Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand UCC
Why in News?
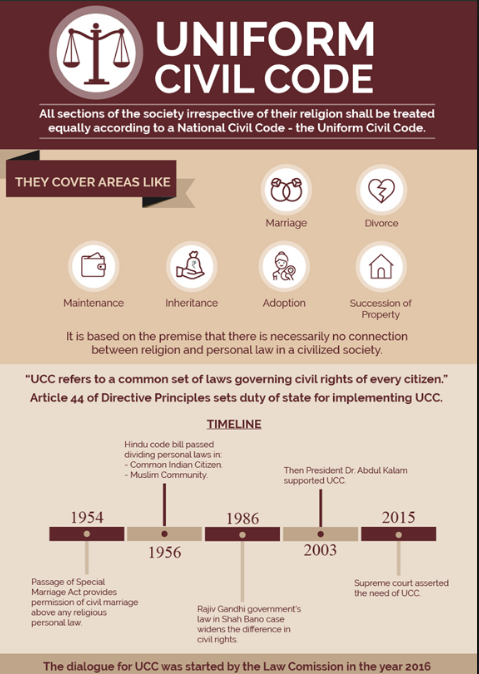
The Uttarakhand High Court observed that live-in relationships were increasing and that the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) aimed to accommodate the rights of women and children born from such relationships.
Key Points
- Court’s Observations:
- The High Court made the observations while hearing petitions challenging provisions of the UCC.
- The State implemented the UCC on 26 January 2025, and mandated registration for live-in relationships.
- The court stated that live-in relationships were increasing and that the law aimed to protect the rights of women and children born from such relationships.
- Privacy Concerns Raised in Court:
- It was argued that the UCC allowed excessive state surveillance and restricted individual choices protected under the right to privacy.
- The law was establishing a “draconian statutory regime” that authorizes inquiries, approvals, and penalties over personal relationships.
- It was stated that while society might not fully accept live-in relationships, the law aimed to adapt to changing times.
- Potential for Harassment and Vigilantism:
- Social activists contended that a critical reading of the UCC suggested it could increase harassment and violence against couples who defy majoritarian views.
- It is warned that the law might encourage vigilantism by groups opposing live-in relationships.
- Concerns were also raised that the law permitted any person to file a complaint questioning the validity of a live-in relationship.
- The mandatory submission of confidential documents, such as Aadhaar, during the registration process was also objected to.
- State Government’s Defense:
- The court questioned the Solicitor General on whether the Uttarakhand government had sought public suggestions before implementing the UCC and whether those suggestions were incorporated.
- It was argued that the UCC did not violate privacy rights and served only as a regulatory mechanism to protect women from injustice. The law resulted from extensive consultations with all stakeholders.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Article 370
Why in News?
On 25 February 2025, Jammu & Kashmir Chief Minister stated that Article 370 was described as a “temporary or transitional” provision because J&K’s status had not been fully formalized at the time of its accession to India in 1947.
Key Points
- Article 370's Temporary Status:
- The Chief Minister asserted that the promise of a plebiscite led to this classification, as J&K’s future was expected to be determined through democratic means.
- He emphasized the need to revisit the Instrument of Accession signed by Dogra ruler Hari Singh and the Government of India in 1947.
- He argued that while J&K’s accession to India became final over time, the conditions and framework that enabled it should have remained unchanged.
- He insisted that both aspects—accession and its governing framework—should be treated equally, rather than considering one as permanent and the other as temporary.
- Post-2019 Changes in J&K:
- He also acknowledged the changing atmosphere in J&K following the abrogation of Article 370 in 2019.
Article 370
- About:
- Article 370 of the Indian constitution granted special status to Jammu and Kashmir.
- It was drafted by N Gopalaswami Ayyangar, a member of the Constituent Assembly of India and was added as a 'temporary provision' in 1949.
- This article allowed Jammu and Kashmir to have its constitution, flag, and autonomy over most matters except defence, foreign affairs, and communications.
- The provision was based on the terms of the Instrument of Accession, which was signed by the ruler of Jammu and Kashmir, Hari Singh, in 1947 following an invasion by Pakistan.
- Repeal of Article 370:
- Presidential Order: In the 2019 Presidential orders, Parliament redefined the "constituent assembly of Jammu and Kashmir" to mean the "Legislative Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir."
- By invoking the President's rule, Parliament then assumed the powers of the Legislative Assembly to revoke Article 370.
- Resolutions in Parliament: On 5th and 6th August 2019, concurrent resolutions were passed by both houses of Parliament, the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha, respectively.
- These resolutions revoked the remaining provisions of Article 370 and replaced them with new provisions.
- Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019: It was passed by Parliament in 2019 to bifurcate the state of Jammu and Kashmir into two Union Territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Presidential Order: In the 2019 Presidential orders, Parliament redefined the "constituent assembly of Jammu and Kashmir" to mean the "Legislative Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir."


Haryana Switch to Hindi
Rise in Consumption of Urea and Di-Ammonium Phosphate (DAP)
Why in News?
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare has expressed concern over the sharp increase in urea and di-ammonium phosphate (DAP) consumption during the ongoing rabi season (2024-25) in multiple states, including Haryana, Gujarat, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, and J&K.
Key Points
- Rising Urea and DAP Consumption:
- Urea and DAP are essential for agricultural productivity, and India relies on imports to meet domestic demand.
- The Agriculture Secretary in a letter to Haryana’s Chief Secretary highlighted excessive fertiliser consumption in some districts.
- He noted that usage had surpassed both the assessed monthly requirement and the previous year’s figures, indicating an imbalance.
- Urea Consumption Trends:
- Haryana’s urea usage rose by 18% compared to the past three-year average, reaching 11,07,205 metric tonnes (MT) from 9,40,549 MT.
- Highest increases were recorded in:
- Charkhi Dadri – 107%
- Yamunanagar – 32%
- Sonepat – 30%
- Other states also recorded significant increases in urea consumption:
- Jharkhand – 35%
- Chhattisgarh – 37%
- J&K – 24%
- Karnataka – 20%
- Bihar – 17%
- Gujarat – 2%
- DAP Consumption Trends:
- Haryana’s DAP usage increased by 18%, reaching 3,25,416 MT from the previous three-year average of 2,75,934 MT.
- Districts with the highest surge:
- Charkhi Dadri – 184%
- Mahendragarh – 65%
- Yamunanagar – 55%
- Ambala – 48%
- Panchkula – 39%
- Rewari – 34%
- Jhajjar – 30%
- Other states also saw notable increases in DAP usage:
- Chhattisgarh – 30%
- Gujarat – 25%
- Bihar – 17%
- Concerns Over Fertiliser Diversion:
- The Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers flagged potential diversions in January.
- Haryana’s Director of Agriculture, Rajnarayan Kaushik, acknowledged that urea might be diverted to industries.
- Factors Driving Increased Usage:
- Paddy Stubble Management: Farmers now use 25-45 kg of urea per acre to manage paddy stubble.
- Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)Fertiliser Usage:
- Consumption rose from 26,000 MT last year to 66,000 MT this season.
- Since NPK has lower nitrogen content than DAP, farmers compensate by using additional urea.
- High-Nitrogen Wheat Varieties:
- Wheat varieties like WH 1270, DBW 187, 303, and 327 require 1.5 times more nitrogen than older varieties.
- Farmers, expecting higher yields, tend to use more urea.
- These varieties now cover an estimated 2.50 lakh acres in Haryana.
- Inter-State Fertiliser Movement:
- Reports indicate fertilisers are being transported to Punjab and Uttar Pradesh from Haryana.
- Some fertilisers are also being diverted to the plywood industry, claimed Rakesh Bains of the Bhartiya Kisan Union (Charuni group).
DAP (Di-Ammonium Phosphate)
- DAP is the second most commonly used fertilizer in India after urea.
- DAP is a preferred fertilizer in India because it contains both Nitrogen and Phosphorus which are primary macro-nutrients and part of 18 essential plant nutrients.
- Fertilizer grade DAP contains 18% Nitrogen and 46% Phosphorus. It is manufactured by reacting Ammonia with Phosphoric acid under controlled conditions in fertilizer plants.
Urea
- Urea is a white crystalline compound commonly used as a synthetic fertilizers in agriculture.
- When applied to the soil or crops, urea is broken down by enzymes into ammonia and carbon dioxide.
- The ammonia then gets converted into ammonium ions, which can be taken up by plant roots and used for growth and development.


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Kota Cares Initiative
Why in News?
To address stress among students preparing for competitive exams and the rising cases of suicides, the Kota district administration recently announced a comprehensive set of reforms for student welfare across the city.
Key Points
- About Kota Cares Initiative:
- 'Kota Cares' is a joint initiative of the district administration, coaching institutes, hostel associations and local communities, launched in December 2024.
- It is a significant step towards improving the educational ecosystem of the city. This initiative can serve as a model for other educational centres not only in Kota but across the country.
- New Guidelines and Features:
- Housing and Financial Aid:
- Security and caution money will be removed from 4,000 hostels.
- Maintenance charges will be limited to Rs 2,000 per year.
- Parents will be given receipts for all payments.
- Defined guidelines for room change and leave policies.
- Safety and Security Measures:
- Compulsory gate-keeper training for all hostel staff.
- Installation of modern security systems including CCTV surveillance and biometric systems.
- Special provisions for women's hostels, which will also include women wardens.
- Mandatory certification for anti-hanging devices and No Objection Certificates (NOC) for fire hazards.
- Regular night attendance checks through personal room visits.
- Student Welfare Initiatives:
- Free access to Chambal Riverfront and Oxygen Zone
- Designated spaces for recreation in all hostels.
- Availability of food services during mid-term holidays.
- Kota Cares Help Desk at Railway Stations and Bus Terminals.
- A citywide network of student support centers.
- Housing and Financial Aid:


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh Economy to Reach USD 2.1 Trillion by 2047
Why in News?
According to a recent Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) report, Madhya Pradesh's economy has the potential to reach USD 2.1 trillion by the year 2047-48, from the current figure of around USD 164.7 billion.
Key Points
- Key Highlights of the Report:
- About:
- The report titled " Envisioning Madhya Pradesh's Economy @ 2047" outlines a vision for economic development, identifying key sectors, policy interventions and investment opportunities that will drive the state's transformation.
- Basis: The report is based on extensive data analysis and stakeholder consultations, including inputs from industry leaders, policy makers and academic experts.
- It serves as a framework to unlock the full economic potential of Madhya Pradesh, ensuring sustainable growth, employment generation and enhanced competitiveness.
- Four Key Areas of the Report:
- Expansion of transport infrastructure such as the development of multi-modal logistics parks and air cargo hubs.
- Skill development and establishment of skill parks to increase the availability of skilled workforce.
- Enhancing the efficiency of Single Window System (SWS) for ease of doing business.
- Schemes to expand MSMEs, such as concessional credit facilities, improving market access and technological upgradation.
- Recommendations of the Report:
- According to the CII Director General, with a proactive state government committed to promoting investment and accelerating growth, Madhya Pradesh is well positioned to increase its contribution to India's GDP from the current 4.6% to 6.0% by 2047-48.
- Further, the report emphasises that Madhya Pradesh will need to focus on manufacturing and industrial expansion to achieve its ambitious development goals.
- Contribution of Agriculture and Manufacturing:
- The agriculture sector currently contributes 43% to Madhya Pradesh's economy, while the share of manufacturing must increase from 7.2% to 22.2% by 2047 to sustain long-term growth.
- About:
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII)
- CII is a non-governmental, not-for-profit, industry-led and industry-managed organisation.
- It works to create and sustain an environment conducive to India's growth by partnering with industry, government and civil society through advisory and consultative processes.
- It was established in 1895 and its headquarters is in New Delhi.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan