Haryana Switch to Hindi
Gram Panchayats Declared TB-Free in Haryana
Why in News?
The Health Department has declared sixty-six gram panchayats in Karnal district in Haryana tuberculosis (TB)-free based on six key indicators.
Key Points
- Assessment and Awards:
- A state-level team conducted an assessment in March 2025 to evaluate the panchayats.
- Recognized panchayats were honored by the Additional Deputy Commissioner.
- To receive TB-Free Gram Panchayat status, a panchayat must meet the required conditions for one year.
- Award Categories:
- 14 panchayats received a silver statue of Mahatma Gandhi with an appreciation certificate for being recognized TB-free for the second time.
- 52 panchayats were awarded a bronze statue of Mahatma Gandhi and certificates for achieving TB-free status for the first time.
- Key Criteria for TB-Free Status:
- Annual sputum sample collection: At least 30 samples per 1,000 population.
- TB prevalence: Fewer than 1 TB patient per 1,000 people.
- Treatment success rate: At least 85%.
- Diagnostic testing: Minimum 60% of TB patients must undergo CBNAAT or TrueNAAT testing.
- Financial aid distribution: 100% disbursal under the Nikshay Poshan Yojana.
- Nutritional support: Provision of nutrition kits to all TB patients.
- Role of Nikshay Mitra Yojana:
- Nikshay Mitra Yojana, launched under TB-Free India, allows citizens, NGOs, corporates, and public representatives to support TB patients.
- Contributors (Nikshay Mitras) provide monthly nutrition kits to aid TB patients in their recovery.
Tuberculosis
- About:
- Tuberculosis is an infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can practically affect any organ of the body. The most common ones are lungs, pleura (lining around the lungs), lymph nodes, intestines, spine, and brain.
- Transmission:
- It is an airborne infection that spreads through close contact with the infected, especially in densely populated spaces with poor ventilation.
- Symptoms:
- Common symptoms of active lung TB are cough with sputum and blood at times, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever and night sweats.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
GI Tag for Kashmir Products
Why in News?
In recognition of Jammu and Kashmir’s cultural heritage, authorities have granted Geographical Indication (GI) status to eight traditional crafts, enhancing their authenticity and boosting their presence in global markets.
Key Points
- Crafts Honored with GI Tags:
- The newly recognized crafts include:
- Kashmiri Pashmina – Renowned for its unmatched softness, made from the fine wool of Changthangi goats.
- Kani Shawls – Woven with intricate patterns using small wooden sticks, showcasing artisans' precision.
- Sozni Embroidery – Features delicate needlework with vibrant floral motifs on shawls and garments.
- Kashmir Hand-Knotted Carpets – Celebrated for durability and exquisite artistry.
- Papier Mâché – Transforms everyday objects into hand-painted artistic pieces.
- Khatamband Woodwork – Intricate geometric ceiling patterns used in traditional Kashmiri homes and mosques.
- Walnut Wood Carving – Produces finely detailed furniture and décor using rich walnut timber.
- Kashmir Saffron – Grown in Pulwama and Budgam, known for its deep red stigmas, intense aroma, and organic cultivation.
- The newly recognized crafts include:
- Protecting Artisans and Promoting Economic Growth:
- The GI status ensures that only products crafted in their designated regions using authentic methods can bear these prestigious labels.
- It safeguards artisans from counterfeit products and enhances the credibility of these crafts in global markets.
- The move follows efforts like introducing a new GI logo for Kashmir carpets to differentiate hand-knotted originals from machine-made imitations.
- The Jammu and Kashmir government, along with initiatives like the World Crafts Council, is promoting these crafts through e-commerce platforms and global exhibitions.
- Positioning Kashmir as a Global Craft Hub:
- Recently recognized as a World Craft City, Kashmir continues to be a center of artistic excellence.
- As demand for authentic handmade products grows, these GI tags will help preserve traditions while driving economic empowerment for local communities.
Geographical Indication (GI)
- A geographical indication (GI) is a designation applied to products originating from a specific geographical area, indicating that the qualities or reputation of the products are inherently linked to that particular origin.
- Article 22 (1) of Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) defines GIs as “indications which identify a good as originating in the territory of a member, or a region or locality in that territory, where a given quality, reputation or other characteristic of the good is essentially attributable to its geographic origin”.
- In many EU nations, GI is classified in two basic categories Protected GI (PGI) and Protected Destination of Origin (PDO). India only has the PGI category.
- This certification is also extended to non-agricultural products, such as handicrafts based on human skills, materials and resources available in certain areas that make the product unique.
- GI is a powerful tool for protecting traditional knowledge, culture and can boost socio-economic development.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bodhgaya Temple
Why in News?
Several Buddhist monks are protesting at Mahabodhi Mahavihara (Bodhgaya Temple) in Bihar demanding repeal of the Bodhgaya Temple Act (BTA), 1949.
Key Points
- About the Issue:
- This protest is being carried out by various Buddhist groups led by All India Buddhist Forum (AIBF) .
- They are opposed to the provision of making Hindu followers members of the Bodhgaya Temple Management Committee (BTMC) under this Act .
- Buddhist monks say that the management of the temple should be completely in the hands of the Buddhist community.
- Bodh Gaya Temple Management Committee (BTMC):
- BTMC was established in 1953 under the Bodhgaya Temple Act, 1949 to manage the Mahabodhi Temple at Bodh Gaya in Bihar.
- This committee has four members from the Buddhist community and four from the Hindu community.
- As per the Act, the District Magistrate (DM) of Gaya is the ex-officio Chairman of the Committee .
- Bodhgaya Temple
- The Mahabodhi Temple located in Bodh Gaya is a sacred place of Buddhism.
- It deals with the life of Lord Buddha and especially his attainment of enlightenment.
- The Mahabodhi Temple was built by Emperor Ashoka in 260 BC after he adopted Buddhism.
- It is one of the earliest Buddhist temples built entirely of bricks.
- It was included in the UNESCO World Heritage List in the year 2002.
- Chinese pilgrim Hiuen Tsang has given a detailed description of this temple.
- The present temple structure was built by the Gupta rulers in the 5th or 6th century AD.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Kosi Mechi Interstate Link Project
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet approved the inclusion of Kosi Mechi Intra-State Link Project of Bihar under the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana-Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (PMKSY-AIBP) .
Key Points
- About the Project:
- Under this project, excess water of Kosi river will be diverted to the Mahananda river basin in Bihar.
- Under this project, the Eastern Kosi Main Canal (EKMC) will be reconstructed, and extended up to the Mechi River .
- The Eastern Koshi Main Canal is a part of the joint Koshi Project (1954) of India and Nepal , which was built to solve the problem of frequent change of course of the Koshi River.
- Objective:
- The main objective of this project is to increase the irrigation capacity in Bihar.
- The scheme will provide additional irrigation facilities to 2,10,516 hectares of area during Kharif season in Araria, Purnia, Kishanganj and Katihar districts of Bihar.
- Sanction of Central Assistance :
- The estimated cost of the project has been fixed at Rs 6,282.32 crore, out of which central assistance of Rs 3,652.56 crore has been sanctioned to Bihar.
- This amount will aid in the development of the project and implementation of its various components.
- Deadline :
- This project is targeted to be completed by March 2029.
- On completion of this project, irrigation facilities will expand in Bihar and it will also help in flood control.
Prime Minister Agricultural Irrigation Scheme (PMKSY)
- AIBP was launched in 1996 with the objective of expediting the implementation of irrigation projects beyond the resource capabilities of the states.
- This is a centrally sponsored scheme (core scheme) launched in the year 2015. The centre-state share will be in the ratio of 75:25. In the case of the north-eastern region and hilly states, this ratio will be 90:10.
- This will benefit around 22 lakh farmers, including 2.5 lakh Scheduled Caste and 2 lakh Scheduled Tribe farmers.
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti launched a mobile application for geo-tagging of components of projects under PMKSY in the year 2020 .
- It has three main components- Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP), Har Khet Ko Pani (HKKP) and Watershed Development.
- Objective:
- Convergence of investments in irrigation at the regional level,
- expanding the cultivable area under assured irrigation (har khet ko pani),
- Improving on-farm water use efficiency to reduce water wastage,
- To introduce sustainable water conservation practices by enhancing recharge of aquifers and exploring the feasibility of reuse of treated municipal water for peri-urban agriculture and to attract greater private investment in a precision irrigation system .
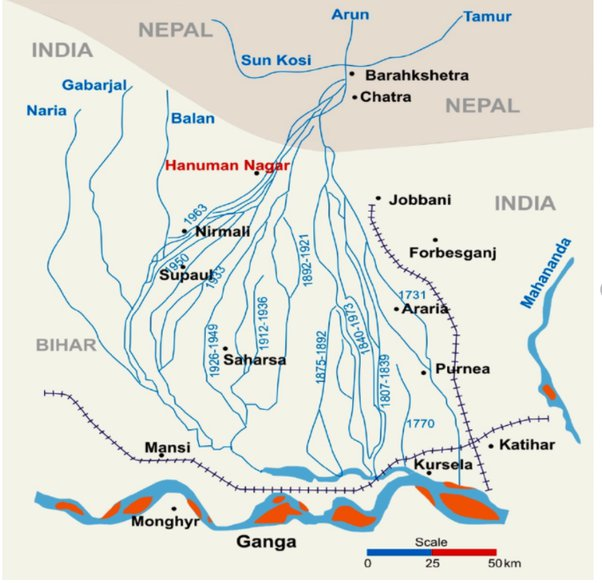
Koshi River
- It is called the 'Sorrow of Bihar' . It originates in the Himalayas at 7,000 metres above sea level from the catchment area of Mount Everest and Kanchenjunga .
- Flowing through China, Nepal and India, this river enters India near Hanuman Nagar and merges with the Ganga River near Kursela in Katihar district of Bihar.
- The Koshi River is formed by the confluence of three main streams: Sun Koshi, Arun Koshi and Tamur Koshi .
- The Koshi river is known for its tendency to change its course and flow westwards , which has moved up to 112 kilometres in the last 200 years, destroying agricultural areas in Darbhanga, Saharsa and Purnia districts.
- Tributaries: The river has several important tributaries, including the Trijanga, Bhutahi Balan, Kamala Balan, and Bagmati , all of which flow through the plains and join the Koshi River.
Mechi River
- It is a trans-boundary river flowing through Nepal and India . It is a tributary of the Mahananda River.
- The Mechi River is a perennial river that originates in the Himalayan inter-valley in the Mahabharat Range in Nepal and then flows through Bihar to join the Mahananda in Kishanganj district.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP became the First State in Ethanol Production
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh has topped the country in the field of ethanol production . In the last eight years, the state has increased its production capacity to 2 billion liters per year and a target is to increase it to 2.5 billion liters per year in the future.
Key Points
- Benefits:
- Increase in ethanol production has led to better prices and increased income to sugarcane farmers. Ethanol production is leading to the establishment of new industries in the state, providing employment to thousands of people. This is boosting economic activities in rural and urban areas.
- Promoting the use of Ethanol-Blended Petrol (EBP) will reduce dependence on petrol and diesel and also reduce pollution. Along with this, it will also help in achieving the target of net-zero emission by the year 2070 .
- Asia's largest ethanol plant has been set up in Gonda district and an ethanol production plant has also been set up at Pipraich sugar mill in Gorakhpur .
- Biofuel Policy-2022 :
- The state government prepared a well-planned Biofuel Policy-2022 to promote Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) .
- The main objective of this policy is to increase the income of farmers and make the environment clean.
- This policy is proving to be an important step towards transforming the state into a major hub of biofuel .
Ethanol
- Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol, is a biofuel produced from various sources such as sugarcane, corn, rice, wheat and biomass .
- Molasses, a by-product of sugar manufacture, is usually the main source for the production of ethanol (anhydrous alcohol) and rectified spirit . Molasses can be classified into the following categories:
- Grade A Molasses: An intermediate by-product obtained from the initial sugar crystal extraction , containing 80–85 % dry matter (DM) .
- B grade Jaggery: Same DM content as A grade Jaggery but with less sugar and no spontaneous crystallisation.
- Class C Molasses (Blackstrap Molasses, Treacle): The final by-product of sugar processing , containing significant amounts of sucrose (about 32% to 42%) . It does not crystallize and is used as a commercial feed ingredient in either liquid or dry form.
- The production process involves the fermentation of sugars by yeast or through petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration.
- Ethanol is 99.9% pure alcohol that can be blended with petrol to create a clean fuel option .
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Finance Commission Grants
Why in News?
The Central Government has distributed Fifteenth Finance Commission grants to Rural Local Bodies (RLBs)/Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in five states (Arunachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Nagaland and Punjab) during the financial year 2024-25.
Key Points
- About the grant:
- These grants are provided in two installments every financial year and are released by the Ministry of Finance based on the recommendations of the Ministry of Panchayati Raj and the Ministry of Jal Shakti (Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation) .
- As the first installment, Madhya Pradesh has been allocated a non-linked grant of Rs 651.7794 crore .
- Use of Grants:
- Unrestricted Grants: These grants enable local self-government institutions (RLBs/PRIs) to meet location-specific requirements under 29 subjects listed in the Eleventh Schedule of the Constitution , except salaries and establishment costs.
- Tied Grants: These funds must be used for the following purposes:
- Maintaining sanitation and ODF (open defecation free) status, which includes household waste management, human excreta and faecal sludge treatment.
- Drinking water supply, rain water harvesting and water recycling.
Panchayati Raj Institutions
- The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 granted constitutional status to Panchayati Raj Institutions and established a uniform structure (three tiers of PRIs), elections , reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes , Scheduled Tribes and women and a system of transfer of funds and functions and officers of the PRIs .
- Panchayats operate at three levels: Gram Sabha (village or group of small villages), Panchayat Samitis (block councils) and Zilla Parishad (at the district level).








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan