Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar's Annual Flood Crisis
Why in News?
Bihar faces devastating floods every year due to its unique geography and decades-old flood control methods.
Key Points
- Flood-Prone Nature of Bihar
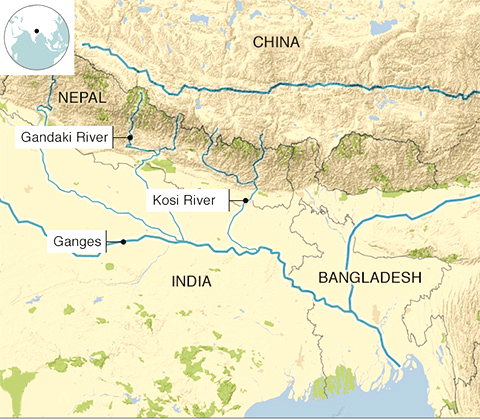
- Bihar is India's most flood-prone state, with 76% of North Bihar's population affected.
- The region is crisscrossed by both snow-fed and rain-fed rivers, increasing flood risk.
- Bihar is located below Nepal, with Himalayan rivers (Kosi, Gandak, Bagmati) flowing into the state.
- These rivers carry high sediment loads due to loose Himalayan soil, leading to overflow during heavy rains.
- Impact of Embankments:
- Embankments along rivers like Kosi were built in the 1950s to control flooding.
- Embankments narrowed river channels, leading to sediment buildup and higher riverbeds, making the rivers more prone to overflow.
- Kosi, known as the "sorrow of Bihar," floods annually despite embankments.
- Recent Flooding (2024):
- Heavy rainfall and Nepal’s release of water from the Kosi barrage led to severe floods in North Bihar.
- Embankments have breached in several districts, affecting 11.84 lakh people.
- The Birpur barrage released 6.6 lakh cusecs of water, the highest in six decades.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Flooding results in crop loss, livestock destruction, damage to infrastructure, and forced migration.
- Bihar government spends Rs 1,000 crore annually on flood relief and management.
- Proposed Solutions:
- Structural: Proposals for dams and additional barrages on Kosi and other rivers.
- Non-structural: Enhancing flood warnings, improving reaction times, public awareness, and training to mitigate flood effects.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Kashmir on the Verge of a New Era: GOC 15 Corps
Why in News?
Recently, Lt Gen Rajiv Ghai, General Officer Commanding (GOC) 15 Corps, reflects on the evolving security situation and development in Kashmir, outlining challenges and future prospects.
Key Points
- GOC (General Officer Commanding) 15 Corps:
- The GOC 15 Corps is the commanding officer of the Indian Army's Chinar Corps, responsible for overseeing military operations in the Kashmir Valley and parts of Jammu and Kashmir.
- The Corps plays a crucial role in counter-insurgency, border security, and maintaining peace in the region.
- Recent Developments in Kashmir:
- Kashmir is at the cusp of a "new beginning," with significant development and a stable security situation over the past year and a half.
- Security forces, including Chinar Corps, J&K Police, and CAPFs, have worked together to maintain peace and stability.
- No new militant recruitment in the last 18 months; active militant numbers have decreased to approximately 80.
- The success of a robust counter-insurgency campaign has reduced terrorism-related incidents significantly.
- Modern technology, including AIOS (Automated Integrated Operating Systems), has been employed to prevent cross-border infiltration.
- Challenges:
- Maintaining the current peaceful and stable situation remains the biggest challenge for security forces.
- The security grid, including counter-infiltration and counter-terrorism measures, must be sustained to consolidate peace in the coming years.
- Way Forward:
- Strengthening Intelligence and Surveillance: Enhancing real-time intelligence sharing and deploying advanced surveillance technologies will help security forces anticipate and prevent potential threats, reducing the risk of infiltration and terrorism.
- Community Engagement and Capacity Building: Building trust with local communities through development initiatives, social outreach, and improved governance can foster cooperation, making counter-terrorism efforts more effective while ensuring long-term stability in the region.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
"Radio Man of India" Sets Record
Why in News?
Ram Singh Boudh from Uttar Pradesh sets a Guinness World Record with his unique radio collection, preserving the legacy of radios.
Key Points
- World Record Radio Collection:
- Ram Singh Boudh, famously known as the "Radio Man of India," has amassed a collection of 1,257 unique radios, dating from the 1920s to 2010.
- His collection surpassed the previous world record of 625 radios held by M Prakash.
- Prime Minister's Recognition:
- Boudh's passion for preserving the legacy of radios gained national recognition when the Prime Minister mentioned him during the Mann Ki Baat radio program in November 2023.
- PM Modi highlighted Boudh’s dedication to keeping radios relevant, noting that his efforts sparked greater curiosity about his collection.
- The Prime Minister acknowledged that Mann Ki Baat itself has revitalized interest in radios and Akashvani (All India Radio), making them popular once again in many households.
Radio Spectrum
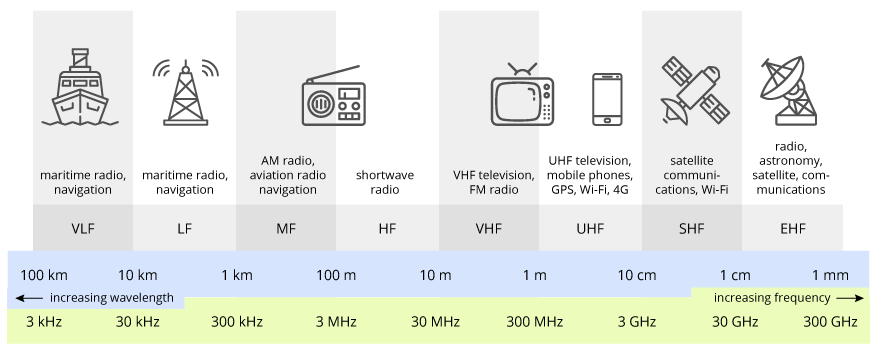
- The radio spectrum (also known as Radio Frequency or RF) is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, electromagnetic waves in this frequency range are called radio frequency bands or simply ‘radio waves’.
- Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. These were discovered by Heinrich Hertz in the late 1880s.
- RF bands spread in the range between 30 kHz and 300 GHz (alternative point of view offers coverage 3 KHz – 300 GHz).
Haryana Switch to Hindi
FMDA Launches Groundwater and Humidity Monitoring Project
Why in News?
Recently, The Faridabad Metropolitan Development Authority (FMDA) has introduced a project to monitor groundwater and humidity levels, aiming to address water depletion issues.
Key Points
- Project Overview:
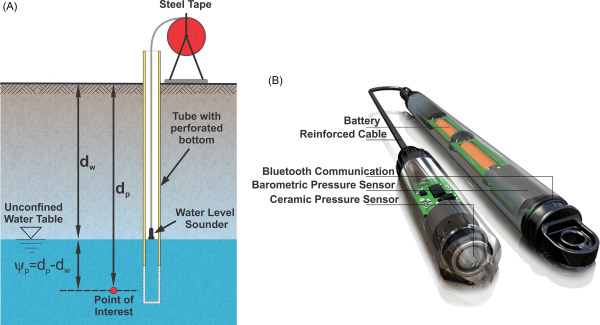
- The FMDA plans to install 100 piezometers in urban areas of Faridabad to monitor groundwater and underground humidity levels.
- The project, costing around Rs 9.5 crore, is part of a pilot initiative also being launched in Gurugram.
- These instruments will provide real-time data, helping authorities understand groundwater conditions and contributing factors for its depletion.
- Technological Setup:
- Piezometers, specialized sensing devices, will measure groundwater pressure and humidity across a radius of 1,000 meters per unit.
- The system will provide 24/7 monitoring, allowing for online data tracking. This technology, developed by APCOS Limited (formerly Water and Power Consultancy Services), falls under the Ministry of Jal Shakti.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)



.jpg)






.png)
.png)





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan