West Bengal
Surface Ozone Pollution
- 10 Apr 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur study reveals that surface ozone pollution is severely affecting India's major food crops, especially in the Indo-Gangetic Plain and central India.
Key Points
- About Surface Ozone Pollution:
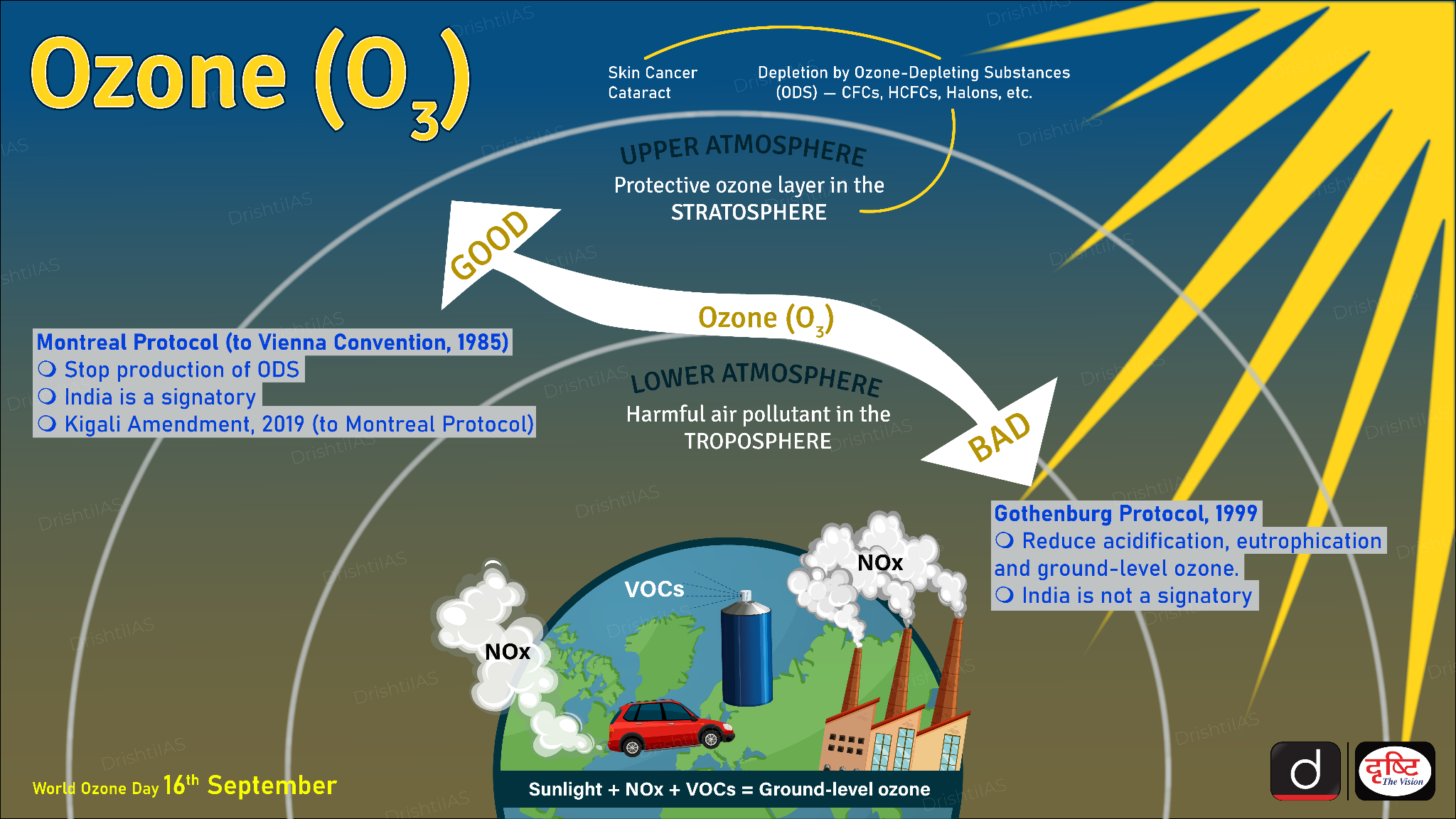
- Surface ozone (O₃) pollution refers to the excess presence of ozone at the Earth’s surface, which is formed through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
- Unlike the ozone layer in the stratosphere, which protects life from harmful ultraviolet radiation, Surface ozone is a harmful pollutant that poses significant health risks and environmental damage.
- Surface ozone (O₃) pollution refers to the excess presence of ozone at the Earth’s surface, which is formed through chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
- About the study:
- Surface ozone pollution is damaging major food crops such as wheat, rice, and maize.
- The study argues that rising ozone pollution jeopardizes India's progress toward Sustainable Development Goal 1 (No Poverty) and Goal 2 (Zero Hunger) by 2030.
- Declining crop yields could directly affect livelihoods and food access, especially for vulnerable populations.
- Key Findings of the Study:
- The research at the Centre for Oceans, River, Atmosphere and Land Sciences (CORAL), highlights the “lesser-known but potent” threat posed by surface ozone.
- Ozone acts as a strong oxidant that damages plant tissues, causes foliar injuries, and leads to significant drops in crop productivity.
- Using data from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase-6 (CMIP6), the study assessed both historical and future trends of ozone-induced damage.
- Without adequate mitigation, wheat yields may decline by up to 20%, while rice and maize could see losses of around 7%.
- In the worst-case scenarios, ozone exposure in key agricultural zones could exceed safe limits by six times.
- The research warns that ozone-related yield losses could undermine India’s ability to ensure food security at home and impact food grain exports to Asian and African nations.
- The research at the Centre for Oceans, River, Atmosphere and Land Sciences (CORAL), highlights the “lesser-known but potent” threat posed by surface ozone.
- Gaps in Current Air Quality Initiatives:
- The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) largely focuses on urban air pollution, leaving agricultural regions underserved.
- The study highlights the need for targeted interventions to monitor and curb surface ozone pollution in farmlands.
- Call for Policy Action:
- The researchers advocate for urgent policy measures to reduce ozone emissions and protect crop health.
- Effective pollution control strategies in agricultural areas could boost food production and help meet both national and global food security goals.
Formation of Surface Level Ozone
- Surface-level ozone is a secondary pollutant, meaning it is not directly emitted but formed through chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- NOx (emitted by vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes) and VOCs (emitted from vehicles, petrol pumps, solvents, and waste burning).
- These reactions occur in the presence of sunlight, making ozone formation more significant during sunny days and warmer seasons.
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP)
- About:
- The NCAP aims to systematically address air pollution by involving all stakeholders and ensuring necessary action.
- Under NCAP, 131 cities have been identified for implementation of city specific action plans.
- Objective:
- This is the first attempt in the country to develop a national framework for air quality management with the goal of time-bound reduction .
- It aims to reduce the concentration of coarse (PM10) and fine particles (PM2.5) by at least 20% over the next five years (base year for comparison – 2017).