage and craftsmanship.
Key Points
- About Dokra Art:
- Dokra is a form of ancient bell metal craft practiced by the Ojha metalsmiths living in states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Telangana.
- The style and also the workmanship of this artisan community varies in different states.
- Crafted using the age-old lost-wax casting method, the sculpture showcases the intricate tribal artistry of Chhattisgarh. Every piece is unique and meticulously handcrafted.
- The dancing girl of Mohenjo-Daro (Harrapan Civilization) is one of the earliest dokra artefacts that is now known.
- Symbolism and Aesthetic Appeal:
- The peacock-shaped boat, embellished with intricate designs and vivid lacquer inlays, embodies elegance, creativity, and cultural depth.
- The tribal figure gently rowing the vessel captures the essence of human-nature harmony—a central motif in Dokra art.
- Crafted from brass, the sculpture naturally acquires a rich patina over time, enhancing its vintage charm and historical appeal.
- More than just a decorative piece, it honours India’s tribal heritage, reflecting a fusion of simplicity, artistic expression, and a profound connection to nature.
- Gold-Plated Tiger Motif Cufflinks:
- The Prime Minister of India gifted the spouse of the Thai Prime Minister a pair of gold-plated cufflinks featuring an intricate tiger motif adorned with pearls.
- The striking tiger face symbolises power, authority, and regal charm.
- Delicate Meenakari detailing—a traditional enamel craft from Rajasthan and Gujarat—adds vibrant colour and artistry to the design.
- The Prime Minister of India gifted the spouse of the Thai Prime Minister a pair of gold-plated cufflinks featuring an intricate tiger motif adorned with pearls.
- Dokra is a form of ancient bell metal craft practiced by the Ojha metalsmiths living in states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Telangana.
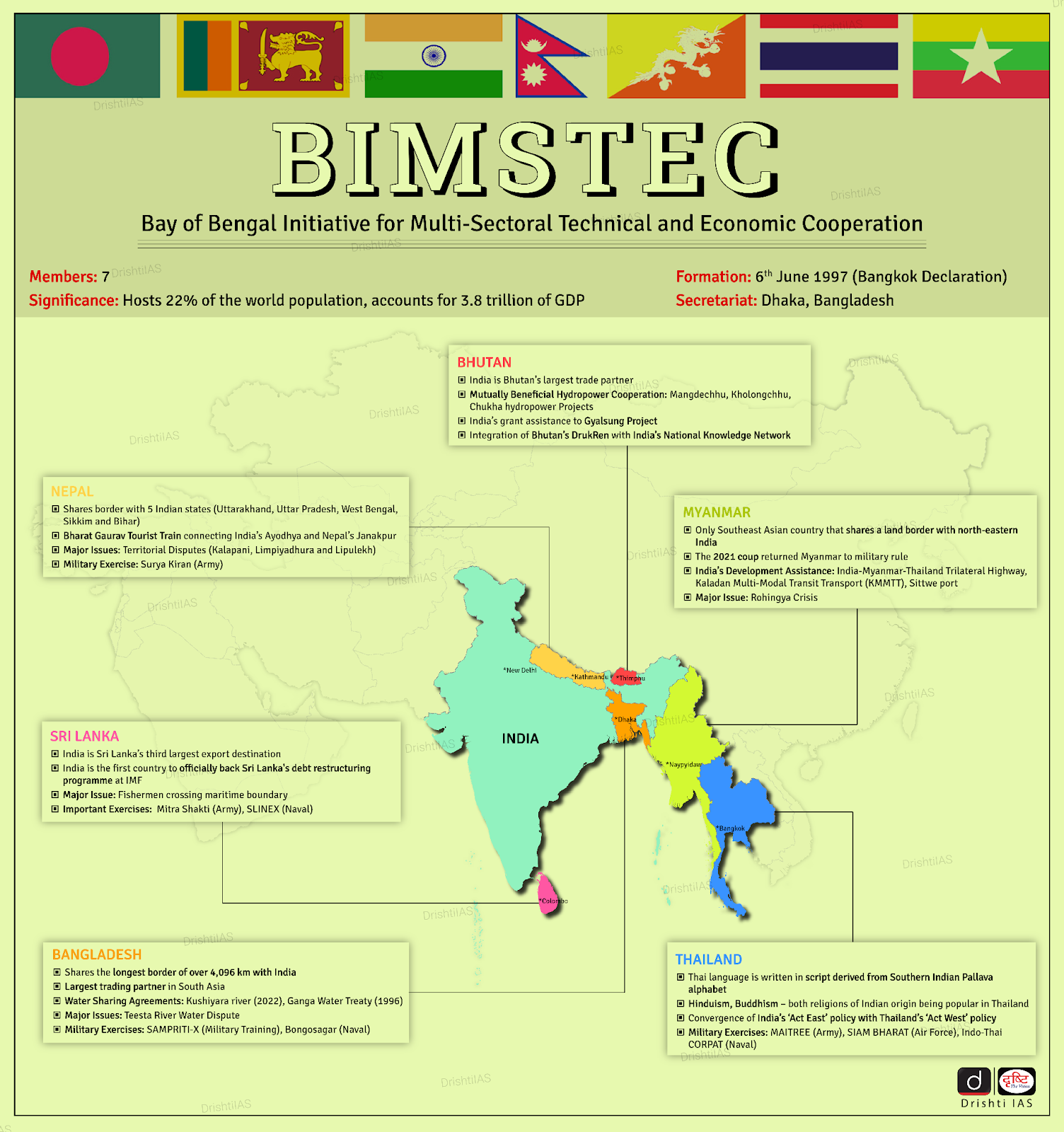
- India’s Active Role at the BIMSTEC Summit:
- The Prime Minister of India took part in the BIMSTEC Summit held in Bangkok, where he lauded the adoption of the BIMSTEC Bangkok Vision 2030 and the BIMSTEC Maritime Transport Agreement.
- He reiterated India’s strong commitment to deepening collaboration across key areas such as regional connectivity, trade, technological innovation, and disaster management in the Bay of Bengal region.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
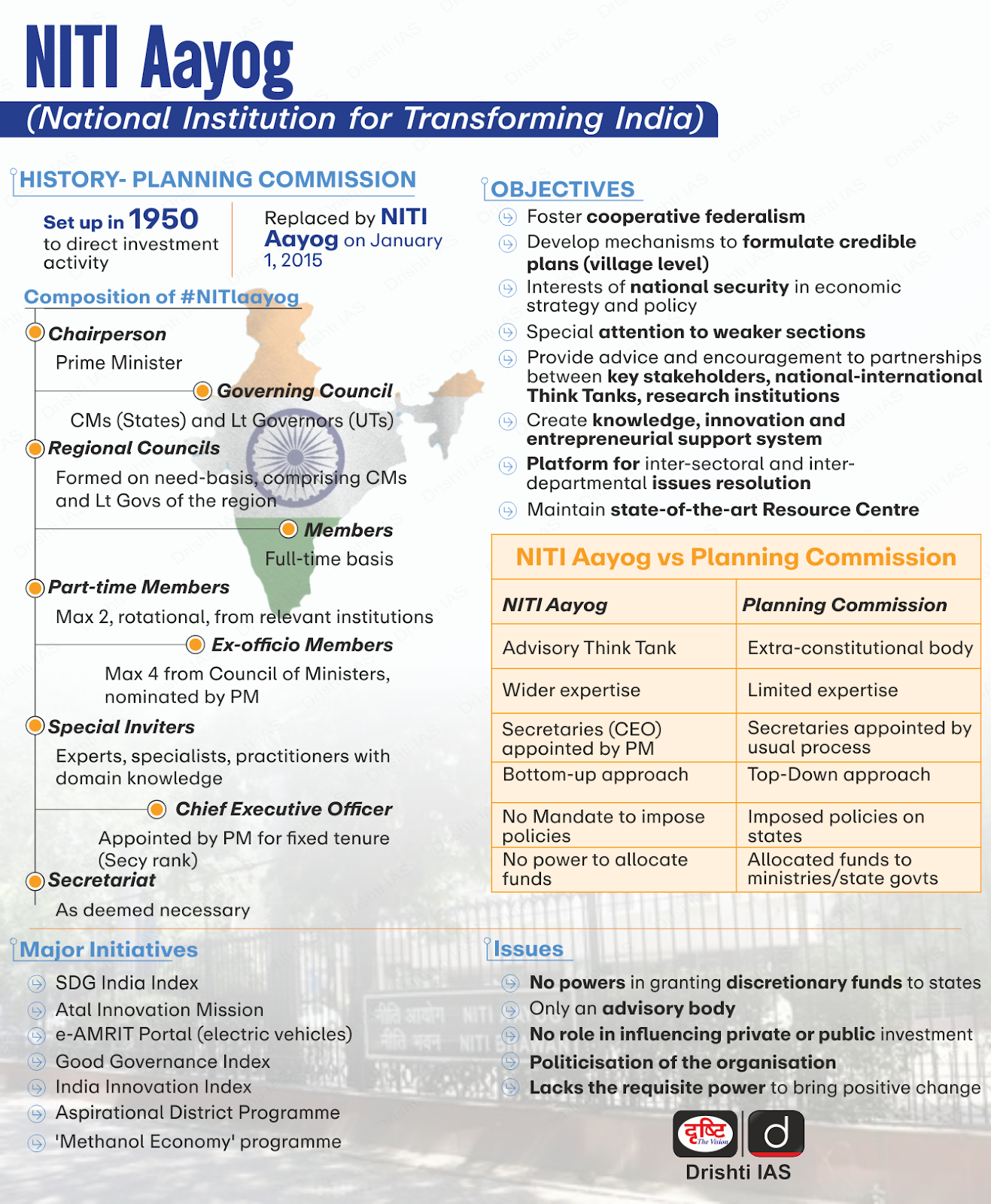
NITI Aayog Workshop in Pune
Why in News?
NITI Aayog, in collaboration with the Government of Maharashtra, organised a one-day workshop focused on the theme "Developing Ecosystem for Assistive Technology in India." at Yashwantrao Chavan Academy Of Development Administration(YASHADA) Pune.
Key Points
- Rising Demand for Assistive Technology in India:
- India is witnessing a growing need for assistive devices due to the increasing number of persons with disabilities, elderly individuals, and people with chronic health conditions.
- These technologies significantly improve their quality of life and play a key role in building a more inclusive and equitable society.
- India’s Potential as an AT Manufacturing Hub:
- With rapid advancements in technology and a thriving start-up ecosystem, India holds great promise to emerge as a global hub for Assistive Technology (AT) manufacturing.
- This growth can meet domestic needs while also contributing to international markets.
- Broad Participation Expected:
- The workshop will bring together around 200 participants, including senior officials from Central and State Governments, international agencies, research institutions, and AT startups.
- They will discuss the current state and future possibilities of assistive technology in the country.
- Key Themes for Discussion:
- Improving access to assistive technology in India
- State-led initiatives promoting AT
- Innovations in AT manufacturing
- Opportunities for global partnerships and collaboration
- Towards a Robust AT Ecosystem:
- Insights and recommendations from the workshop will help shape a national framework to support and expand the AT ecosystem in India.
- These efforts align with the goal of ‘leaving no one behind’ and advancing an inclusive, accessible society for all.
Assistive Technology (AT)
- AT is any item, piece of equipment, software program or product system that is used to increase, maintain or improve the functional capabilities of persons with disabilities.
- Examples:
- Technologies and devices such as prosthetics, braces, walkers, special switches, special-purpose computers, screen readers and specialised curricular software.
- Universal assistive technology coverage implies that everyone, everywhere receives the AT that they need without financial or other hardships.
- Priority Assistive Products List launched by WHO in 2018 include hearing aids, wheelchairs, communication aids, spectacles, artificial limbs, pill organisers, memory aids and other essential items for the elderly and persons with disabilities.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Bharat Ratna Pandit Ravi Shankar Birth Anniversary
Why in News?
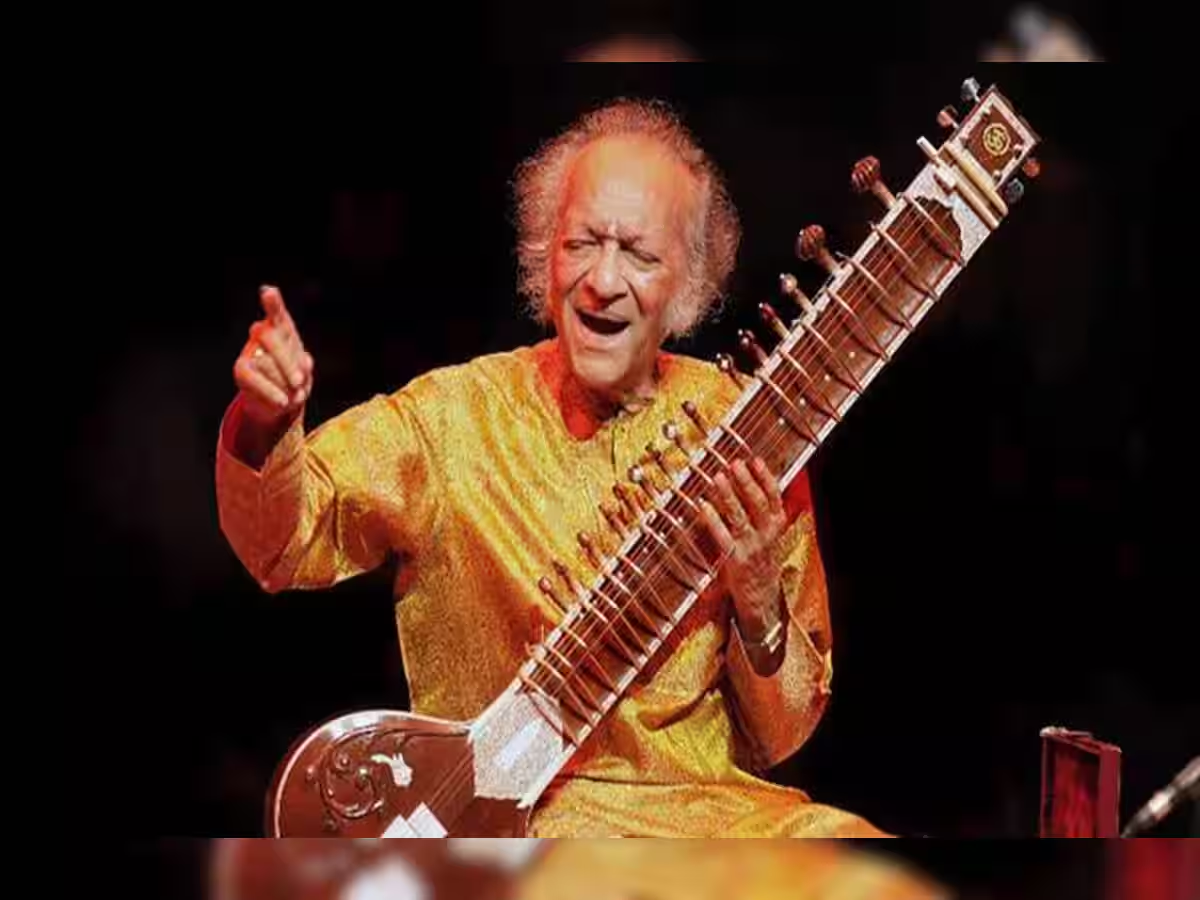
7th April 2025, marks the 103rd birth anniversary of sitar player and composer Pandit Ravi Shankar.
Key Points
- About Pandit Ravi Shankar:
- Pandit Ravi Shankar, born on 7th April 1920 in Varanasi , was a great sitarist and composer of Indian classical music .
- His original name was Ravindra Shankar Chowdhury and he was the seventh son of his father Shyam Shankar Chowdhury and mother Hemangini Devi.
- At the age of 18, he started learning sitar and took initiation from Ustad Allauddin Khan of Maihar.
- He recomposed the famous song "Saare Jahan Se Achcha" at the age of 25.
- He served as the Music Director of All India Radio in New Delhi from the year 1949 to 1956.
- Subsequently, in the 1960s he taught and performed Indian classical music with violinists Yehudi Menuhin and George Harrison, helping to popularise it in the Western world.
- Pandit Ravi Shankar introduced Indian classical music to the western world.
- The Beatles' George Harrison described him as the 'Godfather of World Music'.
- He was also a nominated member of the Rajya Sabha from 1986 to 1992.
- He died on December 11, 2012 at the age of 92.
- Honours and Awards
- He was awarded the country's highest civilian honour, Bharat Ratna, in 1999. Apart from this, he received many honours and awards, which include:
- UNESCO Goodwill Ambassador (1999): Appointed for cultural contributions.
- Padma Bhushan (1967): India's third highest civilian award.
- Padma Vibhushan (1981): Second highest civilian award for exceptional service.
- Kalidas Samman (1986): Madhya Pradesh's premier award for excellence in Indian classical music.
- Sangeet Natak Akademi Award (1987): A mark of excellence in the field of music in India.
- Grammy Awards (four times): Honoured in various categories, including a posthumous Lifetime Achievement Award in 2013.
- He was awarded the country's highest civilian honour, Bharat Ratna, in 1999. Apart from this, he received many honours and awards, which include:
Indian Classical Music
- Introduction:
- Classical Indian music is a complex and ancient form of music with its roots in the Vedas, the oldest texts of Hinduism, dating back to around 1500 BCE.
- It is divided into two main traditions: Hindustani music (prevalent in North India) and Carnatic music (popular in South India).
- Historical Background:
- Indian classical music traces its origins to ancient texts such as the Samaveda, which shows its deep historical background and connection to Indian traditions.
- Importance:
- Preserving the authenticity of the Guru-Shishya tradition (teacher-disciple tradition) in classical music has ensured the transfer of knowledge and skills from one generation to the next.
- Classical music follows a set of rules and conventions (such as the raga system, which has been passed down for generations) that have ensured the preservation of India's musical heritage.
- Classical music plays a role in uniting people from diverse backgrounds by acting as a common cultural thread. It has a role in promoting a sense of national unity through reducing regional, linguistic and religious barriers.
- Classical music includes a combination of various regional styles and instruments, which reflects the cultural diversity of India. This inclusiveness promotes harmony and coordination among different communities.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Fire Department Honored by Goa Government
Why in News?
On 1st April 2025, the Goa Government honored the Uttar Pradesh Fire Department.
Key Points
- About the issue:
- The honour was presented by the Directorate of Fire and Emergency Services, Goa.
- This felicitation ceremony was organised in Panaji, the capital of Goa.
- This honour was given for excellent fire fighting and disaster management services in Mahakumbh 2025 , Prayagraj.
- Achievements of the Fire Department:
- Controlled 185 fire incidents in 45 days, of which 24 were major fire incidents.
- Apart from this, about 86 small fire incidents were brought under control immediately.
- Potential losses of approximately Rs 16.5 crore were averted.
Kumbh Mela
- In the year 2025 Maha Kumbh Mela was held in Prayagraj from 13 January to 26 February 2025 attended by more than 66.30 crore devotees.
- The word ' Kumbh' is derived from the metal 'Kumbhaka' (sacred pot of the nectar of immortality).
- King Harshavardhana of the Pushyabhuti dynasty started organizing the Kumbh Mela in Prayagraj.
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims during which the participants take a bath or dip in the holy river. This congregation takes place at 4 different places, namely:


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Khelo India Games in Bihar
Why in News?
The seventh edition of Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG) will be held from 4th-15th May 2025 in five cities of Bihar – Patna, Rajgir, Gaya, Bhagalpur, and Begusarai.
Key Points
- About the games
- KIYG is a national-level multi-disciplinary sports competition for school and college students in India.
- The Prime Minister launched the first edition of Khelo India School Games at the Indira Gandhi Arena in New Delhi in the year 2018.
- In the year 2019, its name was changed to Khelo India Youth Games.
- These are part of the Khelo India initiative of the Government of India.
- It aims to promote sports culture and recognise sporting talent at the grassroots level.
- These games are organized in two categories:
- School students under the age of 17
- College students under the age of 21.
- The 6th edition of the Khelo India Youth Games was held from 19 to 31January 2024 in four cities of Tamil Nadu: Chennai, Trichy, Madurai, and Coimbatore.
- khelo india App:
- In the year 2019, the Prime Minister launched the Khelo India App to promote sports and fitness.
- This app helps people to stay updated about sports events and promotes a healthy lifestyle.


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Save Shahabad Forest Movement
Why in News?
Activists protest against the plan to cut trees for a pump storage project in Shahabad forest of Rajasthan .
Key Points
- About the Project:
- Shahpur Pump Storage Project is an off-stream closed loop pump storage project. Under this, two reservoirs will be constructed. At the same time , water will be pumped from the nearby Kuno river to fill the proposed lower reservoir.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has approved Hyderabad-based company Greenko Energies Pvt Ltd to set up Shahpur Pumped Storage Project in Shahabad tehsil of Baran district.
- The project covers 624.17 hectares of land in Kalauni, Baint and Mungaoli villages. Of this, 408 hectares of area is forest.
- The project area falls within the Shahabad Conservation Reserve, which is home to wildlife species protected under Schedule-I of the Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act (WPAA) 2022.
- Reasons for protest:
- Under this project, there is a plan to cut more than 4 lakh trees, which will destroy the forest.
- Cutting down trees on such a large scale would have an adverse effect on the climate, and would also stop the absorption of 22.5 lakh metric tons of carbon dioxide that the region absorbs every year.
- The local ecology will be deeply affected and the livelihood of the local residents may also be in danger due to this project.
- Environmentalists say this could cause serious damage to wildlife, flora and rare medicinal herbs .
- Additionally, cutting down trees will lead to soil erosion and may also obstruct important environmental benefits.
- This hydropower project will also adversely impact the movement and welfare of cheetahs introduced from Namibia and South Africa under the Kuno Cheetah Project.
- Under this project, there is a plan to cut more than 4 lakh trees, which will destroy the forest.
- Shahabad Forest:
- The Shahabad forest is rich in biodiversity and is home to protected wildlife species.
- This forest is located in Baran, Rajasthan, very close to the designated habitat for cheetahs in Kuno National Park in Madhya Pradesh.
- The forest area of Shahabad lies between the Madhav National Park and the Cheetah corridor , which would be disrupted by the proposed project.
Kuno River
- The Kuno River flows through the middle of the Kuno National Park and flows from south to north in Madhya Pradesh.
- This river originates from the Vindhya mountain range and passes through various districts of Madhya Pradesh like Guna, Shivpuri, Sheopur and Morena.
- The Kuno River area is also part of India's famous Cheetah Project, which is located in the Kuno National Park.
- The river supports regional biodiversity and plays a vital role in maintaining environmental balance.
Kuno National Park
- Kuno National Park (Sheopur, Madhya Pradesh) was established as a wildlife sanctuary in the year 1981 and was upgraded to a national park in the year 2018
- Geography:
- It consists mainly of dry deciduous forests and the Kuno River, a major tributary of the Chambal , flows through the park.
- It is situated in the Vindhya mountain range .
- Fauna:
- Leopard, striped hyena, Indian wolf, blackbuck, sambar deer, gharial (Kuno River).
- It was selected under the action plan for the introduction of cheetah in India .
- Flora:
- The primary tree species are Kardhaai, Khair and Salai.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Folk Dance Artist Ram Sahai Pandey
Why in News?
On 8th April 2025, Padma Shri awarded folk dance artist Ram Sahay Pandey passed away in Sagar district of Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- About Ram Sahai:
- He was born on 11 March 1933 in Maddhar Patha village of Sagar district.
- He belonged to an agriculturist Brahmin family and was the youngest of four siblings.
- He got Rai dance recognized in 24 countries and established the Bundelkhandi Lok Nritya Natya Kala Parishad.
- In the year 2022, he was awarded Padma Shri.
- Apart from this, in the year 1980 he was awarded the title of 'Nritya Shiromani'.
Rai Dance
- Rai dance is the most famous dance of Bundelkhand.
- This dance is especially performed on special occasions like marriages and birth celebrations.
- Both men and women dance in it. The women who perform the Rai dance are called Bednis and the men are called Mridangdhari.
- Women tie ghungroos to their feet and dress up and dance to the beats of the Mridang. During this time men and women also sing Desi Swaang.
- Rai dance not only keeps the cultural heritage alive but also reveals the hidden folk art and traditions which symbolize the rich cultural heritage of Bundelkhand.
- The Bedia tribe in Madhya Pradesh performs this folk dance.
- It is also performed by women of the Ahir tribe on the occasion of the birth of a child in the Vaishya community.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan