Uttar Pradesh
Decline in Black Carbon Level in Varanasi
- 09 Jul 2024
- 2 min read
Why in News?
According to a study at Banaras Hindu University (BHU), an annual average decline of 0.47 micrograms per cubic metre in carbon level has been observed in Varanasi and the central Indo-Gangetic plains.
Key Points
- The study utilized black carbon data generated under the Aerosol Radiative Forcing over India (ARFI) program of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- An analysis of a decade-long measurement of black carbon mass concentration was conducted at a representative location in the central Indo-Gangetic plain, Varanasi, from 2009 to 2021.
- The purpose of this analysis was to understand the physical, optical, and radiative impact of black carbon in this region.
- The study recorded an average annual decrease of 0.47 micrograms per cubic metre in black carbon levels.
- Black carbon levels also showed a consistent seasonal decline, with a post-monsoon average decrease of 1.86 micrograms per cubic metre and a pre-monsoon average decrease of 0.31 micrograms per cubic metre.
- The study found that the black carbon in Varanasi and central Indo-Gangetic plains mostly originates from distant sources, rather than local factors.
- These particles are transported over long distances from the lower and upper Indo-Gangetic plains, Pakistan, the Middle East, and southern peninsular regions.
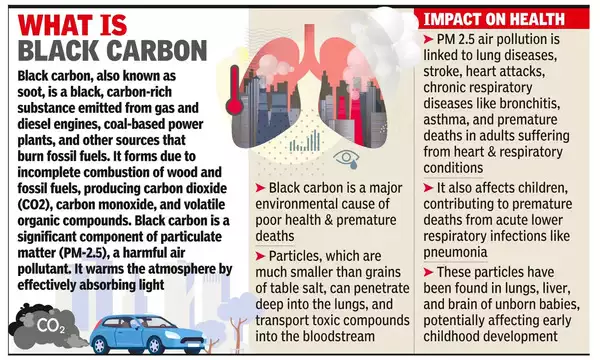
Black Carbon
- Black Carbon (BC) is a short-lived pollutant that is the second-largest contributor to warming the planet behind carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Unlike other greenhouse gas emissions, BC is quickly washed out and can be eliminated from the atmosphere if emissions stop.
- Unlike historical carbon emissions it is also a localised source with greater local impact.
- Black carbon is a kind of an aerosol.