Indian History
76th Anniversary of Accession of Hyderabad
- 18 Sep 2024
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Accession of Hyderabad, Operation Polo, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Princely State, Razakars, Indian National Congress, United Nations, International Court of Justice, Constituent Assembly, British paramountcy.
For Mains: Integration of Hyderabad and other princely states to Indian Union, Role of different leaders in the integration process.
Why in News?
Recently, 17th September 2024 marked the 76th anniversary of the accession of Hyderabad to independent India.
- Operation Polo was launched to prevent Hyderabad from becoming a security threat to the Indian Union.
What are the Key Highlights of the Accession of Hyderabad to India?
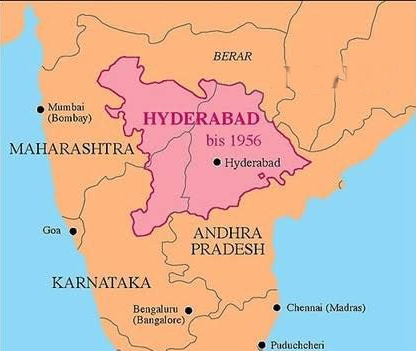
- Background of Hyderabad: Hyderabad was a large landlocked princely state in south India, covering present day Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and the Marathwada region of Maharashtra.
- The population was primarily Hindu (87%) while its ruler, Nizam Osman Ali Khan, was Muslim, supported by a Muslim elite.
- The Nizam and the Ittehad-ul-Muslimeen, a pro-Nizam Muslim party, pushed for Hyderabad’s independence, wanting the state to be on par with India and Pakistan.
- Nizam's Declaration of Independence: In June 1947, Nizam Osman Ali Khan issued a firman declaring Hyderabad’s intention to remain independent after British India’s transfer of power.
- India rejected this arguing that Hyderabad’s location was strategically important to India’s national security.
- A temporary Standstill Agreement (to maintain status quo) was signed to buy time, but Hyderabad still did not accede to India.
- Hyderabad’s Moves Toward Independence: The Nizam had provided Rs. 200 million to Pakistan and stationed a bomber squadron there, intensifying Indian suspicions.
- Hyderabad banned Indian currency, imported arms from Pakistan and expanded its military forces, particularly the Razakars militia.
- Australian aviator Sidney Cotton was hired by the Nizam to smuggle weapons into Hyderabad.
- Role of the Razakars: The Razakars, a militia aligned with the Ittehad-ul-Muslimeen (All India Council for Unity of Muslims) and led by Qasim Razvi, acted to protect the Muslim ruling class against any uprisings.
- The Razakars’ violent suppression of opposition, including atrocities against Hindus, heightened tensions.
- They also targeted Hyderabadi Muslims who favoured merging with India.
- Political Agitation: Internally, Hyderabad faced a Communist uprising in Telangana, a peasant revolt that the Nizam could not quell, weakening his position further.
- The Hyderabad State Congress, affiliated with the Indian National Congress, launched a political agitation for Hyderabad’s integration with India.
- International Appeals: The Nizam sought British support and later attempted to involve US President Harry Truman and the United Nations, but his efforts were unsuccessful.
- After Mountbatten's efforts for a negotiated settlement failed, in August 1948, the Nizam appealed to the UN Security Council and the International Court of Justice, fearing an imminent Indian invasion.
- Operation Polo (Hyderabad Police Action): Sardar Patel was getting anxious as the negotiations with the Nizam dragged on.
- On 13th September 1948, the Indian Army launched “Operation Polo,” a military operation of Hyderabad, citing internal law and order concerns.
- It was referred to as "Police Action" because it was an internal matter of India.
- On 17th September 1948, the Nizam formally surrendered after dismissing Prime Minister Mir Laik Ali and his cabinet.
What is the Significance of Hyderabad's Accession to India?
- Unity and Integrity of India: The integration of Hyderabad into India, despite opposition from the Nizam and Razakars, strengthened the Indian Union’s unity, integrity and stability.
- Triumph of Secularism: It was not only a significant political victory but also a triumph of secularism, as it highlighted the support of Indian Muslims for integration with India.
- Involvement of Indian Muslims on India’s side created a positive impression across the country.
- Prevented Further Crisis: Despite ongoing talks, Hyderabad’s government continued importing arms, preparing for conflict.
- Immediate military operation prevented an insurgency-like situation which might have spiralled across decades with help of foreign powers.
- Use of Force: Arms imports and involvement of foreign powers increased the urgency for India to resolve the Hyderabad issue, which was now seen as a potential security threat.
- Operation Polo showed that India would not shy away from using force for its national interests.
- India’s Successful Diplomacy: India’s combination of diplomatic, military, and logistical strategies, especially the stymieing of arms supplies.
- E.g., Efforts of V.K. Krishna Menon, then Indian High Commissioner in London, literally starved Hyderabad of weapons.
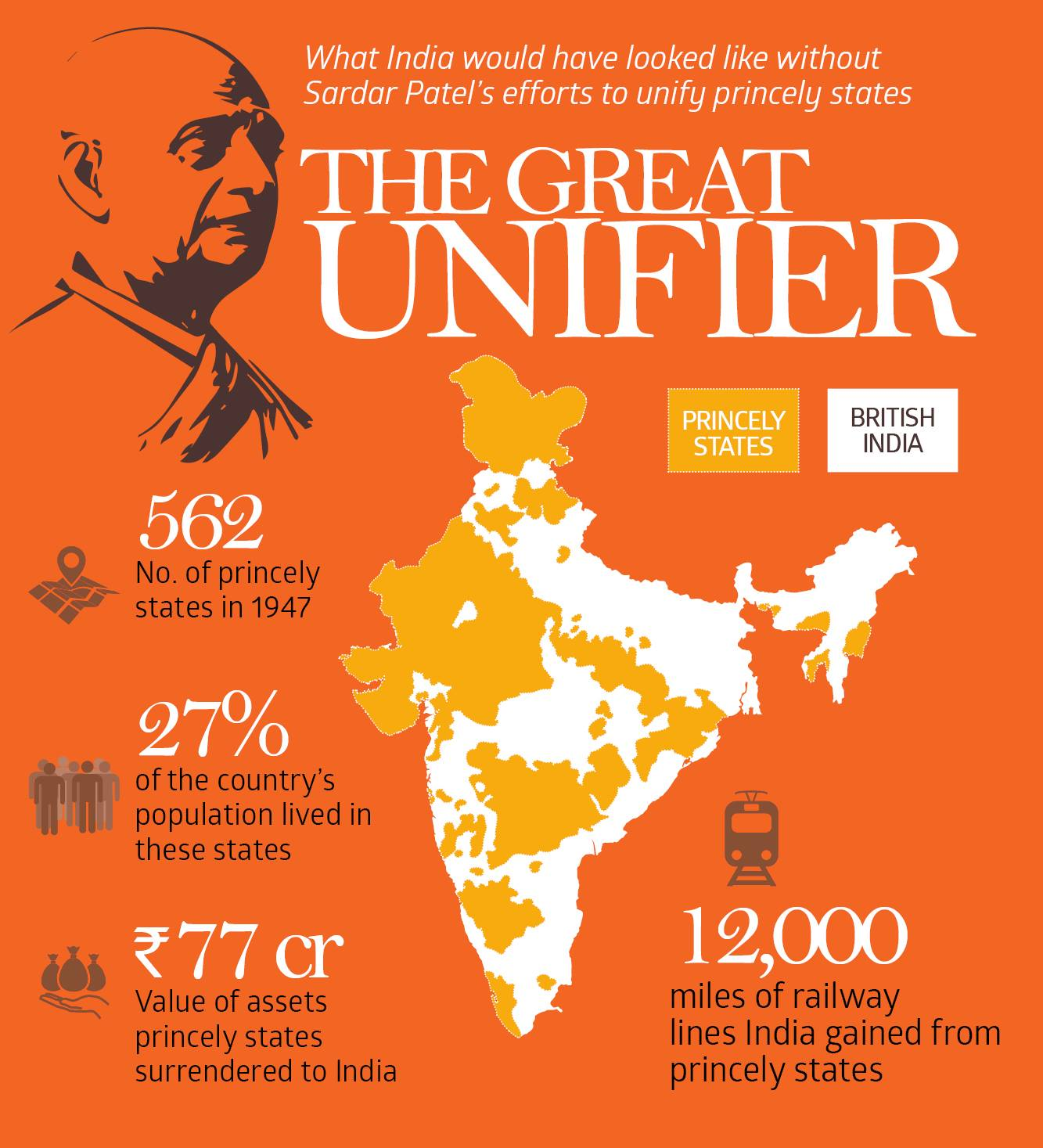
What was the Role of Sardar Patel in Integration of Princely States?
- Role in Interim Government (2nd September 1946): Sardar Patel was allocated the Home, States and Information & Broadcasting portfolios, setting the stage for his crucial role in India's administration even before independence.
- Nehru’s Acknowledgement: A fortnight before independence, on 1st August 1947, JL Nehru invited Patel to join his cabinet, referring to him as the “strongest pillar of the Cabinet.”
- Collaboration with Lord Mountbatten: Patel and Mountbatten worked closely, using a combination of diplomacy and pressure in convincing the princes to accede to India.
- They warned Princely States of the perils of independent existence.
- Creation of States Department (5th July 1947): Patel organised the States Department and appointed V.P. Menon as its Secretary.
- The department aimed to secure the accession of states in defence, foreign affairs, and communications, and maintain Standstill Agreements for common interests.
- Carrot and Stick Approach: Patel charged with negotiating accession, adopted a conciliatory and diplomatic stance, balancing pressure with reassurance.
- E.g., India closed all its borders to Junagadh and stopped the movement of goods, transport and postal articles which forced Junagarh to invite the Government of India to take control.
- Later, a plebiscite was held in which 99% of the population voted to join India.
- E.g., India closed all its borders to Junagadh and stopped the movement of goods, transport and postal articles which forced Junagarh to invite the Government of India to take control.
- Appeal for Friendship and Equality: Patel invited the princes to join independent India as friends, emphasising that it was preferable to make laws together as equals, rather than establish treaties as separate entities.
- Integration’s Impact on India’s Territory: While India lost 3.6 lakh square miles of territory and 81.5 million people during Partition, it gained 5 lakh square miles and 86.5 million people through the integration of princely states.
What was the Role of Other Leaders in Integration of Princely States?
- Lord Mountbatten: Mountbatten played a key role in persuading reluctant monarchs to accede to the Indian Union.
- Princes believed he could guarantee that independent India would adhere to any agreements because he was appointed as the first Governor-General of India.
- JL Nehru: Nehru’s approach was more confrontational.
- In January 1947, he rejected the divine right of kings and by May 1947, he declared that any princely state that refused to join the Constituent Assembly would be treated as an enemy state.
- C. Rajagopalachari: C. Rajagopalachari argued that British control over princely states was based on reality, not an agreement, so it would naturally transfer to independent India as the British successor.
- Congress as an Organisation: The Congress asserted that the princely states were not sovereign entities and could not opt for independence after British paramountcy ended.
Conclusion
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel's leadership was crucial in integrating 562 princely states into India, blending diplomacy and decisive action. Operation Polo secured Hyderabad’s accession, adding 212,000 square kilometres and 17 million people. Government data highlights Patel's efforts in expanding India’s territory by 5 lakh square kilometres post-Partition, solidifying his role as the "Iron Man of India."
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Evaluate the significance of Hyderabad's accession to India in 1948. Critically analyse the role of Sardar Patel in the successful integration of Hyderabad through Operation Polo? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Indian history, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2021)
- The Nizamat of Arcot emerged out of Hyderabad State.
- The Mysore Kingdom emerged out of Vijayanagara Empire.
- Rohilkhand Kingdom was formed out of the territories occupied by Ahmad Shah Durrani.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Q. For the Karachi Session of Indian National Congress in 1931 presided over by Sardar Patel, who drafted the Resolution on Fundamental Rights and Economic Programme? (2010)
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
(d) Dr. B. R. Ambedkar
Ans: (b)