Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar's Annual Flood Crisis
Why in News?
Bihar faces devastating floods every year due to its unique geography and decades-old flood control methods.
Key Points
- Flood-Prone Nature of Bihar
- Bihar is India's most flood-prone state, with 76% of North Bihar's population affected.
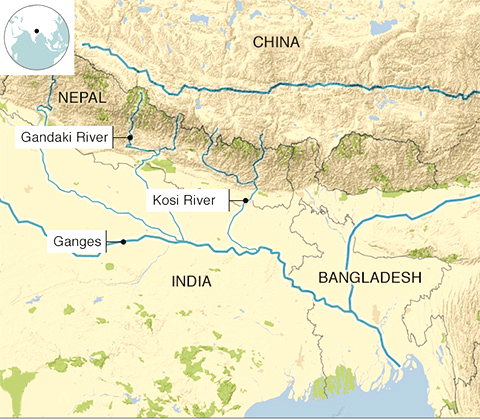
- The region is crisscrossed by both snow-fed and rain-fed rivers, increasing flood risk.
- Bihar is located below Nepal, with Himalayan rivers (Kosi, Gandak, Bagmati) flowing into the state.
- These rivers carry high sediment loads due to loose Himalayan soil, leading to overflow during heavy rains.
- Impact of Embankments:
- Embankments along rivers like Kosi were built in the 1950s to control flooding.
- Embankments narrowed river channels, leading to sediment buildup and higher riverbeds, making the rivers more prone to overflow.
- Kosi, known as the "sorrow of Bihar," floods annually despite embankments.
- Recent Flooding (2024):
- Heavy rainfall and Nepal’s release of water from the Kosi barrage led to severe floods in North Bihar.
- Embankments have breached in several districts, affecting 11.84 lakh people.
- The Birpur barrage released 6.6 lakh cusecs of water, the highest in six decades.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Flooding results in crop loss, livestock destruction, damage to infrastructure, and forced migration.
- Bihar government spends Rs 1,000 crore annually on flood relief and management.
- Proposed Solutions:
- Structural: Proposals for dams and additional barrages on Kosi and other rivers.
- Non-structural: Enhancing flood warnings, improving reaction times, public awareness, and training to mitigate flood effects.


.png)








.png)


.jpg)



 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan