Haryana
Aravalis of Haryana Get Protected Forest Tag
- 16 Aug 2024
- 3 min read
Why in News?
Recently, Haryana has designated 24,353 hectares of Aravali land in five of its districts as protected forest, under the compensatory afforestation swap intended to offset the destruction of tropical rainforests in Great Nicobar.
Key Points
- Though the goal was 26,000 hectares, Haryana was able to secure 24,353 hectares. For the remaining 1,647 hectares, the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) is in discussions with the government of Madhya Pradesh.
- In November 2022, MoEFCC gave its approval, paving the way for a colossal project in Great Nicobar.
- This project involves constructing an international airport, a shipping port, a power plant, and a township, spanning an area of 160 square kilometers.
- More than 80% of this land is part of a pristine tropical forest, resulting in the loss of almost a million trees.
- In February 2023, it was decided that the compensatory afforestation for this forest destruction in an island off India's mainland will be carried out in the Aravalis of Haryana.
- The government of Haryana, which submitted its plan for compensatory afforestation will receive Rs 3,000 crore to revive the Aravalis in five of its districts.
- The five districts are - Gurgaon, Nuh, Rewari, Mahendergarh and Charkhi Dadri.
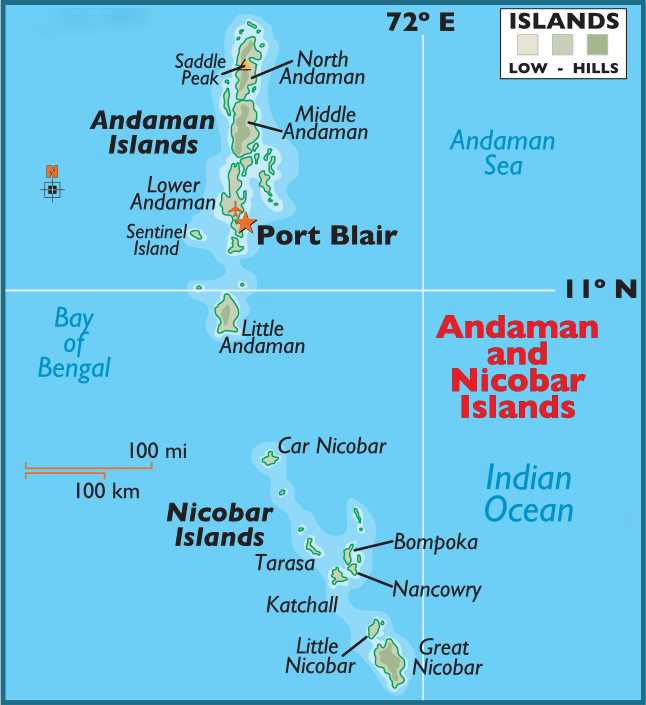
Great Nicobar Island
- Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands, a sparsely inhabited 910-sq-km patch of mainly tropical rainforest in southeastern Bay of Bengal.
- Indira Point on the island, India’s southernmost point, is located 90 nautical miles (<170 km) from Sabang at the northern tip of Sumatra, the largest island of the Indonesian archipelago.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands consist of 836 islands, divided into two groups known as the Andaman Islands located in the north and the Nicobar Islands situated in the south, separated by the 10° Channel which is 150 kilometres wide.
- Great Nicobar has two national parks, a biosphere reserve, small populations of the Shompen, Onge, Andamanese and Nicobarese tribal peoples, and a few thousand non-tribal settlers.